Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
小泉 光生; 伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Wei, T.*; 余語 覚文*; et al.
第45回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2024/11
Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is a non-destructive method applicable for measuring nuclear material using a time-of-flight (TOF) technique with a pulsed neutron source. To realize a high resolution compact NRTA system, use of a short-pulsed neutron source is essential. Laser-driven neutron sources (LDNSs) are well-suit for generating such neutron beams due to their short pulse width. The advances in laser technology will further reduce the system's size and improve practicality. In this study, we demonstrate the measurement of a neutron transmission TOF spectrum of a sample containing indium and silver using the LDNS of the Osaka University. The obtained spectrum was analyzed using the least-square nuclear-resonance fitting program, REFIT, showcasing for the first time the potential of an LDNS for nondestructive areal-density material characterization.
小泉 光生; 伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Lan, Z.*; Wei, T.*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.21916_1 - 21916_9, 2024/09
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:64.46(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Laser-driven neutron sources (LDNSs) can generate strong short-pulse neutron beams, which are valuable for scientific studies and engineering applications. Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is a nondestructive technique used for determining the areal density of each nuclide in a material sample using pulsed thermal and epithermal neutrons. Herein, we report the first successful NRTA performed using an LDNS driven by the Laser for Fast Ignition Experiment at the Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University. The key challenge was achieving a well-resolved resonance transmission spectrum for material analysis using an LDNS with a limited number of laser shots in the presence of strong background noise. We addressed this by employing a time-gated  Li-glass scintillation neutron detector to measure the transmission spectra, reducing the impact of electromagnetic noise and neutron and gamma-ray flashes. Output waveforms were recorded for each laser shot and analyzed offline using a counting method. This approach yielded a spectrum with distinct resonances, which were attributed to
Li-glass scintillation neutron detector to measure the transmission spectra, reducing the impact of electromagnetic noise and neutron and gamma-ray flashes. Output waveforms were recorded for each laser shot and analyzed offline using a counting method. This approach yielded a spectrum with distinct resonances, which were attributed to  In and
In and  Ag, as confirmed through neutron transmission simulation. The spectrum was analyzed using the least-square nuclear-resonance fitting program, REFIT, demonstrating the possibility of using an LDNS for nondestructive areal-density material characterization.
Ag, as confirmed through neutron transmission simulation. The spectrum was analyzed using the least-square nuclear-resonance fitting program, REFIT, demonstrating the possibility of using an LDNS for nondestructive areal-density material characterization.
 Li-glass detector to gamma rays by a coincidence method
Li-glass detector to gamma rays by a coincidence method伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 持丸 貴則*; 堀 順一*; 寺田 和司*; 小泉 光生
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1064, p.169465_1 - 169465_9, 2024/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The response of a gamma-ray spectrometer is generally determined by analyzing full-energy peaks. However, full-energy peaks cannot be measured easily in the case of scintillation detectors that consist of light elements, such as glass scintillators. Only a strong Compton plateau appears in the spectrum of such detectors. Therefore, Compton edgers were used to evaluate the response of these detectors. The response of a low-resolution  Li-glass detector to gamma rays was measured for the first time by a coincidence method with a high-resolution LaBr
Li-glass detector to gamma rays was measured for the first time by a coincidence method with a high-resolution LaBr :Ce detector using cascade gamma rays (2.75 and 1.37 MeV) from a
:Ce detector using cascade gamma rays (2.75 and 1.37 MeV) from a  Na source. Coincidence gates were applied at the peaks of the spectrum of the LaBr
Na source. Coincidence gates were applied at the peaks of the spectrum of the LaBr :Ce detector at the 0.51 MeV annihilation peak, and the sum peaks of a gamma ray and a backscattered gamma ray. By analyzing the gated spectra of the
:Ce detector at the 0.51 MeV annihilation peak, and the sum peaks of a gamma ray and a backscattered gamma ray. By analyzing the gated spectra of the  Li-glass detector, the energy-dependent detector response (i.e., the output strength and its dispersion) was determined.
