Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
和田 裕貴; 柴本 泰照; 日引 俊詞*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 249, p.127219_1 - 127219_16, 2025/10
被引用回数:0Two saturated boiling heat transfer correlations for downward flows in vertical circular pipes depending on wall superheat or wall heat flux as input parameters were developed based on a heat transfer experimental database. Owing to the absence of heat transfer correlations specifically developed for downward flows, existing heat transfer correlations for different flow directions were evaluated to determine their applicability to predicting the downward flow heat transfer coefficient. The results revealed that even the most accurate correlation showed a mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) of 66.5%, highlighting the need for improving predictive performance. In response, the downward flow heat transfer correlation was modeled by integrating a nucleate boiling heat transfer term and a forced convection heat transfer term. The Dong-Hibiki correlation, a two-component, two-phase heat transfer correlation for downward flows, was adopted for the forced convection heat transfer term. The Forster-Zuber correlation, developed as a wall superheat function, and the Cooper correlation, developed as a wall heat flux function, were used for the nucleate boiling term to develop the heat transfer correlations where either wall superheat or wall heat flux is known. Notably, the Dong-Hibiki correlation has been validated over a wide range of experimental conditions. A correction factor was applied to the nucleate boiling term to address errors caused by applying Foster-Zuber and Cooper correlations to downward flows. The two developed correlations achieved an MAPE value of approximately 20%, representing an improvement of roughly 40% over existing correlations of heat transfer coefficients.
相馬 秀; 石垣 将宏*; 柴本 泰照
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 219, p.111455_1 - 111455_12, 2025/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Containment venting is one of the accident mitigation measures during severe accidents in nuclear power plants for preventing overpressure failure of the containment vessels. Because of the capability of releasing hydrogen generated in the containment vessel, the hydrogen risk can be also reduced. In this study, we conducted experiments with the large-scale test facility CIGMA to investigate the light gas transport during the venting action, mainly focusing on the effect of sump water boiling caused by the vent. The CIGMA test vessel initially pressurized by steam, air, and helium (hydrogen simulant) that formed a helium-rich density stratification was depressurized with and without sump water, with different venting flow rates, and at different venting positions. As the sump water became a steam source due to flash boiling, the helium stratification was diluted and the venting time increased twofold compared to the case without sump water, which significantly affected the amount of helium discharged to the atmosphere. Especially for the high venting flow rate condition, the amount of helium remaining in the vessel at the end of depressurization was half that of the case without sump water. Lowering the venting position from within the initial stratification to 3 m below its interface led to a threefold increase in the amount of helium remaining at the same low pressure, because of the longer time until the helium-rich stratification reached the venting position.
Wang, Z.; 松本 俊慶; 柴本 泰照; Duan, G.*
Journal of Computational Physics, 537, p.114072_1 - 114072_29, 2025/09
被引用回数:0In this study, we develop a novel sharp surface tension (SST) model for multiphase particle methods. Our approach integrates surface tension directly into pressure computation, enabling precise representation of pressure discontinuities across interfaces and effectively mitigating parasitic currents. In addition, to improve curvature accuracy, particularly in scenarios involving topological changes, a co-directional scheme is proposed to faithfully consider interfacial normal vectors. Furthermore, we reconstruct the interfacial particle shifting scheme to separately address tangential, normal, and repulsive components, effectively suppressing the common problem of interface particle mixing in multiphase particle methods. The effectiveness and reliability are rigorously validated through a series of numerical tests, including the Rayleigh-Taylor instability, curvature verification, droplet deformation and coalescence, as well as bubble rising and coalescence. The results demonstrate the superior accuracy and robustness of the proposed method, marking a significant advancement in simulations of multiphase flow with surface tension.
