Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 C-stainless steel composites using the improved MPS method
C-stainless steel composites using the improved MPS methodAhmed, Z.*; Wu, S.*; Sharma, A.*; Kumar, R.*; 山野 秀将; Pellegrini, M.*; 横山 諒*; 岡本 孝司*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 250, p.127343_1 - 127343_17, 2025/11
The study aims to measure boron concentration through the unidirectional diffusion of boron within the stainless steel (SS) layers while evaluating the updated model ability to replicate melt relocation behavior and geometry. In the current MPS simulations, one scenario employed dummy walls as heat sources, while another scenario used SS surface particles as heat sources to avoid interference with the melt flow as it reached the bottom of the specimen.
 C
CPham V. H.; 倉田 正輝; 永江 勇二; 石橋 良*; 佐々木 政名*
Corrosion Science, 255, p.113098_1 - 113098_9, 2025/10
Being expected as materials for accident tolerant fuel cladding tube, oxidation behavior and kinetics of silicon carbide (SiC) under extreme conditions like severe accidents must be elucidated. In this study, oxidation tests of SiC at 1400-1600  C for 1-5 h, at atmospheric pressure, under two different flow rates of H
C for 1-5 h, at atmospheric pressure, under two different flow rates of H O/Ar gas mixture have been conducted to investigate the influence of steam flow rate on the formation of SiO
O/Ar gas mixture have been conducted to investigate the influence of steam flow rate on the formation of SiO scale and its subsequent volatilization. The oxidation tests were conducted via a newly developed test facility using laser as a heat source. Oxidation kinetics of SiC was evaluated via mass change of samples before and after the oxidation tests. Parabolic oxidation rate representative for SiO
scale and its subsequent volatilization. The oxidation tests were conducted via a newly developed test facility using laser as a heat source. Oxidation kinetics of SiC was evaluated via mass change of samples before and after the oxidation tests. Parabolic oxidation rate representative for SiO formation and linear volatilization rate reflecting its volatilization were calculated, based on these mass changes. The Arrhenius dependence of the parabolic oxidation and linear volatilization rate constants were then plotted. Results of this study indicated that SiC exhibits excellent performance under the conditions investigated. Steam flow rate has a significant influence on volatilization of SiO
formation and linear volatilization rate reflecting its volatilization were calculated, based on these mass changes. The Arrhenius dependence of the parabolic oxidation and linear volatilization rate constants were then plotted. Results of this study indicated that SiC exhibits excellent performance under the conditions investigated. Steam flow rate has a significant influence on volatilization of SiO but has minor effects over its formation. Oxidation of SiC in steam at high temperature may follow mass gain or mass loss regime, depending on the steam flow rate. Two oxidation patterns were suggested and discussed. In the first oxidation pattern, the SiO
but has minor effects over its formation. Oxidation of SiC in steam at high temperature may follow mass gain or mass loss regime, depending on the steam flow rate. Two oxidation patterns were suggested and discussed. In the first oxidation pattern, the SiO formation is dominated over its volatilization. The second oxidation pattern (steady stage) is reached when the SiO
formation is dominated over its volatilization. The second oxidation pattern (steady stage) is reached when the SiO formation rate is equivalent to its volatilization rate. Time to reach this steady stage was defined, based on the parabolic oxidation rate and linear volatilization rate.
formation rate is equivalent to its volatilization rate. Time to reach this steady stage was defined, based on the parabolic oxidation rate and linear volatilization rate.
Yildirim, A. C.*; Mei, H.*; 戸田 賀奈子*; 青柳 登; 斉藤 拓巳*
Applied Clay Science, 274, p.107853_1 - 107853_9, 2025/09
被引用回数:0Metakaolin-based geopolymers (MKGPs) are ceramic-like materials used for nuclear waste stabilization. Therefore, understanding the sorption of ions on MKGPs is crucial where the cation exchange is considered as the main mechanism, yet the studies based on pH are limited. Thus, this study evaluates the effect of pH on the sorption mechanism of Eu(III) onto Na- and K-MKGPs. Here, time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS) combined with parallel factor analysis, TRLFS in mixed D O/H
O/H O matrices, and extended X-ray absorption fine structure analysis. Eu(III) predominantly forms surface complexes with both MKGPs in the pH range of 4
O matrices, and extended X-ray absorption fine structure analysis. Eu(III) predominantly forms surface complexes with both MKGPs in the pH range of 4  11 at the open air environment, where three distinct surface species were identified at different pH values. The Eu(III) sorption mechanisms of both MKGPs are similar, involving ternary edge-sharing bidentate or monodentate inner-sphere surface complexation of Eu(III) with MKGP and silicate ions released from the MKGP up to pH 8, followed by the precipitation of europium tri-hydroxide within the pores of MKGP. The insights gained from this study will enhance the knowledge on MKGP for pollutant immobilization, thereby mitigating the spread of contaminants in the environment and expanding the potential application areas.