Li-glass detector, the energy-dependent detector response (i.e., the output strength and its dispersion) was determined.
Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 伊藤 史哲*; 小泉 光生; 堀 順一*; 佐野 忠史*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(1), p.23 - 30, 2024/01
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:71.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the short-distance time-of-flight (TOF) measurements, the background events increase exponentially with decreasing the distance, and the high background increases the uncertainty of the measurement data. The moderated neutron beam includes the time-dependent background originating from the neutron moderator, such as 2.2 MeV gamma rays emitted by  H(n,
H(n, ) reaction in the moderator. In this paper, to achieve a compact neutron resonance transmission analysis system with high accuracy, we studied the relationship between the moderator and time-dependent background due to gamma rays. Monte Carlo simulations were carried out with the PHITS and the JENDL-4.0 to investigate the time distributions of neutrons and gamma rays emitted from the moderator. Ratios of the gamma-ray intensity to neutron intensity (S
) reaction in the moderator. In this paper, to achieve a compact neutron resonance transmission analysis system with high accuracy, we studied the relationship between the moderator and time-dependent background due to gamma rays. Monte Carlo simulations were carried out with the PHITS and the JENDL-4.0 to investigate the time distributions of neutrons and gamma rays emitted from the moderator. Ratios of the gamma-ray intensity to neutron intensity (S /S
/S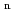 ratio) were calculated for various moderators and flight distances. From the obtained results, moderator designs for maintaining low S
ratio) were calculated for various moderators and flight distances. From the obtained results, moderator designs for maintaining low S /S
/S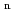 ratio were discussed.
ratio were discussed.
弘中 浩太; Lee, J.; 小泉 光生; 伊藤 史哲*; 堀 順一*; 寺田 和司*; 佐野 忠史*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1054, p.168467_1 - 168467_5, 2023/09
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:71.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)We propose neutron resonance fission neutron analysis (NRFNA), an active nondestructive assay (NDA) technique, to improve the capability to identify and quantify a small amount of fissile material in a sample. NRFNA uses pulsed neutrons to induce fission reactions in the sample. Fission neutrons are detected by a neutron-gamma pulse shape discrimination (PSD) scintillation detector with time-of-flight (TOF) technique. The obtained nuclide-specific resonance peaks in the neutron energy spectrum provide information to identify and quantify a fissile material in the sample. The possibility of using PSD for NRFNA was confirmed through a test experiment using a natural uranium sample. We successfully observed the resonance peaks from  U(n,f) reaction and showed that NRFNA would be useful for measuring a small amount of fissile material in a sample.
U(n,f) reaction and showed that NRFNA would be useful for measuring a small amount of fissile material in a sample.
余語 覚文*; Lan, Z.*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Wei, T.*; 森 隆人*; Golovin, D.*; 早川 岳人*; 岩田 夏弥*; et al.
Physical Review X, 13(1), p.011011_1 - 011011_12, 2023/01
被引用回数:28 パーセンタイル:96.01(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Neutrons are powerful tools for investigating the structure and properties of materials used in science and technology. Recently, laser-driven neutron sources (LDNS) have attracted the attention of different communities, from science to industry, in a variety of applications, including radiography, spectroscopy, security, and medicine. However, the laser-driven ion acceleration mechanism for neutron generation and for establishing the scaling law on the neutron yield is essential to improve the feasibility of LDNS. In this paper, we report the mechanism that accelerates ions with spectra suitable for neutron generation. We show that the neutron yield increases with the fourth power of the laser intensity, resulting in the neutron generation of 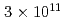 in
in 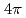 at a maximum, with
at a maximum, with 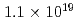 Wcm
Wcm , 900 J, 1.5 ps lasers. By installing a "hand-size" moderator, which is specially designed for the LDNS, it is demonstrated that the efficient generation of epithermal (0.1-100 eV) neutrons enables the single-shot analysis of composite materials by neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA). We achieve the energy resolution of 2.3% for 5.19-eV neutrons 1.8 m downstream of the LDNS. This leads to the analysis of elements and isotopes within sub-
, 900 J, 1.5 ps lasers. By installing a "hand-size" moderator, which is specially designed for the LDNS, it is demonstrated that the efficient generation of epithermal (0.1-100 eV) neutrons enables the single-shot analysis of composite materials by neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA). We achieve the energy resolution of 2.3% for 5.19-eV neutrons 1.8 m downstream of the LDNS. This leads to the analysis of elements and isotopes within sub- s times and allows for high-speed nondestructive inspection.
s times and allows for high-speed nondestructive inspection.
伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 小泉 光生; 余語 覚文*
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.137 - 140, 2023/01
中性子共鳴透過分析(NRTA)は、パルス中性子を計量したい核物質に照射し、飛行時間(TOF)法を用いて測定核物質を非破壊測定する手法であるが、小型・高精度化には短パルスな小型中性子源が必要となる。近年発展著しいレーザー技術を用いたレー ザー駆動中性子源(LDNS)は、そのような中性子源として将来を期待されている。そこで我々はLDNSを用いたNRTAの技術開発を行い、実証実験を行った。その結果について報告する。
Lee, J.; 伊藤 史哲*; 弘中 浩太; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 小泉 光生
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(12), p.1546 - 1557, 2022/12
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:77.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)Compact time-of-flight (TOF) measurement systems are desirable for easy installation in various facilities. To achieve such compact systems, one of the key considerations is the design of the neutron moderator. However, there are only a few reports on systematic studies on moderators considering both neutron energy resolution as well as a neutron intensity. In this paper, to design an epithermal neutron moderator for short-distance TOF measurements, the neutron intensity and energy resolution of epithermal neutrons have been studied using the Monte Carlo simulation code PHITS with JENDL-4.0 for various types of moderators. The neutronic characteristics of a moderator comprising several components were evaluated. The relationships between the moderator dimensions and both the energy resolution and intensity of the epithermal neutrons were determined. From the obtained results, the appropriate high resolution moderator designs for the short-distance TOF measurements were proposed.
Lee, J.; 伊藤 史哲*; 弘中 浩太; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 小泉 光生; 堀 順一*; 寺田 和司*
第43回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2022/11
中性子検出に広く使われているGS20リチウムガラスシンチレータは、応答は速いがn/g弁別能に乏しい。ガンマ線背景事象を適切に評価するためには、ガンマ線に対する応答特性を知る必要がある。特に中性子測定時は減速材中の水素原子核から発生する2.2MeVのガンマ線が主な背景事象となるが、このような高エネルギーガンマ線への応答特性の報告はほとんどない。このため、本研究では、GS20の応答特性についてNa-24ガンマ線源を用いて調べた。
Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 伊藤 史哲*; 高橋 時音; 小泉 光生; 堀 順一*; 寺田 和司*
KURNS Progress Report 2021, P. 97, 2022/07
文部科学省補助金事業「核セキュリティ強化等推進事業費補助金」の下、核不拡散技術開発の一環として、レーザー駆動中性子源(LDNS)を用いたコンパクトな核共鳴透過分析(NRTA)システムの技術開発を行っている。コンパクトなNRTAシステムを構築するためには、中性子の飛行距離を短くすることが重要な要素である。しかし、短距離のTOF測定では、減速材中の水素への中性子捕獲による2.2MeVガンマ線の影響が短距離に比例して指数的に大きくなってしまう。また、LDNSは発展途上であるため、中性子フラックスが十分ではなく、検出効率の高い検出器を用いることが望ましい。このため、我々は、高エネルギーガンマ線に対する検出効率が低く、かつ高い中性子感度を持つ検出器(積層型中性子検出器)を開発してきた。令和3年度の京都大学LINAC実験では、中性子に対する検出効率を上げ、両側にPMTを取り付け、コインシデンス測定によりノイズを除去できるようになった改良型の積層型中性子検出器の性能評価を行い、共鳴TOF測定による良いパフォーマンスを確かめられた。
弘中 浩太; 伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 小泉 光生; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 余語 覚文*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*
第42回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2021/11
中性子共鳴透過分析(NRTA)はパルス中性子源を用いてTOF測定を行うことで核物質を非破壊測定する手法であるが、小型・高精度化には短パルスな小型中性子源が必要となる。近年発展著しいレーザー技術を用いたレーザー駆動中性子源(LDNS)は、そのような中性子源として将来を期待されている。我々はLDNSを用いたNRTAの実現可能性を調べるため、大阪大学LFEXレーザーを用いて中性子TOF測定実験を行った。
伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 堀 順一*; 寺田 和司*; 小泉 光生
KURNS Progress Report 2020, P. 98, 2021/08
文部科学省補助金事業「核セキュリティ強化等推進事業費補助金」の下、核不拡散技術開発の一環として、レーザー駆動中性子源(LDNS)を用いたコンパクトな核共鳴透過分析(NRTA)システムの技術開発を行っている。NRTAにおいては、パルス中性子源から放出される中性子エネルギーが、飛行時間(TOF)法を用いて測定される。LDNSは、短い飛行距離でも高精度なTOF測定を行うために必要となる、短いパルス幅を持つという特性等から注目されている。短距離TOF測定では、減速材中の水素への中性子捕獲による2.2MeVガンマ線の飛来タイミングと、共鳴エネルギー付近の中性子の飛来タイミングが重なり、大きなガンマ線背景事象が存在することとなる。また、LDNSは発展途上であるため、中性子フラックスが十分ではなく、検出効率の高い検出器を用いることが望ましい。このため、我々は、高エネルギーガンマ線に対する検出効率が低く、かつ高い中性子感度を持つ検出器(多層型中性子検出器)を開発してきた。令和3年度の実験結果の一つとして、多層型中性子検出器が、高エネルギーガンマ線に対して低感度であることが確かめられた。
藤井 啓文*; 原 和彦*; 橋本 就吾*; 伊藤 史哲*; 角野 秀一*; Kim, S.*; 河内山 真美; 永嶺 謙忠*; 鈴木 厚人*; 高田 義久*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2013(7), p.073C01_1 - 073C01_20, 2013/07
被引用回数:27 パーセンタイル:75.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The performance of a muon radiography system designed to image the inner structure of a nuclear plant located at a distance of 64 m is evaluated. We conclude that there is an absence of fuel in the pressure vessel during the measurement period and profile the fuel material placed in the storage pool. The obtained data also demonstrate the sensitivity of the system to water-level changes in the reactor well and the dryer-separator pool. It is expected that the system could easily reconstruct a 2 m cubic fuel object. By operating multiple systems, typically four identical systems, viewing the reactor form different directions simultaneously, detection of a 1 m cubic object should be achievable within a period of a few months.
伊藤 史哲; Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 小泉 光生
not registered
【課題】高いN/γ選択性で、高線量の中性子を高効率で測定できる中性子検出器を得る。 【解決手段】このシンチレータ10は、Z方向において、蛍光体層11と光透過層12とが交互に積層された積層構造を具備する。蛍光体層11は、中性子を吸収することによって蛍光を発する蛍光体で構成され、この材料は、例えば従来より知られる中性子検出用のシンチレータの材料である。光透過層12は、この蛍光体が発した蛍光の透過率が高く中性子の吸収が小さい材料で構成される。このシンチレータ10では、中性子、γ線光子が入射した場合に、発光強度(パルス波高)が、中性子とγ線光子とで大きく異なる。これによって、両者の出力の弁別を容易に行うことができる。
伊藤 史哲; Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 小泉 光生
not registered
To obtain a neutron detector capable of measuring high dose neutrons with high neutron/gamma-ray discrimination ability and high efficiency. A scintillator 10 has a layered structure in which a phosphor layer 11 and a light transmission layer 12 are alternatelylaminatedin z direction. The phosphor layer 11 is made of a phosphor material emitting fluorescent light by absorbing neutrons, the material being, for example, a scintillator material used in neutron detectors having alreadybeen known. The light transmission layer 12 is made of a material highly transmitting fluorescent light emitted by the phosphor materialand only slightlyabsorbingneutrons. In the scintillator 10, when neutrons and gamma-ray photons enter it, luminescence intensity (pulse height) due to neutrons is significantly different from that due to gamma-ray photons. It makes it easy to discriminate between outputs due to the two kinds of radiations.
