Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
松下 太樹*; 小沢 耀弘*; 荒木 康史; 藤本 純治*; 佐藤 昌利*
Physical Review B, 111(24), p.245131_1 - 245131_11, 2025/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigate the intrinsic spin Nernst effect (SNE), a transverse spin current induced by temperature gradients, in topological Dirac semimetals (TDSMs) and magnetic Weyl semimetals (MWSMs) with Ising spin-orbit coupling. The intrinsic SNE is described by the spin Berry curvature, which reflects the geometric nature of TDSMs and MWSMs. We clarified that the intrinsic SNE becomes significant when the Fermi energy is near, but slightly deviates from, the energy of the point nodes. In this situation, Bloch electrons with strong spin Berry curvature contribute to the SNE while avoiding carrier compensation between electrons and holes. We found that in TDSMs with small Fermi surfaces, the spin Nernst angle, which measures the efficiency of the SNE, is larger than that observed in heavy metals. This suggests that TDSMs with small Fermi surfaces can achieve efficient heat-to-spin current conversion. In MWSMs, variation in the magnitude of the exchange coupling with magnetic moments significantly changes the SNE, affecting both the direction and magnitude of the spin Nernst current. This implies that ferromagnetic transitions can be used to reverse the spin Nernst current. These results provide the fundamentals for future topological spin caloritronics.
 のワイル電子を活用したスピン制御
のワイル電子を活用したスピン制御荒木 康史; 家田 淳一
まぐね, 20(1), p.12 - 17, 2025/02
スピントロニクスにおいて、スピンの電気的操作に際して発生する電力損失は大きな課題である。このジュール発熱を回避する過程として、我々は電子状態のトポロジカル構造を組み込んだ電場誘起スピントルクの理論を構築した。このトポロジカルな寄与は散逸の影響を受けず、従来のスピン移行トルクに比べて単位電流あたりのトルク効率を著しく向上させる。本原理によるスピントルクの発現は、トポロジカルな電子系の典型例である「ワイル電子」を持つ、強磁性酸化物SrRuO における磁化反転実験によって検証された。
における磁化反転実験によって検証された。
堀内 皓斗*; 荒木 康史; 若林 勇希*; 家田 淳一; 山ノ内 路彦*; 他7名*
Advanced Materials, p.2416091_1 - 2416091_9, 2025/00
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Spin Berry curvature characterizes the band topology as the spin counterpart of Berry curvature and is crucial in generating novel spintronics functionalities. By breaking the crystalline inversion symmetry, the spin Berry curvature is expected to be significantly enhanced; this enhancement will increase the intrinsic spin Hall effect in ferromagnetic materials and, thus, the spin-orbit torques (SOTs). However, this intriguing approach is not applied to devices; generally, the spin Hall effect in ferromagnet/heavy-metal bilayer is used for SOT magnetization switching. Here, SOT-induced partial magnetization switching is demonstrated in a single layer of a single-crystalline Weyl oxide SrRuO (SRO) with a small current density of
(SRO) with a small current density of 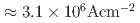 . Detailed analysis of the crystal structure in the seemingly perfect periodic lattice of the SRO film reveals barely discernible oxygen octahedral rotations with angles of
. Detailed analysis of the crystal structure in the seemingly perfect periodic lattice of the SRO film reveals barely discernible oxygen octahedral rotations with angles of 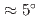 near the interface with a substrate. Tight-binding calculations indicate that a large spin Hall conductivity is induced around small gaps generated at band crossings by the synergy of inherent spin-orbit coupling and band inversion due to the rotations, causing magnetization reversal. The results indicate that a minute atomic displacement in single-crystal films can induce strong intrinsic SOTs that are useful for spin-orbitronics devices.
near the interface with a substrate. Tight-binding calculations indicate that a large spin Hall conductivity is induced around small gaps generated at band crossings by the synergy of inherent spin-orbit coupling and band inversion due to the rotations, causing magnetization reversal. The results indicate that a minute atomic displacement in single-crystal films can induce strong intrinsic SOTs that are useful for spin-orbitronics devices.