Hamdani, A.; 相馬 秀; 安部 諭; 柴本 泰照
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 185, p.105771_1 - 105771_13, 2025/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study, motivated by previous TEPSYS analysis, examined how different temperatures on the 4th and 5th floors of the Fukushima Daiichi Unit 3 reactor building (R/B) influenced non-condensable gas distribution during the 2011 severe accident. Understanding this is vital for assessing risks related to gas accumulation, especially since the hydrogen explosion may have involved multiple stages. An experimental study was conducted using the CIGMA facility, designed to mimic the R/B structure, where steam and helium (as a substitute for hydrogen) were injected for 10,000 seconds to simulate leakage. Two cooling conditions were tested: 50 C (Case 1) and 90
C (Case 1) and 90 C (Case 2). Results showed that the highest concentration of non-condensable gases was often found downstream rather than near the injection point. In Case 1, after 10,000 seconds, helium concentration reached 65% in the middle region (4th floor) and 45% in the top region (5th floor). Analysis indicated that the gas mixture in the middle region posed a potential detonation risk. This study offers crucial insights for enhancing safety measures and risk mitigation strategies in nuclear reactor designs.
C (Case 2). Results showed that the highest concentration of non-condensable gases was often found downstream rather than near the injection point. In Case 1, after 10,000 seconds, helium concentration reached 65% in the middle region (4th floor) and 45% in the top region (5th floor). Analysis indicated that the gas mixture in the middle region posed a potential detonation risk. This study offers crucial insights for enhancing safety measures and risk mitigation strategies in nuclear reactor designs.
佐藤 聡; 和田 裕貴; 柴本 泰照
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 437, p.114020_1 - 114020_14, 2025/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)沸騰遷移後(ポストBT)の熱伝達は、軽水炉における異常過渡および事故時の被覆管表面のドライアウト継続時間やピーク温度を分析する上で不可欠である。ドライアウト継続時間の評価には、リウェット現象が非常に重要だが、高流量および高熱流束条件下でのリウェット速度に関する実験データベースが不足しているため、モデルの開発および検証に十分なデータが存在しない。そこで、単管実験装置を用いて、幅広い熱水力条件下でステップ状の境界条件の変化によって生じるリウェット速度に関するデータベースを構築した。このデータベースと得られたリウェット速度の特性に基づいて、リウェット速度の実験的相関式を提案した。この相関式は、ステップ状過渡変化における液相または気相の質量フラックスの変化をパラメータとして用いることで、リウェット速度を正確に予測する。これは、再冠水過程と比較して、極めて高い質量流束条件下では、液膜前面近傍における気相または液相の質量流束の変化がリウェットに強く影響することを示唆している。
和田 裕貴; 柴本 泰照; 日引 俊*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 239, p.126598_1 - 126598_18, 2025/04
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:21.83(Thermodynamics)This study reviewed the saturated boiling heat transfer research in downward flows. A database of downward flow heat transfer experiments was created using experimental studies. Saturated boiling heat transfer correlations in internal flows were collected, and no downward flow-specific heat transfer correlations were identified. The applicability of heat transfer correlations to downward flow heat transfer experiments was evaluated, and no correlation could predict the heat transfer coefficients accurately for all experimental databases. However, correlations that could predict heat transfer coefficients reasonably well were determined for each channel size. Cooper's correlation [Int. Chem. Eng. Symp. Ser. 86 (1984) 785-792] had a mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) of 11.7% for mini-channels and Kim and Mudawar's correlation [Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 64 (2013) 1239-1256] had an MAPE of 66.5% for macro-channels. Furthermore, because the advection direction between the liquid-phase and the generated bubbles differed depending on the liquid-phase velocity in downward flows, we evaluated the prediction performance of the heat transfer coefficient for the liquid-phase velocity. For some experimental data, the prediction performance of the existing correlation for downward flow heat transfer worsened as the advection velocity of the bubbles decreased. This result is one of the issues to be addressed in the future development of heat transfer correlations.
