Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
廃炉環境国際共同研究センター; 福井大学*
JAEA-Review 2025-007, 120 Pages, 2025/09
日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)廃炉環境国際共同研究センター(CLADS)では、令和5年度英知を結集した原子力科学技術・人材育成推進事業(以下、「本事業」という。)を実施している。本事業は、東京電力ホールディングス株式会社福島第一原子力発電所の廃炉等をはじめとした原子力分野の課題解決に貢献するため、国内外の英知を結集し、様々な分野の知見や経験を従前の機関や分野の壁を越えて緊密に融合・連携させた基礎的・基盤的研究及び人材育成を推進することを目的としている。平成30年度の新規採択課題から実施主体を文部科学省からJAEAに移行することで、JAEAとアカデミアとの連携を強化し、廃炉に資する中長期的な研究開発・人材育成をより安定的かつ継続的に実施する体制を構築した。本研究は、令和3年度に採択された研究課題のうち、「燃料デブリ周辺物質の分析結果に基づく模擬デブリの合成による実機デブリ形成メカニズムの解明と事故進展解析結果の検証によるデブリ特性データベースの高度化」の令和3年度から令和5年度の研究成果について取りまとめたものである。本研究では、酸化物デブリの形成条件の推定研究として、ガス浮遊法や微小な穴を持つタングステンパイプから溶融・噴出させる方法によりウランを含有する模擬燃料粒子を合成し、その生成条件と性状をまとめた。また、JAEAによりサンプリングデータに基づき作成された凝固パス図を再現し、鉄の挙動が熱力学予測と少し異なる結果などを得た。金属デブリの混合・溶融・凝固状態の評価では、溶融させた金属デブリのステンレスへの落下試験や溶融ステンレスの模擬金属デブリへの落下試験を行いその生成物を分析した。その結果ステンレス鋼温度が1000 C程度の場合は溶融金属のZr濃度に関わらず薄い反応相を形成してステンレス鋼損傷が抑制されることがわかり、またB
C程度の場合は溶融金属のZr濃度に関わらず薄い反応相を形成してステンレス鋼損傷が抑制されることがわかり、またB C及びジルカロイのステンレス鋼融体への溶出速度を定量化した。さらに、ステンレス鋼とZrの混合物の各種圧力容器部材や溶接部材との反応速度データを拡充し、大型試験体系での解析可能な簡素化反応速度式を提案した。また、圧力容器下部の材質を参照した大型試験体の実験と反応速度式より、溶融金属と圧力容器構造材との反応による圧力容器下部破損挙動や溶融物流出挙動を評価した。さらに、圧力容器下部におけるデブリ再溶融過程でのウラン化合物とステンレス鋼等の金属物質の反応試験データを拡充し、金属デブリ層へのウラン移行挙動を評価した。また、試験技術の整備として、二酸化ウランとZrと金属との半溶融模擬デブリの合成と分析、CCIM炉とガス浮遊炉を用いた少量のウランの模擬燃料デブリ合成試験の検討を行った。
C及びジルカロイのステンレス鋼融体への溶出速度を定量化した。さらに、ステンレス鋼とZrの混合物の各種圧力容器部材や溶接部材との反応速度データを拡充し、大型試験体系での解析可能な簡素化反応速度式を提案した。また、圧力容器下部の材質を参照した大型試験体の実験と反応速度式より、溶融金属と圧力容器構造材との反応による圧力容器下部破損挙動や溶融物流出挙動を評価した。さらに、圧力容器下部におけるデブリ再溶融過程でのウラン化合物とステンレス鋼等の金属物質の反応試験データを拡充し、金属デブリ層へのウラン移行挙動を評価した。また、試験技術の整備として、二酸化ウランとZrと金属との半溶融模擬デブリの合成と分析、CCIM炉とガス浮遊炉を用いた少量のウランの模擬燃料デブリ合成試験の検討を行った。
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction study山下 享介*; 古賀 紀光*; Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; 藤井 英俊*; 梅澤 修*
Materials Science and Engineering A, 941, p.148602_1 - 148602_11, 2025/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Ferrite-austenite duplex stainless steels offer excellent strength and ductility, making them suitable for extreme environments. In this study,  neutron diffraction during tensile testing at 293 K and 200 K was used to investigate stress partitioning and phase-specific deformation. Phase stress was calculated using a texture-compensated method. At both temperatures, ferrite showed higher phase stress than austenite, acting as the harder phase. At 200 K, both phases exhibited increased strength and work hardening. Austenite showed significant stacking fault formation alongside dislocation migration, while ferrite retained its dislocation-based deformation mode, becoming more effective. Stress contributions from both phases were comparable. No martensitic transformation occurred. Strengthening and enhanced work hardening in both phases led to high strength at 200 K, with ductility similar to that at 293 K.
