Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mohamad, A. B.; Chen, J.*; 井岡 郁夫*; 鈴木 恵理子; 近藤 啓悦; 阿部 陽介; 山下 真一郎; 大久保 成彰; 根本 義之; 岡田 裕史*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 625, p.156513_1 - 156513_9, 2026/04
被引用回数:0Ion irradiation was carried out on Cr coating Zry cladding to investigate their microstructure evolution and mechanical properties. The sample was irradiated at reactor normal operation conditions. Microstructural observation and mechanical testing of non-irradiated samples and irradiated samples were performed to understand irradiation damage to the Cr-coated Zry cladding. Results of High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy and chemical analysis revealed Fe enrichment at the Cr coating and Zr substrate interface of irradiated samples due to irradiation enhanced diffusion or irradiation induced mixing. Irradiation led to the formation of Fe enrichment at the Cr Zr interface approximately 15nm. Moreover, hardening of the Cr coating and Zr substrate regions was observed in the irradiated sample.
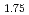 Zn
Zn Mo
Mo O
O
Bao, S.*; Liao, J.*; Huang, Z.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Ma, Z.*; Zhang, B.*; Cheng, S.*; Xu, H.*; Song, Z.*; Dong, S.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 136(9), p.096502_1 - 096502_8, 2026/03
Lattice vibrations can carry angular momentum and magnetic moments under broken inversion or time-reversal symmetry, forming so-called chiral phonons. While such excitations have been explored in nonmagnetic systems via optical probes, their direct detection in magnetic materials and coupling to spin excitations remain largely unexplored. Here, using neutron spectroscopy, sensitive to both nuclear and magnetic scattering, we reveal the magnetic signature of chiral phonons in ferrimagnetic Fe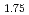 Zn
Zn Mo
Mo O
O with Curie temperature
with Curie temperature 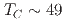 K. Below
K. Below 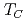 , we observe enhanced magnetic scattering of phonons at small momenta, arising from strong magnon-phonon coupling. In addition, out-of-plane intensity modulation, phonon mode splitting, and field-induced Zeeman shifts are observed, all closely associated with the ferrimagnetic order. These features vanish above
, we observe enhanced magnetic scattering of phonons at small momenta, arising from strong magnon-phonon coupling. In addition, out-of-plane intensity modulation, phonon mode splitting, and field-induced Zeeman shifts are observed, all closely associated with the ferrimagnetic order. These features vanish above 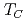 , where phonon spectra are dominated by nuclear scattering. These observations demonstrate the existence of chiral phonons carrying substantial magnetic moments that directly contribute to magnetic scattering, and establish neutron spectroscopy as a powerful, momentum-resolved probe of their magnetic character.
, where phonon spectra are dominated by nuclear scattering. These observations demonstrate the existence of chiral phonons carrying substantial magnetic moments that directly contribute to magnetic scattering, and establish neutron spectroscopy as a powerful, momentum-resolved probe of their magnetic character.
