Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kubo, Kotaro; Zheng, X.; Tanaka, Yoichi; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Jang, S.*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part O; Journal of Risk and Reliability, 237(5), p.947 - 957, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:53.83(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)Probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) is a method used to assess the risks associated with large and complex systems. However, the timing at which nuclear power plant structures, systems, and components are damaged is difficult to estimate if the risk of an external event is evaluated using conventional PRA based on event trees and fault trees. A methodology coupling thermal-hydraulic analysis with external event simulations using Risk Assessment with Plant Interactive Dynamics (RAPID) is therefore proposed to overcome this limitation. A flood propagation model based on Bernoulli's theorem was applied to represent internal flooding in the turbine building of the pressurized water reactor. Uncertainties were also taken into account, including the flow rate of the floodwater source and the failure criteria for the mitigation systems. The simulated recovery actions included the operator isolating the floodwater source and using a drainage pump; these actions were modeled using several simplifications. Overall, the results indicate that combining isolation and drainage can reduce the conditional core damage probability upon the occurrence of flooding by approximately 90%.
Yamaguchi, Akinori*; Yokotsuka, Muneyuki*; Furuta, Masayo*; Kubota, Kazuo*; Fujine, Sachio*; Mori, Kenji*; Yoshida, Naoki; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 21(4), p.173 - 182, 2022/09
Risk information obtained from probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of measures against severe accidents in nuclear facilities. The PRA methods used for reprocessing facilities are considered immature compared to those for nuclear power plants, and to make the methods mature, reducing the uncertainty of accident scenarios becomes crucial. In this paper, we summarized the results of literature survey on the event progression of evaporation to dryness caused by boiling of high-level liquid waste (HLLW) which is a severe accident in reprocessing facilities and migration behavior of associated radioactive materials. Since one of the important characteristics of Ru is its tendency to form volatile compounds over the course of the event progression, the migration behavior of Ru is categorized into four stages based on temperature. Although no Ru has been released in the waste in the high temperature region, other volatile elements such as Cs could be released. Sufficient experimental data, however, have not been obtained yet. It is, therefore, necessary to further clarify the migration behavior of radioactive materials that predominantly depends on temperature in this region.
Yamaguchi, Masaaki; Kato, Tomoko; Suzuki, Yuji*; Makino, Hitoshi
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 27(2), p.72 - 82, 2020/12
An efficient analytical tool to calculate temporal change of topography and repository depth due to uplift and erosion was developed for use in performance assessment of high level radioactive waste geological disposal. The tool was developed as ArcGIS model, incorporating simplified landform development simulation, to enable trial calculation of various conditions such as initial topography, uplift rate and its distributions, and repository location. This tool enables to support decision on which processes, features, and their changes should be taken into account for performance assessment, by calculating topography change and repository depth change under various conditions.
Kubo, Kotaro; Zheng, X.; Tanaka, Yoichi; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Jang, S.*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Proceedings of 30th European Safety and Reliability Conference and 15th Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management Conference (ESREL 2020 and PSAM-15) (Internet), p.2279 - 2286, 2020/11
Probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) is one of the methods used to assess the risks associated with large and complex systems. When the risk of an external event is evaluated using conventional PRA, a particular limitation is the difficulty in considering the timing at which nuclear power plant structures, systems, and components fail. To overcome this limitation, we coupled thermal-hydraulic and external-event simulations using Risk Assessment with Plant Interactive Dynamics (RAPID). Internal flooding was chosen as the representative external event, and a pressurized water reactor plant model was used. Equations based on Bernoulli's theorem were applied to flooding propagation in the turbine building. In the analysis, uncertainties were taken into account, including the flow rate of the flood water source and the failure criteria for the mitigation systems. In terms of recovery action, isolation of the flood water source by the operator and drainage using a pump were modeled based on several assumptions. The results indicate that the isolation action became more effective when combined with drainage.
Kubo, Kotaro; Zheng, X.; Tanaka, Yoichi; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Jang, S.*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications + Monte Carlo 2020 (SNA + MC 2020), p.308 - 315, 2020/10
Dynamic probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) is a method for improving the realism and completeness of conventional PRA. However, enormous calculation costs are incurred by these improvements. One solution is to select an appropriate sampling method. In this paper, we applied the Monte Carlo, Latin hypercube, grid-point, and quasi-Monte Carlo sampling methods to the dynamic PRA of a simplified accident sequence and compared the results for each method. Quasi-Monte Carlo sampling was found to be the most effective method in this case.
Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Inoue, Kazumi; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; Kikuchi, Masaaki*; Sakauchi, Nobuyuki*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-030, 115 Pages, 2015/12
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and bylaw of Ibaraki prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2014. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Sumiya, Shuichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Miyagawa, Naoto; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Inoue, Kazumi; Yoshii, Hideki; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-041, 115 Pages, 2014/01
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, and the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and bylaw of Ibaraki prefecture), this report describes the effluent control results of liquid waste discharged from the JAEA's Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories in the fiscal year 2012, from 1st April 2012 to 31st March 2013. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other facilities were much lower than the authorized limits of the above regulations.
