Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Jiang, X.*; 服部 高典; Xu, X.*; Li, M.*; Yu, C.*; Yu, D.*; Mole, R.*; 矢野 真一郎*; Chen, J.*; He, L.*; et al.
Materials Horizons, 10(3), p.977 - 982, 2023/03
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:88.89(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)現在の蒸気圧縮式冷凍機に代わる環境に優しい冷凍機として、バロカロリック効果に基づく固体冷凍機が世界的に注目されている。一般に、バロカロリック効果が発現する相はいずれも常圧でも存在する。ここでは、それらの物質と違って、KPF が高圧の菱面体晶相を生成することにより、巨大なバロカロリック効果を示すことを実証した。相図は、圧力依存の熱量測定、ラマン散乱測定、中性子回折測定に基づいて構築されたものである。本研究は、巨大バロカロリー効果に、高圧相の生成という新たな手法をもたらすと期待される。
が高圧の菱面体晶相を生成することにより、巨大なバロカロリック効果を示すことを実証した。相図は、圧力依存の熱量測定、ラマン散乱測定、中性子回折測定に基づいて構築されたものである。本研究は、巨大バロカロリー効果に、高圧相の生成という新たな手法をもたらすと期待される。
Wei, D.*; Gong, W.; 都留 智仁; Lobzenko, I.; Li, X.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Do, H.-S.*; Bae, J. W.*; Wagner, C.*; et al.
International Journal of Plasticity, 159, p.103443_1 - 103443_18, 2022/12
被引用回数:28 パーセンタイル:98.38(Engineering, Mechanical)Face-centered cubic single-phase high-entropy alloys (HEAs) containing multi-principal transition metals have attracted significant attention, exhibiting an unprecedented combination of strength and ductility owing to their low stacking fault energy (SFE) and large misfit parameter that creates severe local lattice distortion. Increasing both strength and ductility further is challenging. In the present study, we demonstrate via meticulous experiments that the CoCrFeNi HEA with the addition of the substitutional metalloid Si can retain a single-phase FCC structure while its yield strength (up to 65%), ultimate strength (up to 34%), and ductility (up to 15%) are simultaneously increased, owing to a synthetical effect of the enhanced solid solution strengthening and a reduced SFE. The dislocation behaviors and plastic deformation mechanisms were tuned by the addition of Si, which improves the strain hardening and tensile ductility. The present study provides new strategies for enhancing HEA performance by targeted metalloid additions.
Gatera, A.*; Belmans, J.*; Boussa, S.*; Davin, F.*; De Cock, W.*; De Florio, V.*; Doucet, F.*; Parez, L.*; Pompon, F.*; Ponton, A.*; et al.
Proceedings of 64th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High Intensity and High Brightness Hadron Beams (HB2021), p.186 - 190, 2022/04
The MYRRHA project at SCK CEN, Belgium, aims at coupling a 600 MeV proton accelerator to a subcritical fission core operating at a thermal power of 60 MW. The nominal proton beam for this ADS has an intensity of 4 mA and is delivered in a quasi-CW mode. MYRRHA's linac is designed to be fault tolerant thanks to redundancy implemented in parallel at low energy and serially in the superconducting linac. Phase 1 of the project, named MINERVA, will realise a 100 MeV, 4 mA superconducting linac with the mission of demonstrating the ADS requirements in terms of reliability and of fault tolerance. As part of the reliability optimisation program the integrated prototyping of the MINERVA injector is ongoing at SCK CEN in Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium. The injector test stand aims at testing sequentially all the elements composing the front-end of the injector. This contribution will highlight the beam dynamics choices in MINERVA's injector and their impact on ongoing commissioning activities.
