Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Group for Fukushima Mapping Project
JAEA-Technology 2024-017, 208 Pages, 2025/03
This report presents results of the investigations on the distribution-mapping project of radioactive substances owing to TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) conducted in FY2023. Car-borne surveys, a measurement using survey meters, a walk survey and an unmanned helicopter survey were carried out to obtain air dose rate data to create their distribution maps, and temporal changes of the air dose rates were analyzed. Surveys on depth profile of radiocesium and in-situ measurements as for radiocesium deposition were performed. Based on these measurement results, effective half-lives of the temporal changes in the air dose rates and the deposition were evaluated. Score maps to classify the importance of the measurement points were created, and the temporal changes in the score were analyzed. A system to report the tritium concentration level in seawater to the Nuclear Regulation Authority was operated, and the variation of tritium concentration before and after the discharge of ALPS treated water to the ocean was analyzed. Monitoring data in coastal area performed owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan until FY2023 was analyzed. Using the Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach, we obtained maps that integrated air dose rate distribution data acquired through surveys such as car-borne and walk surveys. Representative life patterns that can be expected after the return to the evacuation-designated restricted area were set, and the cumulative exposure doses were evaluated for the local governments and residents in the area. The measurement results for FY2023 were published on the Web site and measurement data were stored as CSV format. Radiation monitoring and analysis of environmental samples owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan were carried out.
Yoshida, M.*; McDermott, R. M.*; Angioni, C.*; Camenen, Y.*; Citrin, J.*; Jakubowski, M.*; Hughes, J. W.*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Mantica, P.*; Mariani, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 65(3), p.033001_1 - 033001_132, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:91.43(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Progress in physics understanding and theoretical model development of plasma transport and confinement in the ITPA Transport and Confinement Topical Group since the publication of the ITER Physics Basis was summarized focusing on the contributions to ITER and burning plasma prediction and control. This paper provides a general and streamlined overview on the advances that were mainly led by the ITPA TC joint experiments and joint activities for the last 15 years. This paper starts with the scientific strategy and scope of the ITPA TC Topical group and overall picture of the major progress, followed by the progress of each research field: particle transport, impurity transport, ion and electron thermal turbulent transport, momentum transport, impact of 3D magnetic fields on transport, confinement mode transitions, global confinement, and reduced transport modeling.
Licensing Application Group, Fuels and Materials Department
JAEA-Testing 2024-002, 20 Pages, 2024/08
The contamination accident occurred at Plutonium Fuel Research Facility (PFRF) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) Oarai Research and Development Institute on June 6, 2017. During the work of opening the fuel storage container and checking the properties of the contents, the plastic bag that double-packed the inner container burst. The scattering of the fuels contaminated the work room and exposed the worker. The cause of the plastic bag burst was that the enclosed epoxy resin was decomposed by  -rays and the internal pressure increased due to the generated hydrogen gas. The 54 storage containers containing plutonium held at PFRF also at risk of increasing internal pressure. Therefore, an opening inspection was conducted to confirm the contents of the storage container in the hot cell. In addition, the contents of storage containers that may generate gas were stabilized. We are planning to transport the fuel storage containers out to another facility for the decommission of PFRF. The other 9 storage containers include oxide raw material powder: Pu +
-rays and the internal pressure increased due to the generated hydrogen gas. The 54 storage containers containing plutonium held at PFRF also at risk of increasing internal pressure. Therefore, an opening inspection was conducted to confirm the contents of the storage container in the hot cell. In addition, the contents of storage containers that may generate gas were stabilized. We are planning to transport the fuel storage containers out to another facility for the decommission of PFRF. The other 9 storage containers include oxide raw material powder: Pu +  U in excess of 220 g. In order to decrease to less than 220 g (the limit of transport cask), the metal inner containers in the storage container were taken out and repacked in another storage container. This report describes advance measures such as permit application and the details of about storage container opening inspection and metal inner container repacking.
U in excess of 220 g. In order to decrease to less than 220 g (the limit of transport cask), the metal inner containers in the storage container were taken out and repacked in another storage container. This report describes advance measures such as permit application and the details of about storage container opening inspection and metal inner container repacking.
Risk Analysis Research Group, Reactor Safety Research Division, Nuclear Safety Research Center
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-006, 40 Pages, 2024/07
The Risk Analysis Research Group, Reactor Safety Research Division, Nuclear Safety Research Center, Sector of Nuclear Safety Research and Emergency Preparedness, Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been developing OSCAAR, a probabilistic risk assessment program for nuclear facility accidents. OSCAAR has the feature to calculate atmospheric concentrations of radioactive materials using an atmospheric dispersion model. This feature requires the input of meteorological data about wind speed, precipitation rate, atmospheric stability and so on. However, to use numerical weather prediction data created from the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) on OSCAAR, it is necessary to convert the data format to match OSCAAR input format in advance. Therefore, we developed GPV2OSC, a pre-processing program for OSCAAR, to create meteorological data converted from JMA weather prediction data format to OSCAAR input format when the target region and period are specified. This report describes the outline and usage of GPV2OSC.