11 at the open air environment, where three distinct surface species were identified at different pH values. The Eu(III) sorption mechanisms of both MKGPs are similar, involving ternary edge-sharing bidentate or monodentate inner-sphere surface complexation of Eu(III) with MKGP and silicate ions released from the MKGP up to pH 8, followed by the precipitation of europium tri-hydroxide within the pores of MKGP. The insights gained from this study will enhance the knowledge on MKGP for pollutant immobilization, thereby mitigating the spread of contaminants in the environment and expanding the potential application areas.
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction study山下 享介*; 古賀 紀光*; Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; 藤井 英俊*; 梅澤 修*
Materials Science and Engineering A, 941, p.148602_1 - 148602_11, 2025/09
Ferrite-austenite duplex stainless steels offer excellent strength and ductility, making them suitable for extreme environments. In this study,  neutron diffraction during tensile testing at 293 K and 200 K was used to investigate stress partitioning and phase-specific deformation. Phase stress was calculated using a texture-compensated method. At both temperatures, ferrite showed higher phase stress than austenite, acting as the harder phase. At 200 K, both phases exhibited increased strength and work hardening. Austenite showed significant stacking fault formation alongside dislocation migration, while ferrite retained its dislocation-based deformation mode, becoming more effective. Stress contributions from both phases were comparable. No martensitic transformation occurred. Strengthening and enhanced work hardening in both phases led to high strength at 200 K, with ductility similar to that at 293 K.
neutron diffraction during tensile testing at 293 K and 200 K was used to investigate stress partitioning and phase-specific deformation. Phase stress was calculated using a texture-compensated method. At both temperatures, ferrite showed higher phase stress than austenite, acting as the harder phase. At 200 K, both phases exhibited increased strength and work hardening. Austenite showed significant stacking fault formation alongside dislocation migration, while ferrite retained its dislocation-based deformation mode, becoming more effective. Stress contributions from both phases were comparable. No martensitic transformation occurred. Strengthening and enhanced work hardening in both phases led to high strength at 200 K, with ductility similar to that at 293 K.
Cao, T.*; Wei, D.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; 他10名*
Materials Science and Engineering A, 940, p.148534_1 - 148534_16, 2025/09
The thermal stability of microstructure and mechanical performance is crucial for the industrial application of laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) superalloy components in gas turbines and jet engines. This work investigated the microstructural evolution and strengthening mechanism of LPBF Mar-M509 cobalt-based superalloy before and after thermal exposure at 1200  C using multi-scale microstructural characterization and in situ neutron diffraction tensile testing. The as-built Mar-M509 superalloy exhibited a heterogeneous microstructural features with coarse columnar and fine equiaxed grains, both containing dendritic and cellular substructures enriched with nanoscale carbides and high-density dislocations. The ultra high strength of the as-built sample was primarily attributed to dislocation-precipitation synergistic strengthening. After thermal exposure at 1200
C using multi-scale microstructural characterization and in situ neutron diffraction tensile testing. The as-built Mar-M509 superalloy exhibited a heterogeneous microstructural features with coarse columnar and fine equiaxed grains, both containing dendritic and cellular substructures enriched with nanoscale carbides and high-density dislocations. The ultra high strength of the as-built sample was primarily attributed to dislocation-precipitation synergistic strengthening. After thermal exposure at 1200  C for 4 h, the dendritic and cellular substructures disappeared and the dislocation density decreased significantly. This study reveals the microstructural evolution and instability of LPBF Mar-M509 superalloy under high-temperature exposure and the impacts on mechanical properties, which provides critical support for the development of cobalt-based superalloys in high-temperature application fields.
C for 4 h, the dendritic and cellular substructures disappeared and the dislocation density decreased significantly. This study reveals the microstructural evolution and instability of LPBF Mar-M509 superalloy under high-temperature exposure and the impacts on mechanical properties, which provides critical support for the development of cobalt-based superalloys in high-temperature application fields.
