Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yomogida, Takumi; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Okumura, Takuma*; Yamada, Shinya*; Tatsuno, Hideyuki*; Noda, Hirofumi*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Okada, Shinji*; Takatori, Sayuri*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; et al.
Analyst, 149(10), p.2932 - 2941, 2024/03
In this study, we successfully applied a transition-edge sensor (TES) spectrometer as a detector for microbeam X-ray measurements from a synchrotron X-ray light source to determine uranium (U) distribution at the micro-scale and its chemical species in biotite obtained from the U mine. It is difficult to separate the fluorescent X-ray of the U L
 line at 13.615 keV from that of the Rb K
line at 13.615 keV from that of the Rb K line at 13.395 keV in the X-ray fluorescence spectrum with an energy resolution of approximately 220 eV of the conventional silicon drift detector (SDD). Meanwhile, the fluorescent X-rays of U L
line at 13.395 keV in the X-ray fluorescence spectrum with an energy resolution of approximately 220 eV of the conventional silicon drift detector (SDD). Meanwhile, the fluorescent X-rays of U L
 and Rb K
and Rb K were fully separated by TES with 50 eV energy resolution at the energy of around 13 keV. The successful peak separation by TES led to an accurate mapping analysis of trace U in micro-X-ray fluorescence measurements and a decrease in the signal-to-background ratio in micro-X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy.
were fully separated by TES with 50 eV energy resolution at the energy of around 13 keV. The successful peak separation by TES led to an accurate mapping analysis of trace U in micro-X-ray fluorescence measurements and a decrease in the signal-to-background ratio in micro-X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Miura, Hikaru*; Kuribara, Yuichi; Yamamoto, Masayoshi*; Sakaguchi, Aya*; Yamaguchi, Noriko*; Sekizawa, Oki*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; Higaki, Shogo*; Tsumune, Daisuke*; Itai, Takaaki*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10, p.11421_1 - 11421_9, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:67.24(Multidisciplinary Sciences) Cs concentrations in east Japanese rivers
Cs concentrations in east Japanese riversTsuji, Hideki*; Ishii, Yumiko*; Shin, M.*; Taniguchi, Keisuke*; Arai, Hirotsugu*; Kurihara, Momo*; Yasutaka, Tetsuo*; Kuramoto, Takayuki*; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Lee, S*; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 697, p.134093_1 - 134093_11, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:60.14(Environmental Sciences)To investigate the main factors that control the dissolved radiocesium concentration in river water in the area affected by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, the correlations between the dissolved  Cs concentrations at 66 sites normalized to the average
Cs concentrations at 66 sites normalized to the average  Cs inventories for the watersheds with the land use, soil components, topography, and water quality factors were assessed. We found that the topographic wetness index is significantly and positively correlated with the normalized dissolved
Cs inventories for the watersheds with the land use, soil components, topography, and water quality factors were assessed. We found that the topographic wetness index is significantly and positively correlated with the normalized dissolved  Cs concentration. Similar positive correlations have been found for European rivers because wetland areas with boggy organic soils that weakly retain
Cs concentration. Similar positive correlations have been found for European rivers because wetland areas with boggy organic soils that weakly retain  Cs are mainly found on plains. However, for small Japanese river watersheds, the building area ratio in the watershed strongly affected the dissolved
Cs are mainly found on plains. However, for small Japanese river watersheds, the building area ratio in the watershed strongly affected the dissolved  Cs concentration.
Cs concentration.
Tashiro, Koji*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Ohara, Takashi; Hanesaka, Makoto*; Yoshizawa, Yoshinori*; Yamamoto, Hiroko*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Kurihara, Kazuo*; et al.
