Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Zhang, Z.*; 服部 高典; Song, R.*; Yu, D.*; Mole, R.*; Chen, J.*; He, L.*; Zhang, Z.*; Li, B.*
Journal of Applied Physics, 136(3), p.035105_1 - 035105_8, 2024/07
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:35.22(Physics, Applied)バロカロリック材料を用いた固体冷凍は、環境に優しく高効率であるため、過去10年間にわたり世界的に注目されてきた。ここでは、室温付近で立方晶から菱面体晶への相転移を起こすヘキサフルオロ燐酸ナトリウム(NaPF )とヘキサフルオロ砒酸ナトリウム(NaAsF
)とヘキサフルオロ砒酸ナトリウム(NaAsF )における巨大バロカロリック効果を報告する。われわれは中性子粉末回折により、NaPF
)における巨大バロカロリック効果を報告する。われわれは中性子粉末回折により、NaPF の低温相の構造が空間群R
の低温相の構造が空間群R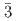 の菱面体構造であることを明らかにした。NaPF
の菱面体構造であることを明らかにした。NaPF とNaAsF
とNaAsF には3つのラマン振動モード(F
には3つのラマン振動モード(F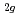 , E
, E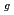 , A
, A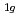 )が存在する。相転移温度はNaPF
)が存在する。相転移温度はNaPF 及びNaAsF
及びNaAsF においてそれぞれdT
においてそれぞれdT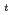 /dP=250K/GPa及び310K/GPaの割合で圧力とともに変化する。NaPF
/dP=250K/GPa及び310K/GPaの割合で圧力とともに変化する。NaPF とNaAsF
とNaAsF の圧力誘起エントロピー変化は、それぞれ約45.2Jkg
の圧力誘起エントロピー変化は、それぞれ約45.2Jkg K
K と35.6Jkg
と35.6Jkg K
K と決定された。飽和駆動圧力は約40MPaであった。高圧下の中性子粉末回折から、バロカロリック効果は立方晶から菱面体晶への圧力誘起相転移に関係していることが示唆された。
と決定された。飽和駆動圧力は約40MPaであった。高圧下の中性子粉末回折から、バロカロリック効果は立方晶から菱面体晶への圧力誘起相転移に関係していることが示唆された。
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Xi, N.*; Gao, Y.-P.*; Ma, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Qi, Z.*; Zhang, S.*; Huang, Z.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(12), p.1883 - 1889, 2023/09
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:93.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The magnetization of a quantum magnet can be pinned at a fraction of its saturated value by collective effects. One example of such a plateau phase is found in spin-1/2 triangular-lattice antiferromagnets. They feature strong geometrical frustration and the plateau phase therein is often interpreted as arising from an order-by-disorder mechanism driven by quantum fluctuations. Here we observe a one-third magnetization plateau under an applied magnetic field in the spin-1 antiferromagnet Na Ni
Ni BiO
BiO with a honeycomb lattice, which, with conventional magnetic interactions, would not be geometrically frustrated. Based on our elastic neutron scattering measurements, we propose the spin structure of the plateau phase to be an unusual partial spin-flop ferrimagnetic order. Our theoretical calculations indicate that bond-anisotropic Kitaev interactions are the source of frustration that produces the plateau. These results suggest that Kitaev interactions provide a different route to frustration and phases driven by quantum fluctuations in high-spin magnets.
with a honeycomb lattice, which, with conventional magnetic interactions, would not be geometrically frustrated. Based on our elastic neutron scattering measurements, we propose the spin structure of the plateau phase to be an unusual partial spin-flop ferrimagnetic order. Our theoretical calculations indicate that bond-anisotropic Kitaev interactions are the source of frustration that produces the plateau. These results suggest that Kitaev interactions provide a different route to frustration and phases driven by quantum fluctuations in high-spin magnets.
Jiang, X.*; 服部 高典; Xu, X.*; Li, M.*; Yu, C.*; Yu, D.*; Mole, R.*; 矢野 真一郎*; Chen, J.*; He, L.*; et al.