Lee, J.; 伊藤 史哲*; 小泉 光生; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*
no journal, ,
文部科学省補助金事業「核セキュリティ強化等推進事業費補助金」の下、核不拡散技術開発の一環として、レーザー駆動中性子源を用いた核共鳴透過分析(NRTA)技術開発を進めている。レーザー駆動中性子源から得られる中性子はMeV程度のエネルギーを有すので、効率良くNRTA実験を行うためには、モデレータを用い、これを適切なエネルギー領域にする必要がある。本発表では、モンテカルロシミュレーションで適切なモデレータの構造の検討を進めたのでその結果を報告する。モデレータとしては、水素含有物質が有効であるが、入射する中性子のエネルギーが高くなると、水素との反応断面積が小さくなり、急激に減速効果が下がる。そのため、入射部に上部モデレータ(Fe, Pb, Be, W)を入れ、さらに、メインモデレータ(CH )で減速する構成にした。計算は、PHITSコードを用いて、モデレータの構造による中性子量などを求めた。
)で減速する構成にした。計算は、PHITSコードを用いて、モデレータの構造による中性子量などを求めた。
伊藤 史哲*; 小泉 光生; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; Lee, J.
no journal, ,
核共鳴透過分析法(NRTA)はアクティブ中性子非破壊測定法の一つで、文部科学省「核セキュリティ強化等推進事業費補助金」事業の技術開発の一環で、技術開発を進めている。この技術を、高精度な核物質測定に適用するには、短パルス中性子源を導入する必要がある。その様な中性子源の一つとして、レーザー駆動中性子源(LDNS)に注目し、NRTAへの適用性検討、および中性子検出器の開発を進めているところである。中性子発生機構の設計、中性子飛行経路の設計及び検出器の設計については、PHITSを用いシミュレーション研究を進めている。
伊藤 史哲*; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; Lee, J.; 小泉 光生; 余語 覚文*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; 西村 博明*; 堀 順一*; et al.
no journal, ,
文部科学省補助金事業「核セキュリティ強化等推進事業費補助金」の下、核不拡散技術開発の一環として、レーザー駆動中性子源を用いた核共鳴透過分析(NRTA)技術開発を行っている。中性子飛行時間(TOF)測定に用いる中性子検出器及び解析手法の開発状況等について報告する。
高橋 時音; 小泉 光生; 伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 鈴木 敏*; 弘中 浩太; 余語 覚文*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; 西村 博明*; et al.
no journal, ,
The technique of NRTA is based on a neutron time-of-flight (TOF) method. Collimated pulsed neuron beams passing through a sample arrive a neutron detector placed at a distance from the neutron source. The neutron kinetic energy is deduced from the flight time between the neutron generator and the detector. Since the neutron reaction cross section of a nuclide has a characteristic resonance structure, neutrons having the resonance energy are strongly absorbed or scattered by the nuclide in a sample. Resonance dips appeared in the transmission spectrum are analyzed to deduce each nuclide areal density. The resolution of the observed dip strongly depends on the flight path length and the neutron pulse width. To realize a compact NRTA system by shortening the flight path length, a short-pulsed neutron generation is required. A laser-driven neutron source (LDNS), which can generate extremely short pulse neutron beams, is considered to potentially be such a short pulse neutron generator for a compact NRTA system. In addition, because laser light can be transported by mirrors, the laser system of the LDNS can be installed in separated place from an NRTA system which has to be in the nuclear controlled area. This enables maintenance of a laser system to be easy. Also, several analyzing system can be operated parallelly by switching laser path. In this presentation, we will overview a proposal of an application of the LDNS to an NRTA system for nuclear non-proliferation.