Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Gao, S.*; 伊東 達矢; 山下 享介*; Harjo, S.; Zhao, L.*; Wang, Q.*
Scripta Materialia, 264, p.116726_1 - 116726_6, 2025/07
被引用回数:0An ultrafine-grained 304 austenitic stainless steel exhibited pronounced serrated Luders deformation at 20 K, with stress and temperature oscillations reaching 200 MPa and 20 K.  neutron diffraction and digital image correlation revealed discontinuous Luders band propagation and burst martensite formation. During deformation, austenite phase stress remained lower than at upper yielding, indicating elastic behavior. Notably, martensite phase stress stayed lower than austenite until fracture, likely due to stress relaxation from burst martensitic transformation at 20 K. The low martensite stress delayed brittle fracture until austenite plastically yielded during uniform deformation.
neutron diffraction and digital image correlation revealed discontinuous Luders band propagation and burst martensite formation. During deformation, austenite phase stress remained lower than at upper yielding, indicating elastic behavior. Notably, martensite phase stress stayed lower than austenite until fracture, likely due to stress relaxation from burst martensitic transformation at 20 K. The low martensite stress delayed brittle fracture until austenite plastically yielded during uniform deformation.
Naeem, M.*; Rehman, A. U.*; Romero Resendiz, L.*; Salamci, E.*; Aydin, H.*; Ansari, P.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Wang, X.-L.*; 他3名*
Communications Materials (Internet), 6, p.65_1 - 65_13, 2025/04
The need for lightweight materials with mechanical integrity at ultralow temperatures drives the development of advanced alloys for cryogenic use. Additive manufacturing via laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) offers a scalable way to create alloys with tailored properties. Here, we show that LPBF-processed Al10SiMg exhibits a high ultimate tensile strength (395 MPa) and uniform elongation (25%) at 15 K. These enhancements stem from grain refinement, increased geometrically necessary dislocations, and stress partitioning between the Al matrix and the stiffer Si phase, aiding strain accommodation.  neutron diffraction reveals that the Si phase, with its higher yield strength, bears most of the load, while the Al matrix undergoes continuous strain hardening, extending deformation capacity. These results highlight Al10SiMg's promise for cryogenic applications such as hydrogen storage, aerospace, and quantum computing hardware.
neutron diffraction reveals that the Si phase, with its higher yield strength, bears most of the load, while the Al matrix undergoes continuous strain hardening, extending deformation capacity. These results highlight Al10SiMg's promise for cryogenic applications such as hydrogen storage, aerospace, and quantum computing hardware.
 GeTe
GeTe to hydrostatic pressure
to hydrostatic pressureWang, Y.*; Zeng, X.-T.*; Li, B.*; Su, C.*; 服部 高典; Sheng, X.-L.*; Jin, W.*
Chinese Physics B, 34(4), p.046203_1 - 046203_6, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)二次元ファンデルワールス強磁性体Fe GeTe
GeTe (FGT)は、その高いキュリー温度、容易な調整性、空気中での優れた構造安定性から、スピントロニクスデバイスへの応用に大きな可能性を秘めている。理論的研究により、外部パラメータとしての圧力が強磁性特性に大きく影響することが示されている。本研究では、5GPaまでの高圧中性子粉末回折(NPD)実験を行い、FGTの静水圧による構造及び磁気特性の変化を調べた。NPDデータは、静水圧による見かけ上の抑制にもかかわらず、FGTにおける強磁性の頑健性を明らかにした。圧力が0から5GPaまで増加すると、キュリー温度は225(5)Kから175(5)Kまで単調減少し、Feの秩序モーメントが劇的に抑制されることがわかった。圧力による構造相転移は5GPaまで観測されなかったが、結合長と結合角の変化を定量的に解析した結果、交換相互作用が大きく変化していることがわかった。
(FGT)は、その高いキュリー温度、容易な調整性、空気中での優れた構造安定性から、スピントロニクスデバイスへの応用に大きな可能性を秘めている。理論的研究により、外部パラメータとしての圧力が強磁性特性に大きく影響することが示されている。本研究では、5GPaまでの高圧中性子粉末回折(NPD)実験を行い、FGTの静水圧による構造及び磁気特性の変化を調べた。NPDデータは、静水圧による見かけ上の抑制にもかかわらず、FGTにおける強磁性の頑健性を明らかにした。圧力が0から5GPaまで増加すると、キュリー温度は225(5)Kから175(5)Kまで単調減少し、Feの秩序モーメントが劇的に抑制されることがわかった。圧力による構造相転移は5GPaまで観測されなかったが、結合長と結合角の変化を定量的に解析した結果、交換相互作用が大きく変化していることがわかった。
Naeem, M.*; Ma, Y.*; Tian, J.*; Kong, H.*; Romero-Resendiz, L.*; Fan, Z.*; Jiang, F.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Wu, Z.*; et al.
