Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Cho, S. H.*; Cho, S. W.*; Lv, Z.*; 関根 由莉奈; Liu, S.*; Zhou, M.*; Nuxoll, R. F.*; Kanatzidis, E. E.*; Ghaffari, R.*; Kim, D.*; et al.
Lab on a Chip, 9 Pages, 2025/00
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Biochemical Research Methods)アミノ酸は体内のタンパク質合成と代謝プロセスに不可欠な物質である。本研究では、運動中の汗からのアミノ酸損失について定量的に調べることを目的とした。汗中のアミノ酸含有量をリアルタイムで分析するため、測定のための技術基盤としてウェアラブルなマイクロ流体システムを構築した。定量分析を実現するため、ウェアラブルデバイスに蛍光アッセイを組み込み、さらにスマートフォンベースの画像化技術を統合させたシステムを開発した。
Hu, F. F.*; Qin, T. Y.*; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; Zhou, L.*; 徐 平光; Parker, J. D.*; 篠原 武尚; Chen, J.*; Wu, S. C.*
Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 306, p.110267_1 - 110267_18, 2024/08
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:65.22(Mechanics)Non-destructive and quantitative mapping of gradient residual strain distribution in surface-hardened railway S38C axles could provide a positive reference for determining service lifetime and maintenance strategy. To tackle this concern, time-of-flight neutron Bragg-edge transmission imaging was employed by real axle samples with and without impacted crater. A novel and simple procedure to formulate the residual strain field was also developed in this work, with the transmission batch code in Appendix A. By mapping the global two- dimensional residual strains, it can be verified that the residual strains into the axle are uniformly distributed in the hoop direction. Subsequently, it was revealed that the axial and hoop residual strains, respectively in the cylinder and the long strip samples prepared from a real S38C hollow axle, indicated a gradient evolution distribution with a depth of  8 mm, covering a range of -5500
8 mm, covering a range of -5500  1000
1000 
 for axial strains and -6500
for axial strains and -6500  1000
1000 
 for hoop strains. More importantly, the maximum compressive lattice strain of the cylinder sample was increased by 15.61%, and 22.35% at the impacting speeds of 100, and 125 m/s, respectively; and that of the long strip sample increased by 29.17%, and 43.70%, respectively. It can thus be concluded that lattice strains have redistributed around the impact crater, demonstrating the local alteration of the residual strain field. These new findings suggest the localized variation in residual strains should be taken into account while evaluating the service damage evolution of railway axles, especially those affected by high-speed impacts during operation.
for hoop strains. More importantly, the maximum compressive lattice strain of the cylinder sample was increased by 15.61%, and 22.35% at the impacting speeds of 100, and 125 m/s, respectively; and that of the long strip sample increased by 29.17%, and 43.70%, respectively. It can thus be concluded that lattice strains have redistributed around the impact crater, demonstrating the local alteration of the residual strain field. These new findings suggest the localized variation in residual strains should be taken into account while evaluating the service damage evolution of railway axles, especially those affected by high-speed impacts during operation.
Qin, T. Y.*; Hu, F. F.*; 徐 平光; Zhang, H.*; Zhou, L.*; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; 菖蒲 敬久; Wu, S. C.*
International Journal of Fatigue, 185, p.108336_1 - 108336_13, 2024/08
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:95.79(Engineering, Mechanical)Gradient distribution of triaxial residual stresses to a depth of several millimeters is retained in middle carbon steel S38C axles after high-frequency induction hardening, which has become a critical concern for fatigue structural integrity. To address this, the axial, hoop, and radial gradient residual strains inside the axles were measured for the first time by advanced neutron diffraction. The SIGINI Fortran subroutine was then adopted to reconstruct the global initial residual stress field from the measured data. Experimental and simulation results show that residual stresses of about -520 MPa (axial), -710 MPa (hoop), and -40 MPa (radial) residual stress were retained below the axle surface. Subsequently, the fatigue crack propagation behavior of S38C axles was numerically investigated in the framework of fracture mechanics. The calculated results clearly show that the compressive residual stresses at a depth of 0?3 mm from the axle surface lead to a low crack growth driving force, and that fatigue cracks do not propagate as long as the crack depth is less than 3.7 mm for hollow S38C axles. These results further indicate that the maximum defect size allowed in routine inspections is acceptable from a safety and economic point of view. Accurate measurement and characterization of the global gradient residual stress field through experiments and simulations can provide an important reference for optimizing the mileage intervals of nondestructive testing (NDT) of surface defects in these surface-strengthened railway axles.