Zheng, R.*; Gong, W.; 他6名*
Acta Materialia, 293, p.121098_1 - 121098_12, 2025/07
Hall-Petch law fails when grains smaller than a critical size, due to grain boundary (GB) kinetics-dominated plasticity. To enhance strength, improving GB stability is a consideration. However, this often requires a significant amount of alloying elements, posing resource challenges. Additionally, practical fabrication of extremely fine grains is still an issue. In our study, we firstly demonstrate a remarkable hardening-by-annealing phenomenon in magnesium (Mg) with relatively large grain sizes of 0.2-0.5  m, even with ultra-low yttrium (Y) addition. We reveal that annealing induces GB segregation/relaxation, effectively limiting the GB kinetics and promoting dislocation-dominated plasticity. Furthermore, the accompanying dislocation annihilation hinders deformation due to dislocation scarcity. As a result, we discovered extraordinary hardening in bulk ultrafine grained Mg-Y ultra-dilute alloy. This work offers a promising avenue for developing energy- and resource-efficient sustainable Mg alloys with superior mechanical properties.
m, even with ultra-low yttrium (Y) addition. We reveal that annealing induces GB segregation/relaxation, effectively limiting the GB kinetics and promoting dislocation-dominated plasticity. Furthermore, the accompanying dislocation annihilation hinders deformation due to dislocation scarcity. As a result, we discovered extraordinary hardening in bulk ultrafine grained Mg-Y ultra-dilute alloy. This work offers a promising avenue for developing energy- and resource-efficient sustainable Mg alloys with superior mechanical properties.
Johansen, M. P.*; Gwynn, J. P.*; Carpenter, J. G.*; Charmasson, S.*; 森 愛理; Orr, B.*; Simon-Cornu, M.*; Osvath, I.*; McGinnity, P.*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 287, p.107706_1 - 107706_8, 2025/07
被引用回数:0Radiological ingestion doses from eating seafood are regularly evaluated near coastal nuclear facilities, following accidents/events and frequently in national studies worldwide. However, a recent global review found that published seafood doses varied greatly depending on which radionuclides were selected for evaluation and that there has been a tendency to omit important radionuclides or focus on less significant ones. This indicates a need for clear guidance on which radionuclides to prioritise in such studies. Here, we use worldwide data for 16 key radionuclides contributing to typical background seafood ingestion dose. We account for the loss of radionuclides during cooking and the radioactive decay of the short-lived  Po. Results indicate that for the typical world consumer, naturally-occurring radionuclides account for
Po. Results indicate that for the typical world consumer, naturally-occurring radionuclides account for  99% of the total seafood ingestion dose, of which about 84% comes from
99% of the total seafood ingestion dose, of which about 84% comes from  Po and 8% from
Po and 8% from  Pb. About 5% comes from
Pb. About 5% comes from 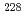 Ra, a far greater proportion than the more frequently-assessed
Ra, a far greater proportion than the more frequently-assessed  Ra (
Ra ( 1%). Other Th- and U-series radionuclides provide far lower contributions (0.07%-0.70%), while
1%). Other Th- and U-series radionuclides provide far lower contributions (0.07%-0.70%), while  C provides about 0.09%. In comparison, the contribution to total seafood ingestion dose from background anthropogenic radionuclides is
C provides about 0.09%. In comparison, the contribution to total seafood ingestion dose from background anthropogenic radionuclides is  1%, with
1%, with  Cs contributing most (0.08%) and
Cs contributing most (0.08%) and  Sr,
Sr,  Tc,
Tc, 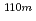 Ag and
Ag and  Pu adding a further 0.05% together. These percentage contributions to dose can vary somewhat depending on consumption patterns (e.g., differing proportions of fish, bivalves, etc.). However,
Pu adding a further 0.05% together. These percentage contributions to dose can vary somewhat depending on consumption patterns (e.g., differing proportions of fish, bivalves, etc.). However,  Po is the dominant contributor irrespective of country-specific diets or restricted diet scenarios (fish-only, seaweed-only, etc.). Study results provide new guidance to improve the design, interpretation and communication of seafood ingestion dose assessments.
Po is the dominant contributor irrespective of country-specific diets or restricted diet scenarios (fish-only, seaweed-only, etc.). Study results provide new guidance to improve the design, interpretation and communication of seafood ingestion dose assessments.