 -decay strength of
-decay strength of  V
VDahl, J. K.*; Larsen, A. C.*; 清水 則孝*; 宇都野 穣
Physical Review C, 113(2), p.024328_1 - 024328_16, 2026/02
 Vに対する核準位密度とガンマ線強度関数を、
Vに対する核準位密度とガンマ線強度関数を、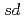 -
-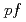 -
-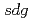 殻をバレンス殻にとった大規模殻模型計算によって調べた。オスロ法による実験データを全体的によく説明し、特に、低エネルギーの
殻をバレンス殻にとった大規模殻模型計算によって調べた。オスロ法による実験データを全体的によく説明し、特に、低エネルギーの 遷移の強度が増大するという特徴を再現することに成功した。そのメカニズムを解明するために、
遷移の強度が増大するという特徴を再現することに成功した。そのメカニズムを解明するために、 遷移の行列要素を軌道角運動量部分とスピン角運動量部分に分け、その干渉項の符号の分布を調べた。その結果、低エネルギーガンマ崩壊に対しては、正の干渉が主であるという新しい知見が得られた。
遷移の行列要素を軌道角運動量部分とスピン角運動量部分に分け、その干渉項の符号の分布を調べた。その結果、低エネルギーガンマ崩壊に対しては、正の干渉が主であるという新しい知見が得られた。
Chen, J.*; 山本 慧; 他13名*
Physical Review Letters, 136(5), p.056702_1 - 056702_8, 2026/02
被引用回数:0The recently developed van der Waals magnets provide a promising platform for spintronics and magnonics. Here, we report the observation of surface magnon propagation in the van der Waals antiferromagnet CrSBr. We find a nearly unidirectional propagation of antiferromagnetic magnon modes, which emerge near the anticrossing of the optical and acoustic magnon bands, in agreement with our theory of magnetostatic waves in antiferromagnets. The propagation direction can be reversed by switching the magnetic field. The observed antiferromagnetic magnons operate in the gigahertz regime due to the weak interlayer exchange coupling. Our results open the pathway for nonreciprocal magnonic applications based on van der Waals antiferromagnets at easily-accessible microwave frequencies.
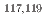 Rh
RhZhang, J. Z.*; Chen, Z. Q.*; Qu, T.*; Wang, Y. K.*; Li, Z. H.*; Orlandi, R.; 他62名*
Physics Letters B, 873, p.140144_1 - 140144_9, 2026/02
被引用回数:0At the RIKEN,  -delayed
-delayed  -ray spectroscopy studies were conducted on
-ray spectroscopy studies were conducted on 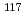 Rh and
Rh and 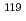 Rh, resulting in the world's first successful identification of a 1/2
Rh, resulting in the world's first successful identification of a 1/2 isomer in these isotope, extending the energy difference between the 9/2
isomer in these isotope, extending the energy difference between the 9/2 and 1/2
and 1/2 states up to neutron number
states up to neutron number  =74. Comparison of the new results with state-of-the-art calculations suggests that triaxial deformation plays a significant role in the evolution of the energy difference, indicating a shape transition from axially symmetric to triaxial deformation within the Rh isotopic series. These findings provide new insights into the structure of neutron-rich nuclei in the atomic number
=74. Comparison of the new results with state-of-the-art calculations suggests that triaxial deformation plays a significant role in the evolution of the energy difference, indicating a shape transition from axially symmetric to triaxial deformation within the Rh isotopic series. These findings provide new insights into the structure of neutron-rich nuclei in the atomic number  region, elucidating the interplay between triaxial deformation and shell evolution.
region, elucidating the interplay between triaxial deformation and shell evolution.
Ji, Y.-Y.*; Ji, W.*; Kim, K.*; Kim, M. J.*; 越智 康太郎; 森下 祐樹; 眞田 幸尚
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 244, p.113781_1 - 113781_12, 2026/02