Zhou, L.*; Zhang, H.*; Qin, T. Y.*; Hu, F. F.*; 徐 平光; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; He, L. H.*; Li, X. H.*; Zhang, J. R.*; et al.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 55(7), p.2175 - 2185, 2024/07
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:78.83(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)High-speed railway S38C axles undergo surface induction hardening for durability, but are susceptible to fatigue cracks from foreign object impact. The neutron diffraction method was employed to measure the residual strain in S38C axles, obtaining microscopic lattice distortion data, for the gradient layer at a depth of 8 mm under the surface. The results showed that after induction-hardening, the microscopic lattice distortion had a gradient distribution, decreasing with the distance from the surface. However, in the case of impacting speed of 600 km/m, the average microscopic lattice distortion increased with the distance from the surface, reaching a maximum augmentation of 55 pct. These findings indicate a strong experimental basis, and improve our understanding of the relationship between macroscopic residual stress and decision-making, in regard to operation and maintenance.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionZhou, Y.*; Song, W.*; Zhang, F.*; Wu, Y.*; Lei, Z.*; Jiao, M.*; Zhang, X.*; Dong, J.*; Zhang, Y.*; Yang, M.*; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 971, p.172635_1 - 172635_7, 2024/01
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:13.75(Chemistry, Physical)The grain orientation-dependent lattice strain evolution of a (TiZrHfNb)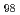
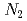 refractory high-entropy alloy (HEA) during tensile loading has been investigated using
refractory high-entropy alloy (HEA) during tensile loading has been investigated using  neutron diffraction. The equivalent strain-hardening rate of each of the primary
neutron diffraction. The equivalent strain-hardening rate of each of the primary 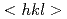 -oriented grain families was found to be relatively low, manifesting the macroscopically weak work-hardening ability of such a body-centered cubic (BCC)-structured HEA. This finding is indicative of a dislocation planar slip mode that is confined in a few single-slip planes and leads to in-plane softening by high pile-up stresses.
-oriented grain families was found to be relatively low, manifesting the macroscopically weak work-hardening ability of such a body-centered cubic (BCC)-structured HEA. This finding is indicative of a dislocation planar slip mode that is confined in a few single-slip planes and leads to in-plane softening by high pile-up stresses.
Yang, D. S.*; Wu, Y.*; Kanatzidis, E. E.*; Avila, R.*; Zhou, M.*; Bai, Y.*; Chen, S.*; 関根 由莉奈; Kim, J.*; Deng, Y.*; et al.
Materials Horizons, 10(11), p.4992 - 5003, 2023/09
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)本論文では、ハード及びソフトハイブリッド材料システムでの3Dプリントによって形成されたマイクロ流体ネットワーク、統合バルブ、およびマイクロスケール光学キュベットにより、汗成分に対してその場で分光および蛍光分析した成果を紹介する。一連の試験により、これらのマイクロキュベットシステムが汗中の銅、塩化物、グルコースの濃度と汗のpHを実験室レベルの精度と感度で評価できることが実証された。
 Fe
Fe intermetallic compound
intermetallic compoundCao, Y.*; Zhou, H.*; Khmelevskyi, S.*; Lin, K.*; Avdeev, M.*; Wang, C.-W.*; Wang, B.*; Hu, F.*; 加藤 健一*; 服部 高典; et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 35(8), p.3249 - 3255, 2023/04
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:23.35(Chemistry, Physical)静水圧や化学圧力は、結晶構造を変化させる効率的な刺激であり、材料科学において電気的、磁気的特性のチューニングによく利用されている。しかし、化学圧力は定量化が困難であり、これら両者の定量的な対応関係はまだよくわかっていない。本研究では、負の熱膨張(NTE)を持つ永久磁石の候補である金属間化合物を調べた。放射光X線その場観察により、AlをドープしたHo Fe
Fe に負の化学圧力があることを明らかにし、単位セル体積の温度・圧力依存性を用いそれを定量的に評価した。また、磁化測定と中性子回折測定を組み合わせることで、磁気秩序に対する化学圧力と静水圧の違いを比較した。興味深いことに、圧力はNTEの抑制と増強を制御するために使用することができた。電子状態計算から、圧力がFermiレベル(EF)に対する主要バンドの上部に影響を与えたことを示しており、これは磁気安定性に影響を与え、それが磁気とNTEを調節する上で重要な役割を果たしていることがわかった。本研究は、圧力の影響を理解し、それを利用して機能性材料の特性を制御する良い例を示している。
に負の化学圧力があることを明らかにし、単位セル体積の温度・圧力依存性を用いそれを定量的に評価した。また、磁化測定と中性子回折測定を組み合わせることで、磁気秩序に対する化学圧力と静水圧の違いを比較した。興味深いことに、圧力はNTEの抑制と増強を制御するために使用することができた。電子状態計算から、圧力がFermiレベル(EF)に対する主要バンドの上部に影響を与えたことを示しており、これは磁気安定性に影響を与え、それが磁気とNTEを調節する上で重要な役割を果たしていることがわかった。本研究は、圧力の影響を理解し、それを利用して機能性材料の特性を制御する良い例を示している。
Zhang, H.*; Wu, S. C.*; Ao, N.*; Zhang, J. W.*; Li, H.*; Zhou, L.*; 徐 平光; Su, Y. H.
