Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Guo, B.*; Chen, H.*; Chong, Y.*; Mao, W.; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Z.*; Jonas, J. J.*; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 268, p.119780_1 - 119780_11, 2024/04
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:94.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)This paper focused on the characterization and mechanism of the dynamic transformation from the alpha to beta phase during the hot deformation of Ti-6Al-4V alloy and pure titanium. The investigation employed in-situ neutron diffraction and atomistic simulations for a comprehensive understanding of the process. Dynamic transformations were observed during deformation of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy and pure titanium below the beta transus temperatures. During isothermal holding after unloading, the in-situ neutron diffraction results for Ti-6Al-4V and pure titanium indicated a sluggish reverse transformation from the beta to alpha phase. The mechanism of dynamic transformation was explored through in-situ neutron diffraction and atomistic simulations, which revealed twofold effects of deformation on dynamic transformation. Firstly, deformation led to a significant rise in the Gibbs energy of the alpha phase relative to the beta phase, expanding the beta phase region and diminishing the alpha phase region. Secondly, deformation lowered the energy barriers associated with dynamic transformation, facilitating the activation of dynamic transformation more readily than in the equilibrium state before deformation.
 phase to
phase to  phase in zirconium alloy revealed by in-situ neutron diffraction during high temperature deformation
phase in zirconium alloy revealed by in-situ neutron diffraction during high temperature deformationGuo, B.*; Mao, W.; Chong, Y.*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Chen, H.*; Jonas, J. J.*; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 242, p.118427_1 - 118427_11, 2023/01
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:68.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dynamic transformation from alpha (HCP) to beta (BCC) phase in a zirconium alloy was revealed by the use of in-situ neutron diffraction during hot compression. The dynamic transformation was unexpectedly detected during isothermal compression at temperatures of 900 C and 950
C and 950 C (alpha + beta two-phase region) and strain rates of 0.01 s
C (alpha + beta two-phase region) and strain rates of 0.01 s and 0.001 s
and 0.001 s , even though equilibrium two-phase states were achieved prior to the hot compression. Dynamic transformation was accompanied by diffusion of Sn from beta to alpha phase, which resulted in changes of lattice parameters and a characteristic microstructure of alpha grains. The details of dynamic transformation are discussed using the evolution of lattice constants.
, even though equilibrium two-phase states were achieved prior to the hot compression. Dynamic transformation was accompanied by diffusion of Sn from beta to alpha phase, which resulted in changes of lattice parameters and a characteristic microstructure of alpha grains. The details of dynamic transformation are discussed using the evolution of lattice constants.
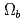 baryons and fine structure of strong interaction
baryons and fine structure of strong interactionChen, H.-X.*; Cui, E.-L.*; 保坂 淳; Mao, Q.*; Yang, H.-M.*
European Physical Journal C, 80(3), p.256_1 - 256_6, 2020/03
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:58.42(Physics, Particles & Fields)The heavy baryon system bounded by the strong interaction has a rich internal structure, so its mass spectra can have the fine structure similar to the line spectra of atom bounded by the electromagnetic interaction. We systematically study the internal structure of  -wave
-wave 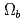 baryons and calculate their
baryons and calculate their  -wave decay properties. The present study, together with our previous studies on their mass spectra and
-wave decay properties. The present study, together with our previous studies on their mass spectra and  -wave decay properties, suggest that all the four excited
-wave decay properties, suggest that all the four excited 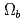 baryons recently discovered by LHCb can be well explained as
baryons recently discovered by LHCb can be well explained as  -wave
-wave 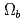 baryons, and their beautiful fine structure is directly related to the rich internal structure of
baryons, and their beautiful fine structure is directly related to the rich internal structure of  -wave
-wave 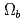 baryons.
baryons.
 -wave bottom baryons within light-cone sum rules
-wave bottom baryons within light-cone sum rulesYang, H.-M.*; Chen, H.-X.*; Cui, E.-L.*; 保坂 淳; Mao, Q.*
European Physical Journal C, 80(2), p.80_1 - 80_17, 2020/02
被引用回数:27 パーセンタイル:79.15(Physics, Particles & Fields)We use the method of light-cone sum rules to study decay properties of  -wave bottom baryons belonging to the
-wave bottom baryons belonging to the 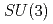 flavor 6
flavor 6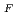 representation. In Cui et al. (Phys Rev D 99:094021, 2019) we have studied their mass spectrum and pionic decays, and found that the
representation. In Cui et al. (Phys Rev D 99:094021, 2019) we have studied their mass spectrum and pionic decays, and found that the 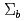 (6097) and
(6097) and 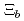 (6227) can be well interpreted as
(6227) can be well interpreted as  -wave bottom baryons of
-wave bottom baryons of 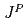 = 3/2
= 3/2 . In this paper we further study their decays into ground-state bottom baryons and vector mesons. We propose to search for a new state
. In this paper we further study their decays into ground-state bottom baryons and vector mesons. We propose to search for a new state 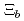 (5/2
(5/2 ), that is the
), that is the 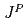 = 5/2
= 5/2 partner state of the
partner state of the 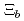 (6227), in the
(6227), in the 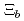 (5/2
(5/2 )
)
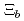 *
*

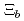 *
*
 decay process. Its mass is 12
decay process. Its mass is 12 5 MeV larger than that of the
5 MeV larger than that of the 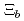 (6227).
(6227).
Ding, F.*; 芦川 直子*; 福本 正勝; 片山 一成*; Mao, H.*; Ding, R.*; Xu, Q.*; Wu, J.*; Xie, C. Y.*; Luo, G.-N.*
no journal, ,
Castellated tungsten samples with different gap width and gap depth are exposed to the scrape-off-layer plasma with the material and plasma evaluation system (MAPES) to investigate effects of castellation configurations on impurity deposition and fuel retention. After the plasma exposure, composition and distribution of the impurity deposited on the inner surface of the gap are investigated. The composition and the distribution of the deposits have a strong dependence of the gap configuration. The amount of the deposits on the inner surface of the inverse trapezoid gap is small compared with that of the rectangular gap with the same top width. For all the samples, the amount of the deposits decreases with the gap width and depth.