Materials Science & Engineering A, 924, p.147819_1 - 147819_10, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Face-centered cubic (fcc) medium-/high-entropy alloys (M/HEAs) typically enhance strength and ductility at cryogenic temperatures via stacking faults, twinning, or martensitic transformation. However, in-situ neutron diffraction on VCoNi MEA at 15 K reveals that strain hardening is driven solely by rapid dislocation accumulation, without these mechanisms. This results in increased yield strength, strain hardening, and fracture strain. The behavior, explained by the Orowan equation, challenges conventional views on cryogenic strengthening in fcc M/HEAs and highlights the role of dislocation-mediated plasticity at low temperatures.
Yang, X.*; Che, G.*; Wang, Y.*; Zhang, P.*; Tang, X.*; Lang, P.*; Gao, D.*; Wang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; 服部 高典; et al.
Nano Letters, 25(3), p.1028 - 1035, 2025/01
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)飽和sp -カーボンナノスレッド(CNTh)は、その高いヤング率と熱伝導率が予測され、大きな関心を集めている。中心環へのヘテロ原子の導入がCNThの形成に影響を与え、化学的に均質な生成物が得られることが示されているが、ペンダント基が重合プロセスに与える影響については、まだ未解明である。本研究では、フェノールの圧力誘起重合を調べ、0.5GPaと4GPa以下で起こる2つの相転移を明らかにした。20GPa以上では、フェノールは水酸基とカルボニル基を持つ重合度4のCNTに重合する。ヒドロキシル基の水素移動は、重合度6のナノスレッドの形成を妨げることがわかった。この発見は、さらなるカラム内重合を阻止する水酸基の重要な役割を浮き彫りにし、今後のメカニズム研究やナノ材料合成に貴重な示唆を与えるものである。
-カーボンナノスレッド(CNTh)は、その高いヤング率と熱伝導率が予測され、大きな関心を集めている。中心環へのヘテロ原子の導入がCNThの形成に影響を与え、化学的に均質な生成物が得られることが示されているが、ペンダント基が重合プロセスに与える影響については、まだ未解明である。本研究では、フェノールの圧力誘起重合を調べ、0.5GPaと4GPa以下で起こる2つの相転移を明らかにした。20GPa以上では、フェノールは水酸基とカルボニル基を持つ重合度4のCNTに重合する。ヒドロキシル基の水素移動は、重合度6のナノスレッドの形成を妨げることがわかった。この発見は、さらなるカラム内重合を阻止する水酸基の重要な役割を浮き彫りにし、今後のメカニズム研究やナノ材料合成に貴重な示唆を与えるものである。
Che, G.*; Fei, Y.*; Tang, X.*; Zhao, Z.*; 服部 高典; 阿部 淳*; Wang, X.*; Ju, J.*; Dong, X.*; Wang, Y.*; et al.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 27(2), p.1112 - 1118, 2025/01
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:65.57(Chemistry, Physical)芳香族分子の圧力誘起重合(PIP)は、様々な炭素系材料を合成するための効果的な方法として浮上してきた。目的とする構造や機能を得るためには、適切な官能基化された分子前駆体の選択が極めて重要である。本研究では、1,4-ジフルオロベンゼン(1,4-DFB)をPIPの構成要素として選択した。1,4-DFBをその場高圧で調べた結果、約12.0GPaで相転移が起こり、18.7GPaで不可逆的な化学反応が起こることがわかった。生成物の構造解析と反応のカイネティクスから、直線的な成長を伴う擬六方晶積層フッ素ダイヤモンドナノスレッドの形成が明らかになった。高圧下のベンゼンの結晶構造と比較して、1,4-DFBは[001]軸に沿って高い圧縮を示す。この異方的な圧縮は、[01 ]軸に沿ったより強いH
]軸に沿ったより強いH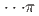 相互作用と、[100]軸と[010]軸に沿った潜在的な圧縮阻害H
相互作用と、[100]軸と[010]軸に沿った潜在的な圧縮阻害H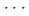 F相互作用に起因し、[01
F相互作用に起因し、[01 ]軸に沿った可能な反応経路を促進する。この研究は、分子スタッキングを調節し、反応経路に影響を与える官能基化の重要な役割を強調している。
]軸に沿った可能な反応経路を促進する。この研究は、分子スタッキングを調節し、反応経路に影響を与える官能基化の重要な役割を強調している。
Xu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Liang, S.*; Zhang, J.*; Fei, Y.*; Wang, Y.*; Gao, D.*; 服部 高典; 阿部 淳*; Dong, X.*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), p.2445 - 2451, 2025/00
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)アルダー-エン反応は、アルケンとアリル水素との化学反応であり、C-C結合を構築する効率的な方法である。従来、この反応には触媒、高温、あるいは光触媒が必要であった。本研究では、触媒を用いずに室温下で加圧することで成功した1-ヘキセンのアルダー-エン反応を報告する。1-ヘキセンは4.3GPaで結晶化し、18GPaで重合してオレフィンを形成する。ガスクロマトグラフィー-質量分析法により、1-ヘキセンが高圧下でのアルダー-エン反応により二量体を生成することを発見した。その場中性子回折から、この反応過程はトポケミカル則に従わないことがわかった。理論計算により、1つのC-H  結合と2つのアルケン