Gu, G. H.*; Jeong, S. G.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Cho, J.*; Kim, H. S.*; 他4名*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 223, p.308 - 324, 2025/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Face-centered cubic (FCC) equi-atomic multi-principal element alloys (MPEAs) exhibit excellent mechanical properties from cryogenic to room temperatures. At room temperature, deformation is dominated by dislocation slip, while at cryogenic temperatures (CTs), reduced stacking fault energy enhances strain hardening with twinning. This study uses in-situ neutron diffraction to analyze the temperature-dependent deformation behavior of Al (CoNiV)
(CoNiV)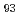 , a dual-phase (FCC/BCC) medium-entropy alloy (MEA). At liquid nitrogen temperature (LNT), deformation twinning in the FCC matrix leads to additional strain hardening through the dynamic Hall-Petch effect, giving the appearance of improved strengthening at LNT. In contrast, BCC precipitates show dislocation slip at both 77 K and 298 K, with temperature-dependent lattice friction stress playing a significant role in strengthening. The study enhances understanding of deformation behaviors and provides insights for future alloy design.
, a dual-phase (FCC/BCC) medium-entropy alloy (MEA). At liquid nitrogen temperature (LNT), deformation twinning in the FCC matrix leads to additional strain hardening through the dynamic Hall-Petch effect, giving the appearance of improved strengthening at LNT. In contrast, BCC precipitates show dislocation slip at both 77 K and 298 K, with temperature-dependent lattice friction stress playing a significant role in strengthening. The study enhances understanding of deformation behaviors and provides insights for future alloy design.
Hamdani, A.; 相馬 秀; 安部 諭; 柴本 泰照
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 185, p.105771_1 - 105771_13, 2025/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study, motivated by previous TEPSYS analysis, examined how different temperatures on the 4th and 5th floors of the Fukushima Daiichi Unit 3 reactor building (R/B) influenced non-condensable gas distribution during the 2011 severe accident. Understanding this is vital for assessing risks related to gas accumulation, especially since the hydrogen explosion may have involved multiple stages. An experimental study was conducted using the CIGMA facility, designed to mimic the R/B structure, where steam and helium (as a substitute for hydrogen) were injected for 10,000 seconds to simulate leakage. Two cooling conditions were tested: 50 C (Case 1) and 90
C (Case 1) and 90 C (Case 2). Results showed that the highest concentration of non-condensable gases was often found downstream rather than near the injection point. In Case 1, after 10,000 seconds, helium concentration reached 65% in the middle region (4th floor) and 45% in the top region (5th floor). Analysis indicated that the gas mixture in the middle region posed a potential detonation risk. This study offers crucial insights for enhancing safety measures and risk mitigation strategies in nuclear reactor designs.
C (Case 2). Results showed that the highest concentration of non-condensable gases was often found downstream rather than near the injection point. In Case 1, after 10,000 seconds, helium concentration reached 65% in the middle region (4th floor) and 45% in the top region (5th floor). Analysis indicated that the gas mixture in the middle region posed a potential detonation risk. This study offers crucial insights for enhancing safety measures and risk mitigation strategies in nuclear reactor designs.
Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Gao, S.*; 伊東 達矢; 山下 享介*; Harjo, S.; Zhao, L.*; Wang, Q.*
Scripta Materialia, 264, p.116726_1 - 116726_6, 2025/07
被引用回数:0An ultrafine-grained 304 austenitic stainless steel exhibited pronounced serrated Luders deformation at 20 K, with stress and temperature oscillations reaching 200 MPa and 20 K.  neutron diffraction and digital image correlation revealed discontinuous Luders band propagation and burst martensite formation. During deformation, austenite phase stress remained lower than at upper yielding, indicating elastic behavior. Notably, martensite phase stress stayed lower than austenite until fracture, likely due to stress relaxation from burst martensitic transformation at 20 K. The low martensite stress delayed brittle fracture until austenite plastically yielded during uniform deformation.
neutron diffraction and digital image correlation revealed discontinuous Luders band propagation and burst martensite formation. During deformation, austenite phase stress remained lower than at upper yielding, indicating elastic behavior. Notably, martensite phase stress stayed lower than austenite until fracture, likely due to stress relaxation from burst martensitic transformation at 20 K. The low martensite stress delayed brittle fracture until austenite plastically yielded during uniform deformation.