UAVによる空中 線スペクトロメトリは迅速な放射線マッピングを可能にするが、飛行高度による減衰、視野効果、汚染の不均一性、地形条件により地上線量率の定量評価は難しい。本研究では福島第一原子力発電所周辺でホバリング飛行による校正と地上測定を組み合わせた実用的手法を開発した。二重指数モデルで高度補正係数を導出し、三脚およびバックパック測定と比較した結果、不均一サイトでの補正は系統誤差を生むが、均一サイトでの校正により一致が改善された。適切な補正を用いれば、UAV空中測定は信頼できる線量率分布評価が可能である。
線スペクトロメトリは迅速な放射線マッピングを可能にするが、飛行高度による減衰、視野効果、汚染の不均一性、地形条件により地上線量率の定量評価は難しい。本研究では福島第一原子力発電所周辺でホバリング飛行による校正と地上測定を組み合わせた実用的手法を開発した。二重指数モデルで高度補正係数を導出し、三脚およびバックパック測定と比較した結果、不均一サイトでの補正は系統誤差を生むが、均一サイトでの校正により一致が改善された。適切な補正を用いれば、UAV空中測定は信頼できる線量率分布評価が可能である。
Guembou Shouop, C. J.; 土屋 晴文
Communications Engineering (Internet), 5, p.11_1 - 11_14, 2026/01
Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) is a powerful non-destructive assay for material characterisation, traditionally requiring large, fixed and costly facilities. Here, we present a compact NRTA system utilising a small  Cf spontaneous neutron source to analyse nuclear materials, offering a mobile and cost-effective alternative to accelerator, D-T, or laser-driven neutron sources. The pilot design, with a total size of 130 cm
Cf spontaneous neutron source to analyse nuclear materials, offering a mobile and cost-effective alternative to accelerator, D-T, or laser-driven neutron sources. The pilot design, with a total size of 130 cm 50 cm
50 cm 50 cm, has an unprecedentedly short flight path of 42 cm, enabling time-of-flight measurements on nuclear material samples. The system's performance is demonstrated through NRTA measurements of simulated samples, including indium, hafnium, and cadmium metal plates. The resulting transmission spectra allow accurate isotope identification below 5 eV. These results underscore the system's potential for enhancing nuclear security, safeguards, and nonproliferation, particularly in scenarios where mobility, rapid deployment, and flexibility are critical. This work is supported by the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like."
50 cm, has an unprecedentedly short flight path of 42 cm, enabling time-of-flight measurements on nuclear material samples. The system's performance is demonstrated through NRTA measurements of simulated samples, including indium, hafnium, and cadmium metal plates. The resulting transmission spectra allow accurate isotope identification below 5 eV. These results underscore the system's potential for enhancing nuclear security, safeguards, and nonproliferation, particularly in scenarios where mobility, rapid deployment, and flexibility are critical. This work is supported by the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like."
五十嵐 淳哉*; 二宮 和彦*; Zheng, J.*; Zhang, Z.*; 福田 美保*; 青野 辰雄*; 箕輪 はるか*; 吉川 英樹*; 末木 啓介*; 佐藤 志彦; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 291, p.107856_1 - 107856_8, 2026/01
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)福島第一原子力発電所(FDNPP)事故に由来する放射性粒子中のプルトニウム同位体比を、サンプル数を増やして高精度に測定し、FDNPP由来Puの指紋として利用可能な代表値を提示した。Pu同位体の原子比は放出源ごとに固有であり、Pu起源推定に有用である。FDNPP事故由来Puについては、事故時に炉内で形成された放射性粒子を対象とすることで全球的フォールアウトの影響を受けにくい評価が可能だが、既報は解析粒子数が少なく原子比推定の不確かさが大きかった。SF-ICP-MSにより7粒子を分析した結果、 Pu/
Pu/ Pu=0.369
Pu=0.369 0.008、
0.008、 Pu/
Pu/ Pu=0.150
Pu=0.150 0.007(原子比)を得た。これらの値は炉心インベントリ計算や周辺環境試料で報告される比と概ね整合し、今後のPu起源推定や環境影響評価の参照指標として有用である。
0.007(原子比)を得た。これらの値は炉心インベントリ計算や周辺環境試料で報告される比と概ね整合し、今後のPu起源推定や環境影響評価の参照指標として有用である。
Su, Y. H.; 篠原 武尚; Parker, J. D.*; 及川 健一; 甲斐 哲也; Gong, W.; 伊東 達矢; Harjo, S.; 相澤 一也; 鬼柳 善明*; et al.