結合と2つのアルケン 結合を含む6員環遷移状態が示され、そのエネルギーは20GPaまで圧縮すると明らかに減少した。本研究は、触媒を用いずに室温でアルダー-エン反応を実現する新規かつ有望な方法を提供し、この重要な反応の応用を拡大するものである。
結合を含む6員環遷移状態が示され、そのエネルギーは20GPaまで圧縮すると明らかに減少した。本研究は、触媒を用いずに室温でアルダー-エン反応を実現する新規かつ有望な方法を提供し、この重要な反応の応用を拡大するものである。
Liu, P.-F.*; Li, X.*; Li, J.*; Zhu, J.*; Tong, Z.*; 古府 麻衣子*; 楡井 真実; Xu, J.*; Yin, W.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
National Science Review, 11(12), p.nwae216_1 - nwae216_10, 2024/12
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:91.22(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Crystalline solids exhibiting inherently low lattice thermal conductivity ( ) are of great importance in applications such as thermoelectrics and thermal barrier coatings. However,
) are of great importance in applications such as thermoelectrics and thermal barrier coatings. However,  cannot be arbitrarily low and is limited by the minimum thermal conductivity related to phonon dispersions. In this work, we report the liquid-like thermal transport in a well-ordered crystalline CsAg
cannot be arbitrarily low and is limited by the minimum thermal conductivity related to phonon dispersions. In this work, we report the liquid-like thermal transport in a well-ordered crystalline CsAg Te
Te , which exhibits an extremely low
, which exhibits an extremely low  value of
value of  0.18 Wm
0.18 Wm K
K . On the basis of first-principles calculations and inelastic neutron scattering measurements, we find that there are lots of low-lying optical phonon modes at
. On the basis of first-principles calculations and inelastic neutron scattering measurements, we find that there are lots of low-lying optical phonon modes at  3.1 meV hosting the avoided-crossing behavior with acoustic phonons. These strongly localized modes are accompanied by weakly bound rattling Ag atoms with thermally induced large amplitudes of vibrations. Using the two-channel model, we demonstrate that coupling of the particle-like phonon modes and the heat-carrying wave-like phonons is essential for understanding the low
3.1 meV hosting the avoided-crossing behavior with acoustic phonons. These strongly localized modes are accompanied by weakly bound rattling Ag atoms with thermally induced large amplitudes of vibrations. Using the two-channel model, we demonstrate that coupling of the particle-like phonon modes and the heat-carrying wave-like phonons is essential for understanding the low  , which is heavily deviated from the
, which is heavily deviated from the 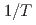 temperature dependence of the standard Peierls theory. In addition, our analysis indicates that the soft structural framework with liquid-like motions of the fluctuating Ag atoms is the underlying cause that leads to the suppression of the heat conduction in CsAg
temperature dependence of the standard Peierls theory. In addition, our analysis indicates that the soft structural framework with liquid-like motions of the fluctuating Ag atoms is the underlying cause that leads to the suppression of the heat conduction in CsAg Te
Te . These factors synergistically account for the ultralow
. These factors synergistically account for the ultralow  value. Our results demonstrate that the liquid-like heat transfer could indeed exist in a well-ordered crystal.