Naeem, M.*; He, H.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Lin, W.*; Kai, J.-J.*; Wu, Z.*; Lan, S.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Acta Materialia, 221, p.117371_1 - 117371_18, 2021/12
被引用回数:31 パーセンタイル:94.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We studied the deformation behavior of CrFeCoNi high-entropy alloy by in situ neutron diffraction at room temperature, intermediate low temperature of 140 K, low temperatures of 40 K (no serrated deformation) and 25 K (with massive serrations). The contributions from different deformation mechanisms to the yield strength and strain hardening have been estimated. The athermal contributions to the yield strength were  183 MPa at all temperatures, while the Peierls stress increased significantly at low temperatures (from 148 MPa at room temperature to 493 MPa at 25 K). Dislocations contributed to
183 MPa at all temperatures, while the Peierls stress increased significantly at low temperatures (from 148 MPa at room temperature to 493 MPa at 25 K). Dislocations contributed to  94% strain hardening at room temperature. Although the dislocation strengthening remained the major hardening mechanism at very low temperatures, the planar faults contribution increased steadily from 6% at room temperature to 28% at 25 K.
94% strain hardening at room temperature. Although the dislocation strengthening remained the major hardening mechanism at very low temperatures, the planar faults contribution increased steadily from 6% at room temperature to 28% at 25 K.
 /La
/La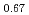 Sr
Sr MnO
MnO heterostructures
heterostructuresZhang, J.*; Chen, M.*; Chen, J.*; 山本 慧; Wang, H.*; Hamdi, M.*; Sun, Y.*; Wagner, K.*; He, W.*; Zhang, Y.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 12, p.7258_1 - 7258_8, 2021/12
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:78.56(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Magnons can transfer information in metals and insulators without Joule heating, and therefore are promising for low-power computation. The on-chip magnonics however suffers from high losses due to limited magnon decay length. In metallic thin films, it is typically on the tens of micrometre length scale. Here, we demonstrate an ultra-long magnon decay length of up to one millimetre in multiferroic/ferromagnetic BiFeO (BFO)/La
(BFO)/La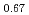 Sr
Sr MnO
MnO (LSMO) heterostructures at room temperature. This decay length is attributed to a magnon-phonon hybridization and is more than two orders of magnitude longer than that of bare metallic LSMO. The long-distance modes have high group velocities of 2.5 km
(LSMO) heterostructures at room temperature. This decay length is attributed to a magnon-phonon hybridization and is more than two orders of magnitude longer than that of bare metallic LSMO. The long-distance modes have high group velocities of 2.5 km as detected by time-resolved Brillouin light scattering. Numerical simulations suggest that magnetoelastic coupling via the BFO/LSMO interface hybridizes phonons in BFO with magnons in LSMO. Our results provide a solution to the long-standing issue on magnon decay lengths in metallic magnets and advance the bourgeoning field of hybrid magnonics.
as detected by time-resolved Brillouin light scattering. Numerical simulations suggest that magnetoelastic coupling via the BFO/LSMO interface hybridizes phonons in BFO with magnons in LSMO. Our results provide a solution to the long-standing issue on magnon decay lengths in metallic magnets and advance the bourgeoning field of hybrid magnonics.
Gatera, A.*; Belmans, J.*; Davin, F.*; De Cock, W.*; Doucet, F.*; Parez, L.*; Pompon, F.*; Ponton, A.*; Vandeplassche, D.*; Bouly, F.*; et al.
Proceedings of 12th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC 21) (Internet), p.675 - 678, 2021/08
The MYRRHA project aims at coupling a 600 MeV proton accelerator to a subcritical fission core operating at a thermal power of 70 MW. The nominal proton beam for this ADS (Accelerator Driven System) has an intensity of 4 mA and is delivered in a quasi-CW mode. Phase 1 of the project will realise a 100 MeV, 4 mA superconducting linac with the mission of ensuring the ADS requirements in terms of reliability and fault tolerance. As part of the reliability optimisation program the integrated prototyping of the MINERVA injector is ongoing. The front-end of the injector is composed of an ECR proton source, an LEBT (Low Energy Beam Transport line) and a four-rod RFQ accelerating the beam to 1.5 MeV. The present contribution focuses on the current beam tests on the RFQ, including beam matching, RF conditioning, assessment of the cavities' performances and accelerated beam characterisation.