Hamdani, A.; 相馬 秀; 安部 諭; 柴本 泰照
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.53 - 59, 2025/03
This paper presents the experimental study and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis on the effect of thermal radiation in the humid atmosphere inside the containment vessel. The experiment was conducted in the Containment InteGral effects Measurement Apparatus (CIGMA) facility at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The numerical analysis was carried out using the open-source CFD code OpenFOAM. The initial gas condition inside the CIGMA containment consists of three gases, helium, air, and water vapor, at room temperature 30  C and a pressure of 1 atm. Initial helium stratification was located 6 m above the bottom vessel, and its molar fraction was 55 %. The initial water vapor molar fraction was set to 0.1% in order to minimize the thermal radiation absorption by the water molecule. Pure helium was injected through a nozzle from the top, leading to increased vessel pressure and a corresponding rise in gas temperature. The numerical validation at low water vapor, i.e., 0.1% H
C and a pressure of 1 atm. Initial helium stratification was located 6 m above the bottom vessel, and its molar fraction was 55 %. The initial water vapor molar fraction was set to 0.1% in order to minimize the thermal radiation absorption by the water molecule. Pure helium was injected through a nozzle from the top, leading to increased vessel pressure and a corresponding rise in gas temperature. The numerical validation at low water vapor, i.e., 0.1% H O, was performed by comparing the transient profile of pressure, gas molar fraction, and temperature with the experimental data. A Weighted Sum of Gray Gases (WSGG) model was implemented in the OpenFOAM solver. The numerical results showed a reasonable agreement compared to the experimental data. In addition, the numerical simulation with various water vapor mass fractions, i.e., 0.0%, 0.1%, 0.3%, 0.5%, and 60%, was performed to analyze the effect of humidity on the radiative heat transfer. The predicted temperature was overestimated when the numerical model neglected thermal radiation. Therefore, it indicated that thermal radiation should be considered when modeling the containment thermohydraulic.
O, was performed by comparing the transient profile of pressure, gas molar fraction, and temperature with the experimental data. A Weighted Sum of Gray Gases (WSGG) model was implemented in the OpenFOAM solver. The numerical results showed a reasonable agreement compared to the experimental data. In addition, the numerical simulation with various water vapor mass fractions, i.e., 0.0%, 0.1%, 0.3%, 0.5%, and 60%, was performed to analyze the effect of humidity on the radiative heat transfer. The predicted temperature was overestimated when the numerical model neglected thermal radiation. Therefore, it indicated that thermal radiation should be considered when modeling the containment thermohydraulic.
岡垣 百合亜; 日引 俊詞*; 柴本 泰照
JAEA-Review 2024-047, 58 Pages, 2025/02
加圧水型原子炉(PWR)の事故シナリオでは、非常用炉心冷却系(ECCS)からの注水(ECC注水)により、低温及び高温の冷却材の混合が不十分な場合、温度成層が形成され、加圧熱衝撃(PTS)が引き起こされる可能性がある。その結果、原子炉圧力容器(RPV)の健全性に影響を与えることが想定されている。そのため、PTSは原子炉の安全性において重要な研究課題であり、原子炉の運転可能期間を決定するRPVの健全性評価に関連してPTS解析は不可欠である。PTS解析は、熱水力解析及び構造解析の連成解析により実施される。特に、熱水力学的側面からのアプローチでは、RPV壁面の温度勾配を予測するために、ダウンカマ(DC)の過渡温度分布に関するデータが必要とされる。したがって、将来的には信頼性の高い数値流体力学(CFD)解析が重要な役割を果たすことが期待されている。本研究では、ROCOM、TOPFLOW、UPTF及びLSTFで行われたPTSに関する実験を対象とした単相流及び二相流CFD解析について、2010年以降に発表された論文を基に、PTS解析に最も影響を及ぼす乱流モデルの観点からレビューを行った。
茂木 孝介; 柴本 泰照; 日引 俊詞*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 237, p.126406_1 - 126406_15, 2025/02
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:36.85(Thermodynamics)We performed Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) simulations of a single-phase turbulent opposing flow mixed convection in a heated vertical circular tube. Previous research has indicated that the Launder-Sharma 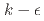 model (hereafter the LS model), one of the most popular RANS turbulence models, overestimates experimental heat transfer coefficients for opposing flows. Although the RANS models have been widely applied to opposing flows in various systems, the mechanism and conditions under which the predictive performance of the LS models fail remain unclear. This study aims to understand the model characteristics and their applicability under various mixed convection conditions. This article investigates the LS model, the LS model with the Yap correction, and the
