Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Massey, D.*; Williams, C. D.*; Mu, J.*; Masters, A. J.*; 元川 竜平; 青柳 登; 上田 祐生; Antonio, M. R.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 127(9), p.2052 - 2065, 2023/03
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:15.83(Chemistry, Physical)There is an ever-increasing body of evidence that metallic complexes, involving amphiphilic ligands, do not form normal solutions in organic solvents. Instead, they form complex fluids with intricate structures. For example, the metallic complexes may aggregate into clusters and these clusters themselves may aggregate into super-clusters. In order to gain a deeper insight into the mechanisms at play, we have used an improved force field to conduct extensive molecular dynamics simulations of a system composed of zirconium nitrate, water, nitric acid, tri- -butyl phosphate and
-butyl phosphate and  -octane. The important new finding is that a dynamic equilibrium between the cis and trans isomers of the metal complex is likely to play a key role in the aggregation behavior. The isolated cis and trans isomers have similar energies but simulation indicates that the clusters consist predominantly of cis isomers. With increasing metal concentration, we hypothesize that more clustering occurs and the chemical equilibrium shifts towards the cis isomer. It is possible that such isomeric effects play a role in the liquid-liquid extraction of other species and the inclusion of such effects in flowsheet modelling may lead to a better description of the process.
-octane. The important new finding is that a dynamic equilibrium between the cis and trans isomers of the metal complex is likely to play a key role in the aggregation behavior. The isolated cis and trans isomers have similar energies but simulation indicates that the clusters consist predominantly of cis isomers. With increasing metal concentration, we hypothesize that more clustering occurs and the chemical equilibrium shifts towards the cis isomer. It is possible that such isomeric effects play a role in the liquid-liquid extraction of other species and the inclusion of such effects in flowsheet modelling may lead to a better description of the process.
成田 弘一*; Nicolson, R. M.*; 元川 竜平; 伊藤 文之*; 森作 員子*; 後藤 みどり*; 田中 幹也*; Heller, W. T.*; 塩飽 秀啓; 矢板 毅; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 58(13), p.8720 - 8734, 2019/07
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:75.87(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Current industrial practices to extract rhodium from virgin ores carry a heavy environmental burden. Improving the efficiency of the hydrometallurgical processes to separate and recover rhodium from other precious metals provides an opportunity to improve the materials and energy balances, but the presence of mixed chloride-rhodium species following leaching by acid chloride media complicates the recovery process. In this work we have applied a broad range of analytical techniques (FT-IR spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, EXAFS, water-transfer analysis, small-angle neutron scattering, NMR spectroscopy, and electrospray mass spectrometry), which together show that the amino-amide reagent preferentially transports chlorido-rhodium species as a 1:2 neutral assembly from aqueous 2.0 M HCl phase into an organic phase. The extractants then ligate in the outer coordination shell of the chloride-rhodium anion, making this an efficient separation process. In this study, we found that protonation to the extractants induced to form a proton chelate ring, which pre-organises the ligand to present an array of charge diffuse C-H bonds. This templated arrangement of positive dipoles favors complexation to the charge diffuse chloride-rhodium anion over the more charge-dense chloride anion.
元川 竜平; 小林 徹; 遠藤 仁; Mu, J.*; Williams, C. D.*; Masters, A. J.*; Antonio, M. R.*; Heller, W. T.*; 長尾 道弘*
ACS Central Science, 5(1), p.85 - 96, 2019/01
被引用回数:56 パーセンタイル:86.16(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We present a hierarchical aggregate model of an organic phase containing a coordination species that acts as a fundamental building unit of higher-order structures formed in the organic phase. We aimed to elucidate the fundamental aspects of the microscopic structure and phase separation occurring in ionic separation and recovery systems during solvent extraction. The coordination species aggregate through a hydrogen-bonding network formed by interaction between the hydrophilic part of the coordination species with extracted water and acid molecules. This reduces the hydrophilic surface area, resulting in subsequent formation of small primal clusters of 2 to 3 nm in diameter. The primal clusters further aggregate due to van der Waals interaction to form large aggregates of  10 nm in diameter. The size of the primal cluster does not depend on the concentration of the coordination species, whereas the size of the large aggregate increases as the aggregation number of the primal clusters increases. We conclude that hybrid interaction is a key driving force in the formation and growth of the hierarchical aggregate and the induction of phase separation of the organic phase.
10 nm in diameter. The size of the primal cluster does not depend on the concentration of the coordination species, whereas the size of the large aggregate increases as the aggregation number of the primal clusters increases. We conclude that hybrid interaction is a key driving force in the formation and growth of the hierarchical aggregate and the induction of phase separation of the organic phase.
 -butyl phosphate/
-butyl phosphate/ -octane mixtures by X-ray and neutron scattering in a wide
-octane mixtures by X-ray and neutron scattering in a wide  range
range元川 竜平; 鈴木 伸一; 小川 紘樹*; Antonio, M. R.*; 矢板 毅
Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 116(4), p.1319 - 1327, 2012/02
被引用回数:38 パーセンタイル:65.36(Chemistry, Physical)Tri- -butyl phosphate (TBP) is an important extractant for separating hexavalent uranium and tetravalent plutonium from used nuclear fuel by solvent extraction. In such solvent extractions using TBP, the organic phase occasionally separates into two organic phases, namely, light and heavy organic phases. The latter one in particular is called the third phase. The purpose of this work is to elucidate the mechanism whereby the third phase forms in biphasic liquid-liquid solvent extraction of heavy metal ions. Toward this end, small- and wide-angle X-ray and neutron scattering experiments were conducted to examine the microscopic structures of TBP/octane mixtures. These investigations of solute associations provide insights into system performance. After the extraction of heavy metal ions, for example, the microscopic structures formed in the organic phase are likely to be correlated with the initial microscopic structures, which are revealed here. SWAXS and SWANS, with accurate estimations of incoherent scattering intensities for all solution samples, revealed the following: (1) TBP self-associates in octane, and the average distance between two TBP molecules in the TBP assemblies is evaluated as 0.9-1.0 nm; (2) the shape of the TBP assembly is ellipsoidal; and (3) the attractive interaction among TBP assemblies in octane is miniscule, and thus, they tend to be dispersed homogeneously due to the excluded volume effect.