neutron diffraction during tensile testing at 293 K and 200 K was used to investigate stress partitioning and phase-specific deformation. Phase stress was calculated using a texture-compensated method. At both temperatures, ferrite showed higher phase stress than austenite, acting as the harder phase. At 200 K, both phases exhibited increased strength and work hardening. Austenite showed significant stacking fault formation alongside dislocation migration, while ferrite retained its dislocation-based deformation mode, becoming more effective. Stress contributions from both phases were comparable. No martensitic transformation occurred. Strengthening and enhanced work hardening in both phases led to high strength at 200 K, with ductility similar to that at 293 K.
 ders band-assisted high uniform ductility in ultrastrong ferrous medium-entropy alloy via hierarchical microstructure
ders band-assisted high uniform ductility in ultrastrong ferrous medium-entropy alloy via hierarchical microstructureKwon, H.*; Lee, J. H.*; Zargaran, A.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Wang, J.*; Gu, G. H.*; Lee, B.-J.*; Bae, J. W.*; Kim, H. S.*
International Journal of Plasticity, 190, p.104378_1 - 104378_18, 2025/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Engineering, Mechanical)In this work, we harness a hierarchical microstructure to simultaneously tailor strengthening and deformation mechanisms in a Co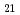 Cr
Cr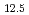 Fe
Fe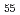 Ni
Ni Mo
Mo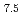 (at%) ferrous medium-entropy alloy (MEA). A simple thermomechanical process (cold rolling and 90 s annealing) produces ultrafine recrystallized grains, non-recrystallized grains with substructures, and intragranular nanoprecipitates. This structure, with high dislocation density and fine grains, yields a high strength of
(at%) ferrous medium-entropy alloy (MEA). A simple thermomechanical process (cold rolling and 90 s annealing) produces ultrafine recrystallized grains, non-recrystallized grains with substructures, and intragranular nanoprecipitates. This structure, with high dislocation density and fine grains, yields a high strength of  1.60 GPa but can risk premature fracture. To overcome this, L
1.60 GPa but can risk premature fracture. To overcome this, L ders deformation, enabled by ultrafine grain boundaries and stress-induced martensitic transformation at pre-existing nucleation sites, is employed. Stable L
ders deformation, enabled by ultrafine grain boundaries and stress-induced martensitic transformation at pre-existing nucleation sites, is employed. Stable L ders band propagation delays strain hardening and enables large uniform ductility. As a result, a tensile strength of
ders band propagation delays strain hardening and enables large uniform ductility. As a result, a tensile strength of  1.84 GPa and uniform elongation of
1.84 GPa and uniform elongation of  20% are achieved, matching the best tensile properties among reported multi-principal element alloys.
20% are achieved, matching the best tensile properties among reported multi-principal element alloys.
Gu, G. H.*; Jeong, S. G.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Cho, J.*; Kim, H. S.*; 他4名*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 223, p.308 - 324, 2025/07
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:75.81(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Face-centered cubic (FCC) equi-atomic multi-principal element alloys (MPEAs) exhibit excellent mechanical properties from cryogenic to room temperatures. At room temperature, deformation is dominated by dislocation slip, while at cryogenic temperatures (CTs), reduced stacking fault energy enhances strain hardening with twinning. This study uses in-situ neutron diffraction to analyze the temperature-dependent deformation behavior of Al (CoNiV)
(CoNiV)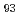 , a dual-phase (FCC/BCC) medium-entropy alloy (MEA). At liquid nitrogen temperature (LNT), deformation twinning in the FCC matrix leads to additional strain hardening through the dynamic Hall-Petch effect, giving the appearance of improved strengthening at LNT. In contrast, BCC precipitates show dislocation slip at both 77 K and 298 K, with temperature-dependent lattice friction stress playing a significant role in strengthening. The study enhances understanding of deformation behaviors and provides insights for future alloy design.