model (hereafter the LS model), one of the most popular RANS turbulence models, overestimates experimental heat transfer coefficients for opposing flows. Although the RANS models have been widely applied to opposing flows in various systems, the mechanism and conditions under which the predictive performance of the LS models fail remain unclear. This study aims to understand the model characteristics and their applicability under various mixed convection conditions. This article investigates the LS model, the LS model with the Yap correction, and the 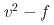 model. The LS model remarkably over predicts the Nusselt number and the friction coefficient under highly buoyant conditions. The error for the Nusselt number was more than 90% for
model. The LS model remarkably over predicts the Nusselt number and the friction coefficient under highly buoyant conditions. The error for the Nusselt number was more than 90% for 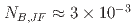 , where
, where 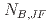 is a controlling parameter. The conditions under which the prediction of the LS model fails are linked to those under which reverse flow occurs near the heated wall. The reverse flow condition is given by
is a controlling parameter. The conditions under which the prediction of the LS model fails are linked to those under which reverse flow occurs near the heated wall. The reverse flow condition is given by 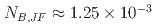 . This condition could be used where the LS model cannot be applied. The LS model with Yap correction and
. This condition could be used where the LS model cannot be applied. The LS model with Yap correction and 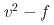 model can predict experimental data successfully from forced convection to mixed convection conditions
model can predict experimental data successfully from forced convection to mixed convection conditions 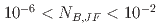 . For natural convection-dominant conditions
. For natural convection-dominant conditions 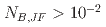 , the LS model with the Yap correction was numerically unstable and could not obtain a converged numerical solution; however, the
, the LS model with the Yap correction was numerically unstable and could not obtain a converged numerical solution; however, the 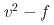 model stably reproduced the experimental data. By optimizing the model constants included in the Yap correction, the stability and accuracy of the calculation can be improved under highly buoyant opposing flow conditions.
model stably reproduced the experimental data. By optimizing the model constants included in the Yap correction, the stability and accuracy of the calculation can be improved under highly buoyant opposing flow conditions.
佐藤 聡; 日引 俊*; 池田 遼; 柴本 泰照
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 180, p.105593_1 - 105593_11, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)加圧水型原子炉(PWR)の冷却材喪失事故では、ダウンカマーに流入するコールドレグに注入された緊急炉心冷却(ECC)水の流れにより、原子炉圧力容器(RPV)内壁に加圧熱衝撃(PTS)が発生するリスクがある。PTSは、ECC水によるダウンカマー壁の急冷によって発生し、ECC水の温度、壁面へのジェットの衝突位置と速度、壁面上の液膜の速度、液膜の厚さ、下降流の広がりなどに強く影響される。したがって、コールドレグからダウンカマーに流出するECC水の流れは、PTS事象に強く影響する可能性がある。この流動現象を理解するために、円管からの自由流出に関する研究をレビューした。流動条件の分類、流動条件間の遷移条件、端部深さ比、円管内の流れの自由表面形状、管から流出するナッペの形状に関する実験結果は、ほぼ一致した形で得られている。これに対し、コールドレグからダウンカマーへの流れを考慮する場合、自由空間ではなく狭い隙間への流れ、円管出口の角の丸みの存在、炉心からコールドレグへ流れる蒸気流の影響など、特殊な状況での流れ場を扱う必要がある。しかし、これらの要因を考慮した先行研究は少ないため、今後蓄積すべき知見としてまとめた。
Zheng, X.; 玉置 等史; 柴本 泰照; 丸山 結
日本原子力学会誌ATOMO , 66(11), p.565 - 569, 2024/11
, 66(11), p.565 - 569, 2024/11
原子力安全の継続的な改善のためにはリスク情報と不確かさ情報を活用した合理的な意思決定が重要であり、近年ではこれを効率的に実施するために人工知能/機械学習(AI/ML)を活用することが期待されている。本報では、原子力分野におけるAI/MLの活用例を調査し、日本原子力研究開発機構が行うAI/MLを活用した動的確率論的リスク評価(PRA)と不確かさ評価・感度解析の研究状況を紹介する。具体的には、決定論的解析コードと機械学習による代替評価モデルを柔軟に共用できる多忠実シミュレーション手法を構築することで、ランダムサンプリングを用いた動的PRAとソースターム不確かさ評価・グローバル感度解析の効率的な実施を可能とした。
成川 隆文*; 高田 孝*; Zheng, X.; 玉置 等史; 柴本 泰照; 丸山 結; 高田 毅士
Proceedings of Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management & Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management (PSAM17 & ASRAM2024) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2024/10
Despite the advancements in dynamic probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) methods that account for the dynamics of event progression, establishing risk importance measures for these methods remains a significant research challenge. This study proposes novel risk importance measures from the perspective of the risk triplet: Timing-Based Worth (TBW) for the timing of scenario occurrence (scenario diversity), Frequency-Based Worth (FBW) for the frequency (probability) of scenarios, and Consequence-Based Worth (CBW) for the consequences of scenarios. To assess the effectiveness of these measures, a static PRA using the event tree method and a dynamic PRA using the continuous Markov chain Monte Carlo (CMMC) method are performed on a simplified reliability model. The results indicate that the proposed measures facilitate a comprehensive risk importance evaluation, incorporating resilience effects (the time margin) and consequence mitigation, alongside traditional frequency-based evaluations. This advancement is anticipated to improve the utilization of risk information derived from dynamic PRA.
