Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
宮本 斉児; 杉原 正芳*; 新谷 吉郎*; 中村 幸治*; 利光 晋一*; Lukash, V. E.*; Khayrutdinov, R. R.*; 杉江 達夫; 草間 義紀; 芳野 隆治*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 87(11), p.1816 - 1827, 2012/11
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:73.09(Nuclear Science & Technology)Vertical displacement events (VDEs) and disruptions usually take place under intervention of vertical stability (VS) control and the vertical electromagnetic force induced on vacuum vessels is potentially influenced. This paper presents assessment of the force that arises from the VS control in ITER VDEs using a numerical simulation code DINA. The focus is on a possible malfunctioning of the VS control circuit: radial magnetic field is unintentionally applied to the direction of enhancing the vertical displacement further. Since this type of failure usually causes the largest forces (or halo currents) observed in the present experiments, this situation must be properly accommodated in the design of the ITER vacuum vessel. DINA analysis shows that although the VS control modifies radial field, it does not affect plasma motion and current quench behavior including halo current generation because the vacuum vessel shields the field created by the VS control coils. Nevertheless, the VS control modifies the force on the vessel by directly acting on the eddy current carried by the conducting structures of the vessel. Although the worst case was explored in a range of plasma inductance and pattern of VS control, the result confirmed that the force is still within the design margin.
Imbeaux, F.*; Citrin, J.*; Hobirk, J.*; Hogeweij, G. M. D.*; K chl, F.*; Leonov, V. M.*; 宮本 斉児; 中村 幸治*; Parail, V.*; Pereverzev, G. V.*; et al.
chl, F.*; Leonov, V. M.*; 宮本 斉児; 中村 幸治*; Parail, V.*; Pereverzev, G. V.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(8), p.083026_1 - 083026_11, 2011/08
被引用回数:38 パーセンタイル:80.80(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In order to prepare adequate current ramp-up and ramp-down scenarios for ITER, present experiments from various tokamaks have been analysed by means of integrated modelling in view of determining relevant heat transport models for these operation phases. A set of empirical heat transport models for L-mode has been validated on a multi-machine experimental dataset for predicting the 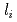 dynamics within
dynamics within  0.15 accuracy during current ramp-up and ramp-down phases. The most accurate heat transport models are then applied to projections to ITER current ramp-up, focusing on the baseline inductive scenario (main heating plateau current of
0.15 accuracy during current ramp-up and ramp-down phases. The most accurate heat transport models are then applied to projections to ITER current ramp-up, focusing on the baseline inductive scenario (main heating plateau current of 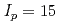 MA). These projections include a sensitivity study to various assumptions of the simulation. While the heat transport model is at the heart of such simulations, more comprehensive simulations are required to test all operational aspects of the current ramp-up and ramp-down phases of ITER scenarios. Recent examples of such simulations, involving coupled core transport codes, free-boundary equilibrium solvers and a poloidal field (PF) systems controller are also described, focusing on ITER current ramp-down.
MA). These projections include a sensitivity study to various assumptions of the simulation. While the heat transport model is at the heart of such simulations, more comprehensive simulations are required to test all operational aspects of the current ramp-up and ramp-down phases of ITER scenarios. Recent examples of such simulations, involving coupled core transport codes, free-boundary equilibrium solvers and a poloidal field (PF) systems controller are also described, focusing on ITER current ramp-down.
Imbeaux, F.*; Basiuk, V.*; Budny, R.*; Casper, T.*; Citrin, J.*; Fereira, J.*; 福山 淳*; Garcia, J.*; Gribov, Y. V.*; 林 伸彦; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
In order to prepare adequate current ramp-up and ramp-down scenarios for ITER, present experiments from various tokamaks have been analysed by means of integrated modelling in view of determining relevant heat transport models for these operation phases. The most accurate heat transport models are then applied to projections to ITER current ramp-up, focusing on the baseline inductive scenario (main heating plateau current of Ip = 15 MA). These projections include a sensitivity studies to various assumptions of the simulation. Recent examples of such simulations, involving coupled core transport codes, free boundary equilibrium solvers and a poloidal field (PF) systems controller are described in the second part of the paper, focusing on ITER current ramp-down.
Imbeaux, F.*; Basiuk, V.*; Budny, R.*; Casper, T.*; Citrin, J.*; Fereira, J.*; 福山 淳*; Garcia, J.*; Gribov, Y. V.*; 林 伸彦; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/10
ITERでの電流立ち上げ・立ち下げシナリオの準備に向けて、これら運転状態においてどの熱輸送モデルが適切であるかを決定するために、代表的なトカマクでの現在の実験結果を統合モデルシミュレーションにより解析した。本研究では、トカマク実験の解析結果をもとに、ITER標準誘導運転(プラズマ電流15MA)の電流立ち上げ・立ち下げシナリオでの予測を行った。統合モデルシミュレーション結果を、ASDEX Upgrade, C-Mod, DIII-D, JET, Tore Supraのオーミック加熱プラズマ及び外部加熱・電流駆動プラズマ実験データと比較することにより、さまざまな輸送モデルの検証を行った。最も実験結果の再現性の良かった幾つかのモデルを用いて、ITERの電流立ち上げ・立ち下げ段階での電子密度・電流密度プロファイルの予測を行った。電子温度プロファイルには輸送モデルによって大きな差が見られたが、最終的な電流密度プロファイルはモデル間でよく一致することがわかった。
Hender, T. C.*; Wesley, J. C.*; Bialek, J.*; Bondeson, A.*; Boozer, A. H.*; Buttery, R. J.*; Garofalo, A.*; Goodman, T. P.*; Granetz, R. S.*; Gribov, Y.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S128 - S202, 2007/06
被引用回数:1010 パーセンタイル:98.25(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)本論文は、1999年の"ITER Physics Basis"の刊行以降に世界各国の装置で得られた重要な成果について記述したものであり、本章ではMHD安定性及びディスラプションに関する成果が記述されている。MHD安定性に関しては、(1)鋸歯状振動,(2)新古典テアリングモード,(3)抵抗性壁モード,(4)誤差磁場,(5)先進シナリオにおけるMHD安定性に関する成果が記述されていて、ディスラプションに関しては、(1)ディスラプションの特徴・原因・頻度,(2)サーマルクエンチによるエネルギーの損失と堆積,(3)電流クエンチのダイナミクス,(4)ディスラプションにより発生する逃走電子,(5)統合モデルとシミュレーション,(6)ディスラプションの回避・予測・緩和に関する成果が記述されている。
河上 翔*; 大野 哲靖*; 渡邊 清政*; 柴田 欣秀; 岡本 征晃*; 宮本 斉児; 諫山 明彦; 杉原 正芳*; 河野 康則; Lukash, V. E.*; et al.