, a dual-phase (FCC/BCC) medium-entropy alloy (MEA). At liquid nitrogen temperature (LNT), deformation twinning in the FCC matrix leads to additional strain hardening through the dynamic Hall-Petch effect, giving the appearance of improved strengthening at LNT. In contrast, BCC precipitates show dislocation slip at both 77 K and 298 K, with temperature-dependent lattice friction stress playing a significant role in strengthening. The study enhances understanding of deformation behaviors and provides insights for future alloy design.
Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Gao, S.*; 伊東 達矢; 山下 享介*; Harjo, S.; Zhao, L.*; Wang, Q.*
Scripta Materialia, 264, p.116726_1 - 116726_6, 2025/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)An ultrafine-grained 304 austenitic stainless steel exhibited pronounced serrated Luders deformation at 20 K, with stress and temperature oscillations reaching 200 MPa and 20 K.  neutron diffraction and digital image correlation revealed discontinuous Luders band propagation and burst martensite formation. During deformation, austenite phase stress remained lower than at upper yielding, indicating elastic behavior. Notably, martensite phase stress stayed lower than austenite until fracture, likely due to stress relaxation from burst martensitic transformation at 20 K. The low martensite stress delayed brittle fracture until austenite plastically yielded during uniform deformation.
neutron diffraction and digital image correlation revealed discontinuous Luders band propagation and burst martensite formation. During deformation, austenite phase stress remained lower than at upper yielding, indicating elastic behavior. Notably, martensite phase stress stayed lower than austenite until fracture, likely due to stress relaxation from burst martensitic transformation at 20 K. The low martensite stress delayed brittle fracture until austenite plastically yielded during uniform deformation.
竹田 武司
JAEA-Data/Code 2025-005, 106 Pages, 2025/06
JAEAでは、加圧水型軽水炉(PWR)解析のためのRELAP5/MOD3.3コードの入力データを、主に大型非定常実験装置(LSTF)の参照4ループPWRである敦賀発電所2号機の設計情報を基に作成してきた。PWR解析に関する代表的なOECD/NEAの活動として、BEMUSEプログラムの枠組みにおける低温側配管大破断冷却材喪失事故(LBLOCA)の計算が挙げられる。また、わが国の新規制基準に係るPWRの炉心損傷防止対策の有効性評価事象には、低温側配管LBLOCA時の非常用炉心冷却系(ECCS)の再循環機能喪失事象が含まれる。本検討において、PWRの安全設計上想定すべき設計基準事故の一つであるLBLOCAを解析するための入力データを整備した。本報告書では、PWRLBLOCA解析の入力データの主な特徴を示す。PWRの原子炉容器、加圧器(PZR)、高温側配管、蒸気発生器(SG)、SG二次系、クロスオーバーレグ、低温側配管、ECCSなどをモデル化し、参照4ループPWRを2ループで模擬した。その際、PZRは3ループ分を模擬するループAに接続し、破断口は1ループ分を模擬するループBに設置した。PWRのコンポーネントのノード分割は、LSTFのコンポーネントのノード分割を参照した。また、PWRLBLOCA解析の主な入力データに対して、解釈を加えるとともに、設定根拠などの付加情報を提供した。さらに、整備した入力データを用いて、ECCS再循環機能喪失事象を対象とした過渡解析を実施した。RELAP5/MOD3.3コードによる既往研究の計算と比較することにより、過渡解析は概ね妥当であることを確認した。加えて、RELAP5/MOD3.3コードを用いて感度解析を実施し、破断口の流出係数や代替再循環注水流量が燃料棒被覆管表面温度に及ぼす影響を明らかにした。本報告書では、設定した条件の範囲内での感度解析結果について示し、ECCS再循環機能喪失事象に対する既往研究の計算内容の一部を補完する。
Park, M.-H.*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 292, p.121061_1 - 121061_13, 2025/06
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:95.60(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dual-phase (DP) steel, composed of soft ferrite and hard martensite, offers excellent strength-ductility balance and low cost. This study found that refining the DP microstructure enhanced both yield strength and strain hardening, improving strength and ductility. Digital image correlation (DIC) revealed strain localization in ferrite, but refinement reduced strain differences between ferrite and martensite, suppressing crack initiation. More ferrite/martensite interfaces promoted plasticity in martensite via enhanced deformation constraint.  neutron diffraction showed martensite bore higher phase stress, which increased with refinement. By combining
neutron diffraction showed martensite bore higher phase stress, which increased with refinement. By combining  -DIC and neutron data, individual stress-strain curves for ferrite and martensite were constructed for the first time, explaining the strength-ductility synergy through interphase constraint. These findings offer guidance for designing heterostructured materials to overcome the strength-ductility trade-off.