Han, J.*; 内村 友宏*; 荒木 康史; Yoon, J.-Y.*; 竹内 祐太郎*; 山根 結太*; 金井 駿*; 家田 淳一; 大野 英男*; 深見 俊輔*
Nature Physics, 20(7), p.1110 - 1117, 2024/07
被引用回数:26 パーセンタイル:98.22(Physics, Multidisciplinary)量子状態の幾何学的構造を特徴づける基礎的な量として、「量子計量」と「ベリー曲率」が存在する。ベリー曲率は、凝縮系において多種の重要な現象に寄与することが知られている。一方、量子計量も新たなトポロジカル物理現象の起源となることが予想されているが、特に常温常圧下においては、その効果はほとんど探索されていない。本研究では、トポロジカルカイラル反強磁性体Mn Snと白金の接合系を用い、界面でのナノスピン構造を介して、電子系の量子計量構造の制御に成功した。ベリー曲率ではなく量子計量特有の効果として、時間反転反対称でかつ電子散乱に対して頑強な、二次非線形ホール効果を測定した。更に、界面スピン構造は弱磁場及び界面スピン軌道相互作用によって急峻に変調されるため、量子計量構造も鋭敏に制御可能であることを示した。本研究成果により、量子状態に内在する量子計量構造を活用したトポロジカル物理現象が室温環境下でも可能になり、且つ応用面においても非線形素子を構築する助けとなることが期待される。
Snと白金の接合系を用い、界面でのナノスピン構造を介して、電子系の量子計量構造の制御に成功した。ベリー曲率ではなく量子計量特有の効果として、時間反転反対称でかつ電子散乱に対して頑強な、二次非線形ホール効果を測定した。更に、界面スピン構造は弱磁場及び界面スピン軌道相互作用によって急峻に変調されるため、量子計量構造も鋭敏に制御可能であることを示した。本研究成果により、量子状態に内在する量子計量構造を活用したトポロジカル物理現象が室温環境下でも可能になり、且つ応用面においても非線形素子を構築する助けとなることが期待される。
 topological Fermi superfluids
topological Fermi superfluids田島 裕之*; 関野 裕太*; 内野 瞬
Physical Review B, 105(6), p.064508_1 - 064508_9, 2022/02
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:45.43(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)スピン トポロジカル・フェルミ超流動体におけるバルクの光学スピン輸送の性質を調べた。具体的には、冷却原子気体の実験で実現可能なp波相互作用する1次元フェルミ系を考えた。弱結合から強結合領域までの系のトポロジカルな性質を描写するためBCS-Leggett理論を適用し、スピン輸送が多体効果をどのように反映するかを示した。我々は光学スピン伝導率を調べることで、トポロジカル転移を検出できることを見つけ、Majoranaゼロモードの低エネルギー有効モデルの有用性も議論した。
トポロジカル・フェルミ超流動体におけるバルクの光学スピン輸送の性質を調べた。具体的には、冷却原子気体の実験で実現可能なp波相互作用する1次元フェルミ系を考えた。弱結合から強結合領域までの系のトポロジカルな性質を描写するためBCS-Leggett理論を適用し、スピン輸送が多体効果をどのように反映するかを示した。我々は光学スピン伝導率を調べることで、トポロジカル転移を検出できることを見つけ、Majoranaゼロモードの低エネルギー有効モデルの有用性も議論した。
山本 慧; Thiang, G. C.*; Pirro, P.*; Kim, K.-W.*; Everschor-Sitte, K.*; 齊藤 英治*
Physical Review Letters, 122(21), p.217201_1 - 217201_5, 2019/05
被引用回数:29 パーセンタイル:81.14(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We propose a topological characterization of Hamiltonians describing classical waves. Applying it to the magnetostatic surface spin waves that are important in spintronics applications, we settle the speculation over their topological origin. For a class of classical systems that includes spin waves driven by dipole-dipole interactions, we show that the topology is characterized by vortex lines in the Brillouin zone in such a way that the symplectic structure of Hamiltonian mechanics plays an essential role. We define winding numbers around these vortex lines and identify them to be the bulk topological invariants for a class of semimetals. Exploiting the bulk-edge correspondence appropriately reformulated for these classical waves, we predict that surface modes appear but not in a gap of the bulk frequency spectrum. This feature, consistent with the magnetostatic surface spin waves, indicates a broader realm of topological phases of matter beyond spectrally gapped ones.