International Journal of Fatigue, 166, p.107296_1 - 107296_11, 2023/01
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:82.83(Engineering, Mechanical)Abnormal damages in railway axles can lead to a significant hazard to running safety and reliability. To this end, a surface treatment was selected to effectively inhibit fatigue crack initiation and growth. In this study, a single edge notch bending fatigue test campaign with artificial notches was conducted to elucidate the fatigue crack non-propagation behavior in railway S38C axles subjected to an induction hardening process. The fatigue cracking behavior in the gradient structure was revealed by optical microscopy, electron backscatter diffraction, and fractography. The microhardness distribution was measured using a Vickers tester. The obtained results show that the microhardness of the strengthening layer is nearly triple that of the matrix. Owing to the gradient microstructures and hardness, as well as compressive residual stress, the fatigue long crack propagates faster once it passes through the hardened zone (approximately 2.0 mm in the radial depth). Thereafter, local retarding (including deflection, branching, and blunting) of the long crack occurs because of the relatively coarse ferrite and pearlite in the transition region and matrix. Totally, this fatigue cracking resistance is reasonably believed to be due to the gradient microstructure and residual stress. These findings help to tailor a suitable detection strategy for maximum defects or cracks in railway axles.
Naeem, M.*; Zhou, H.*; He, H.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; Zhu, Y.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Applied Physics Letters, 119(13), p.131901_1 - 131901_7, 2021/09
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:77.22(Physics, Applied)We investigated the in situ deformation behavior of the CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy at a cryogenic temperature of 140 K and compared it with deformation at room temperature. The sample exhibited higher strength and larger ductility at the cryogenic temperature. The CrCoNi alloy remained single-phase face-centered cubic at room temperature, while deformation at 140 K resulted in a martensitic transformation to the hexagonal close-packed structure. The phase transformation, an additional deformation mechanism to stacking faults, twinning, and dis- location slip, resulted in a higher work hardening at cryogenic temperature. The study addresses the structure metastability in the CrCoNi alloy, which led to the formation of epsilon-martensite from the intrinsic stacking faults.
Li, R.*; Pang, C.*; 雨倉 宏*; Ren, F.*; H bner, R.*; Zhou, S.*; 石川 法人; 大久保 成彰; Chen, F.*
bner, R.*; Zhou, S.*; 石川 法人; 大久保 成彰; Chen, F.*
Nanotechnology, 29(42), p.424001_1 - 424001_8, 2018/10
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:26.36(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)銀イオン注入法と高速重イオン照射法を組み合わせることで、Nd:YAG(Nbをドープしたイットリウム・アルミニウム・ガーネット)結晶中に埋め込まれている銀ナノ粒子を制御性良く変形させることができた。本研究では、Nd:YAG結晶中に埋め込まれた球形状の銀ナノ粒子に高速重粒子線を照射することで、銀ナノ粒子を変形させることを試みた。今回、照射前後の表面プラズモン共鳴の微小な変化を検知できることを利用して、照射による金属ナノ粒子のわずかな変形を検出することにも成功した。また、離散双極子近似(DDA)計算と組み合わせることで、その変形度を定量化する手法を開発した。
 C level structure by
C level structure by  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopy細見 健二; Ma, Y.*; 味村 周平*; 青木 香苗*; 大樂 誠司*; Fu, Y.*; 藤岡 宏之*; 二ツ川 健太*; 井元 済*; 垣口 豊*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2015(8), p.081D01_1 - 081D01_8, 2015/08
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:64.57(Physics, Multidisciplinary) 線分光によって
線分光によって Cハイパー核のレベル構造を精密に測定した。ゲルマニウム検出器群Hyperball2を用いて、
Cハイパー核のレベル構造を精密に測定した。ゲルマニウム検出器群Hyperball2を用いて、 C
C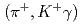 反応からの4本の
反応からの4本の 線遷移を同定することに成功した。基底状態スピン二重項
線遷移を同定することに成功した。基底状態スピン二重項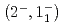 のエネルギー間隔は直接遷移
のエネルギー間隔は直接遷移
 線により、
線により、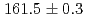 (stat)
(stat)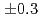 (syst)keVと測定された。また、励起準位である
(syst)keVと測定された。また、励起準位である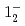 と
と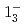 について、それぞれ、
について、それぞれ、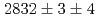 , keVと
, keVと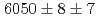 , keVと励起エネルギーを決定した。これらの測定された
, keVと励起エネルギーを決定した。これらの測定された Cの励起エネルギーは反応分光による
Cの励起エネルギーは反応分光による ハイパー核の実験研究において決定的な基準となる。
ハイパー核の実験研究において決定的な基準となる。
 Re
ReZhang, Y. H.*; Guo, S.*; Zhou, X. H.*; Ma, L.*; Guo, W. T.*; 大島 真澄; 藤 暢輔; 小泉 光生; 長 明彦; 木村 敦; et al.