value. Our results demonstrate that the liquid-like heat transfer could indeed exist in a well-ordered crystal.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionNaeem, M.*; Ma, Y.*; Knowles, A. J.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Wang, X.-L.*; Romero Resendiz, L.*; 他6名*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 916, p.147374_1 - 147374_8, 2024/11
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:63.37(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Heterostructured materials (HSMs) improve the strength-ductility trade-off of alloys, but their cryogenic performance under real-time deformation is unclear. We studied heterostructured CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy via  neutron diffraction at 77 K and 293 K. A significant mechanical mismatch between fine and coarse grains led to an exceptional yield strength of 918 MPa at 293 K, increasing to 1244 MPa at 77 K with a uniform elongation of 34%. This strength-ductility synergy at 77 K is attributed to high dislocation pile-up density, increased planar faults, and martensitic transformation. Compared to homogeneous alloys, HSMs show promise for enhancing cryogenic mechanical performance in medium-/high-entropy alloys.
neutron diffraction at 77 K and 293 K. A significant mechanical mismatch between fine and coarse grains led to an exceptional yield strength of 918 MPa at 293 K, increasing to 1244 MPa at 77 K with a uniform elongation of 34%. This strength-ductility synergy at 77 K is attributed to high dislocation pile-up density, increased planar faults, and martensitic transformation. Compared to homogeneous alloys, HSMs show promise for enhancing cryogenic mechanical performance in medium-/high-entropy alloys.
 -
- transitions
transitionsYang, Q.*; Yang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Fei, Y.*; Li, F.*; Zheng, H.*; Li, K.*; Han, Y.*; 服部 高典; Zhu, P.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.7778_1 - 7778_9, 2024/09
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:88.46(Multidisciplinary Sciences)明るい一重項励起子と三重項励起子を同時に発現する発光材料は、オプトエレクトロニクス、サイネージ、情報暗号化において大きな可能性を秘めている。しかしながら、高性能の白色発光を実現するためには、蛍光と燐光の寄与が不均衡であることが大きな障害となっている。ここでは、水素結合の協同効果による圧力処理エンジニアリングによって、n- -
- 遷移の混合を実現し、イソフタル酸(IPA)中で三重項状態の発光を7%から40%に高めることで、この課題に対処した。加圧処理したIPAでは、蛍光と燐光のハイブリッドに基づく優れた白色発光が得られ、フォトルミネッセンス量子収率は当初の19%(青色発光)から75%に増加した。その場での高圧IRスペクトル、X線回折、中性子回折から、圧力の上昇に伴い水素結合が連続的に強化されることが明らかになった。さらに、この強化された水素結合は、圧力処理後も常圧条件下まで保持され、バランスの取れた一重項/三重項励起子集団のための効率的な系間交差を目的としたIPAに与え、効率的な白色発光をもたらした。この研究は、有機低分子の三重項状態を明るくするルートを提案するだけでなく、一重項励起子と三重項励起子の比率を調節して、高性能の白色発光を構築するものである。
遷移の混合を実現し、イソフタル酸(IPA)中で三重項状態の発光を7%から40%に高めることで、この課題に対処した。加圧処理したIPAでは、蛍光と燐光のハイブリッドに基づく優れた白色発光が得られ、フォトルミネッセンス量子収率は当初の19%(青色発光)から75%に増加した。その場での高圧IRスペクトル、X線回折、中性子回折から、圧力の上昇に伴い水素結合が連続的に強化されることが明らかになった。さらに、この強化された水素結合は、圧力処理後も常圧条件下まで保持され、バランスの取れた一重項/三重項励起子集団のための効率的な系間交差を目的としたIPAに与え、効率的な白色発光をもたらした。この研究は、有機低分子の三重項状態を明るくするルートを提案するだけでなく、一重項励起子と三重項励起子の比率を調節して、高性能の白色発光を構築するものである。
Zhu, L.*; He, H.*; Naeem, M.*; Sun, X.*; Qi, J.*; Liu, P.*; Harjo, S.; 中島 健次; Li, B.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Physical Review Letters, 133(12), p.126701_1 - 126701_6, 2024/09
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:48.32(Physics, Multidisciplinary)It has long been suspected that magnetism could play a vital role in the phase stability of multi- component high-entropy alloys. However, the nature of the magnetic order, if any, has remained elusive. Here, by using elastic and inelastic neutron scattering, we demonstrate evidence of antiferromagnetic order below  80 K and strong spin fluctuations persisting to room temperature in a single-phase face-centered cubic (fcc) CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. Despite the chemical complexity, the magnetic structure in CrMnFeCoNi can be described as
80 K and strong spin fluctuations persisting to room temperature in a single-phase face-centered cubic (fcc) CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. Despite the chemical complexity, the magnetic structure in CrMnFeCoNi can be described as  -Mn-like, with the magnetic moments confined in alternating (001) planes and pointing toward the
-Mn-like, with the magnetic moments confined in alternating (001) planes and pointing toward the 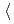 111
111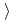 direction. Combined with first-principles calculation results, it is shown that the antiferromagnetic order and spin fluctuations help stabilized the fcc phase in CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy.