Zheng, X.; 玉置 等史; 柴本 泰照; 丸山 結; 高田 毅士; 成川 隆文*; 高田 孝*
Proceedings of Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management & Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management (PSAM17 & ASRAM2024) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/10
Traditional frequency-based risk importance measures (RIMs) have demonstrated its practicability in the nuclear regulation. The authors investigate the definitions of existing RIMs and associated applications in risk-informed nuclear regulations, for instance, the risk-informed categorization of structures, systems, and components (SSCs), risk-informed changes to technical specifications, etc. However, when evaluating mitigation effects of accident countermeasures, importance assessments involving consequence and timing has the potential of providing valuable information for decision making. By widely using numerical simulations of possible accident progressions, dynamic PRA enables a straightforward assessment of risk triplets. Recent advancements in the development of dynamic PRA tend to explicitly incorporate the dynamics of accident progression and failure events into risk assessment, and it allows a provision of more detailed risk information. The approach to appropriate estimation of risk importance within this framework has not been established, exposing a significant research challenge in the use of risk information for decision making in the nuclear industry. Possible accident sequences are sampled using RAPID by randomly branching, and risk triplets are quantified, including key quantities such as source term release amount and release timing to the environment, and the associated frequencies. Risk triplets are used to calculate the new RIMs to rank the importance of pivotal headings in the event tree model. As the exemplary results of the analysis, source term release amount and timing are largely influenced by the mode of containment failure and the termination timing of reactor coolant injection. As the conclusion, when issues such as timing or seriousness of consequence are important for judgement, dynamic PRA and the new RIMs is capable of supporting decision making by providing more detailed risk information.
茂木 孝介; 柴本 泰照; 日引 俊詞*; 塚本 直史*; 金子 順一*
JAEA-Review 2024-039, 45 Pages, 2024/09
既往研究において様々な対向複合対流の熱伝達相関式が提案されているが、それらは様々な試験装置、流路形状、試験流体、熱流動パラメータの範囲で実施された実験結果に基づいている。従って、使用に際してその適用範囲や外挿性を踏まえた上でどの相関式を選択すべきかを整理しておくことは重要である。本稿では既存の対向複合対流の熱伝達相関式についてレビューした。また、複数の既往実験データと各相関式との比較を行い、相関式の予測性能を評価した。その結果、Jackson and Fewster相関式、Churchill相関式、Swanson and Catton (IJHMT)相関式は、全ての実験データを精度良く予測可能であった。さらに、代表長さに水力等価直径を用いることにより流路形状の違いに関わらず相関式が適用可能であり、支配パラメータの無次元化により試験流体によらず相関式が適用可能であることを確認した。
安部 諭; 柴本 泰照
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 202, p.110461_1 - 110461_16, 2024/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)During a severe accident in a nuclear containment vessel, jets released from the primary system exhibit complex thermohydraulic behavior due to buoyancy effects and impingement on internal obstacles such as inner walls and floors. Thus, the obstacle-influenced jets are of interest in recent research activities. This paper describes an experimental investigation of the behavior of jets passing through a grid-type obstacle. The flow field was acquired by a particle image velocimetry system. The experiment captured the jet fragmentation by the grid-type obstacle and their recoupling. The mean velocity field obtained by postprocessing indicates a "Rectifying effect," with the axial velocity increasing at the center and the magnitude of the radial velocity decreasing. The meandering flow was suppressed due to this effect. In the near grid-obstacle region, the axial turbulence intensity was relatively large at the edge of each fragmented region due to shear stress. Moreover, the spatial distribution of the radial turbulence fluctuation became more complex. Further investigation is required to clarify the budget of the transport equation for turbulence fluctuation. The experimental data shown in this paper is useful for computational fluid dynamics validation.