Macromolecules, 51(11), p.3911 - 3922, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:17.66(Polymer Science)Koike, Katsuaki*; Kubo, Taiki*; Liu, C.*; Masoud, A.*; Amano, Kenji; Kurihara, Arata*; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Lanyon, B.*
Tectonophysics, 660, p.1 - 16, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:67.81(Geochemistry & Geophysics)This study integrates 3D models of rock fractures from different sources and hydraulic properties aimed at identifying relationships between fractures and permeability. A geostatistical method (GEOFRAC) that can incorporate orientations of sampled data was applied to 50,900 borehole fractures for spatial modeling of fractures over a 12 km by 8 km area, to a depth of 1.5 km. GEOFRAC produced a plausible 3D fracture model, in that the orientations of simulated fractures correspond to those of the sample data and the continuous fractures appeared near a known fault. Small-scale fracture distributions with dominant orientations were also characterized around the two shafts using fracture data from the shaft walls. By integrating the 3D model of hydraulic conductivity using sequential Gaussian simulation with the GEOFRAC fractures from the borehole data, the fracture sizes and directions that strongly affect permeable features were identified.
Tashiro, Koji*; Hanesaka, Makoto*; Yamamoto, Hiroko*; Wasanasuk, K.*; Jayaratri, P.*; Yoshizawa, Yoshinori*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; et al.
Kobunshi Rombunshu, 71(11), p.508 - 526, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:22.16(Polymer Science)The crystal structure analysis of various polymer substances has been reviewed on the basis of wide-angle high-energy X-ray and neutron diffraction data. The progress in structural analytical techniques of polymer crystals have been reviewed at first. The structural models proposed so far were reinvestigated and new models have been proposed for various kinds of polymer crystals including polyethylene, poly(vinyl alcohol), poly(lactic acid) and its stereocomplex etc. The hydrogen atomic positions were also clarified by the quantitative analysis of wide-angle neutron diffraction data, from which the physical properties of polymer crystals have been evaluated theoretically. The bonded electron density distribution has been estimated for a polydiacetylene single crystal on the basis of the so-called X-N method or by the combination of structural information derived from X-ray and neutron diffraction data analysis. Some comments have been added about future developments in the field of structure-property relationship determination.
Yokoyama, Takeshi*; Mizuguchi, Mineyuki*; Nabeshima, Yuko*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Yamada, Taro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 20(6), p.834 - 837, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:33.42(Instruments & Instrumentation)Transthyretin (TTR) is a tetrameric protein. TTR misfolding and aggregation are associated with human amyloid diseases. Dissociation of the TTR tetramer is believed to be the rate-limiting step in the amyloid fibril formation cascade. Low pH is known to promote dissociation into monomer and the formation of amyloid fibrils. In order to reveal the molecular mechanisms underlying pH sensitivity and structural stabilities of TTR, neutron diffraction studies were conducted using the IBARAKI Biological Crystal Diffractometer with the time-of-flight method. Crystals for the neutron diffraction experiments were grown up to 2.5 mm for four months. The neutron crystal structure solved at 2.0
for four months. The neutron crystal structure solved at 2.0  revealed the protonation states of His88 and the detailed hydrogen-bond network depending on the protonation states of His88. This hydrogen-bond network is involved in monomer-monomer and dimer-dimer interactions, suggesting that the double protonation of His88 by acidification breaks the hydrogen-bond network and causes the destabilization of the TTR tetramer. Structural comparison with the X-ray crystal structure at acidic pH identified the three amino acid residues responsible for the pH sensitivity of TTR. Our neutron model provides insights into the molecular stability related to amyloidosis.
revealed the protonation states of His88 and the detailed hydrogen-bond network depending on the protonation states of His88. This hydrogen-bond network is involved in monomer-monomer and dimer-dimer interactions, suggesting that the double protonation of His88 by acidification breaks the hydrogen-bond network and causes the destabilization of the TTR tetramer. Structural comparison with the X-ray crystal structure at acidic pH identified the three amino acid residues responsible for the pH sensitivity of TTR. Our neutron model provides insights into the molecular stability related to amyloidosis.
Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Yamada, Taro*; Tomoyori, Katsuaki; Ohara, Takashi; Katagiri, Masaki*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 20(6), p.994 - 998, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:85.77(Instruments & Instrumentation)The IBARAKI biological crystal diffractometer, iBIX, is a high-performance time-of-flight neutron single-crystal diffractometer for elucidating mainly the hydrogen, protonation and hydration structures of biological macromolecules in various life processes. Since the end of 2008, iBIX has been available to user's experiments supported by Ibaraki University. Since August 2012, an upgrade of the 14-existing detectors has begun and 16 new detectors have been installed for iBIX. The total measurement efficiency of the present diffractometer has been impoved by one order of magnitude from the previous one with the increasing of accelerator power. In December 2012, commissioning of the new detectors was successful, and collection of the diffraction dataset of ribonucrease A as a standard protein was attempted in order to estimate the performance of the upgraded iBIX in comparison with previous results. The resolution of diffraction data, equivalence among intensities of symmetry-related reflections and reliability of the refined structure have been improved dramatically. iBIX is expected to be one of the highest-performance neutron single-crystal diffractometers for biological macromolecules in the world.