Group for Fukushima Mapping Project
JAEA-Technology 2023-024, 176 Pages, 2024/03
This report presents results of the investigations on the distribution-mapping project of radioactive substances owing to TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) conducted in FY2022. Car-borne surveys, a measurement using survey meters, a walk survey and an unmanned helicopter survey were carried out to obtain air dose rate data to create their distribution maps, and temporal changes of the air dose rates were analyzed. Surveys on depth profile of radiocesium and in-situ measurements as for radiocesium deposition were performed. Based on these measurement results, effective half-lives of the temporal changes in the air dose rates and the deposition were evaluated. Score maps to classify the importance of the measurement points were created, and the factors causing changes in the score when monitoring data from multiple years were used were discussed. The range of fluctuation of past tritium concentration data in seawater was determined, and the causes of the fluctuation were discussed. Monitoring data in coastal area performed in 2022 owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan was summarized, and temporal changes in cesium-137 were analyzed. Using the Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach, we obtained maps that integrated air dose rate distribution data acquired through surveys such as car-borne and walk surveys with respect to the region within 80 km from the FDNPS and Fukushima Prefecture. The measurement results for FY2022 were published on the "Database for Radioactive Substance Monitoring Data", and measurement data were stored as CSV format. Radiation monitoring and analysis of environmental samples owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan were carried out.
HTGR Design Group, HTGR Project Management Office
JAEA-Technology 2023-019, 39 Pages, 2024/01
In order to realize the development of the demonstration reactor of High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) with a target of starting operation in the 2030s, as indicated in the "Basic Policy for GX Realization" (Cabinet Decision on February 10, 2023) and the Working Group on Innovative Reactors of METI, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been working on the development of a standard for the development of a HTGR under the Atomic Energy Society of Japan and the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers. In addition, JAEA has been commissioned by the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) to conduct the "Demonstration Project for Mass Hydrogen Production Technology Using Ultra-High Temperatures" and has been promoting a hydrogen production project using the HTTR (High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor). Furthermore, in collaboration with the National Nuclear Laboratory (NNL) of the United Kingdom and the National Centre for Nuclear Research (NCBJ) of Poland, JAEA are aiming to strengthen the international competitiveness of HTGR technology by further upgrading the HTGR technology developed in Japan through the construction and operation of the HTTR. In response to the growing interest in HTGR development in Japan and abroad, we have developed FAQs on HTGR related technologies in order to provide accurate technical information on HTGRs.
Reactor Integral Test Working Group, JENDL Committee
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-004, 132 Pages, 2023/06
The reactor integral test working group organized in the JENDL committee has prepared the benchmark database which is devoted to performance evaluation and validation testing of JENDL-5 regarding simulation of nuclear fission reactors applications, and the report "JAEA-Data/Code 2017-006" for the aforementioned benchmark database was published in 2017. After the publication of the report, the benchmark database has been extended energetically in Japan Atomic Energy Agency under the cooperation of the JENDL Committee. The database contributes improvement of reliability of JENDL-5. This report is a summary of the aforementioned extended database, and the report is expected to be efficiently utilized for not only the developments of nuclear data library in future but also integral tests of released nuclear data libraries.
Group for Fukushima Mapping Project
JAEA-Technology 2022-026, 152 Pages, 2023/01
This report presents results of the investigations on the distribution-mapping project of radioactive substances owing to TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) conducted in FY2021. Car-borne surveys, a flat ground measurement using survey meters, a walk survey and an unmanned helicopter survey were carried out to obtain air dose rate data to create air dose rate distribution maps, and temporal changes of the air dose rates were analyzed. Surveys on depth profile of radiocesium and in-situ measurements as for radiocesium deposition were performed. Based on these measurement results, effective half-lives of the temporal changes in the air dose rates and the deposition were evaluated. Score maps to classify the importance of the measurement points were created for Fukushima Prefecture and the 80 km zone from the FDNPS, and the factors causing changes in the score when monitoring data from multiple years were used were discussed. Monitoring data in coastal area performed owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan until 2020 was summarized, and temporal changes in cesium-137 were analyzed. Using the Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach, we obtained maps that integrated the air dose rate distribution data obtained in this project with respect to the region within 80 km from the FDNPS and Fukushima Prefecture. The measurement results for FY2021 were published on the "Expansion Site of Distribution Map of Radiation Dose", and measurement data were stored as CSV format. Radiation monitoring and analysis of environmental samples owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan were carried out.