Materials Science & Engineering A, 951, p.149607_1 - 149607_16, 2026/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Local variations in residual stress/strain and microstructure during fatigue crack growth in compact tension specimens of SUS304 austenitic stainless steel were investigated using complementary methods: pulsed neutron Bragg-edge imaging (NBEI), neutron diffraction (ND), digital image correlation (DIC) and electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD). Surface strain fields were evaluated using DIC and EBSD. NBEI provided two-dimensional averaged microstructure information, whereas ND yielded detailed three-dimensional distributions of residual lattice (elastic) strain and stress. This study particularly focused on how NBEI is helpful in understanding overall damage characteristics in the vicinity of a crack tip two-dimensionally. Distribution of microstructural parameters associated with crack growth, such as lattice constant, crystallite size, and texture, across the entire specimen was considered using Bragg-edge spectral analysis. The plastic zone in front of the crack tip, characterized by reduced crystallite size, was observed during crack propagation. After final fracture, two distinct zones with reduced crystallite size were identified: one caused by localized plastic deformation near the crack tip, and the other by bending at the back end of the specimen. This paper introduces the four experimental techniques and describes their respective features. Each method has its own advantages and limitations; However, by integrating their results, a more comprehensive understanding of the overall stress/strain field can be achieved.
Villagrasa, C.*; Baiocco, G.*; Chaoui, Z.-E.-A.*; Dingfelder, M.*; Incerti, S.*; Kundr t, P.*; Kyriakou, I.*; 松谷 悠佑; 甲斐 健師; Parisi, A.*; et al.
t, P.*; Kyriakou, I.*; 松谷 悠佑; 甲斐 健師; Parisi, A.*; et al.
PLOS ONE (Internet), 21(1), p.e0340500_1 - e0340500_22, 2026/01
被引用回数:0電離放射線被ばくの生物学的影響を理解するために重要なナノ線量測定は、分子スケールでの原子相互作用を再現するMonte Carlo Track Structure (MCTS)コードにより評価可能である。数十年にわたり独立して開発された様々なMCTSコードは、生物組織の主成分である液体水中の電子線の相互作用について、異なる物理モデルと断面積データセットを使用してきた。本研究では、様々なMCTSコード内の相互作用断面積の違いによって生じるナノ線量測定計算の不確実性を評価した。7つのMCTSコード(Geant4-DNA, PARTRAC, PHITS, MCwater、およびPTra)の計算結果から、平均電離数や2回以上の電離が起こる確率などの分子スケールの物理量に大きな相違があることが明らかとなった。最も大きな相違が確認されたのは低エネルギー電子で、相互作用断面積の寄与が不確実性の主要因であることがわかった。本成果より、断面積の相違が複雑なDNA損傷などの生物学的影響に無視できない影響を与えることが浮き彫りになった。
 Fe
Fe O
O
Lenander, E. Y.*; Nielsen, F. B.*; Lass, J.*; Hansen, U. B.*; Krighaar, K. M. L.*; Preuss, A.*; Weber, T.*; Enderle, M.*; Jacobsen, H.*; Stuhr, U.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 113(1), p.014424_1 - 014424_14, 2026/01
被引用回数:0The frustrated magnet Bi Fe
Fe O
O has been reported to exhibit complex spin dynamics coexisting with conventional spin wave excitations. The magnetic Fe
has been reported to exhibit complex spin dynamics coexisting with conventional spin wave excitations. The magnetic Fe (
(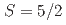 ) ions are arranged into a distorted two-dimensional Cairo pentagonal lattice with weak couplings between the layers, developing long-ranged noncollinear antiferromagnetic order below 245 K. In order to enable studies and modeling of the complex dynamics close to
) ions are arranged into a distorted two-dimensional Cairo pentagonal lattice with weak couplings between the layers, developing long-ranged noncollinear antiferromagnetic order below 245 K. In order to enable studies and modeling of the complex dynamics close to 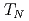 , we have reexamined the magnetic excitations across the complete energy scale (
, we have reexamined the magnetic excitations across the complete energy scale (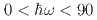 meV) at 10 K. We discover two distinct gaps, which can be explained by introducing, respectively, easy axis and easy plane anisotropy on the two unequivalent Fe sites. We develop a refined spin Hamiltonian that accurately accounts for the dispersion of essentially all spin-wave branches across the full spectral range, except around 40 meV, where a splitting and dispersion are observed. Polarization analysis shows that the system has magnetic anisotropic fluctuations, consistent with our model. A continuum of scattering is observed above the spin wave branches and is found to principally be explained by an instrumental resolution effect. The full experimental mapping of the excitation spectrum and the refined spin Hamiltonian provides a foundation for future quantitative studies of spin waves coexisting with unconventional magnetic fluctuations in this frustrated magnet found at higher temperatures.