-DIC and neutron data, individual stress-strain curves for ferrite and martensite were constructed for the first time, explaining the strength-ductility synergy through interphase constraint. These findings offer guidance for designing heterostructured materials to overcome the strength-ductility trade-off.
友田 陽*; Harjo, S.; 徐 平光; 諸岡 聡; Gong, W.; Wang, Y.*
Metals, 15(6), p.610_1 - 610_19, 2025/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Lattice parameters of product and matrix phases in steels have been measured using in situ X-ray and neutron diffraction during forward and reverse transformations. These parameters are influenced by temperature, transformation-induced internal stresses, alloying element partitioning, crystal defects, and magnetic strains. Disentangling these contributions is essential for understanding lattice behavior. This review explores internal strain (stress) associated with ferrite, pearlite, bainite, martensite, and reverse austenite transformations, emphasizing the distinction between diffusional and displacive mechanisms. It also examines how plastic deformation of austenite affects subsequent bainite or martensite formation. The roles of dislocations and vacancies are identified as critical areas for further research.
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction study伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 287, p.120767_1 - 120767_16, 2025/04
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:75.81(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Incorporating solute hydrogen into Fe-Cr-Ni-based austenitic stainless steels enhances both strength and ductility, providing a promising solution to hydrogen embrittlement by causing solid-solution strengthening and assisting deformation twinning. However, its impacts on the relevant lattice defects evolution ( , dislocations, stacking faults, and twins) during deformation remains unclear. This study compared the tensile deformation behavior in an Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%) austenitic steel with 7600 atom ppm hydrogen-charged (H-charged) and without hydrogen-charged (non-charged) using
, dislocations, stacking faults, and twins) during deformation remains unclear. This study compared the tensile deformation behavior in an Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%) austenitic steel with 7600 atom ppm hydrogen-charged (H-charged) and without hydrogen-charged (non-charged) using  neutron diffraction. Hydrogen effects on the lattice expansion, solid-solution strengthening, stacking fault probability, stacking fault energy, dislocation density, and strain/stress for twin evolution were quantitatively evaluated to link them with the macroscale mechanical properties. The H-charged sample showed improvements in yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with earlier findings. However, solute hydrogen exhibited minimal influences on the evolution of dislocation and stacking fault. This fact contradicts the previous reports on hydrogen-enhanced dislocation and stacking fault evolutions, the latter of which can be responsible for the enhancement of twinning. The strain for twin evolution was smaller in the H-charged sample compared to the non-charged one. Nevertheless, when evaluated as the onset stress for twin evolution, there was minimal change between the two samples. These findings suggest that the increase in flow stress due to the solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen is a root cause of accelerated deformation twinning at a smaller strain, leading to an enhanced work-hardening rate and improved uniform elongation.
neutron diffraction. Hydrogen effects on the lattice expansion, solid-solution strengthening, stacking fault probability, stacking fault energy, dislocation density, and strain/stress for twin evolution were quantitatively evaluated to link them with the macroscale mechanical properties. The H-charged sample showed improvements in yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with earlier findings. However, solute hydrogen exhibited minimal influences on the evolution of dislocation and stacking fault. This fact contradicts the previous reports on hydrogen-enhanced dislocation and stacking fault evolutions, the latter of which can be responsible for the enhancement of twinning. The strain for twin evolution was smaller in the H-charged sample compared to the non-charged one. Nevertheless, when evaluated as the onset stress for twin evolution, there was minimal change between the two samples. These findings suggest that the increase in flow stress due to the solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen is a root cause of accelerated deformation twinning at a smaller strain, leading to an enhanced work-hardening rate and improved uniform elongation.
