金属錯体によるナノクラスター化現象の精密構造解析に基づいた古典的平衡論解析の拡張
Extension of the classical equilibrium analysis based on precise structure analysis of clustering phenomena by metal complexes
岡村 浩之 

 ; 上田 祐生
; 上田 祐生 

 ; 元川 竜平
; 元川 竜平 

 ; Mu, J.*; Masters, A. J.*; Antonio, M. R.*
; Mu, J.*; Masters, A. J.*; Antonio, M. R.*
Okamura, Hiroyuki; Ueda, Yuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Mu, J.*; Masters, A. J.*; Antonio, M. R.*
溶質濃度が高い実用的な液-液抽出条件下では、有機相中で金属-抽出剤錯体クラスターが生成することがある。このような条件においては、金属-抽出剤の化学量論を決定するスロープ解析法の適用が困難になり、理想からのずれは、非線形や非整数の傾きとして現れる。そこで本研究では、クラスター形成を考慮した、実用的な液-液系のための新たな抽出平衡解析法を開発し、古典的平衡論解析の拡張に挑戦した。分子動力学(MD)シミュレーションのスナップショットを解析したところ、 -オクタン中で1から9個のZr(NO
-オクタン中で1から9個のZr(NO )
) (TBP)
(TBP) 錯体が凝集したクラスターを形成していることが明らかになり、各クラスターの組成とモル分率を算出できた。
錯体が凝集したクラスターを形成していることが明らかになり、各クラスターの組成とモル分率を算出できた。 個のZr(NO
個のZr(NO )
) (TBP)
(TBP) 錯体から構成されるクラスターの抽出平衡を考慮し、MD解析で得られた各クラスターのモル分率と分配比から、抽出平衡定数K
錯体から構成されるクラスターの抽出平衡を考慮し、MD解析で得られた各クラスターのモル分率と分配比から、抽出平衡定数K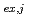 (
( = 1-9)を算出した。得られたK
= 1-9)を算出した。得られたK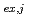 から計算した分配比の曲線は、実験値とよく一致することが明らかになった。したがって、MDシミュレーションにより、クラスター化/凝集液-液抽出系における実験値を正確に再現できることが明らかになり、古典的平衡論解析の拡張に成功した。
から計算した分配比の曲線は、実験値とよく一致することが明らかになった。したがって、MDシミュレーションにより、クラスター化/凝集液-液抽出系における実験値を正確に再現できることが明らかになり、古典的平衡論解析の拡張に成功した。
Under practical liquid-liquid extraction conditions with high solute concentrations, clusters of metal-extractant complexes can form in the organic phase. In these conditions, application of the slope analysis method for determining metal-extractant stoichiometry becomes difficult, and the deviations from ideal appear as non-linear responses and non-integer slopes. In this study, we developed novel extraction equilibrium analysis for practical liquid-liquid systems with consideration of the cluster formation and investigated the extension of the classical equilibrium analysis. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation snapshots indicate the formation of aggregated clusters of 1 to 9 Zr(NO )
) (TBP)
(TBP) complexes in
complexes in  -octane, leading to the determination of composition and molar fraction of each cluster. Considering the extraction equilibrium of clusters composed of
-octane, leading to the determination of composition and molar fraction of each cluster. Considering the extraction equilibrium of clusters composed of  Zr(NO
Zr(NO )
) (TBP)
(TBP) complexes, the extraction equilibrium constants K
complexes, the extraction equilibrium constants K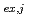 (
( = 1-9) were calculated from the distribution ratio and the molar fraction for each cluster obtained by the MD analysis. The distribution curve calculated from the obtained K
= 1-9) were calculated from the distribution ratio and the molar fraction for each cluster obtained by the MD analysis. The distribution curve calculated from the obtained K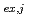 values agrees well with the experimental values. Therefore, MD simulation can accurately reproduce the experimental values in the clustering/aggregation liquid-liquid extraction system, which enabled us to extend the classical equilibrium analysis.
values agrees well with the experimental values. Therefore, MD simulation can accurately reproduce the experimental values in the clustering/aggregation liquid-liquid extraction system, which enabled us to extend the classical equilibrium analysis.