荒木 康史
no journal, ,
The main focus of this presentation is the theory of spin current generation in topological Dirac semimetals (TDSMs), the newly-found three-dimensional topological materials. TDSMs are characterized by pair(s) of doubly-degenerate nodal points (Dirac points) in their momentum-space band structures, which are observed by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) in Na Bi and Cd
Bi and Cd As
As . I focus on a lattice-strained TDSM, to obtain an additional contribution to the spin current generation. I propose that an electric field applied to the strained TDSM gives rise to a nonlinear spin Hall current, namely the spin current perpendicular to and quadratic in the electric field. The spin current response is obtained by the Boltzmann transport theory, regarding the strain as a pseudomagnetic field for the Dirac electrons. This nonlinear effect implies that one can obtain a rectified (dc) pure spin current out of an alternating (ac) electric field, which renders the TDSM an efficient spin-current injector.
. I focus on a lattice-strained TDSM, to obtain an additional contribution to the spin current generation. I propose that an electric field applied to the strained TDSM gives rise to a nonlinear spin Hall current, namely the spin current perpendicular to and quadratic in the electric field. The spin current response is obtained by the Boltzmann transport theory, regarding the strain as a pseudomagnetic field for the Dirac electrons. This nonlinear effect implies that one can obtain a rectified (dc) pure spin current out of an alternating (ac) electric field, which renders the TDSM an efficient spin-current injector.
荒木 康史
no journal, ,
Topological Dirac seimetals (TDSMs) form a new class of three-dimensional topological semimetals, characterized by pair(s) of doubly-degenerate nodal points (Dirac points) in their momentum(k)-space band structures. They show the intrinsic spin Hall effect (SHE), which comes from the k-space topology around the Dirac points. This spin Hall conductivity is topologically protected, while it cannot be easily tuned or enhanced at linear response. In order to overcome this problem, I theoretically propose that an electric field applied to a lattice-strained TDSM gives rise to an additional "nonlinear spin Hall current", namely the spin current perpendicular to and quadratic in the electric field. The spin current response is obtained by the Boltzmann transport theory, regarding the strain as a pseudomagnetic field for the Dirac electrons. The nonlinear SHE arises as the hybrid of the regular Hall effect driven by the pseudomagnetic field (strain) and the anomalous Hall effect from the k-space topology. This behavior implies that one can obtain a rectified (dc) pure spin current out of an alternating (ac) electric field, which renders the TDSM an efficient spin-current injector.
Han, J.*; 内村 友宏*; 荒木 康史; Yoon, J.-Y.*; 竹内 祐太郎*; 山根 結太*; 金井 駿*; 家田 淳一; 大野 英男*; 深見 俊輔*
no journal, ,
The quantum metric and Berry curvature are two fundamental and distinct factors that describe the geometry of quantum eigenstates. While the role of the Berry curvature in governing various condensed-matter states has been investigated extensively, the quantum metric, which was also predicted to induce topological phenomena of equal importance, has rarely been studied. Recently, a breakthrough has been made in observing the quantum-metric nonlinear transport in a van der Waals magnet, but the effect is limited at cryogenic temperature and is tuned by strong magnetic fields of several teslas. In our study, we demonstrate room-temperature manipulation of the quantum-metric structure of electronic states through its interplay with the interfacial spin texture in a topological chiral antiferromagnet/heavy metal Mn3Sn/Pt heterostructure, which is manifested in a time-reversal-odd second-order Hall effect (ScHE). We show the flexibility of controlling the quantum-metric structure with moderate magnetic fields and verify the quantum-metric origin of the observed ScHE by theoretical modeling. Our results open the possibility of building applicable nonlinear devices by harnessing the quantum-metric structure of electronic states.