Naeem, M.*; Rehman, A. U.*; Romero Resendiz, L.*; Salamci, E.*; Aydin, H.*; Ansari, P.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Wang, X.-L.*; 他3名*
Communications Materials (Internet), 6, p.65_1 - 65_13, 2025/04
The need for lightweight materials with mechanical integrity at ultralow temperatures drives the development of advanced alloys for cryogenic use. Additive manufacturing via laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) offers a scalable way to create alloys with tailored properties. Here, we show that LPBF-processed Al10SiMg exhibits a high ultimate tensile strength (395 MPa) and uniform elongation (25%) at 15 K. These enhancements stem from grain refinement, increased geometrically necessary dislocations, and stress partitioning between the Al matrix and the stiffer Si phase, aiding strain accommodation.  neutron diffraction reveals that the Si phase, with its higher yield strength, bears most of the load, while the Al matrix undergoes continuous strain hardening, extending deformation capacity. These results highlight Al10SiMg's promise for cryogenic applications such as hydrogen storage, aerospace, and quantum computing hardware.
neutron diffraction reveals that the Si phase, with its higher yield strength, bears most of the load, while the Al matrix undergoes continuous strain hardening, extending deformation capacity. These results highlight Al10SiMg's promise for cryogenic applications such as hydrogen storage, aerospace, and quantum computing hardware.
林崎 康平; 廣岡 瞬; 山田 忠久*; 砂押 剛雄*; 村上 龍敏; 齋藤 浩介
Ceramics (Internet), 8(1), p.24_1 - 24_12, 2025/03
Zirconolite is a wasteform that can immobilize Pu. Herein, zirconolites comprising Ce as a Pu simulant and Al as a charge compensator of Ce/Pu were synthesized by sintering raw CaO, ZrO , TiO
, TiO , CeO
, CeO , and Al
, and Al O
O powder mixtures at 1400
powder mixtures at 1400 C in static air. The reduction behavior and phase transformation of zirconolites during their heat treatment in an Ar-H
C in static air. The reduction behavior and phase transformation of zirconolites during their heat treatment in an Ar-H gas flow were investigated. All zirconolite compositions first underwent reduction at
gas flow were investigated. All zirconolite compositions first underwent reduction at  1050
1050 C by forming a small domain of perovskite phase. Ce-Al co-doped zirconolite showed a smaller fraction of phase transformation in perovskite than Ce-doped zirconolite, indicating the advantage of using a charge compensator to prevent perovskite formation.
C by forming a small domain of perovskite phase. Ce-Al co-doped zirconolite showed a smaller fraction of phase transformation in perovskite than Ce-doped zirconolite, indicating the advantage of using a charge compensator to prevent perovskite formation.
北條 智彦*; 小山 元道*; 熊井 麦弥*; Zhou, Y.*; 柴山 由樹; 城 鮎美*; 菖蒲 敬久; 齋藤 寛之*; 味戸 沙耶*; 秋山 英二*
ISIJ International, 65(2), p.284 - 296, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Stress and plastic strain distributions and those partitioning behaviors of ferrite and retained austenite were investigated in the medium manganese (Mn) and the transformation-induced plasticity-aided bainitic ferrite (TBF) steels, and the martensitic transformation behaviors of retained austenite during Luders elongation and work hardening were analyzed using synchrotron X-ray diffraction at SPring-8. The stress and plastic strain of retained austenite and volume fraction of retained austenite were remarkably changed during Luders deformation in the medium Mn steel, implying that the medium Mn steel possessed inhomogeneous deformation at the parallel part of the tensile specimen. On the other hand, the distributions of the stress, plastic strain and volume fraction of retained austenite were homogeneous and the homogeneous deformation occurred at the parallel part of the tensile specimen at the plastic deformation regime with work hardening in the medium Mn and TBF steels. The martensitic transformation of retained austenite at uders deformation in the medium Mn steel was possessed owing to the application of high stress and preferential deformation at retained austenite, resulting in a significant increase in the plastic deformation and reduction of stress in the retained austenite. The martensitic transformation of retained austenite at the plastic deformation regime with work hardening was induced by the high dislocation density and newly applied plastic deformation in retained austenite in the medium Mn steel whereas the TBF steel possessed gradual transformation of retained austenite which is applied high tensile stress and moderate plastic deformation.
Naeem, M.*; Ma, Y.*; Tian, J.*; Kong, H.*; Romero-Resendiz, L.*; Fan, Z.*; Jiang, F.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Wu, Z.*; et al.