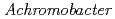 protease I at pD 8.0; Protonation states and hydration structure in the free-form
protease I at pD 8.0; Protonation states and hydration structure in the free-formOnishi, Yuki*; Yamada, Taro*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Sakiyama, Fumio*; Masaki, Takeharu*; Niimura, Nobuo*
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta; Proteins and Proteomics, 1834(8), p.1642 - 1647, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:23.68(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)The structure of the free-form of 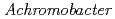 protease I (API) at pD 8.0 was refined by simultaneous use of single crystal X-ray and neutron diffraction data sets to investigate the protonation states of key catalytic residues of the serine protease. Occupancy refinement of the catalytic triad in the active site of API free-form showed that ca. 30% of the imidazole ring of H57 and ca. 70% of the hydroxyl group of S194 were deuterated. This observation indicates that a major fraction of S194 is protonated in the absence of a substrate. The protonation state of the catalytic triad in API was compared with the bovine
protease I (API) at pD 8.0 was refined by simultaneous use of single crystal X-ray and neutron diffraction data sets to investigate the protonation states of key catalytic residues of the serine protease. Occupancy refinement of the catalytic triad in the active site of API free-form showed that ca. 30% of the imidazole ring of H57 and ca. 70% of the hydroxyl group of S194 were deuterated. This observation indicates that a major fraction of S194 is protonated in the absence of a substrate. The protonation state of the catalytic triad in API was compared with the bovine  -trypsin-BPTI complex. The comparison led to the hypothesis that close contact of a substrate with S194 could lower the acidity of its hydroxyl group, thereby allowing H57 to extract the hydrogen from the hydroxyl group of S194. H210, which is a residue specific to API, does not form a hydrogen bond with the catalytic triad residue D113. Instead, H210 forms a hydrogen bond network with S176, H177 and a water molecule. The close proximity of the bulky, hydrophobic residue W169 may protect this hydrogen bond network, and this protection may stabilize the function of API over a wide pH range.
-trypsin-BPTI complex. The comparison led to the hypothesis that close contact of a substrate with S194 could lower the acidity of its hydroxyl group, thereby allowing H57 to extract the hydrogen from the hydroxyl group of S194. H210, which is a residue specific to API, does not form a hydrogen bond with the catalytic triad residue D113. Instead, H210 forms a hydrogen bond network with S176, H177 and a water molecule. The close proximity of the bulky, hydrophobic residue W169 may protect this hydrogen bond network, and this protection may stabilize the function of API over a wide pH range.
 -thrombin-bivalirubin complex at pD 5.0; Protonation states and hydration structure of the enzyme-product complex
-thrombin-bivalirubin complex at pD 5.0; Protonation states and hydration structure of the enzyme-product complexYamada, Taro*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Onishi, Yuki*; Tamada, Taro; Tomoyori, Katsuaki; Masumi, Kenji*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Kuroki, Ryota; Niimura, Nobuo*
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta; Proteins and Proteomics, 1834(8), p.1532 - 1538, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:48.29(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)The protonation states and hydration structures of the  -thrombin-bivalirubin complex were studied by joint XN refinement of the single crystal X-ray and neutron diffraction data at resolutions of 1.6 and 2.8
-thrombin-bivalirubin complex were studied by joint XN refinement of the single crystal X-ray and neutron diffraction data at resolutions of 1.6 and 2.8  , respectively. The atomic distances were estimated by carrying out X-ray crystallographic analysis at 1.25
, respectively. The atomic distances were estimated by carrying out X-ray crystallographic analysis at 1.25  resolution. The complex represents a model of the enzyme-product (EP) complex of
resolution. The complex represents a model of the enzyme-product (EP) complex of  -thrombin. The neutron scattering length maps around the active site suggest that the side chain of H57/H was deuterated. The joint XN refinement showed that occupancies for D
-thrombin. The neutron scattering length maps around the active site suggest that the side chain of H57/H was deuterated. The joint XN refinement showed that occupancies for D 1 and D
1 and D 2 of H57/H were 1.0 and 0.7, respectively. However, no significant neutron scattering length density was observed around the hydroxyl oxygen O
2 of H57/H were 1.0 and 0.7, respectively. However, no significant neutron scattering length density was observed around the hydroxyl oxygen O of S195/H, which was close to the carboxylic carbon atom of dFPR-COOH. These observations suggest that the O
of S195/H, which was close to the carboxylic carbon atom of dFPR-COOH. These observations suggest that the O atom of S195/H is deprotonated and maintains its nucleophilicity in the EP complex. In addition to the active site, the hydration structures of the S1 subsite and the Exosite I, which are involved in the recognition of bivalirudin, are presented.