He, H.*; Naeem, M.*; Zhang, F.*; Zhao, Y.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Wang, B.*; Wu, X.*; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; et al.
Nano Letters, 21(3), p.1419 - 1426, 2021/02
被引用回数:41 パーセンタイル:95.42(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)In CrCoNi, a so-called medium-entropy alloy, an fcc-to-hcp phase transformation has long been anticipated. Here, we report an in situ loading study with neutron diffraction, which revealed a bulk fcc-to-hcp phase transformation in CrCoNi at 15 K under tensile loading. By correlating deformation characteristics of the fcc phase with the development of the hcp phase, it is shown that the nucleation of the hcp phase was triggered by intrinsic stacking faults. The confirmation of a bulk phase transformation adds to the myriads of deformation mechanisms available in CrCoNi, which together underpin the unusually large ductility at low temperatures.
Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; 浅井 雅人; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; 浅井 雅人; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(6), p.064602_1 - 064602_9, 2020/12
被引用回数:45 パーセンタイル:98.14(Physics, Nuclear)原子番号119及び120を持つ超重元素の合成を目指した探索実験を、それぞれ Ti+
Ti+ Bk及び
Bk及び Ti+
Ti+ Cf核融合-粒子蒸発反応を用いて、ガス充填型反跳分離装置TASCAにて実施した。4ヶ月間におよぶビーム照射実験を行ったが、どちらの元素も検出されず、その生成断面積の上限値は65fb及び200fbであった。119, 120番元素が観測されなかった理由について、安定の島領域の超重元素の核分裂障壁の高さを予測する様々な理論計算値を用いて、核融合-粒子蒸発反応の概念を用いて議論した。
Cf核融合-粒子蒸発反応を用いて、ガス充填型反跳分離装置TASCAにて実施した。4ヶ月間におよぶビーム照射実験を行ったが、どちらの元素も検出されず、その生成断面積の上限値は65fb及び200fbであった。119, 120番元素が観測されなかった理由について、安定の島領域の超重元素の核分裂障壁の高さを予測する様々な理論計算値を用いて、核融合-粒子蒸発反応の概念を用いて議論した。
 particles triggered strong interaction with LaFeO
particles triggered strong interaction with LaFeO framework for total and preferential CO oxidation
framework for total and preferential CO oxidationZheng, Y.*; Xiao, H.*; Li, K.*; Wang, Y.*; Li, Y.*; Wei, Y.*; Zhu, X.*; Li, H.-W.*; 松村 大樹; Guo, B.*; et al.
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 12(37), p.42274 - 42284, 2020/09
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:74.29(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Interactions between the active components with the support are one of the fundamentally factors in determining the catalytic performance of a catalyst. In this study, we investigated the interaction between CeO and LaFeO
and LaFeO , the two important oxygen storage materials in catalysis area, by tuning the sizes of CeO
, the two important oxygen storage materials in catalysis area, by tuning the sizes of CeO particles and highlight a two-fold effect of the strong oxide-oxide interaction in determining the catalytic activity and selectivity for preferential CO oxidation in hydrogen feeds. It is found that the anchoring of ultra-fine CeO
particles and highlight a two-fold effect of the strong oxide-oxide interaction in determining the catalytic activity and selectivity for preferential CO oxidation in hydrogen feeds. It is found that the anchoring of ultra-fine CeO particles at the framework of three-dimensional-ordered macroporous LaFeO
particles at the framework of three-dimensional-ordered macroporous LaFeO surface results in a strong interaction between the two oxides that induces the formation of abundant uncoordinated cations and oxygen vacancy at the interface. This discovery demonstrates that in hybrid oxide-based catalysts, tuning the interaction among different components is essential for balancing the catalytic activity and selectivity.
surface results in a strong interaction between the two oxides that induces the formation of abundant uncoordinated cations and oxygen vacancy at the interface. This discovery demonstrates that in hybrid oxide-based catalysts, tuning the interaction among different components is essential for balancing the catalytic activity and selectivity.