Materials Horizons, 10(3), p.977 - 982, 2023/03
被引用回数:26 パーセンタイル:93.14(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)現在の蒸気圧縮式冷凍機に代わる環境に優しい冷凍機として、バロカロリック効果に基づく固体冷凍機が世界的に注目されている。一般に、バロカロリック効果が発現する相はいずれも常圧でも存在する。ここでは、それらの物質と違って、KPF が高圧の菱面体晶相を生成することにより、巨大なバロカロリック効果を示すことを実証した。相図は、圧力依存の熱量測定、ラマン散乱測定、中性子回折測定に基づいて構築されたものである。本研究は、巨大バロカロリー効果に、高圧相の生成という新たな手法をもたらすと期待される。
が高圧の菱面体晶相を生成することにより、巨大なバロカロリック効果を示すことを実証した。相図は、圧力依存の熱量測定、ラマン散乱測定、中性子回折測定に基づいて構築されたものである。本研究は、巨大バロカロリー効果に、高圧相の生成という新たな手法をもたらすと期待される。
 BaCo(PO
BaCo(PO )
)
Sheng, J.*; Wang, L.*; Candini, A.*; Jiang, W.*; Huang, L.*; Xi, B.*; Zhao, J.*; Ge, H.*; Zhao, N.*; Fu, Y.*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(51), p.e2211193119_1 - e2211193119_9, 2022/12
被引用回数:34 パーセンタイル:93.63(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Although considerable progress has been made in the theoretical understanding of the low-dimensional frustrated quantum magnets, experimental realizations of a well-established scaling analysis are still scarce. This is particularly true for the two-dimensional antiferromagnetic triangular lattices. Owing to the small exchange strength, the newly discovered compound Na BaCo(PO
BaCo(PO )
) provides a rare opportunity for clarifying the quantum criticality in an ideal triangular lattice with quantum spin S=1/2. In addition to the establishment of the complete phase diagrams, the spin Hamiltonian with a negligible interplane interaction has been determined through the spin wave dispersion in the polarized state, which is consistent with the observation of a two-dimensional quantum critical point with the Bose-Einstein condensation of diluted free bosons.
provides a rare opportunity for clarifying the quantum criticality in an ideal triangular lattice with quantum spin S=1/2. In addition to the establishment of the complete phase diagrams, the spin Hamiltonian with a negligible interplane interaction has been determined through the spin wave dispersion in the polarized state, which is consistent with the observation of a two-dimensional quantum critical point with the Bose-Einstein condensation of diluted free bosons.
藤原 理賀*; 森田 克洋*; Mole, R.*; 満田 節生*; 遠山 貴巳*; 矢野 真一郎*; Yu, D.*; 曽田 繁利*; 桑井 智彦*; 幸田 章宏*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.3429_1 - 3429_7, 2020/07
被引用回数:52 パーセンタイル:92.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Observation of a quantum spin liquid (QSL) state is one of the most important goals in condensed-matter physics, as well as the development of new spintronic devices that support next-generation industries. The QSL in two-dimensional quantum spin systems is expected to be due to geometrical magnetic frustration, and thus a kagome-based lattice is the most probable playground for QSL. Here, we report the first experimental results of the QSL state on a square-kagome quantum antiferromagnet, KCu AlBiO
AlBiO (SO
(SO )
) Cl. Comprehensive experimental studies via magnetic susceptibility, magnetisation, heat capacity, muon spin relaxation, and inelastic neutron scattering measurements reveal the formation of a gapless QSL at very low temperatures close to the ground state. The QSL behavior cannot be explained fully by a frustrated Heisenberg model with nearest-neighbor exchange interactions, providing a theoretical challenge to unveil the nature of the QSL state.
Cl. Comprehensive experimental studies via magnetic susceptibility, magnetisation, heat capacity, muon spin relaxation, and inelastic neutron scattering measurements reveal the formation of a gapless QSL at very low temperatures close to the ground state. The QSL behavior cannot be explained fully by a frustrated Heisenberg model with nearest-neighbor exchange interactions, providing a theoretical challenge to unveil the nature of the QSL state.
Li, B.*; 川北 至信; 河村 聖子; 菅原 武*; Wang, H.*; Wang, J.*; Chen, Y.*; 河口 沙織*; 河口 彰吾*; 尾原 幸治*; et al.
Nature, 567(7749), p.506 - 510, 2019/03
被引用回数:327 パーセンタイル:99.52(Multidisciplinary Sciences)冷却は現代社会では、世界における25-30%の電力が空調や食料保存に用いられるように、重要である。従来の気化、圧縮で冷却を行う方法は、温暖化などの観点から限界が来ている。有望な代替手段として固体の熱量効果を用いた冷却方法が注目を集めている。しかしながら、この方法は、現在候補に挙げられている物質ではエントロピー変化の小ささや巨大な磁場を必要とするところなどから性能に限界がある。そこで我々は柔粘性結晶における圧力誘起の相転移で冷却が起こる巨大圧力熱量効果を報告する。柔粘性結晶の一つであるネオペンチルグリコールのエントロピー変化は室温近傍において単位キログラム、単位温度あたり、約389ジュールであった。圧力下の中性子散乱実験の結果から、そのような巨大圧力熱量効果は分子配向の非秩序化、巨大な圧縮率、極めて非線形性の強い格子ダイナミクスの組み合わせに由来することが明らかになった。我々の研究により、柔粘性結晶における巨大圧力熱量効果発現の微視的機構が明らかとなり、次世代の固体を使った冷却技術の確立に筋道を付けることができた。