相馬 秀; 石垣 将宏*; 安部 諭; 柴本 泰照
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 56(7), p.2524 - 2533, 2024/07
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:75.80(Nuclear Science & Technology)When analyzing containment thermal-hydraulics, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a powerful tool because multi-dimensional and local analysis is required for some accident scenarios. According to the previous study, neglecting steam bulk condensation in the CFD analysis leads to a significant error in boundary layer profiles. Validating the condensation model requires the experimental data near the condensing surface, however, available boundary layer data is quite limited. It is also important to confirm whether the heat and mass transfer analogy (HMTA) is still valid in the presence of bulk condensation. In this study, the boundary layer measurements on the vertical condensing surface in the presence of air were performed with the rectangular channel facility WINCS, which was designed to measure the velocity, temperature, and concentration boundary layers. We set the laminar flow condition and varied the Richardson number (1.0-23) and the steam volume fraction (0.35-0.57). The experimental results were used to validate CFD analysis and HMTA models. For the former, we implemented a bulk condensation model assuming local thermal equilibrium into the CFD code and confirmed its validity. For the latter, we validated the HMTA-based correlations, confirming that the mixed convection correlation reasonably predicted the sum of wall and bulk condensation rates.
和田 裕貴; 廣瀬 意育; 柴本 泰照
Ultrasonics, 141, p.107346_1 - 107346_16, 2024/07
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:70.65(Acoustics)Ultrasound tomography of bubbly two-phase flows using machine learning (ML) was investigated by performing two-dimensional ultrasound numerical simulations using a finite element method simulator. To date, studies on ultrasound tomography for two-phase flow measurements have been conducted only for some bubbles. However, in an actual bubbly flow, numerous bubbles are complexly distributed in the cross-section of the flow channel. This limitation of previous studies originates from the transmission characteristics of ultrasound waves through a medium. The transmission characteristics of ultrasound waves are different from those of other probe signals, such as radiation, electrical, and optical signals. In this study, the feasibility of combining ultrasound tomography with ML was evaluated for dense bubble distributions with up to 20 bubbles (cross-sectional average void fraction of approximately 0.29). We investigated the effects of the temporal length of the received waveform and number of sensors to optimize the system on the prediction performance of the bubble distribution. The simultaneous driving of the installed sensors was simulated to reduce the measurement time for the entire cross-section and verify the applicability of the method. Thus, it was confirmed that ultrasound tomography using ML has sufficient prediction performance, even for a complex bubble distribution with many bubbles, and that the cross-sectional average void fraction can be predicted with high accuracy.