Woo, W.*; Naeem, M.*; Jeong, J.-S.*; Lee, C.-M.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; He, H.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 781, p.139224_1 - 139224_7, 2020/04
被引用回数:39 パーセンタイル:93.25(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)To elucidate deformation behavior behind the exceptional mechanical properties of CrCoNi based medium entropy alloys, the deformation related microstructural parameters were determined by using in situ neutron diffraction and peaks profile analysis methods. Superior tensile strength and elongation of the CrCoNi alloy is relevant to higher twin fault probability (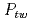 , up to 3.8%) and dislocation density (
, up to 3.8%) and dislocation density ( , up to 9.7
, up to 9.7  10
10 m
m ) compared to those (1.3% and 3.4
) compared to those (1.3% and 3.4  10
10 m
m , respectively) of the CrCoNiFe at 293K. Meanwhile, at 140K, the
, respectively) of the CrCoNiFe at 293K. Meanwhile, at 140K, the 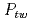 of the CrCoNiFe significantly increased up to 4.4% with the stable
of the CrCoNiFe significantly increased up to 4.4% with the stable  of
of  5.0
5.0  10
10 m
m and its mechanical properties overwhelm those of the CrCoNi at 273K. Such twinning dominant deformation mechanism at low temperature is also assured by lower stacking fault energy (SFE) of the CrCoNiFe at 140K compared to those of the CrCoNi and CrCoNiFe alloys at 293K.
and its mechanical properties overwhelm those of the CrCoNi at 273K. Such twinning dominant deformation mechanism at low temperature is also assured by lower stacking fault energy (SFE) of the CrCoNiFe at 140K compared to those of the CrCoNi and CrCoNiFe alloys at 293K.
Al-Shayeb, B.*; Sachdeva, R.*; Chen, L.-X.*; Ward, F.*; Munk, P.*; Devoto, A.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Olm, M. R.*; Bouma-Gregson, K.*; 天野 由記; et al.
Nature, 578(7795), p.425 - 431, 2020/02
被引用回数:223 パーセンタイル:99.47(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Phage typically have small genomes and depend on their bacterial hosts for replication. We generated metagenomic datasets from many diverse ecosystems and reconstructed hundreds of huge phage genomes, between 200 kbp and 716 kbp in length. Thirty four genomes were manually curated to completion, including the largest phage genomes yet reported. Expanded genetic repertoires include diverse and new CRISPR-Cas systems, tRNAs, tRNA synthetases, tRNA modification enzymes, initiation and elongation factors and ribosomal proteins. Phage CRISPR have the capacity to silence host transcription factors and translational genes, potentially as part of a larger interaction network that intercepts translation to redirect biosynthesis to phage-encoded functions. Some phage repurpose bacterial systems for phage-defense to eliminate competing phage. We phylogenetically define seven major clades of huge phage from human and other animal microbiomes, oceans, lakes, sediments, soils and the built environment. We conclude that large gene inventories reflect a conserved biological strategy, observed across a broad bacterial host range and resulting in the distribution of huge phage across Earth's ecosystems.