-butyl phosphate (TBP) is an important extractant for separating hexavalent uranium and tetravalent plutonium from used nuclear fuel by solvent extraction. In such solvent extractions using TBP, the organic phase occasionally separates into two organic phases, namely, light and heavy organic phases. The latter one in particular is called the third phase. The purpose of this work is to elucidate the mechanism whereby the third phase forms in biphasic liquid-liquid solvent extraction of heavy metal ions. Toward this end, small- and wide-angle X-ray and neutron scattering experiments were conducted to examine the microscopic structures of TBP/octane mixtures. These investigations of solute associations provide insights into system performance. After the extraction of heavy metal ions, for example, the microscopic structures formed in the organic phase are likely to be correlated with the initial microscopic structures, which are revealed here. SWAXS and SWANS, with accurate estimations of incoherent scattering intensities for all solution samples, revealed the following: (1) TBP self-associates in octane, and the average distance between two TBP molecules in the TBP assemblies is evaluated as 0.9-1.0 nm; (2) the shape of the TBP assembly is ellipsoidal; and (3) the attractive interaction among TBP assemblies in octane is miniscule, and thus, they tend to be dispersed homogeneously due to the excluded volume effect.
岡村 浩之; 上田 祐生; 元川 竜平; Mu, J.*; Masters, A. J.*; Antonio, M. R.*
no journal, ,
溶質濃度が高い実用的な液-液抽出条件下では、有機相中で金属-抽出剤錯体クラスターが生成することがある。このような条件においては、金属-抽出剤の化学量論を決定するスロープ解析法の適用が困難になり、理想からのずれは、非線形や非整数の傾きとして現れる。そこで本研究では、クラスター形成を考慮した、実用的な液-液系のための新たな抽出平衡解析法を開発し、古典的平衡論解析の拡張に挑戦した。分子動力学(MD)シミュレーションのスナップショットを解析したところ、 -オクタン中で1から9個のZr(NO
-オクタン中で1から9個のZr(NO )
) (TBP)
(TBP) 錯体が凝集したクラスターを形成していることが明らかになり、各クラスターの組成とモル分率を算出できた。
錯体が凝集したクラスターを形成していることが明らかになり、各クラスターの組成とモル分率を算出できた。 個のZr(NO
個のZr(NO )
) (TBP)
(TBP) 錯体から構成されるクラスターの抽出平衡を考慮し、MD解析で得られた各クラスターのモル分率と分配比から、抽出平衡定数K
錯体から構成されるクラスターの抽出平衡を考慮し、MD解析で得られた各クラスターのモル分率と分配比から、抽出平衡定数K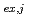 (
( = 1-9)を算出した。得られたK
= 1-9)を算出した。得られたK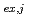 から計算した分配比の曲線は、実験値とよく一致することが明らかになった。したがって、MDシミュレーションにより、クラスター化/凝集液-液抽出系における実験値を正確に再現できることが明らかになり、古典的平衡論解析の拡張に成功した。
から計算した分配比の曲線は、実験値とよく一致することが明らかになった。したがって、MDシミュレーションにより、クラスター化/凝集液-液抽出系における実験値を正確に再現できることが明らかになり、古典的平衡論解析の拡張に成功した。
岡村 浩之; 上田 祐生; 元川 竜平; Mu, J.*; Masters, A. J.*; Antonio, M. R.*
no journal, ,
近年、有機溶媒中での金属-抽出剤錯体クラスターの形成が液-液抽出において重要な役割を果たすことが示された。液-液抽出に関しては、多数の反応機構が提案されているが、溶質濃度が高い条件においては、金属-抽出剤の化学量論を評価するスロープ解析法の適用が困難になる。そこで本研究では、抽出過程における有機相中でのクラスター凝集体形成を考慮した、実用的な液-液系のための溶媒抽出平衡解析を行った。分子動力学(MD)シミュレーションを行ったところ、 -オクタン中で1から9個のZr(NO
-オクタン中で1から9個のZr(NO )
) (TBP)
(TBP) 錯体が凝集したクラスターを形成していることが見出され、各クラスターの組成とモル分率を算出できた。さらに、抽出平衡反応を検討することで、MD解析で得られたパラメータから各クラスターの抽出平衡定数K
錯体が凝集したクラスターを形成していることが見出され、各クラスターの組成とモル分率を算出できた。さらに、抽出平衡反応を検討することで、MD解析で得られたパラメータから各クラスターの抽出平衡定数K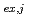 (
( = 1-9)を求めることができ、K
= 1-9)を求めることができ、K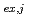 から計算した分配比の曲線は、実験値とよく一致した。したがって、1回のMDシミュレーションからクラスター化/凝集液-液抽出系における分配比曲線を正確に再現でき、スロープ解析法の限界を克服することに成功した。
から計算した分配比の曲線は、実験値とよく一致した。したがって、1回のMDシミュレーションからクラスター化/凝集液-液抽出系における分配比曲線を正確に再現でき、スロープ解析法の限界を克服することに成功した。