no journal, ,
JT-60Uの大量ネオンガスパフによるディスラプション実験において、電流減衰の初期段階の内部インダクタンス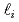 の増加が電流減衰時間の値に影響を及ぼすことが以前実験的に検証されたが、物理機構は十分解明されていなかった。本研究では、2次元軸対称シミュレーションコードDINAを用いることにより、ディスラプション中の電子温度分布が
の増加が電流減衰時間の値に影響を及ぼすことが以前実験的に検証されたが、物理機構は十分解明されていなかった。本研究では、2次元軸対称シミュレーションコードDINAを用いることにより、ディスラプション中の電子温度分布が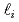 の時間変化に与える影響を解析した。まず、電子温度分布を空間一定とした場合、
の時間変化に与える影響を解析した。まず、電子温度分布を空間一定とした場合、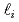 は実験での観測とは逆に時間的に減少した。次に、実験時に得られた電子温度分布を用いて計算した場合、
は実験での観測とは逆に時間的に減少した。次に、実験時に得られた電子温度分布を用いて計算した場合、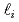 は時間的にほぼ一定となった。このことは、電子温度の分布を考慮することで
は時間的にほぼ一定となった。このことは、電子温度の分布を考慮することで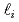 を実験結果を再現する方向に近づけることができるものの、これだけでは不十分であることを示唆している。今回の計算では計測の困難さなどの理由から空間一定としているパラメータがあるが、これらの分布も
を実験結果を再現する方向に近づけることができるものの、これだけでは不十分であることを示唆している。今回の計算では計測の困難さなどの理由から空間一定としているパラメータがあるが、これらの分布も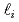 の時間変化に影響を及ぼしている可能性がある。
の時間変化に影響を及ぼしている可能性がある。
河上 翔*; 柴田 欣秀*; 渡邊 清政*; 大野 哲靖*; 梶田 信*; 岡本 征晃*; 諫山 明彦; 杉原 正芳*; 河野 康則; Lukash, V. E.*; et al.
no journal, ,
トカマク型核融合装置においてディスラプションが発生すると第一壁や真空容器に熱的・電磁的な負荷を与えることから、ディスラプションの特性を理解して予測・回避・緩和のためのシナリオを確立することが重要である。今回、ディスラプション発生時のプラズマ電流の減衰過程に関して、JT-60Uの実験結果と2次元軸対称MHD平衡計算コードDINAの計算結果とを比較した。DINAの計算においてパワーバランスから解いた電子温度を用いた場合、プラズマ電流の時間発展は実験に比べて速い減衰となった。また、電子温度を100eV、実効電荷を17で一定値として計算した場合、プラズマ電流とプラズマ断面積の減衰は実験とよい一致を示したが、ディスラプション開始時刻における内部インダクタンスは実験値より低くなり、その時間発展も実験とは異なるものとなった。DINAでは電子温度分布を一定としているが、実際は一定ではない分布を持つことから、内部インダクタンスの差異の原因の1つとして電子温度分布が考えられる。
柴田 欣秀; 諫山 明彦; 松永 剛; 河野 康則; 宮本 斉児*; Lukash, V. E.*; Khayrutdinov, R.*
no journal, ,
JT-60Uのディスラプション実験において、プラズマ電流の減衰をディスラプションシミュレーションコード(DINA)と計測された電子温度分布を用いて計算した。本研究では電子温度が数百eVの分布を持つ電流クエンチ初期と、電子温度が急激に減少するミニコラプス発生後のプラズマ電流を解析した。電流クエンチ初期の解析では、電流減衰時間が違う放電で電子温度の振る舞いが異なっていた。電流減衰時間が短い放電では、熱クエンチ直後の電子温度分布は既にピークしており、電流クエンチ中にあまり変化しなかった。しかし、電子温度が非常にピークした分布であるため、プラズマへの急激な電流拡散が発生し、プラズマインダクタンスが大きく増加してプラズマ電流が早く減衰している。一方、電流減衰時間が長い放電では、熱クエンチ直後の電子温度分布は電流減衰時間が短い放電に比べて広がりを持っており、電流クエンチ中に電子温度分布の収縮が観測された。その電子温度の収縮によりプラズマ電流は内部へ拡散するが、最終的な電子温度分布は早い電流減衰に比べて幅広いため、プラズマインダクタンスの変化は小さく、電流減衰時間が長くなっていることがDINAの計算により分かった。電子温度が急激に減少するミニコラプス発生後については、そのように低い電子温度(100eV以下)ではプラズマ抵抗によりプラズマ電流が減衰することがわかった。