atom of S195/H is deprotonated and maintains its nucleophilicity in the EP complex. In addition to the active site, the hydration structures of the S1 subsite and the Exosite I, which are involved in the recognition of bivalirudin, are presented.
Kubo, Taiki*; Koike, Katsuaki*; Liu, C.*; Kurihara, Arata*; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki
Chigaku Zasshi, 122(1), p.139 - 158, 2013/03
Numerical simulations have been the most effective method for estimating flow pattern, flux, and flow velocity of the groundwater to precisely characterize large-scale groundwater systems. Spatial modeling of the 3D distribution of hydraulic conductivity over a study area is indispensable to obtain accurate simulation results. However, such spatial modeling is difficult in most cases due to the limitations of hydraulic conductivity data in terms of their volume and location. To overcome these problems and establish an advanced technique, we adopt geostatistics and combine a fracture distribution model with measured conductivity data, selecting the Tono area situated in Gifu Prefecture, central Japan for the field study. The size of the main target area covers 12 km (E-W) by 8 km (N-S), with a depth range of 1.5 km, and it is chiefly underlain by Cretaceous granite. Because the distribution of 395 hydraulic test data acquired along the 25 deep boreholes was biased, the data values were compared to the dimensions of simulated fractures using GEOFRAC. As a result, a positive correlation was identified. Using a regression equation for the correlation, hydraulic conductivity values were assigned to every simulated fracture. Then, a sequential Gaussian simulation (SGS) was applied to construct a 3D spatial model of hydraulic conductivity using those assumed values and actual test data. The plausibility of the resulting model was confirmed through the continuity of high and low permeable zones. The next step is a groundwater flow simulation using MODFLOW and the model. The simulation results were regarded to be appropriate because distribution of hydraulic head, locations of major discharge points, and anisotropy of hydraulic behavior of the Tsukiyoshi fault correspond to the results of observations.
Saegusa, Jun; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Yasuda, Ryo; Kurihara, Kazuo; Arai, Shigeki; Kuroki, Ryota; Matsuhashi, Shimpei; Ozawa, Takashi; Goto, Hiroaki; Takano, Takao; et al.
Health Physics, 104(3), p.243 - 250, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.48(Environmental Sciences)After the Nuclear accident on March 2011, water discharge from many outdoor swimming pools in the Fukushima prefecture was suspended out of concern that radiocesium in the pool water would flow into farmlands. We have reviewed the existing flocculation method for decontaminating pool water and established a practical decontamination method by demonstrating the process at several pools in the Fukushima prefecture.
Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Tagami, Masahiko; Amano, Kenji; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Kurihara, Arata; Yamada, Yasuhiro*; Koike, Katsuaki*
Chishitsugaku Zasshi, 119(2), p.59 - 74, 2013/02
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is developing a geoscientific research project, Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project, in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. A series of geological mapping, reflection seismic survey, borehole investigation and geological investigations around research galleries are carried out to identify the distribution and the heterogeneity of fractures and faults that are potential major flow-pass of groundwater as field investigations. This paper describes geological investigations in the MIU project, focused on the evaluation of their effectiveness in order to understand the deep underground geological environment.