Waste Technical Standards Working Group
JAEA-Review 2021-063, 85 Pages, 2022/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has set up a Waste Technical Standards Working Group within the Sector of Decommissioning and Radioactive Wastes Management of Japan Atomic Energy Agency as of FY2015. In this Working Group, we discussed methods for corresponding to the technical standards on confirmation related to waste disposal, etc. This annual report summarizes the results of discussion in FY2020 regarding a revision of the Operational Procedures Manual for Quality Control of Radioactive Waste Disposal based on a consideration of an acceleration on waste segregation and optimization of decommissioning waste processing. Moreover, measures which is dealt with the revision of the regulation were examined.
Shielding Integral Test Working Group, JENDL Committee
JAEA-Research 2021-015, 86 Pages, 2022/03
The major revised version of Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (JENDL), JENDL-4.0, was released in May, 2010. Thus Shielding Integral Test Working Group in JENDL Committee has performed benchmark tests of JENDL-4.0 for the shielding and fusion neutronics fields in order to verify accuracy of JENDL-4.0. We adopted many benchmark experiments: 1) the in-situ and Time-of-Flight (TOF) experiments with DT neutrons at JAEA/FNS, 2) the TOF experiments with DT neutrons at Osaka Univ./OKTAVIAN, 3) the aluminum, iron, nickel and lead experiments with DT neutrons at IPPE, Russia, 4) the iron and stainless steel experiments at ORNL/TSF, US, 5) the ASPIS iron experiment at Winfrith, England, 6) the iron experiments with  Cf neutron source at KfK, Germany and 7) the iron experiments with
Cf neutron source at KfK, Germany and 7) the iron experiments with  Cf neutron source at NIST, US. These experiments were analyzed by using the Monte Carlo code MCNP4 or MCNP5 and/or Sn codes ANISN, DOT3.5 and DORT with mainly JENDL-3.3 and JENDL-4.0. The calculated results demonstrated that JENDL-4.0 led to better agreements with the measured data due to revisions of JENDL-3.3 problems.
Cf neutron source at NIST, US. These experiments were analyzed by using the Monte Carlo code MCNP4 or MCNP5 and/or Sn codes ANISN, DOT3.5 and DORT with mainly JENDL-3.3 and JENDL-4.0. The calculated results demonstrated that JENDL-4.0 led to better agreements with the measured data due to revisions of JENDL-3.3 problems.
Group for Fukushima Mapping Project
JAEA-Technology 2021-025, 159 Pages, 2022/01
This report presents results of the investigations on the distribution-mapping project of radioactive substances owing to TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) conducted in FY2020. Car-borne surveys, a flat ground measurement using survey meters, a walk survey and an unmanned helicopter survey were carried out to obtain air dose rate data. Air dose rate distribution maps were created and temporal changes of the air dose rates were analyzed. Regarding radiocesium deposition into the ground, surveys on depth profile of radiocesium and in-situ measurements were performed. Based on these measurement results, effective half-lives of the temporal changes in the air dose rates and the deposition were evaluated. In the examination of scoring for classifying the importance of measurement points, a score map was created for Fukushima Prefecture and the 80 km zone from the FDNPS, and the factors causing changes in the score when monitoring data from multiple years were used were discussed. Using the Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach, we obtained maps that integrated the air dose rate distribution data obtained from aircraft monitoring, car-borne surveys, and walk surveys with respect to the region within 80 km from the FDNPS and Fukushima Prefecture. The measurement results for FY2020 were published on the "Expansion Site of Distribution Map of Radiation Dose", and measurement data were stored as CSV format. Radiation monitoring and analysis of environmental samples owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan were carried out.
Covariance Data Utilization and Promotion Working Group, JENDL Committee
JAEA-Review 2021-014, 139 Pages, 2021/09
The Covariance Data Utilization and Promotion Working Group organized in the JENDL committee has worked for three years to study the following five issues: (1) to identify uncertainties which have not yet been quantified or which are too difficult to be quantified, (2) to identify uncertainties which have been quantified, but whose reasonable bases are too weak, (3) to propose realistic methods to assure the reliability of the covariance data, (4) to propose actions which should be taken in the fields of nuclear data measurement, evaluation and application to promote the covariance data utilization, and (5) to make a recommendation how the covariance data are treated and positioned in Japanese evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL. This final report summarizes the outcomes of this working group. This report is organized as follows. First, the fundamental information/issues on the nuclear data uncertainties are briefly described, and then the current status and issues of the covariance data evaluation and utilization in the fields of the nuclear data measurement, evaluation and application are presented. Furthermore, several methods to assure the reliability of the covariance data are proposed, and finally, some guidelines such that what kind of covariance data provided in the evaluated nuclear data files are desirable, and what kinds of attention the users should take care in utilizing the covariance data are proposed as a conclusion of the working group.