meV) at 10 K. We discover two distinct gaps, which can be explained by introducing, respectively, easy axis and easy plane anisotropy on the two unequivalent Fe sites. We develop a refined spin Hamiltonian that accurately accounts for the dispersion of essentially all spin-wave branches across the full spectral range, except around 40 meV, where a splitting and dispersion are observed. Polarization analysis shows that the system has magnetic anisotropic fluctuations, consistent with our model. A continuum of scattering is observed above the spin wave branches and is found to principally be explained by an instrumental resolution effect. The full experimental mapping of the excitation spectrum and the refined spin Hamiltonian provides a foundation for future quantitative studies of spin waves coexisting with unconventional magnetic fluctuations in this frustrated magnet found at higher temperatures.
Rossi, F.; Lee, J.; 吉見 優希*; 芝 知宙; 寺田 和司*; 堀 順一*
第46回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2025/12
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency is developing a non-destructive system to detect fissile nuclear materials within a sample combining resonance analysis from prompt fission neutrons, capture gamma-rays, and transmitted neutrons. The detection setup includes an array of plastic scintillators at the sample and a downstream  Li scintillator. Recent improvements focus on better neutron/gamma discrimination using advanced EJ-276D plastic scintillators and optimized pulse shape discrimination analysis. Tests were conducted at the Kyoto University time-of-flight facility with natural and enriched uranium samples. This paper presents the latest design updates and experimental results from the system's development. This work is supported by MEXT under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like".
Li scintillator. Recent improvements focus on better neutron/gamma discrimination using advanced EJ-276D plastic scintillators and optimized pulse shape discrimination analysis. Tests were conducted at the Kyoto University time-of-flight facility with natural and enriched uranium samples. This paper presents the latest design updates and experimental results from the system's development. This work is supported by MEXT under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like".
白藤 雅也; 佐野 恭平; 堀内 雅一; 加藤 茜; 渡邉 一樹; 谷川 聖史; 丸山 創; 北尾 貴彦; Conner, J.*; LaFleur, A.*; et al.
第46回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2025/12
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency, in collaboration with the U.S. Department of Energy and Los Alamos National Laboratory, initiated a joint research project to develop the Advanced Hulls Measurement and Monitoring System (A-HMMS) for quantifying trace amounts of nuclear material in hull drums. Monte Carlo simulations using the MCNP code confirmed that the presence of water significantly attenuates neutron count rates. However, sufficient sensitivity to plutonium mass variations was observed, indicating that measurements are feasible even with water present. Passive NDA methods based on the Cm/Pu ratio were found to be limited due to curium decay over long-term storage, necessitating the use of active interrogation techniques. Small-scale experiments validated the simulation results and demonstrated that waste type and source position significantly affect count rates, highlighting the need for waste-specific calibration curves. Full-scale testing is planned to evaluate system performance under realistic conditions and optimize the A-HMMS design.
 Cf中性子源を用いた卓上型中性子共鳴透過分析装置の開発
Cf中性子源を用いた卓上型中性子共鳴透過分析装置の開発土屋 晴文; Guembou Shouop, C. J.