Lin, Z. M.*; Liu, B. X.*; Ming, K. S.*; 徐 平光; Yin, F. X.*; Zheng, S. J.*
Scripta Materialia, 263, p.116692_1 - 116692_7, 2025/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Complementary layer thickness effects on strength and plasticity in Q235 and SUS304 steels provide a novel strategy to realize high strength and high plasticity of heterogeneous Q235/SUS304 multilayered steel. In this work, the tensile deformation behaviors and fracture characteristics of vacuum hot-rolled Q235/SUS304 multilayered steel with various layer thicknesses ranging from 223  m to 5
m to 5  m were deeply investigated. The tensile strength improved with the reduction of layer thickness, and the uniform elongation were first increasing and then decreasing with the decrease of layer thickness, and the peak value appeared at the layer thickness of 20
m were deeply investigated. The tensile strength improved with the reduction of layer thickness, and the uniform elongation were first increasing and then decreasing with the decrease of layer thickness, and the peak value appeared at the layer thickness of 20  m. Interestingly, the fracture elongation forms a high plateau value within the 10
m. Interestingly, the fracture elongation forms a high plateau value within the 10 20
20  m range. Further analysis reveals that the severe strain localization in the brittle SUS304 thin layers is delayed by the ductile Q235 layers, which is mainly attributed to the different texture evolution and dislocation configuration characteristics during tensile deformation.
m range. Further analysis reveals that the severe strain localization in the brittle SUS304 thin layers is delayed by the ductile Q235 layers, which is mainly attributed to the different texture evolution and dislocation configuration characteristics during tensile deformation.
Park, M.-H.*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 292, p.121061_1 - 121061_13, 2025/06
被引用回数:1Dual-phase (DP) steel, composed of soft ferrite and hard martensite, offers excellent strength-ductility balance and low cost. This study found that refining the DP microstructure enhanced both yield strength and strain hardening, improving strength and ductility. Digital image correlation (DIC) revealed strain localization in ferrite, but refinement reduced strain differences between ferrite and martensite, suppressing crack initiation. More ferrite/martensite interfaces promoted plasticity in martensite via enhanced deformation constraint.  neutron diffraction showed martensite bore higher phase stress, which increased with refinement. By combining
neutron diffraction showed martensite bore higher phase stress, which increased with refinement. By combining  -DIC and neutron data, individual stress-strain curves for ferrite and martensite were constructed for the first time, explaining the strength-ductility synergy through interphase constraint. These findings offer guidance for designing heterostructured materials to overcome the strength-ductility trade-off.
-DIC and neutron data, individual stress-strain curves for ferrite and martensite were constructed for the first time, explaining the strength-ductility synergy through interphase constraint. These findings offer guidance for designing heterostructured materials to overcome the strength-ductility trade-off.
青山 高士; Choudhary, S.*; Pandaleon, A.*; Burns, J. T.*; Kokaly, M.*; Restis, J.*; Ross, J.*; Kelly, R. G.*
Corrosion, 81(6), p.609 - 621, 2025/06
This study presents a new test method for inducing controlled corrosion damage within simulated fastener holes of aluminum alloys, aimed at pretreating fatigue test specimens. The method involves insulating the outer surface while exposing the fastener hole surface to electrolytes containing 0.66 M NaCl + 0.1 M AlCl  with varying concentrations of K
with varying concentrations of K  S
S  O
O  . The evolution of corrosion damage within the fastener hole was examined as a function of exposure duration, electrolyte composition, and volume, as well as the effect of galvanic coupling with a SS316 cathode. Results indicate that fissure depth increases with an increase in K
. The evolution of corrosion damage within the fastener hole was examined as a function of exposure duration, electrolyte composition, and volume, as well as the effect of galvanic coupling with a SS316 cathode. Results indicate that fissure depth increases with an increase in K  S
S  O
O  concentration but does not progress further after 24-48 hours of exposure in the chemical, or freely-corroding, exposure test. In contrast, galvanic coupling with a SS316 plate significantly accelerates corrosion, leading to much deeper fissures in a shorter time. The importance of electrolyte replenishment has been explored using electrochemical measurements, revealing the impact of evolving electrolyte chemistry. Beyond its application in fatigue specimen pretreatment, this method provides a simple yet effective approach for studying localized corrosion and evaluating mitigation strategies for fastener holes in aerospace structures.
concentration but does not progress further after 24-48 hours of exposure in the chemical, or freely-corroding, exposure test. In contrast, galvanic coupling with a SS316 plate significantly accelerates corrosion, leading to much deeper fissures in a shorter time. The importance of electrolyte replenishment has been explored using electrochemical measurements, revealing the impact of evolving electrolyte chemistry. Beyond its application in fatigue specimen pretreatment, this method provides a simple yet effective approach for studying localized corrosion and evaluating mitigation strategies for fastener holes in aerospace structures.