Group for Fukushima Mapping Project
JAEA-Technology 2020-014, 158 Pages, 2020/12
This report presents results of the investigations on the distribution-mapping project of radioactive substances owing to TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) conducted in FY2019. Car-borne surveys, a flat ground measurement using survey meters, a walk survey and an unmanned helicopter survey were carried out to obtain air dose rate data. Air dose rate distribution maps were created and temporal changes of the air dose rates were analyzed. Regarding radiocesium deposition into the ground, surveys on depth profile of radiocesium and in-situ measurements were performed. Based on these measurement results, effective half-lives of the temporal changes in the air dose rates and the deposition were evaluated. In the examination of scoring to classify the importance of measurement points, we created a score map of Fukushima Prefecture and that within 80 km from the FDNPS based on the "score" method developed in 2018. The way of monitoring radioactive materials in land area was examined and the representativeness of monitoring points was proposed. Using the Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach, we obtained maps that integrated the air dose rate distribution data obtained from aircraft monitoring, car-borne surveys, and walk surveys with respect to the region within 80 km from the FDNPS and Fukushima Prefecture. The measurement results for FY2019 were published on the "Expansion Site of Distribution Map of Radiation Dose", and measurement data were stored as CSV format. Radiation monitoring and analysis of environmental samples owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan were carried out.
Radiation Risk Analysis Research Group, Risk Analysis and Applications Research Division
JAEA-Testing 2020-001, 65 Pages, 2020/03
The Nuclear Safety Research Center (NSRC) has developed a Level 3 Probabilistic Risk Assessment (PRA) code, the OSCAAR (Off-Site Consequence Analysis code for Atmospheric Release in Reactor Accident). Using a source-term derived from a severe accident analysis code, OSCAAR calculates the downwind transport, airborne dispersion, and ground deposition of radioactive materials as well as the radiation dose and then can evaluate the effect of early and late protective actions and health effect. The NSRC also developed the OSCAAR Code Package that has a Windows-based interface and framework for performing consequence analysis in order to create or modify input files, execute the OSCAAR and postprocess the output files efficiently and conveniently. The report is a user's manual for the OSCAAR Code Package.
Group for Fukushima Mapping Project
JAEA-Technology 2019-019, 135 Pages, 2020/03
After the accident at TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), distribution situation survey on radioactive materials have been conducted with financially supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (later the Nuclear Regulatory Agency) from June 2011 to FY2018. Results obtained in the project in FY2018 are presented in this report. Car-borne surveys, a flat ground measurement using survey meters, a walk survey and an unmanned helicopter survey were carried out to obtain air dose rate data. Air dose rate distribution maps were created and temporal changes of air dose rate were analyzed. Regarding radiocesium deposition in the soil, depth profile survey in the soil and in-situ measurement were performed. Based on these measurement results, effective half-life of the air dose rate and the deposition were evaluated. Considering radiation monitoring data obtained in previous surveys and the installation positions of existing monitoring posts, we tried to make the "score" of the importance of measurement points. Using the Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach, we obtained a map that integrated the air dose rate distribution data obtained from aircraft monitoring, car-borne surveys, and walk surveys for the entire region within 80 km from the FDNPS. The measurement results for FY2018 were published on the "Expansion Site of Distribution Map of Radiation Dose", and measurement data were stored as CSV format. Radiation monitoring and environmental sample analysis owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan were carried out.
Development Group for LWR Advanced Technology
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-017, 59 Pages, 2020/03
ECUME (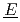 ffective
ffective 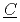 hemistry database of fission products
hemistry database of fission products 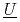 nder
nder 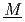 ultiphase r
ultiphase r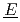 action) is the database for the analyses of FP chemistry which strongly affects all the FP behaviors in a severe accident (SA) of nuclear facility like LWR. ECUME consists of three kinds of datasets: CRK (dataset for
action) is the database for the analyses of FP chemistry which strongly affects all the FP behaviors in a severe accident (SA) of nuclear facility like LWR. ECUME consists of three kinds of datasets: CRK (dataset for 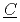 hemical
hemical 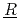 eaction
eaction 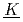 inetics), EM (
inetics), EM (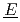 lemental
lemental 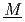 odel set) and TD (
odel set) and TD (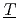 hermo
hermo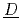 ynamic dataset). The present version of ECUME is prepared especially for the more accurate evaluation of cesium and iodine distribution in a reactor and release amount into an environment which should be of crucial importance towards the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings (1F) and the enhancement of LWR safety after the 1F SA.
ynamic dataset). The present version of ECUME is prepared especially for the more accurate evaluation of cesium and iodine distribution in a reactor and release amount into an environment which should be of crucial importance towards the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings (1F) and the enhancement of LWR safety after the 1F SA.