Chinese Physics Letters, 24(5), p.1203 - 1206, 2007/05
タンデム加速器からの重イオン( Al)ビームを用い、多重
Al)ビームを用い、多重 線検出装置GEMINI-IIにより、重イオン核反応後の即発
線検出装置GEMINI-IIにより、重イオン核反応後の即発 線を測定し、
線を測定し、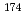 Reの高励起状態の準位構造を調べた。
Reの高励起状態の準位構造を調べた。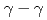 同時計数データを解析した。既知の
同時計数データを解析した。既知の![$$pi 1/2^-[541] bigotimes nu 1/2^-[521]$$](/search/images/EROHA0JAGEXTEXRNLM0TIMK3EBOGE0LHN30GS1LFOMQFY1TVEAYS4MS4FVNTKMRRLUSA.gif) 回転バンドとの結合関係から、新しい回転バンドが同定された。近傍核の系統性から、このバンドは
回転バンドとの結合関係から、新しい回転バンドが同定された。近傍核の系統性から、このバンドは![$$pi 1/2^-[541] bigotimes nu 5/2^-[512]$$](/search/images/EROHA0JAGEXTEXRNLM0TIMK3EBOGE0LHN30GS1LFOMQFY1TVEA0S4MS4FVNTKMJSLUSA.gif) 配位の上に立つ基底状態回転バンドであることを提唱した。新しいバンドは低スピン指標逆転現象を示し、新たな理論解析の必要性を示唆する結果となった。
配位の上に立つ基底状態回転バンドであることを提唱した。新しいバンドは低スピン指標逆転現象を示し、新たな理論解析の必要性を示唆する結果となった。
Qin, T. Y.*; Zhang, H.*; Zhou, L.*; Ao, N.*; 徐 平光; Su, Y. H.; Wu, S. C.*; 菖蒲 敬久
no journal, ,
The S38C railway axles are developed for Shinkansen (Bullet Train) through high-frequency induction hardening and the residual stresses are introduced into the axle with a depth of several millimeters. Residual stresses seriously affect the fatigue mechanical strength and fatigue life of engineering structures, and the accurate determination and the optimization control of the three-dimensional (3D) residual stress distribution of high-speed railway S38C axles are increasingly necessary for improving the axle service life. Here, the residual stresses of the S38C axle samples were measured by using the RESA (residual stress analyzer) angle dispersive neutron diffractometer at JRR-3 (Japan research reactor No.3). The large axle samples were electro-discharge machined into: (a) 3 mmH 3 mmA
3 mmA 20 mmR comb-shape stress-free coupons with a comb spacing of 1 mm to relieve the transformation induced residual stresses and determine the stress-free lattice spacing, d0; (b) sectioned bar sample 120mmA
20 mmR comb-shape stress-free coupons with a comb spacing of 1 mm to relieve the transformation induced residual stresses and determine the stress-free lattice spacing, d0; (b) sectioned bar sample 120mmA 15mmR
15mmR  15mmH) and sectioned fan sample (91mmR
15mmH) and sectioned fan sample (91mmR 158mmH
158mmH 15mmA) to well measure the stress distribution in limited beam time. The residual stress distribution of the large axle samples was obtained in three directions (axial(A), radial(R) and hoop(H)) from the surface to the core. Unlike previous studies that only focused on the axial residual stresses of the axle, we found that the hoop residual stresses also have considerable values, which verified the necessity of 3D residual stress testing. Subsequently, according to the residual stress field and basic mechanical properties of the S38C axle obtained by experiments, the 3D residual stress field is reconstructed in the real axle by using an iterative technique. These results are much valuable to reveal the fatigue failure behavior of high-speed railway axles after surface strengthening and to optimize the non-destructive inspection interval.