Birkholzer, J. T.*; Graupner, B. J.*; Harrington, J.*; Jayne, R.*; Kolditz, O.*; Kuhlman, K. L.*; LaForce, T.*; Leone, R. C.*; Mariner, P. E.*; McDermott, C.*; et al.
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 42, p.100685_1 - 100685_17, 2025/06
The DECOVALEX initiative is an international research collaboration (www.decovalex.org), initiated in 1992, for advancing the understanding and modeling of coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical (THMC) processes in geological systems. DECOVALEX stands for "DEvelopment of COupled Models and VALidation against EXperiments". DECOVALEX emphasizes joint analysis and comparative modeling of the complex perturbations and coupled processes in geologic repositories and how these impact long-term performance predictions. More than fifty research teams associated with 17 international DECOVALEX partner organizations participated in the comparative evaluation of eight modeling tasks covering a wide range of spatial and temporal scales, geological formations, and coupled processes. This Virtual Special Issue on DECOVALEX-2023 provides an in-depth overview of these collaborative research efforts and how these have advanced the state-of-the-art of understanding and modeling coupled THMC processes. While primarily focused on radioactive waste, much of the work included here has wider application to many geoengineering topics.
 -nonyl N,N-dimethylammonio)-propyl sulfate, present in isotropic solutions above its upper critical solution temperature
-nonyl N,N-dimethylammonio)-propyl sulfate, present in isotropic solutions above its upper critical solution temperature丹治 珠緒*; 楠 裕翔*; 中川 太一; 高瀬 つぎ子*; 上田 祐生; 元川 竜平; Hinze, W. L.*; 高貝 慶隆*
Langmuir, 41(21), p.13184 - 13191, 2025/06
被引用回数:0The thermosensitive zwitterionic surfactant, C APSO
APSO , in solution displays a liquid-liquid miscibility gap exhibiting an upper critical solution temperature (UCST) in contrast to the lower critical temperature as is characteristic of nonionic surfactants. In this study, the micellar and aggregational properties of this surfactant in its homogeneous isotropic one phase region above the UCST was examined using surface tension and small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) measurements. The critical micelle concentration (CMC) of C
, in solution displays a liquid-liquid miscibility gap exhibiting an upper critical solution temperature (UCST) in contrast to the lower critical temperature as is characteristic of nonionic surfactants. In this study, the micellar and aggregational properties of this surfactant in its homogeneous isotropic one phase region above the UCST was examined using surface tension and small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) measurements. The critical micelle concentration (CMC) of C APSO
APSO was determined in both H
was determined in both H O and D
O and D O at 40 and 70
O at 40 and 70 C as well as the cloud point temperature determined over a surfactant concentration range of 0.05-0.70 M. The CMC values were in the range of 48-55 mM (40
C as well as the cloud point temperature determined over a surfactant concentration range of 0.05-0.70 M. The CMC values were in the range of 48-55 mM (40 C) and 61-65 mM (70
C) and 61-65 mM (70 C), respectively. The SANS data was analyzed using a core-shell model in which the C
C), respectively. The SANS data was analyzed using a core-shell model in which the C APSO
APSO is represented by a nonyl hydrophobic core and polar [(N,N-dimethylammonio)-propylsulfate] headgroup shell. Results revealed that the C
is represented by a nonyl hydrophobic core and polar [(N,N-dimethylammonio)-propylsulfate] headgroup shell. Results revealed that the C APSO
APSO micelle aggregates are spherical in shape with a core diameter of 2.56 nm and shell thickness of 2.28 nm and an aggregation number of 30 at 40
micelle aggregates are spherical in shape with a core diameter of 2.56 nm and shell thickness of 2.28 nm and an aggregation number of 30 at 40 C. The data at 70
C. The data at 70 C indicated that the aggregates were slightly larger in size, i.e., core diameter of 2.70 nm and shell thickness of 2.52 nm with an aggregation number of 35. At a fixed surfactant concentration, the aggregation number and size slightly decreased with a decrease in temperature from 70 to 40
C indicated that the aggregates were slightly larger in size, i.e., core diameter of 2.70 nm and shell thickness of 2.52 nm with an aggregation number of 35. At a fixed surfactant concentration, the aggregation number and size slightly decreased with a decrease in temperature from 70 to 40 C.