 -ray spectrum in
-ray spectrum in  U(
U( )
)牧井 宏之; 西尾 勝久; 廣瀬 健太郎; Orlandi, R.; L guillon, R.; 小川 達彦; Soldner, T.*; K
guillon, R.; 小川 達彦; Soldner, T.*; K ster, U.*; Pollitt, A.*; Hambsch, F.-J.*; et al.
ster, U.*; Pollitt, A.*; Hambsch, F.-J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 100(4), p.044610_1 - 044610_7, 2019/10
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:73.85(Physics, Nuclear)The prompt fission  -ray energy spectrum for cold-neutron induced fission of
-ray energy spectrum for cold-neutron induced fission of  U was measured in the energy range
U was measured in the energy range 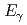 = 0.8 - 20,MeV, by gaining a factor of about 10
= 0.8 - 20,MeV, by gaining a factor of about 10 in statistics compared to the measurements performed so far. The spectrum exhibits local bump structures at
in statistics compared to the measurements performed so far. The spectrum exhibits local bump structures at 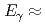 4,MeV and
4,MeV and  6,MeV, and also a broad one at
6,MeV, and also a broad one at  15,MeV. In order to understand the origins of these bumps, the
15,MeV. In order to understand the origins of these bumps, the  -ray spectra were calculated using a statistical Hauser-Feshbach model, taking into account the de-excitation of all the possible primary fission fragments. It is shown that the bump at
-ray spectra were calculated using a statistical Hauser-Feshbach model, taking into account the de-excitation of all the possible primary fission fragments. It is shown that the bump at  4,MeV is created by the transitions between the discrete levels in the fragments around
4,MeV is created by the transitions between the discrete levels in the fragments around  Sn, and the bump at
Sn, and the bump at  6,MeV mostly comes from the complementary light fragments. It is also indicated that a limited number of nuclides, which have high-spin states at low excitation energies, can contribute to the bump structure around
6,MeV mostly comes from the complementary light fragments. It is also indicated that a limited number of nuclides, which have high-spin states at low excitation energies, can contribute to the bump structure around 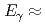 15,MeV, induced by the transition feeding into the low-lying high-spin states.
15,MeV, induced by the transition feeding into the low-lying high-spin states.
 Ca+
Ca+ Bk leading to formation of the element Ts (Z=117)
Bk leading to formation of the element Ts (Z=117)Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; 浅井 雅人; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; 浅井 雅人; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(5), p.054306_1 - 054306_16, 2019/05
被引用回数:24 パーセンタイル:90.61(Physics, Nuclear) Ca+
Ca+ B融合反応を用いて117番元素(Ts)合成実験を行い、117番元素に起因すると思われる4つの
B融合反応を用いて117番元素(Ts)合成実験を行い、117番元素に起因すると思われる4つの 崩壊連鎖を観測した。うち2つは長い崩壊連鎖で、
崩壊連鎖を観測した。うち2つは長い崩壊連鎖で、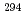 Tsの
Tsの 崩壊に起因するものと同定された。他の2つは短い崩壊連鎖で、
崩壊に起因するものと同定された。他の2つは短い崩壊連鎖で、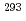 Tsの
Tsの 崩壊に起因すると考えると矛盾しない。今回の結果と過去の文献値を比較したところ、今回の我々の結果は過去の文献値をほぼ再現し、117番元素合成の事実を強く再確認する結果となった。
崩壊に起因すると考えると矛盾しない。今回の結果と過去の文献値を比較したところ、今回の我々の結果は過去の文献値をほぼ再現し、117番元素合成の事実を強く再確認する結果となった。
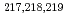 At revealed by in-source laser spectroscopy
At revealed by in-source laser spectroscopyBarzakh, A. E.*; Cubiss, J. G.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Seliverstov, M. D.*; Andel, B.*; Antalic, S.*; Ascher, P.*; Atanasov, D.*; Beck, D.*; Biero , J.*; et al.
, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(5), p.054317_1 - 054317_9, 2019/05
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:76.6(Physics, Nuclear)Hyperfine-structure parameters and isotope shifts for the 795-nm atomic transitions in 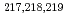 At have been measured at CERN-ISOLDE, using the in-source resonance-ionization spectroscopy technique. Magnetic dipole and electric quadrupole moments, and changes in the nuclear mean-square charge radii, have been deduced. A large inverse odd-even staggering in radii, which may be associated with the presence of octupole collectivity, has been observed. Namely, the radius of the odd-odd isotope
At have been measured at CERN-ISOLDE, using the in-source resonance-ionization spectroscopy technique. Magnetic dipole and electric quadrupole moments, and changes in the nuclear mean-square charge radii, have been deduced. A large inverse odd-even staggering in radii, which may be associated with the presence of octupole collectivity, has been observed. Namely, the radius of the odd-odd isotope 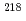 At has been found to be larger than the average.
At has been found to be larger than the average.
 Ge
Ge
Wo, H.*; Wang, Q.*; Shen, Y.*; Zhang, X.*; Hao, Y.*; Feng, Y.*; Shen, S.*; He, Z.*; Pan, B.*; Wang, W.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 122(21), p.217003_1 - 217003_5, 2019/05
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:42.22(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report neutron scattering measurements of single-crystalline YFe Ge
Ge in the normal state, which has the same crystal structure as the 122 family of iron pnictide superconductors. YFe
in the normal state, which has the same crystal structure as the 122 family of iron pnictide superconductors. YFe Ge
Ge does not exhibit long-range magnetic order but exhibits strong spin fluctuations. Like the iron pnictides, YFe
does not exhibit long-range magnetic order but exhibits strong spin fluctuations. Like the iron pnictides, YFe Ge
Ge displays anisotropic stripe-type antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations at (
displays anisotropic stripe-type antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations at (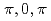 ). More interesting, however, is the observation of strong spin fluctuations at the in-plane ferromagnetic wave vector (
). More interesting, however, is the observation of strong spin fluctuations at the in-plane ferromagnetic wave vector (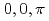 ). These ferromagnetic spin fluctuations are isotropic in the (
). These ferromagnetic spin fluctuations are isotropic in the (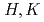 ) plane, whose intensity exceeds that of stripe spin fluctuations. Both the ferromagnetic and stripe spin fluctuations remain gapless down to the lowest measured energies. Our results naturally explain the absence of magnetic order in YFe
) plane, whose intensity exceeds that of stripe spin fluctuations. Both the ferromagnetic and stripe spin fluctuations remain gapless down to the lowest measured energies. Our results naturally explain the absence of magnetic order in YFe Ge
Ge and also imply that the ferromagnetic correlations may be a key ingredient for iron-based materials.
and also imply that the ferromagnetic correlations may be a key ingredient for iron-based materials.
 Sr
Sr )
) Rh
Rh Sn
Sn from a lattice dynamics study
from a lattice dynamics studyCheung, Y. W.*; Hu, Y. J.*; 今井 正樹*; 谷奥 泰明*; 金川 響*; 村川 譲一*; 森山 広大*; Zhang, W.*; Lai, K. T.*; 吉村 一良*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(16), p.161103_1 - 161103_5, 2018/10
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:66.85(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Approaching a quantum critical point has been an effective route to stabilize superconductivity. While the role of magnetic QCPs has been extensively discussed, similar exploration of a structural QCP is scarce. Using inelastic X-ray scattering, we examine the phonon spectrum of the nonmagnetic quasi-skutterudite (Ca Sr
Sr )
) Rh
Rh Sn
Sn , which represents a precious system to explore the interplay between structural instabilities and superconductivity by tuning the Ca concentration x. We unambiguously detect the softening of phonon modes around the M point on cooling towards the structural transition. Intriguingly, at x = 0:85, the soft mode energy squared at the M point extrapolates to zero at -5.7 K, providing the first compelling microscopic evidence of a structural QCP in (Ca
, which represents a precious system to explore the interplay between structural instabilities and superconductivity by tuning the Ca concentration x. We unambiguously detect the softening of phonon modes around the M point on cooling towards the structural transition. Intriguingly, at x = 0:85, the soft mode energy squared at the M point extrapolates to zero at -5.7 K, providing the first compelling microscopic evidence of a structural QCP in (Ca Sr
Sr )
) Rh
Rh Sn
Sn . The enhanced phonon density-of-states at low energy provides the essential ingredient for realizing strong-coupling superconductivity near the structural QCP.