 1-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) synthase, the enzyme controlling the psychoactivity of
1-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) synthase, the enzyme controlling the psychoactivity of 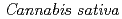
Shoyama, Yoshinari*; Tamada, Taro; Kurihara, Kazuo; Takeuchi, Ayako*; Taura, Futoshi*; Arai, Shigeki; Blaber, M.*; Shoyama, Yukihiro*; Morimoto, Satoshi*; Kuroki, Ryota
Journal of Molecular Biology, 423(1), p.96 - 105, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:82 Percentile:89.48(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology) 1-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) synthase catalyzes the oxidative cyclization of cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) into THCA, the precursor of the primary psychoactive agent
1-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) synthase catalyzes the oxidative cyclization of cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) into THCA, the precursor of the primary psychoactive agent  1-tetrahydrocannabinol in
1-tetrahydrocannabinol in 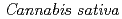 . The structure-function relationship of THCA synthase was investigated by X-ray structure determination (2.75
. The structure-function relationship of THCA synthase was investigated by X-ray structure determination (2.75  resolution) and mutational analysis. Specific amino acid residues were identified in the active site of THCA synthase that are involved in the oxidative cyclization of the CBGA substrate.
resolution) and mutational analysis. Specific amino acid residues were identified in the active site of THCA synthase that are involved in the oxidative cyclization of the CBGA substrate.
Ishibashi, Masayuki; Kurihara, Arata*; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Sasao, Eiji
JAEA-Research 2012-018, 48 Pages, 2012/07
This document presents about updating of geological models at the Phase 2 in the Mizunami underground research laboratory project. In the phase 2, the geological models has been updated four times (Shaft180 geological model, Pilot500 geological model, Sustage200 geological model, Stage300 geological model) based on geological mapping date and/or some borehole investigation data at the shafts and research galleries. These geological models represent distributions of lithofacies and/or geological structures based on each geological investigation. In order to evaluate relationship between understanding of geological environments and progress of investigations, to organize the history of geological models updating is important.
Kosaka, Hiroshi; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Kurihara, Arata*; Onoe, Hironori
JAEA-Research 2012-012, 100 Pages, 2012/07
In this study, groundwater flow and particle tracking simulations using hydrogeological models have been carried out in order to evaluate the relationship between understanding of groundwater flow characteristics and the amount of information that is increased by the progress of investigations. The influences of difference of the method for interpretation of hydrogeology have been also evaluated. As a result, uncertainties of the groundwater flow characteristics were decreased by increasing the amount of information. It was also found that the distribution of large-scale discrete features and the heterogeneity of groundwater flow characteristics affect the groundwater flow characteristics. Furthermore, the method to identify the target of further investigation and to make plan for the investigation were proposed.
Yokoyama, Takeshi*; Mizuguchi, Mineyuki*; Nabeshima, Yuko*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Yamada, Taro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Ohara, Takashi*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tomoyori, Katsuaki*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; et al.
Journal of Structural Biology, 177(2), p.283 - 290, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:83.20(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Yoshida, Atsuro*; Higashi, Yuma*; Narabayashi, Tadashi*; Khoo Chong Weng, W.*; Arae, Kunihiko*; Tsuji, Masashi*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Kurihara, Akikazu
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/10
One of the design basis accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactor is sodium-water reaction at steam generator (SG). In case of a defect occurred on a heat transfer tube, the high-pressure water/vapor will spout into the low-pressure sodium surrounding outside the tube. As sodium is ordinarily quite reactive with water, this will initiate sodium-water reactions accompanied by high chemical heat generation. The liquid droplet in the reaction steam outflow would impinge on neighboring tubes to cause erosion, while the chemical reaction will cause corrosion, eventually may lead to secondary tube failure. Focusing on the erosion part, this study is to evaluate the liquid droplet impingement erosion (LDIE) rate on neighboring tubes caused by SG heat transfer tube rupture. In this paper, as a basic study, the pressure and temperature distribution of high -pressure two-phase free jet into the air is measured.
Kubo, Taiki*; Koike, Katsuaki*; Kurihara, Arata*; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki
Heisei-23 Nendo (2011 Nen) Shigen, Sozai Gakkai Shuki Taikai Koenshu, p.369 - 370, 2011/09
no abstracts in English