C.
 Co
Co )Sn studied by
)Sn studied by  SR
SRCai, Y.*; Yoon, S.*; Sheng, Q.*; Zhao, G.*; Seewald, E. F.*; Ghosh, S.*; Ingham, J.*; Pasupathy, A. N.*; Queiroz, R.*; Lei, H.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 111(21), p.214412_1 - 214412_17, 2025/06
We study the magnetic properties of the metallic kagome system (Fe Co
Co )Sn by a combination of muon spin relaxation (
)Sn by a combination of muon spin relaxation ( SR), magnetic susceptibility, and scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) measurements in single crystal specimens with Co concentrations
SR), magnetic susceptibility, and scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) measurements in single crystal specimens with Co concentrations  = 0, 0.11, 0.8. In the undoped antiferromagnetic compound FeSn, we find possible signatures for a previously unidentified phase that sets in at
= 0, 0.11, 0.8. In the undoped antiferromagnetic compound FeSn, we find possible signatures for a previously unidentified phase that sets in at 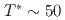 ~K, well beneath the Neel temperature
~K, well beneath the Neel temperature 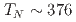 ~K as indicated by a peak in the relaxation rate 1/
~K as indicated by a peak in the relaxation rate 1/ observed in zero field (ZF) and longitudinal field (LF)
observed in zero field (ZF) and longitudinal field (LF)  SR measurements, with a corresponding anomaly in the ac and dc susceptibility, and an increase in the static width 1/
SR measurements, with a corresponding anomaly in the ac and dc susceptibility, and an increase in the static width 1/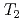 in ZF-
in ZF- SR measurements. No signatures of spatial symmetry breaking are found in STM down to 7~K. Related to the location and motion of muons in FeSn, we confirmed a previous report that about 40% of the implanted muons reside at a field-cancelling high symmetry site at
SR measurements. No signatures of spatial symmetry breaking are found in STM down to 7~K. Related to the location and motion of muons in FeSn, we confirmed a previous report that about 40% of the implanted muons reside at a field-cancelling high symmetry site at 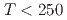 ~K, while an onset of thermal hopping changes the site occupancy at higher temperatures. In Fe
~K, while an onset of thermal hopping changes the site occupancy at higher temperatures. In Fe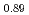 Co
Co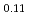 Sn, where disorder eliminated the field-cancellation effect, all the implanted muons exhibit precession and/or relaxation in the ordered state. In Fe
Sn, where disorder eliminated the field-cancellation effect, all the implanted muons exhibit precession and/or relaxation in the ordered state. In Fe Co
Co Sn, we find canonical spin glass behavior with freezing temperature
Sn, we find canonical spin glass behavior with freezing temperature 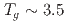 ~K; the ZF and LF-
~K; the ZF and LF- SR time spectra exhibit results similar to those observed in dilute alloy spin glasses CuMn and AuFe, with a critical behavior of
SR time spectra exhibit results similar to those observed in dilute alloy spin glasses CuMn and AuFe, with a critical behavior of  at
at 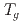 and
and 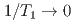 as
as 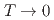 . The absence of spin dynamics at low temperatures makes a clear contrast to the spin dynamics observed by
. The absence of spin dynamics at low temperatures makes a clear contrast to the spin dynamics observed by  SR in many geometrically frustrated spin systems on insulating kagome, pyrochlore, and triangular lattices. The spin glass behavior of CoSn doped with dilute Fe moments is shown to originate primarily from the randomness of doped Fe moments rather than due to geometrical frustration of the underlying lattice.
SR in many geometrically frustrated spin systems on insulating kagome, pyrochlore, and triangular lattices. The spin glass behavior of CoSn doped with dilute Fe moments is shown to originate primarily from the randomness of doped Fe moments rather than due to geometrical frustration of the underlying lattice.