 single layer with a spontaneous oxygen atomic displacement
single layer with a spontaneous oxygen atomic displacement堀内 皓斗*; 若林 勇希*; 荒木 康史; 家田 淳一; 山ノ内 路彦*; 他6名*
no journal, ,
Perovskite oxide SrRuO (SRO), which is also known as a ferromagnetic Weyl semimetal, is promising for realizing efficient spin-orbitronics devices. Here, we demonstrated an SOT-induced magnetization switching in a single-phased ferromagnetic SRO single layer. An important finding is that 7.5
(SRO), which is also known as a ferromagnetic Weyl semimetal, is promising for realizing efficient spin-orbitronics devices. Here, we demonstrated an SOT-induced magnetization switching in a single-phased ferromagnetic SRO single layer. An important finding is that 7.5  10% of the magnetization in the 26 nm-thick SRO film was stably switched by the in-plane-current application. To clarify the reason for the obtained SOT in our SRO single layer, where spatial inversion symmetry seemingly is maintained, we closely analyzed the crystal structure using annular bright-field scanning transmission electron microscopy (ABF-STEM). We found that oxygen octahedral rotation (
10% of the magnetization in the 26 nm-thick SRO film was stably switched by the in-plane-current application. To clarify the reason for the obtained SOT in our SRO single layer, where spatial inversion symmetry seemingly is maintained, we closely analyzed the crystal structure using annular bright-field scanning transmission electron microscopy (ABF-STEM). We found that oxygen octahedral rotation ( 5 degrees) occurs especially near the interface between SRO and STO. By comparing the results with our theoretical calculation based on the tight-binding model, the observed partial single-layer magnetization switching can be attributed to the octahedral rotation and the associated large intrinsic spin Hall effect near the interface. We obtained a small switching current density of 3.1
5 degrees) occurs especially near the interface between SRO and STO. By comparing the results with our theoretical calculation based on the tight-binding model, the observed partial single-layer magnetization switching can be attributed to the octahedral rotation and the associated large intrinsic spin Hall effect near the interface. We obtained a small switching current density of 3.1  5.3 MA cm
5.3 MA cm , one order of magnitude smaller than conventional SOT systems consisting of a ferromagnet/heavy metal bilayer. This result implies that only a tiny spontaneous displacement of atoms in perovskite oxides plays a pivotal role in spin-orbitronics device applications.
, one order of magnitude smaller than conventional SOT systems consisting of a ferromagnet/heavy metal bilayer. This result implies that only a tiny spontaneous displacement of atoms in perovskite oxides plays a pivotal role in spin-orbitronics device applications.