. The enhanced phonon density-of-states at low energy provides the essential ingredient for realizing strong-coupling superconductivity near the structural QCP.
 -spectroscopy at an intense cold neutron beam facility
-spectroscopy at an intense cold neutron beam facilityJentschel, M.*; Blanc, A.*; de France, G.*; K ster, U.*; Leoni, S.*; Mutti, P.*; Simpson, G.*; Soldner, T.*; Ur, C.*; Urban, W.*; et al.
ster, U.*; Leoni, S.*; Mutti, P.*; Simpson, G.*; Soldner, T.*; Ur, C.*; Urban, W.*; et al.
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 12(11), p.P11003_1 - P11003_33, 2017/11
被引用回数:38 パーセンタイル:85.29(Instruments & Instrumentation)A highly efficient array of high-purity germanium (HPGe) detectors was developed and operated at the cold neutron beam facility PF1B of the Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL) to carry out nuclear structure studies, via measurements of  -rays following neutron-induced capture and fission reactions. The setup consisted of a collimation system producing a pencil beam with a thermal capture equivalent flux of about 10
-rays following neutron-induced capture and fission reactions. The setup consisted of a collimation system producing a pencil beam with a thermal capture equivalent flux of about 10 ns
ns cm
cm at the target position and negligible neutron halo. The target was surrounded by an array of eight to ten anti-Compton shielded EXOGAM Clover detectors, four to six anti-Compton shielded large coaxial GASP detectors and two standard Clover detectors. For a part of the campaign the array was combined with 16 LaBr
at the target position and negligible neutron halo. The target was surrounded by an array of eight to ten anti-Compton shielded EXOGAM Clover detectors, four to six anti-Compton shielded large coaxial GASP detectors and two standard Clover detectors. For a part of the campaign the array was combined with 16 LaBr :(Ce) detectors from the FATIMA collaboration.
:(Ce) detectors from the FATIMA collaboration.
 Sr
Sr )
) Rh
Rh Sn
Sn
Cheung, Y. W.*; Hu, Y. J.*; Goh, S. K.*; 金子 耕士; 筒井 智嗣; Logg, P. W.*; Grosche, F. M.*; 金川 響*; 谷奥 泰明*; 今井 正樹*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 807(3), p.032002_1 - 032002_4, 2017/04
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:83.41(Physics, Condensed Matter)(Ca Sr
Sr )
) Rh
Rh Sn
Sn is a member of the substitution series (Ca
is a member of the substitution series (Ca Sr
Sr )
) Rh
Rh Sn
Sn which has recently been argued to feature a structural quantum critical point at
which has recently been argued to feature a structural quantum critical point at 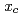 = 0.9. In the stoichiometric compound Sr
= 0.9. In the stoichiometric compound Sr Rh
Rh Sn
Sn , the structural transition at
, the structural transition at 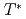
 138 K has been shown to be a second-order phase transition. Moving towards xc, we examine the character of the structural transition in (Ca
138 K has been shown to be a second-order phase transition. Moving towards xc, we examine the character of the structural transition in (Ca Sr
Sr )
) Rh
Rh Sn
Sn (i.e.
(i.e.  = 0.5,
= 0.5, 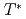
 55 K) using electrical resistivity, heat capacity and X-ray scattering. The absence of the thermal hysteresis in specific heat around
55 K) using electrical resistivity, heat capacity and X-ray scattering. The absence of the thermal hysteresis in specific heat around 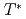 , and the continuous evolution of the superlattice reflection detected by X-ray diffraction are consistent with the scenario that the structural transition associated with a modulation vector
, and the continuous evolution of the superlattice reflection detected by X-ray diffraction are consistent with the scenario that the structural transition associated with a modulation vector  = (0.5, 0.5, 0) in (Ca
= (0.5, 0.5, 0) in (Ca Sr
Sr )
) Rh
Rh Sn
Sn remains second-order on approaching the quantum critical point.
remains second-order on approaching the quantum critical point.
