Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mitsuda, Tomoaki*; Kobayashi, Ippei*; Kosugi, Shinya*; Fujita, Naoki*; Saito, Yuichi; Hori, Fuminobu*; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Kaneno, Yasuyuki*; Nishida, Kenji*; Soneda, Naoki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 272, p.49 - 52, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:56.58(Instruments & Instrumentation)Kosugi, Shinya*; Fujita, Naoki*; Matsui, Toshiyuki*; Hori, Fuminobu*; Saito, Yuichi; Ishikawa, Norito; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Iwase, Akihiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 269(9), p.869 - 872, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.56(Instruments & Instrumentation)Effects of thermal annealing on ion-irradiation induced ferromagnetism of FeRh bulk alloy and the related structural change were investigated by means of superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) and extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS), respectively. Depending on the annealing temperature from 100 to 500  C, the magnetization induced by 10 MeV iodine ion irradiation and the lattice structure of the alloy were remarkably changed. After 500
C, the magnetization induced by 10 MeV iodine ion irradiation and the lattice structure of the alloy were remarkably changed. After 500  C annealing, the magnetization and the lattice ordering of the alloy become similar to the states before the irradiation. The experimental result indicates that the thermal relaxation of irradiation-induced atomic disordering dominates the magnetic state of ion-irradiated FeRh alloy.
C annealing, the magnetization and the lattice ordering of the alloy become similar to the states before the irradiation. The experimental result indicates that the thermal relaxation of irradiation-induced atomic disordering dominates the magnetic state of ion-irradiated FeRh alloy.
Fujita, Tomoo; Taniguchi, Naoki; Matsui, Hiroya; Tanai, Kenji; Maekawa, Keisuke; Sawada, Atsushi; Makino, Hitoshi; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Shibata, Masahiro; et al.
JAEA-Research 2011-001, 193 Pages, 2011/03
This report summarizes the progress of research and development on geological disposal during the surface-based investigation phase (2001-2005) in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory project, of which aims are to apply the design methods of geological disposal and mass transport analysis to actual geological conditions obtained from the surface-based investigations in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory project as an example of actual geological environment.
Mitsuda, Tomoaki*; Kobayashi, Ippei*; Kosugi, Shinya*; Fujita, Naoki*; Saito, Yuichi; Hori, Fuminobu*; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Kaneno, Yasuyuki*; Nishida, Kenji*; Soneda, Naoki*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 408(2), p.201 - 204, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:69.42(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Fujita, Naoki*; Matsui, Toshiyuki*; Kosugi, Shinya*; Sato, Takahiro; Saito, Yuichi; Takano, Katsuyoshi; Koka, Masashi; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Seki, Shu*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 49(6), p.060211_1 - 060211_3, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:45.63(Physics, Applied)Ida, Katsumi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Yoshinuma, Mikiro*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Nagaoka, Kenichi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Osakabe, Masaki*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; Funaba, Hisamichi*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(9), p.095024_1 - 095024_9, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:73.73(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dynamics of ion internal transport barrier (ITB) formation and impurity transport both in the Large Helical Device (LHD) heliotron and JT-60U tokamak are described. Significant differences between heliotron and tokamak plasmas are observed. The location of the ITB moves outward during the ITB formation regardless of the sign of magnetic shear in JT-60U and the ITB becomes more localized in the plasma with negative magnetic shear. In LHD, the low Te/Ti ratio ( 1) of the target plasma for the high power heating is found to be necessary condition to achieve the ITB plasma and the ITB location tends to expand outward or inward depending on the condition of the target plasmas. Associated with the formation of ITB, the carbon density tends to be peaked due to inward convection in JT-60U, while the carbon density becomes hollow due to outward convection in LHD. The outward convection observed in LHD contradicts the prediction by neoclassical theory.
1) of the target plasma for the high power heating is found to be necessary condition to achieve the ITB plasma and the ITB location tends to expand outward or inward depending on the condition of the target plasmas. Associated with the formation of ITB, the carbon density tends to be peaked due to inward convection in JT-60U, while the carbon density becomes hollow due to outward convection in LHD. The outward convection observed in LHD contradicts the prediction by neoclassical theory.
Iwatsuki, Teruki; Sato, Haruo; Tanai, Kenji; Inagaki, Manabu; Sawada, Atsushi; Niinuma, Hiroaki; Ishii, Eiichi; Maekawa, Keisuke; Tomura, Goji; Sanada, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2009-002, 156 Pages, 2009/05
The research and development plan for geological investigation, engineering technology and safety assessment during the drilling of a shaft down to intermediate depth are summarized according to the Midterm Plan till 2009 Fiscal year of JAEA. This report describes subject, current status and programme in the "Phase 2: Construction phase" (investigations during construction of the underground facilities). Furthermore regarding R&D plan in next Midterm Plan of JAEA, preliminary ideas are summarized.
Fujita, Naoki*; Kosugi, Shinya*; Zushi, Yoshihiro*; Matsui, Toshiyuki*; Saito, Yuichi; Iwase, Akihiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 267(6), p.921 - 924, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.36(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ostermeyer, M.*; Kong, H.-J.*; Kovalev, V. I.*; Harrison, R. G.*; Fotiadi, A. A.*; M gret, P.*; Kalal, M.*; Slezak, O.*; Yoon, J. W.*; Shin, J. S.*; et al.
gret, P.*; Kalal, M.*; Slezak, O.*; Yoon, J. W.*; Shin, J. S.*; et al.