Materials Science & Engineering A, 924, p.147819_1 - 147819_10, 2025/02
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:75.81(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Face-centered cubic (fcc) medium-/high-entropy alloys (M/HEAs) typically enhance strength and ductility at cryogenic temperatures via stacking faults, twinning, or martensitic transformation. However, in-situ neutron diffraction on VCoNi MEA at 15 K reveals that strain hardening is driven solely by rapid dislocation accumulation, without these mechanisms. This results in increased yield strength, strain hardening, and fracture strain. The behavior, explained by the Orowan equation, challenges conventional views on cryogenic strengthening in fcc M/HEAs and highlights the role of dislocation-mediated plasticity at low temperatures.
丸山 修平; 山本 章夫*; 遠藤 知弘*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 14 Pages, 2025/00
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study proposes new hybrid data assimilation (DA) methods to effectively use experimental data represented in two different ways in the DA process for reducing nuclear-data-induced uncertainties. Conventional DA methods often assume a linear model, where data in a DA database are represented by their differential coefficients, i.e., nuclear data sensitivity coefficients. In contrast, more rigorous and versatile DA methods based on sampling techniques have been proposed recently. These sampling-based DA methods describe data for DA using results derived from direct transport calculations performed with perturbed nuclear data samples. The proposed hybrid DA methods simultaneously use both types of data described by sensitivity coefficients and sampling results and thus are called "hybrid." Two hybrid DA methods are proposed herein: the simple hybrid DA and efficient hybrid DA methods. Among these, the simple method is based on a straightforward concept that uses a random sampling technique. In contrast, the efficient method employs a more technical method that effectively combines a new deterministic sampling technique with sensitivity coefficients to reduce statistical uncertainties associated with the simple method. The efficient method is expected to be a candidate to achieve high precision and rigorous DA with a realistic sample size.
伊東 達矢; Xu, S.*; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 貝沼 亮介*
Shape Memory and Superelasticity, 9 Pages, 2025/00
The microstructure, crystal structures, cold workability, and martensitic transformation temperatures of several Cu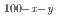 Mn
Mn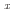 Al
Al (40
(40 
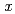
 55; 10
55; 10 
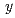
 13; at%) alloys were analyzed. For the first time, martensitic transformation was revealed Mn-rich Cu-Mn-Al alloys. The surface relief of the martensite phase reversibly appeared and disappeared during cooling and heating, along with small thermal hysteresis, implying a thermoelastic transformation. The crystal structures of the parent and martensite phases are B2 and 2M(BCT), respectively, with c
13; at%) alloys were analyzed. For the first time, martensitic transformation was revealed Mn-rich Cu-Mn-Al alloys. The surface relief of the martensite phase reversibly appeared and disappeared during cooling and heating, along with small thermal hysteresis, implying a thermoelastic transformation. The crystal structures of the parent and martensite phases are B2 and 2M(BCT), respectively, with c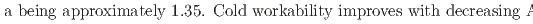 Mn
Mn Al
Al (at%) sample. This alloy demonstrates moderate cold workability and cost-effectiveness, exhibiting potential as an alternative for conventional shape memory alloys in various applications.
(at%) sample. This alloy demonstrates moderate cold workability and cost-effectiveness, exhibiting potential as an alternative for conventional shape memory alloys in various applications.
 neutron diffraction measurement during tensile deformation
neutron diffraction measurement during tensile deformation山下 享介*; 諸岡 聡; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; 北條 智彦*; 興津 貴隆*; 藤井 英俊*
ISIJ International, 64(14), p.2051 - 2060, 2024/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)An Fe-0.15C-5Mn-0.5Si-0.05Nb steel annealed at 660 C and 685
C and 685 C showed L
C showed L ders deformation followed by high work hardening, with variations in L
ders deformation followed by high work hardening, with variations in L ders strain and hardening behavior.
ders strain and hardening behavior.  neutron diffraction during tensile tests analyzed phase stresses, strength contributions, and austenite orientation. Deformation-induced martensite contributed
neutron diffraction during tensile tests analyzed phase stresses, strength contributions, and austenite orientation. Deformation-induced martensite contributed  1000 MPa to strength near tensile failure, while austenite mainly enhanced ductility via transformation-induced plasticity. Austenite transformed to martensite during L
1000 MPa to strength near tensile failure, while austenite mainly enhanced ductility via transformation-induced plasticity. Austenite transformed to martensite during L ders deformation regardless of orientation, though 311-oriented grains tended to remain along the tensile direction.