Han, J.*; 内村 友宏*; 荒木 康史; Yoon, J.-Y.*; 竹内 祐太郎*; 山根 結太*; 金井 駿*; 家田 淳一; 大野 英男*; 深見 俊輔*
no journal, ,
物質の特異な電子物性を実現する要素として、電子波動関数の幾何構造が注目されている。波数空間内の幾何構造はベリー曲率と量子計量という2つの量により特徴づけられる。ベリー曲率が異常ホール効果等の内因性効果の起源として活発に研究が行われている一方、量子計量については、電流ノイズや超流動・超伝導の不安定性等に寄与する理論予測はあるが、量子計量の効果を物質中で制御し観測することは困難であった。本講演では、カイラル反強磁性体Mn Snにおける量子計量を室温下で制御し観測に成功した、我々の実験及び理論研究の成果について報告する。実験では(0001)配向のMn
Snにおける量子計量を室温下で制御し観測に成功した、我々の実験及び理論研究の成果について報告する。実験では(0001)配向のMn Snと重金属Ptのヘテロ構造を用い、面内磁場印加下で2次高調波成分の非線形ホール電圧を観測した。この非線形ホール効果は反強磁性転移温度直下の室温で強く現れ、磁場方向に追随して360
Snと重金属Ptのヘテロ構造を用い、面内磁場印加下で2次高調波成分の非線形ホール電圧を観測した。この非線形ホール効果は反強磁性転移温度直下の室温で強く現れ、磁場方向に追随して360 の周期性を示した(図参照)。我々はMn
の周期性を示した(図参照)。我々はMn Sn界面の強束縛模型を用いたモデル計算を行い、測定された非線形ホール効果が、磁場で制御を受けたMn
Sn界面の強束縛模型を用いたモデル計算を行い、測定された非線形ホール効果が、磁場で制御を受けたMn Sn電子の量子計量構造に起因することを示した。これは界面Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya相互作用によるスピン構造のカンティングにより現れる、空間反転対称性が強く破れた電子状態に由来する。この電子状態は電場の1次摂動で量子計量に比例したベリー曲率を得るため、電場の2次でホール電圧を示す。モデル計算では量子計量からの非線形ホール効果への寄与を他のメカニズムと比較することにより、測定結果が量子計量の効果であることを確かめた。本研究成果は非線形伝導のデバイス応用に向け、量子計量の制御の重要性を示唆するものである。
Sn電子の量子計量構造に起因することを示した。これは界面Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya相互作用によるスピン構造のカンティングにより現れる、空間反転対称性が強く破れた電子状態に由来する。この電子状態は電場の1次摂動で量子計量に比例したベリー曲率を得るため、電場の2次でホール電圧を示す。モデル計算では量子計量からの非線形ホール効果への寄与を他のメカニズムと比較することにより、測定結果が量子計量の効果であることを確かめた。本研究成果は非線形伝導のデバイス応用に向け、量子計量の制御の重要性を示唆するものである。
荒木 康史
no journal, ,
量子幾何は物質中の電子波動関数が持つ歪み構造を特徴づける概念であり、波数空間内では「ベリー曲率」「量子計量」といった量により特徴づけられる。電子状態の混成によるバンド交差やバンド反転近傍の波数領域では、量子幾何構造が強く発現する傾向にある。量子幾何は電子物性に対し、不純物等による散乱の影響を受けない内因性の寄与を与える。特に輸送特性に関しては多彩な効果に寄与することが、理論・実験双方での精力的な研究により解明されてきている。その代表例としては、ベリー曲率からは異常ホール効果や異常ネルンスト効果、量子計量からは電流ノイズや非線形ホール効果等が挙げられる。講演者は、このような量子幾何の内因性効果に関する知見を発展させ、磁性や電子スピン自由度に関わる量子幾何の効果を解明すべく理論研究を行ってきた。特に、磁気秩序や非一様磁気構造の下で理論構築及びモデル計算を行い、磁性体中での磁化の制御過程(スピントルク)や輸送特性(複素インピーダンス、非線形ホール効果)に対する量子幾何の寄与を明らかにしてきた。これらの内因性効果に由来する過程は不純物散乱に影響されないため、外因性効果に比べジュール熱損失が少ないという利点を持つ。そのため、一連の研究で得られた知見は、スピントロニクスにおけるデバイスの集積化に向けた物質選択・設計に際しても量子幾何の重要性を提示し、有用な指導原理として働くと期待している。本講演では講演者がこれまでに行ってきた研究のうち、特に以下の3系統の研究成果について、その後の研究の進展も含め解説する。(1)非一様磁気構造に働く内因性スピントルク、(2)磁気電気結合に由来した内因性の創発インダクタンス、(3)磁気構造を介した量子計量構造の制御と検証
松下 太樹*; 小沢 耀弘*; 荒木 康史; 藤本 純治*; 佐藤 昌利*
no journal, ,
スピンカロリトロニクスは排熱によるスピンの制御を目的とする研究分野である。スピンゼーベック効果(温度勾配に沿った方向のスピン伝導)とスピンネルンスト効果(温度勾配に垂直な方向のスピン伝導)は、当該研究分野における中心的な現象であり、温度勾配によるスピン流の生成を可能にする。そのため、スピンゼーベック効果は様々な系で研究されてきた。一方で、スピンネルンスト効果は微視的理論が長らく不在であり、その理論研究は乏しかった。また、大きなスピンネルンスト効果を実現する条件は整理されておらず、効率的な熱流-スピン流変換の指針の提案が望まれている。最近、スピンネルンスト効果の微視的理論が提案された。この微視的理論は、ラッティンジャーの重力理論に依拠しており、低温極限でスピン流が非物理的な発散をせず、スピン流のモットの関係式を満たすなど望ましい性質を持つ。さらに、スピンネルンスト効果の内因性機構がスピンベリー曲率と呼ばれる幾何学的量により記述されることも明らかとなった。スピンベリー曲率は、ディラック点やワイル点の周りで発散的に増大する。そのため、ディラック半金属やワイル半金属の幾何学的性質が、大きなスピンネルンスト効果を実現する可能性がある。本発表においては、ディラック半金属と磁性ワイル半金属における内因性スピンネルンスト効果の理論研究の成果を報告する。はじめに、内因性スピンネルンスト効果の公式を示し、強いスピンネルンスト効果が得られる条件を整理する。その後、ディラック半金属と磁性ワイル半金属におけるスピンネルンスト効果について、点ノードのエネルギーに対する依存性を議論し、これらのトポロジカル物質の幾何学的性質が大きなスピンネルンスト効果を実現し、効率的な熱流-スピン流変換に利用できることを示す。