Shi, W.*; 町田 昌彦; 山田 進; 岡本 孝司
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 184, p.105710_1 - 105710_10, 2025/06
被引用回数:0最近、原子炉建屋内の少ない観測点で測定された空間線量値から放射線源分布を逆推定する方法としてLASSO(Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator)が提案された。しかし、空間線量値を測定する際には誤差が含まれるが、この誤差が逆推定結果の精度にどのように影響するかは解析されていなかった。そこで本論文では、LASSOに対する不確実性解析を行い、Candesの理論に基づく不確実性推定関数を提案した。実際に、モンテカルロ法の1つであるParticle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS)を使用して得られた不確実性を持つ数値を入力値として用いたテスト計算を実施し、計算結果の誤差が提案された推定関数に従うことを示した。これにより、LASSOは推定された不確実性の範囲内で放射線源分布を求めることができる方法であることが確認できた。
Hartzell, S.*; Furutani, K. M.*; Parisi, A.*; 佐藤 達彦; 加瀬 優紀*; Deglow, C.*; Friedrich, T.*; Beltran, C. J.*
Radiation (Internet), 5(2), p.21_1 - 21_24, 2025/06
Microdosimetry is essential in particle therapy for understanding the biological effects of treatments by quantifying energy depositions within microscopic volumes. The calculation of the microdosimetric distributions can be carried out with physical models such as the Kiefer-Chatterjee (KC) track structure function and the Sato analytical microdosimetric function (AMF). Comprehensive comparisons across these physical models are lacking. The AMF is calculated for spherical domains, while the KC is traditionally calculated for a cylindrical domain. This study introduces a novel version of the KC function for spherical domains, allowing a direct comparison with AMF. The influence of each function on the calculation of the relative biological effectiveness (RBE) in carbon ion radiotherapy (CIRT) was evaluated.
方野 量太; 阿部 拓海; Cibert, H.*
JAEA-Research 2024-019, 22 Pages, 2025/05
マイナーアクチノイドの核変換を目的とする加速器駆動システム(ADS)は未臨界状態で運転される。ADSの未臨界度管理においては、燃焼反応度の予測が重要であるが、予測精度の検証のためには、特に第一サイクル運転時では燃焼反応度を精度良く測定する必要がある。本検討では、燃焼反応度測定手法としてCurrent-To-Flux(CTF)法に着目し、連続エネルギーモンテカルロ計算コードSERPENT2を用いて固定源燃焼計算を実施し、炉内に配置する核分裂計数管を模したタリーを用いることで、CTF法によるADS通常運転時の燃焼反応度測定のシミュレーションを実施した。シミュレーション結果から測定手法起因の燃焼反応度測定不確かさの推定を行い、燃焼期間に依らず燃焼反応度に対して10%程度のバイアスが生じ、その検出器位置依存性が体系外側で小さいことを明らかにした。
Auh, Y. H.*; Neal, N. N.*; Arole, K.*; Regis, N. A.*; Nguyen, T.*; 小川 修一*; 津田 泰孝; 吉越 章隆; Radovic, M.*; Green, M. J.*; et al.
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 17(21), p.31392 - 31402, 2025/05
MXenes are a promising class of 2D nanomaterials and are of particular interest for gas barrier application. However, MXene nanosheets naturally bear a negative charge, which prevents assembly with negatively charged polymers, such as polyacrylic acid (PAA), into gas barrier coatings. Here, we present MXene- and PAA-based layer-by-layer (MXene/PAA LbL) multilayers formed by leveraging hydrogen bonding interactions. When assembled in acidic conditions, MXene/PAA LbL films exhibit conformal, pin-hole free, nacre-like structures. The MXene/PAA LbL films yield high blocking capability and low permeability (0.14 0.01 cc mm m
0.01 cc mm m day
day MPa
MPa ) for hydrogen gas. These nacre-like structures are also electronically conductive (up to 370
) for hydrogen gas. These nacre-like structures are also electronically conductive (up to 370 30 S cm
30 S cm ). Specifically, the reversible deconstruction of these films under basic conditions is experimentally verified. This study shows that hydrogen bonding interactions can be leveraged to form MXene LbL multilayers as gas barriers, electronically conducive coatings, and deconstructable thin films via pH control.
). Specifically, the reversible deconstruction of these films under basic conditions is experimentally verified. This study shows that hydrogen bonding interactions can be leveraged to form MXene LbL multilayers as gas barriers, electronically conducive coatings, and deconstructable thin films via pH control.