Giant barocaloric effects in sodium hexafluorophosphate and hexafluoroarsenate
ヘキサフルオロ燐酸ナトリウムとヘキサフルオロ砒酸ナトリウムにおける巨大バロカロリック効果
Zhang, Z.*; 服部 高典 

 ; Song, R.*; Yu, D.*; Mole, R.*; Chen, J.*; He, L.*; Zhang, Z.*; Li, B.*
; Song, R.*; Yu, D.*; Mole, R.*; Chen, J.*; He, L.*; Zhang, Z.*; Li, B.*
Zhang, Z.*; Hattori, Takanori; Song, R.*; Yu, D.*; Mole, R.*; Chen, J.*; He, L.*; Zhang, Z.*; Li, B.*
バロカロリック材料を用いた固体冷凍は、環境に優しく高効率であるため、過去10年間にわたり世界的に注目されてきた。ここでは、室温付近で立方晶から菱面体晶への相転移を起こすヘキサフルオロ燐酸ナトリウム(NaPF )とヘキサフルオロ砒酸ナトリウム(NaAsF
)とヘキサフルオロ砒酸ナトリウム(NaAsF )における巨大バロカロリック効果を報告する。われわれは中性子粉末回折により、NaPF
)における巨大バロカロリック効果を報告する。われわれは中性子粉末回折により、NaPF の低温相の構造が空間群R
の低温相の構造が空間群R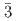 の菱面体構造であることを明らかにした。NaPF
の菱面体構造であることを明らかにした。NaPF とNaAsF
とNaAsF には3つのラマン振動モード(F
には3つのラマン振動モード(F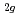 , E
, E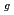 , A
, A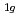 )が存在する。相転移温度はNaPF
)が存在する。相転移温度はNaPF 及びNaAsF
及びNaAsF においてそれぞれdT
においてそれぞれdT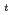 /dP=250K/GPa及び310K/GPaの割合で圧力とともに変化する。NaPF
/dP=250K/GPa及び310K/GPaの割合で圧力とともに変化する。NaPF とNaAsF
とNaAsF の圧力誘起エントロピー変化は、それぞれ約45.2Jkg
の圧力誘起エントロピー変化は、それぞれ約45.2Jkg K
K と35.6Jkg
と35.6Jkg K
K と決定された。飽和駆動圧力は約40MPaであった。高圧下の中性子粉末回折から、バロカロリック効果は立方晶から菱面体晶への圧力誘起相転移に関係していることが示唆された。
と決定された。飽和駆動圧力は約40MPaであった。高圧下の中性子粉末回折から、バロカロリック効果は立方晶から菱面体晶への圧力誘起相転移に関係していることが示唆された。
Solid-state refrigeration using barocaloric materials is environmentally friendly and highly efficient, making it a subject of global interest over the past decade. Here, we report giant barocaloric effects in sodium hexafluorophosphate (NaPF ) and sodium hexafluoroarsenate (NaAsF
) and sodium hexafluoroarsenate (NaAsF ) that both undergo a cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transition near room temperature. We have determined that the low-temperature phase structure of NaPF
) that both undergo a cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transition near room temperature. We have determined that the low-temperature phase structure of NaPF is a rhombohedral structure with space group R
is a rhombohedral structure with space group R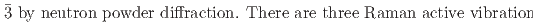 and NaAsF
and NaAsF , i.e., F
, i.e., F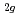 , E
, E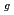 , and A
, and A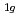 . The phase transition temperature varies with pressure at a rate of dT
. The phase transition temperature varies with pressure at a rate of dT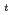 /dP = 250 and 310 K/GPa for NaPF
/dP = 250 and 310 K/GPa for NaPF and NaAsF
and NaAsF . The pressure-induced entropy changes of NaPF
. The pressure-induced entropy changes of NaPF and NaAsF
and NaAsF are determined to be around 45.2 and 35.6J kg
are determined to be around 45.2 and 35.6J kg K
K , respectively. The saturation driving pressure is about 40 MPa. The pressure-dependent neutron powder diffraction suggests that the barocaloric effects are related to the pressure-induced cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transitions.
, respectively. The saturation driving pressure is about 40 MPa. The pressure-dependent neutron powder diffraction suggests that the barocaloric effects are related to the pressure-induced cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transitions.