Laser and Particle Beams, 26(3), p.297 - 362, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:55.22(Physics, Applied)Umeda, Koji; Oi, Takao; Osawa, Hideaki; Oyama, Takuya; Oda, Chie; Kamei, Gento; Kuji, Masayoshi*; Kurosawa, Hideki; Kobayashi, Yasushi; Sasaki, Yasuo; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-050, 82 Pages, 2007/12
This report shows the annual report which shows the summarized results and topic outline of each project on geological disposal technology in the fiscal year of 2006.
Fujita, Tomoo; Taniguchi, Naoki; Matsui, Hiroya; Tanai, Kenji; Nishimura, Mayuka; Kobayashi, Yasushi; Hiramoto, Masayuki; Maekawa, Keisuke; Sawada, Atsushi; Makino, Hitoshi; et al.
JAEA-Research 2007-045, 140 Pages, 2007/03
This report summarizes the progress of research and development on geological disposal during the surface-based investigation phase (2001-2005) in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory project (HOR), of which aims are to apply the design methods of geological disposal and mass transport analysis to actual geological environments and derive future subjects based on the results. The design methods of geological disposal were reviewed based on the recent knowledge and the advertences were identified. Then the parameters for virtual design of engineered barrier system, backfill deposition hole and tunnel were set up based on actual geological conditions obtained from the surface-based investigations in HOR as an example of actual geological environment. The conceptual structure from site investigation and evaluation to mass transport analysis was represented as a work flow at first. Then following this work flow a series of procedures for mass transport analysis were carried out based on actual geological conditions obtained from the surface-based investigations in HOR to illustrate the functioning of the work flow and the applicability of this methodology. Consequently, knowledge that will help follow-up or future execution and planning activities was obtained.
Aoyanagi, Shigeo; Yui, Mikazu; Tanai, Kenji; Kawakami, Susumu; Fujita, Tomoo; Taniguchi, Naoki; Shibata, Masahiro; Konishi, Kazuhiro; Nishimura, Mayuka; Kikuchi, Hirohito*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2006-014, 61 Pages, 2006/03
no abstracts in English
 thin films
thin filmsOkada, Hiroshi*; Fujita, Naoki*; Lee, H.-S.*; Wakahara, Akihiro*; Yoshida, Akira*; Oshima, Takeshi; Ito, Hisayoshi
Journal of Electronic Materials, 32(9), p.L5 - L8, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.36(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Masato*; Takahashi, Rieko*; Asano, Hidekazu*; Taniguchi, Naoki; Fujita, Tomoo
no journal, ,
Susceptibility of hydrogen embrittlement of carbon steel weld joint was evaluated by slow strain rate testing (SSRT) in consideration of a diffusive hydrogen concentration and a presence of a fine flaw which is hard to detect by ultrasonic testing due to the dimension. In order to avoid an effect of metallurgical micro structure, normalized specimens were prepared to the SSRT. The results of SSRT showed the rupture elongation decreases with an increase in hydrogen concentration. And observation of the fracture surface and measurement of the hydrogen concentration in the specimens showed a generation of a crack initiated from fine flaw at up to a certain value of hydrogen concentration. Although decreasing of fracture strain was observed on the specimens fracture morphology, it was evaluated as no significant effect in comparison with the effect of the concentration of the diffusive hydrogen in the specimens. These results suggest that a presence of a fine flaw has a small impact on the hydrogen embrittlement of weld joint.
Ishikawa, Norito; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Takagaki, Masafumi*; Suzuki, Motohiro*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Zushi, Yoshihiro*; Fujita, Naoki*; Hori, Fuminobu*; Seki, Shuhei*; Tsukuda, Satoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
It is already found that magnetic transition temperature of Fe-50at.%Rh changes by high-energy ion irradiation. This irradiation-induced changes in magnetic properties has been investigated by magnetic force microscopy. It has been found that microscopic magnetic structure appears after ion-irradiation, and the structure changes depending on the ion-fluence. The observed structure was not the same as that observed for Fe-rich ferromagnetic Fe-45at.%Rh alloys.
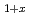 Al
Al Ge
Ge (PO
(PO )
) by neutron diffraction
by neutron diffractionFujita, Yasuhiro*; Takahashi, Haruyuki*; Sakuma, Takashi*; Igawa, Naoki
no journal, ,
The crystal structures of Li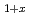 Al
Al Ge
Ge (PO
(PO )
) (x=0,0.5) were analyzed out by the Rietveld method applying the neutron powder diffraction data to investimate the increasing of the ionic conduction. We could refine those structures with a space group,
(x=0,0.5) were analyzed out by the Rietveld method applying the neutron powder diffraction data to investimate the increasing of the ionic conduction. We could refine those structures with a space group,  -3
-3 . The Rietveld analyses reveal that Li mainly occupied at 3
. The Rietveld analyses reveal that Li mainly occupied at 3 site and partially at 18
site and partially at 18 site in those compound. It was found that the site occupancy for 18 site of Li
site in those compound. It was found that the site occupancy for 18 site of Li Al
Al Ge
Ge (PO
(PO )
) was higher than that of LiGe
was higher than that of LiGe (PO
(PO )
) .
.
Iwase, Akihiro*; Zushi, Yoshihiro*; Nakatani, Tomoya*; Fujita, Naoki*; Hori, Fuminobu*; Oshima, Ryuichiro*; Seki, Shuhei*; Saito, Yuichi; Chiba, Atsuya; Adachi, Masahiro; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English