岡垣 百合亜; 日引 俊詞*; 柴本 泰照
International Journal of Energy Research, 2024, p.5114542_1 - 5114542_37, 2024/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Energy & Fuels)In pressurized water reactor accident scenarios, the injection of water from the ECCS (ECC injection) might induce a PTS, affecting the RPV integrity. Therefore, PTS is a vital research issue in reactor safety, and its analysis is essential for evaluating the integrity of RPVs, which determines the reactor life. The PTS analysis comprises a coupled analysis between thermal-hydraulic and structural analysis. The thermal-hydraulic approach is particularly crucial, and reliable Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations should play a vital role in the future because predicting the temperature gradient of the RPV wall requires data on the transient temperature distribution of the downcomer. Since one-dimensional codes cannot predict the complex three-dimensional flow features during ECC injection, PTS is one reactor safety issue where CFD can benefit from complement evaluations with thermal-hydraulic system analysis codes. This study reviewed the code validation efforts for turbulence models most affecting PTS analysis based on papers published since 2010 on single- and two-phase flow CFD analysis for the experiment on PTS performed in the ROCOM, TOPFLOW, UPTF, and LSTF. The results revealed that in single-phase flow CFD analysis, where knowledge and experience are sufficient, various turbulence models have been considered, and many analyses using LES have been reported. For two-phase flow analysis of air-water conditions, interface capturing/tracking methods were used in addition to two-fluid models. The standard k- and SST k-
and SST k- models were still in the validated phase, and various turbulence models have yet to be fully validated. In the two-phase flow analysis of steam-water conditions, many studies have used two-fluid models and RANS, and NEPTUNE_CFD, in particular, has been reported to show excellent prediction performance based on years of accumulated validation.
models were still in the validated phase, and various turbulence models have yet to be fully validated. In the two-phase flow analysis of steam-water conditions, many studies have used two-fluid models and RANS, and NEPTUNE_CFD, in particular, has been reported to show excellent prediction performance based on years of accumulated validation.
廣瀬 意育; 安部 諭; 石垣 将宏*; 柴本 泰照; 日引 俊*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 169, p.105085_1 - 105085_13, 2024/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Immersed boundary methods (IBMs) have been developed as complementary methods for computational fluid dynamics (CFD). They allow a flow simulation in a mock-up model that includes complex-shaped inner structures and/or boundaries with a non-body conformal mesh. Such a model might force us to create a complicated body-fitted mesh with a high cost in the conventional CFD (CCFD) approach. We focus on the Brinkman penalization (BP) method and its extended version, which we call here the extended Brinkman penalization method (EBP), among the different types of IBMs, aiming to apply them to the phenomena that occur during severe accidents in a nuclear reactor containment vessel and explore the possibility that the methods can partially replace the CCFD. In this paper, as a preliminary step to validate the applicability of these methods, we measure the jet flow rectified by a grating-type structure used for the validation of numerical techniques and apply them to simulate the behavior of an upward jet rectified by a horizontally placed grating-type structure modeled as an immersed body. This type of structure is generally used in reactor buildings, and it is crucial to evaluate their influence on gaseous flows because the behaviors of hydrogen produced during severe accidents may be influenced by them. The structure is selected as our subject because it has moderate complexity, enabling us to examine the effects of the IBMs and compare them with CCFD. We investigate whether these methods can reproduce a result of corresponding CCFD in which the grating is modeled as body-conformal mesh and show that the former can produce the latter with equivalent accuracy. All these results are also compared with the experimental data on the flow velocity distributions downstream of the grating measured using particle image velocimetry.
廣瀬 意育; 柴本 泰照; 日引 俊*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 168, p.105027_1 - 105027_17, 2024/03
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:43.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study reviewed the literature that measured critical heat flux (CHF) for downward flow in round pipes and arranged the proposed correlations. Each correlation shows relatively good prediction accuracy for experimental data from their literature, but the accuracies sometimes decrease for experimental data from other literature. No correlation accurately predicts all the experimental data of the literature, indicating an issue in extrapolating existing correlations. Therefore, we developed a correlation that can accurately predict the experimental data of the collected literature. First, we used a neural network to select the essential dimensionless quantities that comprise the correlation. Then, we regarded the prediction accuracy when all candidate dimensionless quantities extracted from the literature were used for the input variables of the network as the achievable limit prediction accuracy and searched for the minimum combination of dimensionless quantities required to achieve it. The results showed that only the dimensionless mass flux and the ratio of the heating length to the channel diameter are the essential parameters to achieve it. We developed a correlation equation using these two dimensionless quantities and achieved 17.6% of the average prediction accuracy. This result considerably improved existing correlation equations with 25%-40% average prediction accuracy for the same experimental data.