15mmA) to well measure the stress distribution in limited beam time. The residual stress distribution of the large axle samples was obtained in three directions (axial(A), radial(R) and hoop(H)) from the surface to the core. Unlike previous studies that only focused on the axial residual stresses of the axle, we found that the hoop residual stresses also have considerable values, which verified the necessity of 3D residual stress testing. Subsequently, according to the residual stress field and basic mechanical properties of the S38C axle obtained by experiments, the 3D residual stress field is reconstructed in the real axle by using an iterative technique. These results are much valuable to reveal the fatigue failure behavior of high-speed railway axles after surface strengthening and to optimize the non-destructive inspection interval.
Hu, F. F.*; Qin, T. Y.*; Su, Y. H.; Ao, N.*; Zhou, L.*; 徐 平光; Parker, J. D.*; 篠原 武尚; Wu, S. C.*
no journal, ,
High-frequency induction hardened S38C axles are widely applied in Japan Shinkansen and China bulletin trains. Due to well-designed surface treatment, these axles produce a large gradient change in the material structure from the axle surface to the core, resulting in a large-layer depth of residual strain and microhardness. It is well known that the residual strain of a real component is of great importance for its long-cycle service assessment, mainly at the reduced non-destructive detect interval and low maintenance cost. Fortunately, the neutron beam has a high penetrating capacity, which provides the advantage of using Bragg-edge transmission imaging to characterize the residual strain and microstructure inside large engineering components. In our study, ring shaped specimens of the axle were prepared. The neutron transmission imaging experiments were conducted at RADEN in J-PARC MLF under proposal Nos. 2022A0298 and 2023A0069. The obtained results reveal that the 0-5 mm area of the axle surface is compressive residual strain, while the core region is the combination of the tensile residual strain and the compressive residual strain. In the presentation, we will also analyze and compare the changes in residual strain and microstructure in defective S38C axles at various fatigue stages. We are expecting to employ pulsed neutron imaging data to assess the fatigue resistance of the axle.
Qin, T. Y.*; Hu, F. F.*; 徐 平光; Zhang, H.*; Zhou, L.*; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; 菖蒲 敬久; Wu, S. C.*
no journal, ,
Gradient compressive residual stress with a depth of several millimeters exists in railway S38C hollow axles subject to surface induction hardening, which is a challenging problem for structural integrity assessment. To address this, the axial, hoop, and radial residual stress values inside the axles are measured by neutron diffraction technology. By integrating the limited neutron diffraction data, an innovative nodal stress based coordinate assignment (INSCA) approach was then proposed, to numerically reconstruct the global initial residual stress field in three dimensions for S38C axles. The comparison between simulations and experiments clearly show that approximately 515 MPa (axial), 710 MPa (hoop), and 43 MPa (radial) compressive residual stresses were retained underneath the induction hardened martensite layer, which also validates the newly-developed INSCA method. By including the measured axial- and hoop-direction residual stresses, the crack propagation behavior of railway S38C axles were investigated, in terms of fracture mechanics. It was clearly shown that the presence of compressive residual stress leads to a lower driving force of crack propagation, in terms of stress intensity factor range (
 ). Such smaller
). Such smaller 
 also indicates that this compressive residual stress can effectively prolong the service lifetime of high-speed railway axles subjected to induction hardening treatment.
also indicates that this compressive residual stress can effectively prolong the service lifetime of high-speed railway axles subjected to induction hardening treatment.
Zhou, L.*; Zhang, H.*; Qin, T. Y.*; Ao, N.*; 徐 平光; Su, Y. H.; He, L. H.*; Parker, J. D.*; 篠原 武尚; 菖蒲 敬久; et al.
no journal, ,
The neutron diffraction is widely applied to evaluate various microstructures and residual stresses while the neutron Bragg-Edge imaging is increasingly employed to obtain 2D mapping. Here, the microstructure and residual strain in induction-hardened S38C steel railway axles were complementarily measured by using the GPPD time-of-flight power diffractometer at CSNS (China spallation neutron source), the RESA angle dispersive neutron diffractometer at JRR-3 and the RADEN energy-resolved neutron imaging system at J-PARC. The full neutron patterns from GPPD about the gradient microstructure were Rietveld analyzed, and the related parameters from the surface to the core were found in good consistence with the microstructure mapping from RADEN. The 3 3
3 20 mm
20 mm comb-shape d0 samples were used on RESA, and the residual stress distribution in three directions was evaluated successfully. These results suggest a complementary use of various neutron instruments is valuable in engineering.
comb-shape d0 samples were used on RESA, and the residual stress distribution in three directions was evaluated successfully. These results suggest a complementary use of various neutron instruments is valuable in engineering.