Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -based materials; A View on valence-fluctuating EuIr
-based materials; A View on valence-fluctuating EuIr Si
Si
Usachov, D. Yu*; Tarasov, A. V.*; Schulz, S.*; Bokai, K. A.*; Tupitsyn, I. I.*; Poelchen, G.*; Seiro, S.*; Caroca-Canales, N.*; Kliemt, K.*; Mende, M.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 102(20), p.205102_1 - 205102_11, 2020/11
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:50.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Using photoelectron diffraction (PED) and magnetic dichroism measurements, we explore the electronic and magnetic properties of the near-surface region of the valence-fluctuating material EuIr Si
Si . We present and discuss the methodology for modeling of the 4
. We present and discuss the methodology for modeling of the 4 photoemission spectra, PED patterns and magnetic dichroism for rare-earth-based materials. For the Eu-terminated surface we found that the topmost Eu layer is divalent and exhibits a ferromagnetic order below 10 K. The valency of the next Eu layer, that is the 5th atomic layer, is about 2.8 at low temperature that is close to the valency in the bulk. The properties of the Si-terminated surface are drastically different. The first subsurface Eu layer (4th atomic layer below the surface) behaves divalently and orders ferromagnetically at much higher temperature. Experimental data indicate, however, that there is an admixture of trivalent Eu in this layer, resulting in its valency of about 2.1. The next deeper lying Eu layer (8th atomic layer below the surface) behaves mixed-valently, but the estimated valency of 2.4 is notably lower than the value in the bulk. The obtained results create a background for further studies of exotic surface properties of 4
photoemission spectra, PED patterns and magnetic dichroism for rare-earth-based materials. For the Eu-terminated surface we found that the topmost Eu layer is divalent and exhibits a ferromagnetic order below 10 K. The valency of the next Eu layer, that is the 5th atomic layer, is about 2.8 at low temperature that is close to the valency in the bulk. The properties of the Si-terminated surface are drastically different. The first subsurface Eu layer (4th atomic layer below the surface) behaves divalently and orders ferromagnetically at much higher temperature. Experimental data indicate, however, that there is an admixture of trivalent Eu in this layer, resulting in its valency of about 2.1. The next deeper lying Eu layer (8th atomic layer below the surface) behaves mixed-valently, but the estimated valency of 2.4 is notably lower than the value in the bulk. The obtained results create a background for further studies of exotic surface properties of 4 -based materials, and allow to derive information related to valency and magnetism of individual rare-earth layers in a rather extended area near the surface.
-based materials, and allow to derive information related to valency and magnetism of individual rare-earth layers in a rather extended area near the surface.
平原 徹*; Otrokov, M. M.*; 佐々木 泰祐*; 角田 一樹*; 友弘 雄太*; 日下 翔太郎*; 奥山 裕磨*; 一ノ倉 聖*; 小林 正起*; 竹田 幸治; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.4821_1 - 4821_8, 2020/09
被引用回数:53 パーセンタイル:90.85(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We fabricate a novel magnetic topological heterostructure Mn Bi
Bi Te
Te /Bi
/Bi Te
Te where multiple magnetic layers are inserted into the topmost quintuple layer of the original topological insulator Bi
where multiple magnetic layers are inserted into the topmost quintuple layer of the original topological insulator Bi Te
Te . A massive Dirac cone (DC) with a gap of 40-75 meV at 16 K is observed. By tracing the temperature evolution, this gap is shown to gradually decrease with increasing temperature and a blunt transition from a massive to a massless DC occurs around 200-250 K. Magnetic measurements show that there are two distinct Mn components in the system that corresponds to the two heterostructures; MnBi
. A massive Dirac cone (DC) with a gap of 40-75 meV at 16 K is observed. By tracing the temperature evolution, this gap is shown to gradually decrease with increasing temperature and a blunt transition from a massive to a massless DC occurs around 200-250 K. Magnetic measurements show that there are two distinct Mn components in the system that corresponds to the two heterostructures; MnBi Te
Te /Bi
/Bi Te
Te is paramagnetic at 6 K while Mn
is paramagnetic at 6 K while Mn Bi
Bi Te
Te /Bi
/Bi Te
Te is ferromagnetic with a negative hysteresis (critical temperature 20 K). This novel heterostructure is potentially important for future device applications.
is ferromagnetic with a negative hysteresis (critical temperature 20 K). This novel heterostructure is potentially important for future device applications.
 Te
Te
Shikin, A. M.*; Estyunin, D. A.*; Klimovskikh, I. I.*; Filnov, S. O.*; Kumar, S.*; Schwier, E. F.*; 宮本 幸治*; 奥田 太一*; 木村 昭夫*; 黒田 健太*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10, p.13226_1 - 13226_13, 2020/08
被引用回数:73 パーセンタイル:95.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Modification of the gap at the Dirac point (DP) in axion antiferromagnetic topological insulator MnBi Te
Te and its electronic and spin structure have been studied by angle- and spin-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) under laser excitation at various temperatures, light polarizations and photon energies. We have distinguished both large and reduced gaps at the DP in the ARPES dispersions, which remain open above the N
and its electronic and spin structure have been studied by angle- and spin-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) under laser excitation at various temperatures, light polarizations and photon energies. We have distinguished both large and reduced gaps at the DP in the ARPES dispersions, which remain open above the N el temperature of
el temperature of 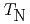 = 24.5 K. We propose that the gap above
= 24.5 K. We propose that the gap above 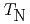 remains open due to a short-range magnetic field generated by chiral spin fluctuations. Spin-resolved ARPES, XMCD and circular dichroism ARPES measurements show a surface ferromagnetic ordering for the large gap sample and apparently significantly reduced effective magnetic moment for the reduced gap sample.
remains open due to a short-range magnetic field generated by chiral spin fluctuations. Spin-resolved ARPES, XMCD and circular dichroism ARPES measurements show a surface ferromagnetic ordering for the large gap sample and apparently significantly reduced effective magnetic moment for the reduced gap sample.
