Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tomita, Ryohei; Tomita, Jumpei; Suzuki, Daisuke; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Miyamoto, Yutaka
Hosha Kagaku, (48), p.1 - 15, 2023/09
Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) is the method to detect secondary ions produced by the sputtering of primary ions. SIMS is one of effective method to measure isotopic composition of particles containing nuclear material in environmental sample for safeguards. We are a group member of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)'s network of analytical laboratories and have developed analytical techniques using SIMS and other mass spectrometers for nuclear safeguards. We will introduce the principle of SIMS and analytical techniques developed by our group to measure isotopic composition of uranium particles which having a particle diameter of micron order in environmental sample for safeguards.
Kabumoto, Hiroshi; Nakagawa, Sohei; Matsuda, Makoto
JAEA-Conf 2022-002, 146 Pages, 2023/03
"The 34th Meeting for Tandem Accelerators and their Associated Technologies" was held on July 21-22, 2022 organized by Nuclear Science Research Institute of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This meeting was held only on-line for preventing the spread of COVID-19 infection. The purpose of this meeting is contribution of development for related technology and of management of facilities through exchange of information among the researchers and engineers using and operating electrostatics accelerator facilities like tandem accelerators. There were 25 presentations which contains current status report of facility, technical development of accelerator, research of application. The total number of participants was a hundred, from 26 universities, research organizations and industries. This meeting consisted of only oral session, a poster session was not carried out because of on-line meeting. This proceeding compiles the contents of report papers in the meeting.
Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Ozu, Akira; Toh, Yosuke
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Virtual Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2021/08
Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Virtual Annual Meeting (Internet), 8 Pages, 2021/08
Yamamoto, Masahiko; Do, V. K.; Taguchi, Shigeo; Kuno, Takehiko; Takamura, Yuzuru*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 327(1), p.433 - 444, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)A simple, practical, and reliable analytical method for determination of Na, K, Ca, Sr, and Ba by liquid electrode plasma optical emission spectrometry is developed. Appropriate emission lines for quantification, interferences from co-existing elements, and effect of measurement conditions with cell damage have been investigated. The spike and recovery tests using actual sample have been performed for method validation, and negligible sample matrix effect has been observed. Consequently, the method is successfully applied to several radioactive wastes. The obtained data have been agreed well with data from computer calculation and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry within 10% difference.
Takahashi, Yoshiyuki*; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 62(8), p.452 - 456, 2020/08
, 62(8), p.452 - 456, 2020/08
no abstracts in English
Ozu, Akira; Maeda, Makoto; Komeda, Masao; Toh, Yosuke
Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2019), Vol.1, p.101 - 104, 2020/08
Toh, Yosuke
JAEA-Conf 2019-001, p.47 - 52, 2019/11
no abstracts in English
Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Proceedings of INMM 60th Annual Meeting (Internet), 7 Pages, 2019/07
 Zr determination with isotope dilution ICP-MS
Zr determination with isotope dilution ICP-MSAsai, Shiho; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Konda, Miki; Suzuki, Daisuke; Magara, Masaaki; Kimura, Takaumi; Ishihara, Ryo*; Saito, Kyoichi*; Yamada, Shinsuke*; Hirota, Hideyuki*
Talanta, 185, p.98 - 105, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:30.40(Chemistry, Analytical)Estimating the risks associated with radiation from long-lived fission products (LLFP) in radioactive waste is essential to ensure the long-term safety of potential disposal sites. In this study, the amount of  Zr, a LLFP, was determined by ICP-MS after separating Zr from a spent nuclear fuel solution using a microvolume anion-exchange cartridge (TEDA cartridge). The TEDA cartridge achieved highly selective separation of Zr regardless of its small bed volume of 0.08 cm
Zr, a LLFP, was determined by ICP-MS after separating Zr from a spent nuclear fuel solution using a microvolume anion-exchange cartridge (TEDA cartridge). The TEDA cartridge achieved highly selective separation of Zr regardless of its small bed volume of 0.08 cm . The time taken to complete the Zr separation was 1.2 min with a flow rate of 1.5 mL/min, which was 10 times faster than that for a conventional anion-exchange resin column. Almost all the other elements were removed, leading to accurate measurement of
. The time taken to complete the Zr separation was 1.2 min with a flow rate of 1.5 mL/min, which was 10 times faster than that for a conventional anion-exchange resin column. Almost all the other elements were removed, leading to accurate measurement of  Zr. The result connects experimental value to theoretical prediction provided by ORIGEN2, which requires verification. With the measured value, we demonstrated that the theoretical value is reliable enough to estimate radiation risks.
Zr. The result connects experimental value to theoretical prediction provided by ORIGEN2, which requires verification. With the measured value, we demonstrated that the theoretical value is reliable enough to estimate radiation risks.
Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Heyse, J.*; Paradela, C.*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 59th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2018/07
 by Knudsen effusion mass spectrometry
by Knudsen effusion mass spectrometryNakajima, Kunihisa; Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 491, p.183 - 189, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:69.63(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)One of the main chemical forms of cesium in the gas phase during severe accidents of light water reactor is expected to be cesium metaborate, CsBO , by thermodynamic equilibrium calculation considering reaction with boron. But accuracy of the thermodynamic data of gaseous metaborate, CsBO
, by thermodynamic equilibrium calculation considering reaction with boron. But accuracy of the thermodynamic data of gaseous metaborate, CsBO (g), has been judged as poor quality. Thus, Knudsen effusion mass spectrometric measurement of CsBO
(g), has been judged as poor quality. Thus, Knudsen effusion mass spectrometric measurement of CsBO was carried out to obtain reliable thermodynamic data. The evaluated values of standard enthalpy of formation of CsBO
was carried out to obtain reliable thermodynamic data. The evaluated values of standard enthalpy of formation of CsBO (g),
(g), 
 H
H
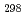 (CsBO
(CsBO ,g), by the 2nd and 3rd law treatments are -700.7
,g), by the 2nd and 3rd law treatments are -700.7 10.7 kJ/mol and -697.0
10.7 kJ/mol and -697.0 10.6 kJ/mol, respectively, and agree with each other within the errors, which suggests our data are reliable. Further, it was found that the existing data of the Gibbs energy function and the standard enthalpy of formation agreed well with the values evaluated in this study, which indicates the existing thermodynamic data are also reliable.
10.6 kJ/mol, respectively, and agree with each other within the errors, which suggests our data are reliable. Further, it was found that the existing data of the Gibbs energy function and the standard enthalpy of formation agreed well with the values evaluated in this study, which indicates the existing thermodynamic data are also reliable.
Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Kureta, Masatoshi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Seya, Michio; et al.
EUR-28795-EN (Internet), p.684 - 693, 2017/00
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Maeda, Makoto; Kureta, Masatoshi
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 6 Pages, 2016/07
From a viewpoint of nuclear safeguards and nuclear security, it has recently become important to develop a non-destructive assay (NDA) system that accurately determines the amount of special nuclear materials (SNMs) in various samples such as spent fuels, next generation MA-Pu fuels and fuel debris. One candidate of those NDA techniques is neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA). It relies on a neutron time-of-flight measurement and is a well-established method to apply for the accurate evaluations of nuclear data, including total cross sections and resonance parameters. The potential of NRTA to quantify SNM in complex materials has been already demonstrated by performing NRTA measurement at IRMM/GELINA under collaboration of JAEA and JRC. However, a present NRTA system usually has a large electron accelerator facility to generate intense neutrons, whereas this is very difficult to apply to various facilities that need to measure SNM. Therefore a compact NRTA system would be required for practical applications of quantifying SNM in a variety of samples. In order to realize a compact NRTA system, we are developing a prototype with a D-T neutron generator that has a pulse width of 10  s and an average maximum neutron yield ranging from
s and an average maximum neutron yield ranging from 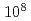 n/s to
n/s to 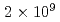 n/s. Numerical calculations were used to optimize the system performance to quantify SNM and MA in spent and MA-Pu fuels. In this presentation, those numerical calculation results, together with a brief description of the prototype, are presented. In addition, we discuss a future prospect of a compact NRTA system equipped with a neutron source with a shorter pulse width (ex. 100 ns) and a more intense neutron yield.
n/s. Numerical calculations were used to optimize the system performance to quantify SNM and MA in spent and MA-Pu fuels. In this presentation, those numerical calculation results, together with a brief description of the prototype, are presented. In addition, we discuss a future prospect of a compact NRTA system equipped with a neutron source with a shorter pulse width (ex. 100 ns) and a more intense neutron yield.