第46回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2025/12
Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) is a non-destructive assay capable of identifying and quantifying nuclear materials with high precision, making it a promising tool for applications in nuclear security, safeguards, and non-proliferation. Conventional NRTA systems typically employ accelerators or neutron generators as neutron sources. As a result, they are large, require heavy shielding, and are difficult to implement in facilities with limited space or in field environments. To overcome these limitations, we developed a table-top NRTA system that utilizes a  Cf neutron source instead of an accelerator or a neutron generator. The apparatus has dimensions of approximately 130 cm
Cf neutron source instead of an accelerator or a neutron generator. The apparatus has dimensions of approximately 130 cm  50 cm
50 cm  50 cm, enabling easy transport and on-site deployment. Performance tests were conducted using indium and silver plates as surrogate samples for nuclear materials. The experimental transmission spectra exhibited resonance dips consistent with those of expected transmission spectra incorporating the system response function. From these comparisons, the isotopic areal densities were successfully quantified within experimental uncertainty. This study demonstrates, for the first time, that isotope identification and quantitative evaluation can be achieved using a table-top NRTA system without accelerators and neutron generators, and suggests its potential applicability to nuclear facilities, ports, and other space-limited locations.
50 cm, enabling easy transport and on-site deployment. Performance tests were conducted using indium and silver plates as surrogate samples for nuclear materials. The experimental transmission spectra exhibited resonance dips consistent with those of expected transmission spectra incorporating the system response function. From these comparisons, the isotopic areal densities were successfully quantified within experimental uncertainty. This study demonstrates, for the first time, that isotope identification and quantitative evaluation can be achieved using a table-top NRTA system without accelerators and neutron generators, and suggests its potential applicability to nuclear facilities, ports, and other space-limited locations.
Rossi, F.; Lee, J.; 吉見 優希*; 弘中 浩太; 小泉 光生; 芝 知宙; 寺田 和司*; 堀 順一*
ESARDA Bulletin (Internet), 67, p.59 - 67, 2025/12
ISCN is developing an advanced neutron resonance analysis system for the identification and quantification of fissile materials. This system integrates three complementary techniques: NRTA, NRCA, and NRFNA, enabling simultaneous detection and improving sensitivity for fissile material identification. To evaluate the system's performance, we conducted a series of experiments using natural uranium samples with a thickness from 1.5 to 6.0 mm enclosed in a 2 cm thick box made of lead. The results show that even if the presence of lead generates significant background noise due to neutron scattering and reflection, a clear identification of  U signatures is possible. These findings highlight the system's versatility and effectiveness in shielding scenarios, offering a promising tool for nuclear security and nonproliferation applications. By enabling concurrent measurements, the system improves accuracy and provides an innovative method for enhancing regulatory and safeguard efforts in the nuclear industry. This work is supported by MEXT under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like".
U signatures is possible. These findings highlight the system's versatility and effectiveness in shielding scenarios, offering a promising tool for nuclear security and nonproliferation applications. By enabling concurrent measurements, the system improves accuracy and provides an innovative method for enhancing regulatory and safeguard efforts in the nuclear industry. This work is supported by MEXT under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like".
中川 洋; Ubbink, J.*
Food Hydrocolloids, 168, p.111453_1 - 111453_9, 2025/12
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:92.46(Chemistry, Applied)エクストルージョン条件下での植物タンパク質のテクスチャー化の分子メカニズムを、タンパク質の二次構造に対する加熱、冷却、せん断の影響を切り離すことにより、二次構造レベルで解明した。剪断を伴わない加熱では、ネイティブな -ヘリックスと分子内
-ヘリックスと分子内 -シートがランダムドメインに展開し、次いで分子間
-シートがランダムドメインに展開し、次いで分子間 -シートが形成され、凝集が誘導される。冷却中、分子間
-シートが形成され、凝集が誘導される。冷却中、分子間 シートはますます秩序化し、ランダムドメインは部分的に非ネイティブ
シートはますます秩序化し、ランダムドメインは部分的に非ネイティブ 構造へと折り畳まれる。加熱と剪断を組み合わせることで、加熱単独よりもより広範な
構造へと折り畳まれる。加熱と剪断を組み合わせることで、加熱単独よりもより広範な シートが形成される。その結果、
シートが形成される。その結果、 リッチ構造は、タンパク質鎖の絡み合ったネットワークと凝集性のタンパク質マトリックスを提供する。
リッチ構造は、タンパク質鎖の絡み合ったネットワークと凝集性のタンパク質マトリックスを提供する。
大平 直也*; 樹神 克明; 伊藤 大介*; 齊藤 泰司*; Parker, J. D.*; 篠原 武尚
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 45, p.102005_1 - 102005_7, 2025/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Lead-bismuth eutectic has emerged as a promising candidate for liquid metal coolant for Gen-IV nuclear reactors. Lead-bismuth eutectic is a unique material that expands gradually within the solid state. It may induce pipe deformation or rupture if it solidifies in a pipe or a container. In this study, the strain distributions of lead-bismuth eutectic in stainless-steel cups were evaluated using wavelength-resolved neutron imaging method. The wettability-improved case exhibited significantly larger compressive strain than in the others. The adhesion between lead-bismuth eutectic and the inner surface of the cup was a critical issue in the present study.