Sato, Shoichi*; Ichimura, Makoto*; Yamaguchi, Yusuke*; Katano, Makoto*; Imai, Yasutaka*; Murakami, Tatsuya*; Miyake, Yuichiro*; Yokoyama, Takuro*; Moriyama, Shinichi; Kobayashi, Takayuki; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 5, p.S2067_1 - S2067_4, 2010/12
Ion cyclotron emissions (ICEs) due to deuterium-deuterium fusion-product (FP) ions on JT-60U are studied. ICE due to H-ions is identified from the difference of the toroidal wave number of 2nd ICE(D). The parameter dependence for the appearance of ICE(H) is investigated from the experimental conditions and also is studied by using "Escape Particle Orbit analysis Code (EPOC)".
 Zn from the roots to the shoots in Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator
Zn from the roots to the shoots in Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator 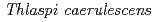 by PETIS
by PETISSekimoto, Hitoshi*; Kawachi, Naoki; Watanabe, Satoshi; Yamaguchi, Yoshie*; Ozawa, Toyoaki*; Shima, Daisuke*; Ishikawa, Sayuki*; Fujimaki, Shu; Suzui, Nobuo; Ishii, Satomi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2008-055, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2007, P. 108, 2008/11
 -rays; Guineagrass and sorghum
-rays; Guineagrass and sorghumNakagawa, Hitoshi*; Inafuku, Masashi*; Kusaba, Makoto*; Yamaguchi, Hiroyasu*; Morishita, Toshikazu*; Morita, Ryohei*; Nishimura, Minoru*; Hoeman, S.*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Hase, Yoshihiro; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 72, 2008/03
no abstracts in English
Sekimoto, Hitoshi*; Kawachi, Naoki; Honda, Shuzo*; Yamaguchi, Yoshie*; Kato, Shota*; Yoneyama, Kaori*; Fujimaki, Shu; Suzui, Nobuo; Ishii, Satomi; Watanabe, Satoshi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 124, 2008/03
no abstracts in English
 ray
rayMorita, Ryohei*; Morishita, Toshikazu*; Nakagawa, Hitoshi*; Nishimura, Minoru*; Yamaguchi, Hiroyasu*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 78, 2007/02
no abstracts in English
Fuchimukai, Junichi*; Yamaguchi, Hitoshi*; Meguro, Yoshihiro; Kubota, Toshio*; Igarashi, Shukuro*
Solvent Extraction Research and Development, Japan, 13, p.139 - 146, 2006/00
no abstracts in English
Okasaka, Kazunobu*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Oyama, Hitoshi*; Hara, Tamio*; Yamaguchi, Naohiro*; Ando, Kozo*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 39(1), p.70 - 81, 2000/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.78(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Kabasawa, Satsuki; Yamaguchi, Masaaki; Ebashi, Takeshi; Makino, Hitoshi; Minari, Eriko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Koo, Shigeru*; Makino, Hitoshi; Yamaguchi, Masaaki; Ebashi, Takeshi; Takahashi, Hirokazu*; Tsuchiya, Terumitsu*; Mitsuyama, Kazuaki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kato, Tomoko; Makino, Hitoshi; Takeuchi, Shinji; Miyahara, Kaname; Maekawa, Keisuke; Yamaguchi, Masaaki; Iijima, Kazuki; Amano, Kenji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Sawada, Atsushi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Koo, Shigeru*; Yamaguchi, Masaaki; Makino, Hitoshi; Tsuchiya, Terumitsu*; Kanzaki, Tametoki*
no journal, ,
A deep borehole disposal has been considered as a disposal option and various technical studies in various countries have been reported in recent years. This study summarizes the main points for discussion on deep borehole disposal and the technical issues for its implementation through research of and comparison among multiple examples in other countries. In addition, we will try to examine the points and issues of deep borehole disposal more specifically through, for example, case studies on the drilling of deep boreholes and the maintenance of the borehole walls, which are one of the important prerequisites for the implementation of deep borehole disposal.
Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Koizumi, Satoshi; Ojima, Hitoshi*; Isoyama, Ryo*; Ishiwatari, Yoshiyuki*; Kodama, Hiroto*; Takeda, Hisanori*; Fukita, Hitoshi*; Takashima, Yoshiyuki*
no journal, ,
Resin-filler composites were investigated by small-angle neutron scattering (SANS). Two types of fillers, talc and TiO , were employed and compounded with polypropylene in this study. The dispersion state of the fillers was examined by SANS measurements. In addition, the size distribution of the fillers was separately measured through the laser right scattering and SEM. The calculated scattering function including the polydispersity of fillers whose size distribution reflects the results of laser right scattering and SEM consistently reproduced the experimental SANS scattering profiles.
, were employed and compounded with polypropylene in this study. The dispersion state of the fillers was examined by SANS measurements. In addition, the size distribution of the fillers was separately measured through the laser right scattering and SEM. The calculated scattering function including the polydispersity of fillers whose size distribution reflects the results of laser right scattering and SEM consistently reproduced the experimental SANS scattering profiles.
 ray; Guinea grass and sorghum
ray; Guinea grass and sorghumNakagawa, Hitoshi*; Inafuku, Masashi*; Kusaba, Makoto*; Yamaguchi, Hiroyasu*; Morishita, Toshikazu*; Morita, Ryohei*; Nishimura, Minoru*; Hoeman, S.*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Hase, Yoshihiro; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English