ders deformation regardless of orientation, though 311-oriented grains tended to remain along the tensile direction.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionNaeem, M.*; Ma, Y.*; Knowles, A. J.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Wang, X.-L.*; Romero Resendiz, L.*; 他6名*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 916, p.147374_1 - 147374_8, 2024/11
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:62.38(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Heterostructured materials (HSMs) improve the strength-ductility trade-off of alloys, but their cryogenic performance under real-time deformation is unclear. We studied heterostructured CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy via  neutron diffraction at 77 K and 293 K. A significant mechanical mismatch between fine and coarse grains led to an exceptional yield strength of 918 MPa at 293 K, increasing to 1244 MPa at 77 K with a uniform elongation of 34%. This strength-ductility synergy at 77 K is attributed to high dislocation pile-up density, increased planar faults, and martensitic transformation. Compared to homogeneous alloys, HSMs show promise for enhancing cryogenic mechanical performance in medium-/high-entropy alloys.
neutron diffraction at 77 K and 293 K. A significant mechanical mismatch between fine and coarse grains led to an exceptional yield strength of 918 MPa at 293 K, increasing to 1244 MPa at 77 K with a uniform elongation of 34%. This strength-ductility synergy at 77 K is attributed to high dislocation pile-up density, increased planar faults, and martensitic transformation. Compared to homogeneous alloys, HSMs show promise for enhancing cryogenic mechanical performance in medium-/high-entropy alloys.
Harjo, S.; Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Steel Science (ISSS 2024), p.205 - 208, 2024/11
This study aimed to elucidate the effect of grain size on the deformation behavior of TRIP steel. We prepared metastable austenitic Fe-24Ni-0.3C steel samples with average grain sizes of 35 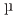 m (coarse grain: CG) and 0.5
m (coarse grain: CG) and 0.5 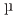 m (ultrafine-grain: UFG) for in situ neutron diffraction studies during tensile deformation at room temperature. Our observations revealed increases in dislocation density in both samples prior to DIMT, indicating that plastic deformation precedes DIMT regardless of grain size. In the UFG sample, a significant rise in dislocation density occurred just around the yielding point with minimal increases in macroscopic plastic strain. Additionally, the dislocations exhibited strong dipole arrangements.
m (ultrafine-grain: UFG) for in situ neutron diffraction studies during tensile deformation at room temperature. Our observations revealed increases in dislocation density in both samples prior to DIMT, indicating that plastic deformation precedes DIMT regardless of grain size. In the UFG sample, a significant rise in dislocation density occurred just around the yielding point with minimal increases in macroscopic plastic strain. Additionally, the dislocations exhibited strong dipole arrangements.
Mao, W.*; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 伊東 達矢; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 278, p.120233_1 - 120233_13, 2024/10
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:96.93(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Using a hybrid method of in situ neutron diffraction and digital image correlation, we found that ultrafine-grained 304 stainless steel exhibits Luders deformation after yielding, in which the deformation behavior changes from a cooperation mechanism involving dislocation slip and martensitic transformation to one primarily governed by martensitic transformation, as the temperature decreases from 295 K to 77 K. Such martensitic transformation-governed Luders deformation delays the activation of plastic deformation in both the austenite parent and martensite product, resulting in delayed strain hardening. This preserves the strain-hardening capability for the later stage of deformation, thereby maintaining a remarkable elongation of 29% while achieving a high tensile strength of 1.87 GPa at 77 K.
柴山 由樹; 北條 智彦*; 小山 元道*; 秋山 英二*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 88, p.1010 - 1016, 2024/10
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:66.68(Chemistry, Physical)The effect of plastic deformation on the hydrogen embrittlement behavior of high-strength martensitic steels was investigated using a U-bend test. The hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility appeared to be enhanced with increasing plastic strain. Based on fractographic and stress-strain analyses, the maximum principal stress dominated the hydrogen embrittlement fracture. Although the apparent enhancement with increasing plastic deformation was observed, the origin of the enhancement was increased residual stress arising from the evolution of graded plastic strain during U-bending. We conclude that residual stress rather than plastic strain induced by plastic deformation strongly affects hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility in deformed high-strength steel components.