 Si
Si as a reference for the Luttinger theorem and antiferromagnetism in trivalent heavy-fermion YbRh
as a reference for the Luttinger theorem and antiferromagnetism in trivalent heavy-fermion YbRh Si
Si
G ttler, M.*; Generalov, A.*; 藤森 伸一; Kummer, K.*; Chikina, A.*; Seiro, S.*; Danzenb
ttler, M.*; Generalov, A.*; 藤森 伸一; Kummer, K.*; Chikina, A.*; Seiro, S.*; Danzenb cher, S.*; Koroteev, Yu. M.*; Chulkov, E. V.*; Radovic, M.*; et al.
cher, S.*; Koroteev, Yu. M.*; Chulkov, E. V.*; Radovic, M.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 10, p.796_1 - 796_7, 2019/02
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:56.67(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Application of the Luttinger Theorem (LT) to the canonical heavy-fermion Kondo Lattice (KL) material YbRh Si
Si suggests that its large 4f-derived Fermi surface (FS) in the paramagnetic (PM) regime should be similar in shape and volume to that of the divalent local moment anti-ferromagnet (AFM) EuRh
suggests that its large 4f-derived Fermi surface (FS) in the paramagnetic (PM) regime should be similar in shape and volume to that of the divalent local moment anti-ferromagnet (AFM) EuRh Si
Si in its PM regime. This leads to the tempting opportunity to explore a new experimental realization of the LT in general and how the large FS may change upon the AFM transition below 70 mK in YbRh
in its PM regime. This leads to the tempting opportunity to explore a new experimental realization of the LT in general and how the large FS may change upon the AFM transition below 70 mK in YbRh Si
Si in particular. A detailed knowledge of the FS reconstruction might be essential to disclose the properties of this phase, which is a precursor of quantum criticality and superconductivity. Using angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES), we observe a large FS for PM EuRh
in particular. A detailed knowledge of the FS reconstruction might be essential to disclose the properties of this phase, which is a precursor of quantum criticality and superconductivity. Using angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES), we observe a large FS for PM EuRh Si
Si essentially the same as the one seen in YbRh
essentially the same as the one seen in YbRh Si
Si in the KL state at a temperature of 1 K. Across the EuRh
in the KL state at a temperature of 1 K. Across the EuRh Si
Si AFM transition we found an extensive fragmentation of the FS due to Brillouin zone folding, intersection and resulting hybridization of the Doughnut and Jungle gym Fermi-surface sheets. Our results on EuRh
AFM transition we found an extensive fragmentation of the FS due to Brillouin zone folding, intersection and resulting hybridization of the Doughnut and Jungle gym Fermi-surface sheets. Our results on EuRh Si
Si indicate that the formation of the AFM state in YbRh
indicate that the formation of the AFM state in YbRh Si
Si is very likely also connected with large changes in the FS, which have to be taken into account in the controversial analysis and discussion of anomalies observed at the quantum critical point in this system.
is very likely also connected with large changes in the FS, which have to be taken into account in the controversial analysis and discussion of anomalies observed at the quantum critical point in this system.
 Se
Se induced by cobalt adatom in the absence of ferromagnetic ordering
induced by cobalt adatom in the absence of ferromagnetic orderingYe. M.*; Eremeev, S. V.*; 黒田 健太*; Krasovskii, E. E.*; Chulkov, E. V.*; 竹田 幸治; 斎藤 祐児; 岡本 和晃*; Zhu, S. Y.*; 宮本 幸治*; et al.
Physical Review B, 85(20), p.205317_1 - 205317_5, 2012/05
被引用回数:63 パーセンタイル:88.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)トポロジカル絶縁体Bi Se
Se の表面にコバルトを蒸着した系に対して、コバルトの物性に注目して、トンネル分光,角度分解光電子分光,磁気円二色性及び理論計算を組合せて得られた研究成果である。原子力機構としての貢献は、磁気円二色性を用いてコバルトの磁性を調べた部分である。トポロジカル絶縁体表面では磁性元素が強磁性を示すという理論的予想があるが、今回の実験では、Bi
の表面にコバルトを蒸着した系に対して、コバルトの物性に注目して、トンネル分光,角度分解光電子分光,磁気円二色性及び理論計算を組合せて得られた研究成果である。原子力機構としての貢献は、磁気円二色性を用いてコバルトの磁性を調べた部分である。トポロジカル絶縁体表面では磁性元素が強磁性を示すという理論的予想があるが、今回の実験では、Bi Se
Se とコバルトとの組合せでは強磁性を示さないという実験的証拠を示すことができた。
とコバルトとの組合せでは強磁性を示さないという実験的証拠を示すことができた。