Japanese Nuclear Data Comitteee, Shielding Integral Test Working Group (FY2006-2010)
JAEA-Research 2018-017, 72 Pages, 2019/03
Integral tests of neutron and photon production data in cross-section libraries based on the Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library, Version 3.3 (JENDL-3.3) have been performed by using shielding benchmarks. An evaluation scheme for shielding benchmark analysis established in the Japanese Nuclear Data Committee (JNDC) was applied to the integral test for 28 materials in 22 medium-heavy nuclei and the compounds such as Lithium, Oxygen, LiF, TEFLON:(CF )n, Sodium, Aluminum, Li
)n, Sodium, Aluminum, Li AlO
AlO , LiAlO
, LiAlO , Silicon, SiC, Titanium, Li
, Silicon, SiC, Titanium, Li TiO
TiO , Vanadium, Chromium, Manganese, Iron, Cobalt, Nickel, SS304, Copper, Arsenic, Selenium, Zirconium, Li
, Vanadium, Chromium, Manganese, Iron, Cobalt, Nickel, SS304, Copper, Arsenic, Selenium, Zirconium, Li ZrO
ZrO , Niobium, Molybdenum, Tungsten and Mercury. Calculations were made by using a continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MCNP and multi-group discrete ordinates codes ANISN, DORT and TORT. Calculations with JENDL-3.2, ENDF/B-VI, EFF-2, FENDL-1 and FENDL-2 were also made for comparison. The results of JENDL-3.3 were generally satisfactory and the cross-section libraries generated with JENDL-3.3 were validated to shielding applications for fission and fusion reactors.
, Niobium, Molybdenum, Tungsten and Mercury. Calculations were made by using a continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MCNP and multi-group discrete ordinates codes ANISN, DORT and TORT. Calculations with JENDL-3.2, ENDF/B-VI, EFF-2, FENDL-1 and FENDL-2 were also made for comparison. The results of JENDL-3.3 were generally satisfactory and the cross-section libraries generated with JENDL-3.3 were validated to shielding applications for fission and fusion reactors.
Hotchi, Hideaki; J-PARC RCS Beam Commissioning Group
Proceedings of 61st ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High-Intensity and High-Brightness Hadron Beams (HB 2018) (Internet), p.20 - 25, 2018/07
no abstracts in English
Waste Technical Standards Working Group
JAEA-Review 2017-017, 112 Pages, 2017/11
In Japan Atomic Energy Agency, JAEA, a Waste Technical Standards Working Group has established since FY2015. The Working Group is composed of the members from waste management sections in each site in JAEA and from Radioactive Waste Management and Disposal Project Department. In this Working Group, we discussed quality management on conditioning waste packages, methodologies to evaluate the radioactivity concentration and measures for dismantling waste. This annual report summarizes the results of discussion in FY2016.
Reactor Integral Test Working Group, JENDL Committee
JAEA-Data/Code 2017-006, 152 Pages, 2017/05
A benchmark database which is devoted to the evaluation of the future JENDL against the criticality of light water reactors was prepared, where the ICSBEP and IRPhEP handbooks by OECD/NEA were utilized effectively. Specific features of this report can be described as follows: (1) The recommendation for benchmarking is based on careful reviewing for the document and related information. Validity of the original benchmark evaluation is carefully checked, and numerical results obtained with JENDL-4.0 are considered. (2) Heterogeneity effect of PuO particles dispersed in fuel medium is consistently quantified for the MOX fuel-loaded experimental data. This precise evaluation is realized by the newly developed finite fuel pin bundle model with the Monte Carlo neutron transport code. (3) Sensitivity analysis is conducted in order to specify nuclear data whose difference between recent nuclear data libraries significantly affects the critical parameter calculation.
particles dispersed in fuel medium is consistently quantified for the MOX fuel-loaded experimental data. This precise evaluation is realized by the newly developed finite fuel pin bundle model with the Monte Carlo neutron transport code. (3) Sensitivity analysis is conducted in order to specify nuclear data whose difference between recent nuclear data libraries significantly affects the critical parameter calculation.