 -fission and recoil-
-fission and recoil- -
- -fission events observed in the reaction
-fission events observed in the reaction  Ca +
Ca +  Am
AmForsberg, U.*; Rudolph, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; Di Nitto, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Fahlander, C.*; Gates, J. M.*; Golubev, P.*; Gregorich, K. E.*; Gross, C. J.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Fahlander, C.*; Gates, J. M.*; Golubev, P.*; Gregorich, K. E.*; Gross, C. J.*; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 953, p.117 - 138, 2016/09
被引用回数:46 パーセンタイル:94.44(Physics, Nuclear) Ca +
Ca +  Am反応による115番元素合成実験で観測された
Am反応による115番元素合成実験で観測された 崩壊連鎖について、最近我々が報告したドイツGSIで測定したデータと過去に報告されたロシアDubna及び米国LBNLで測定されたデータのすべてを使い、その起源を調査した。それらのデータの中に、反跳核-
崩壊連鎖について、最近我々が報告したドイツGSIで測定したデータと過去に報告されたロシアDubna及び米国LBNLで測定されたデータのすべてを使い、その起源を調査した。それらのデータの中に、反跳核- -(
-( )-核分裂タイプの短い崩壊連鎖が14事象観測されており、そのうちのいくつかは中性子が2個放出されてできる
)-核分裂タイプの短い崩壊連鎖が14事象観測されており、そのうちのいくつかは中性子が2個放出されてできる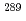 Mc起源であるとこれまで解釈されてきた。一方、今回我々は、これらの短い崩壊連鎖のほとんどが、中性子が3個放出されてできる
Mc起源であるとこれまで解釈されてきた。一方、今回我々は、これらの短い崩壊連鎖のほとんどが、中性子が3個放出されてできる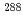 Mc起源であり、崩壊連鎖の途中でEC崩壊して核分裂したものであろうと再同定した。
Mc起源であり、崩壊連鎖の途中でEC崩壊して核分裂したものであろうと再同定した。
 -delayed fission and
-delayed fission and  decay of
decay of 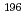 At
AtTruesdale, V. L.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ghys, L.*; Huyse, M.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Sels, S.*; Andel, B.*; Antalic, S.*; Barzakh, A.*; Capponi, L.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 94(3), p.034308_1 - 034308_11, 2016/09
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:60.15(Physics, Nuclear)A nuclear-decay spectroscopy study of the neutron-deficient isotope 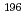 At is reported where an isotopically pure beam was produced using the selective Resonance Ionization Laser Ion Source and On-Line Isotope Mass Separator (CERN). The fine-structure
At is reported where an isotopically pure beam was produced using the selective Resonance Ionization Laser Ion Source and On-Line Isotope Mass Separator (CERN). The fine-structure  decay of
decay of 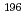 At allowed the low-energy excited states in the daughter nucleus
At allowed the low-energy excited states in the daughter nucleus 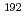 Bi to be investigated. A
Bi to be investigated. A  -delayed fission study of
-delayed fission study of 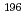 At was also performed. A mixture of symmetric and asymmetric fission-fragment mass distributions of the daughter isotope
At was also performed. A mixture of symmetric and asymmetric fission-fragment mass distributions of the daughter isotope 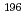 Po (populated by
Po (populated by  decay of
decay of 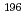 At) was deduced based on the measured fission-fragment energies. A
At) was deduced based on the measured fission-fragment energies. A  DF probability
DF probability 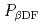 (
(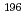 At) = 9(1)
At) = 9(1) 10
10 was determined.
was determined.