Konda, Miki; Asai, Shiho; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Magara, Masaaki
JAEA-Technology 2015-054, 22 Pages, 2016/03
Isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS) with ICP-MS is reliable method for determination of Zr-93, which is one of the long-lived fission products found in spent nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive wastes. In order to use an isotope standard solution of zirconium as the spike for IDMS, dissolving a commercially available solid isotope standard is indispensable. Prior to the dissolution of the Zr-91 isotope standard, solubility of metal zirconium in a mixture of HNO and HF was evaluated using zirconium metal chips. Then, 2 mg of the Zr-91 isotope standard was dissolved with 0.2 mL of 1 M HNO
and HF was evaluated using zirconium metal chips. Then, 2 mg of the Zr-91 isotope standard was dissolved with 0.2 mL of 1 M HNO -3 v/v% HF mixed solution, followed by adjusting the concentration of Zr-91 to approximately 1,000
-3 v/v% HF mixed solution, followed by adjusting the concentration of Zr-91 to approximately 1,000  g/g. IDMS, in which a natural isotopic abundance standard solution of zirconium was used as the spike, was employed for the determination of the concentration of Zr-91 in the prepared Zr-91 isotope standard solution. The concentration of Zr-91 in the prepared Zr-91 isotope standard solution was (9.6
g/g. IDMS, in which a natural isotopic abundance standard solution of zirconium was used as the spike, was employed for the determination of the concentration of Zr-91 in the prepared Zr-91 isotope standard solution. The concentration of Zr-91 in the prepared Zr-91 isotope standard solution was (9.6 1.0)
1.0)  10
10
 g/g, which is in good agreement with the predicted concentration. This indicates that the Zr-91 metal isotope standard was completely dissolved with sufficient chemical stability. Additionally, no impurities were detected in the prepared Zr-91 isotope standard solution. These positive results denote that the Zr-91 isotope standard solution with the preferable quality for IDMS of Zr-93 can be obtained by the proposed dissolution procedures.
g/g, which is in good agreement with the predicted concentration. This indicates that the Zr-91 metal isotope standard was completely dissolved with sufficient chemical stability. Additionally, no impurities were detected in the prepared Zr-91 isotope standard solution. These positive results denote that the Zr-91 isotope standard solution with the preferable quality for IDMS of Zr-93 can be obtained by the proposed dissolution procedures.
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Kureta, Masatoshi; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; Heyse, J.*; Paradela, C.*; Mondelaers, W.*; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-36-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2015/12
Neutron Resonance Densitometry (NRD) was developed as a non-destructive assay to quantify U and Pu isotopes in particle-like debris. NRD is composed of neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) and Neutron Resonance Capture Analysis (NRCA) or Prompt Gamma-ray Analysis (PGA). NRCA/PGA in NRD plays a role of identifying impurities in debris under the high-radiation field primarily caused by  Cs. For this purpose, a novel LaBr
Cs. For this purpose, a novel LaBr
 -ray detector employing specific shields has been newly developed. With the developed
-ray detector employing specific shields has been newly developed. With the developed  -ray detector, a demonstration NRCA experiment was performed at a neutron time of flight facility GELINA (Belgium). As a result, samples (Hf, Gd, Ni) placed in a black box that is completely sealed by third party were successfully identified by the experiment. This presentation explains the design concept of the
-ray detector, a demonstration NRCA experiment was performed at a neutron time of flight facility GELINA (Belgium). As a result, samples (Hf, Gd, Ni) placed in a black box that is completely sealed by third party were successfully identified by the experiment. This presentation explains the design concept of the  ray detector including its detection principle and details of the demonstration NRCA experiment.
ray detector including its detection principle and details of the demonstration NRCA experiment.
Seya, Michio; Naoi, Yosuke; Kobayashi, Naoki; Nakamura, Takahisa; Hajima, Ryoichi; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Kureta, Masatoshi; Nakamura, Hironobu; Harada, Hideo
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-35-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2015/01
The Integrated Support Center for Nuclear Non-proliferation and Nuclear Security (ISCN) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting (based on collaborations with JAEA other centers) the following basic technology development programs of advanced non-destructive detection/measurement of nuclear material for nuclear security and nuclear non-proliferation. (1) The demonstration test of the Pu-NDA system for spent fuel assembly using PNAR and SINRD (JAEA/USDOE(LANL) collaboration, completed in JFY2013), (2) Basic development of NDA technologies using laser Compton scattered  -rays (Demonstration of an intense mono-energetic
-rays (Demonstration of an intense mono-energetic  -ray source), (3) Development of alternative to He-3 neutron detection technology, (4) Development of neutron resonance densitometry (JAEA/JRC collaboration)This paper introduces above programs.
-ray source), (3) Development of alternative to He-3 neutron detection technology, (4) Development of neutron resonance densitometry (JAEA/JRC collaboration)This paper introduces above programs.
 I in environmental samples by AMS and NAA using an anion exchange resin disk
I in environmental samples by AMS and NAA using an anion exchange resin diskSuzuki, Takashi; Bamba, Shigeru*; Kitamura, Toshikatsu; Kabuto, Shoji*; Isogai, Keisuke*; Amano, Hikaru
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 259(1), p.370 - 373, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:68.77(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Ochi, Yoshihiro; Golovkin, I.*; Mancini, R.*; Uschmann, I.*; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; Fujita, Kazuhisa*; Louis, S.*; Nakai, Mitsuo*; Shiraga, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 74(3), p.1683 - 1687, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:48.46(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Saito, Takeru; Asaoka, Hidehito
Journal of Trace and Microprobe Techniques, 19(4), p.571 - 579, 2001/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:14.74(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English