Ou-Yang, Z.-X.*; Gubler, P.; 岡 眞*; Wang, G.-J.*; Wu, J.-J.*
Physical Review D, 112(11), p.114034_1 - 114034_13, 2025/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We propose an extension of the QCD sum rules, termed the resonance sum rules, to access resonance poles in the complex energy plane. By strategically introducing a contour in the complex plane and conformal mapping, the method intends to reach resonance poles on the second Riemann sheet. To validate this approach, we apply resonance sum rules to the square-well potential model, for which the pole locations are known. The analysis demonstrates a successful extraction of the pole positions and residues for both the S-wave and P-wave resonances. The results are in good agreement with the analytic solutions, with discrepancies within 5% for the pole positions and 20% for the residues. This framework provides a basis for future applications to realistic hadronic resonances, promising new insights into spectral properties of QCD.
Catumba, G.*; 平口 敦基; Hou, G. W.-S.*; Jansen, K.*; Kao, Y.-J.*; David Lin, C.-J.*; Ramos, A.*; Sarkar, M.*
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 466, p.145_1 - 145_10, 2025/12
SU(2)ゲージ場を持つカストディアル2ヒッグス二重項模型を格子上で研究する。この模型は標準模型と同じ大域的対称性を持つが、ヒッグス場が追加されることでスカラースペクトルが拡大し、大域的対称性の自発的破れが発生する可能性が出てくる。カストディアル2ヒッグス二重項模型のスペクトルと走るゲージ結合定数を、カットオフが300から600GeVで標準模型での物理量が一定となる線上で研究した。結果として追加したBSMスカラー場の実現可能な質量の下限は、Wボソンの質量よりはるかに小さいことがわかった。そして、この研究で選択した4点相互作用の結合定数では、BSM状態の1つに対する推定された下限質量は約 0.2
0.2
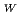 で、カットオフに依存しないことがわかった。
で、カットオフに依存しないことがわかった。
出井 俊太郎; 柴田 真仁*; 根岸 久美*; 杉浦 佑樹; 天野 由記; Bateman, K.*; Wilson, J.*; 横山 立憲; 鏡味 沙耶; 武田 匡樹; et al.
Results in Earth Sciences (Internet), 3, p.100097_1 - 100097_16, 2025/12
高レベル放射性廃棄物の地層処分において、セメントと泥岩の相互作用による化学的擾乱領域が形成され、岩盤中の核種移行特性に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。本研究では、11年前に幌延深地層研究センターの140m調査坑道に施工されたセメント(普通ポルトランドセメント(OPC)および低アルカリ性セメント(LAC))と泥岩の界面における変質状態について調査した。複数の分析手法を組み合わせることで、セメントの溶解、方解石やC-(A-)S-H相などの二次鉱物の析出、モンモリロナイトの陽イオン交換、泥岩の空隙率の低下など、セメントと岩石の界面における主要な反応が特定された。また、空隙率の低下による拡散の低下や、変質した泥岩中の二次鉱物への取り込みによる収着の促進など、セメントと泥岩の相互作用が放射性核種の移行に及ぼす影響についても明らかになった。