direction. Combined with first-principles calculation results, it is shown that the antiferromagnetic order and spin fluctuations help stabilized the fcc phase in CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy.
 Zr +
Zr +  at 27 MeV/nucleon
at 27 MeV/nucleonHwang, J.*; Chillery, T.*; 堂園 昌伯*; 今井 伸明*; 道正 新一郎*; 炭竃 聡之*; 千賀 信幸*; 大田 晋輔*; 中山 梓介; 他49名*
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2024(9), p.093D03_1 - 093D03_12, 2024/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)核変換は高レベル廃棄物の再処理、特に使用済み燃料から Zrのような長寿命核種を処理するための有望な手段であると考えられている。これらの核種に対する核反応データを蓄積することは、核変換の検討や反応機構を包括的に理解するために不可欠である。本研究では、
Zrのような長寿命核種を処理するための有望な手段であると考えられている。これらの核種に対する核反応データを蓄積することは、核変換の検討や反応機構を包括的に理解するために不可欠である。本研究では、 Zrに対する陽子入射反応からの残留核生成断面積を、核子当たり27MeVのエネルギーで逆運動学法を用いて測定した。理研RIBFのOEDOビームラインを用いて、
Zrに対する陽子入射反応からの残留核生成断面積を、核子当たり27MeVのエネルギーで逆運動学法を用いて測定した。理研RIBFのOEDOビームラインを用いて、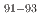 Nb,
Nb, 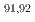 Zr,
Zr, 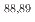 Yの各同位体の生成断面積を導出した。励起関数について、TALYSやCCONEによる理論予測は、本研究や先行研究の実験値と概ね良い一致を示した。本研究で測定された断面積は、廃棄物処理に関する将来の検討のための貴重なデータとなる。
Yの各同位体の生成断面積を導出した。励起関数について、TALYSやCCONEによる理論予測は、本研究や先行研究の実験値と概ね良い一致を示した。本研究で測定された断面積は、廃棄物処理に関する将来の検討のための貴重なデータとなる。
Ying, H.*; Yang, X.*; He, H.*; Yan, A.*; An, K.*; Ke, Y.*; Wu, Z.*; Tang, S.*; Zhang, Z.*; Dong, H.*; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 250, p.116181_1 - 116181_7, 2024/09
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:41.92(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Nanoscale chemical fluctuations and their effect on the deformation behavior of CrFeCoNi-based high-entropy alloys (HEAs) were investigated using small-angle scattering and in situ neutron diffraction measurements. Small-angle scattering results demonstrated the presence of nano ( 10 nm) chemical fluctuations in the as-prepared CrFeCoNiPd HEAs, which was attributed to the negative mixing of enthalpy and the significant atomic radius difference between Pd and the constituent elements in the CrFeCoNi-based alloys. Subsequent tensile tests demonstrated that the yield and tensile strengths of the as-prepared CrFeCoNiPd HEA surpass those of the as-prepared CrMnFeCoNi HEA. Neutron diffraction data analysis revealed an anomalous response of dislocation evolution with the strain.
10 nm) chemical fluctuations in the as-prepared CrFeCoNiPd HEAs, which was attributed to the negative mixing of enthalpy and the significant atomic radius difference between Pd and the constituent elements in the CrFeCoNi-based alloys. Subsequent tensile tests demonstrated that the yield and tensile strengths of the as-prepared CrFeCoNiPd HEA surpass those of the as-prepared CrMnFeCoNi HEA. Neutron diffraction data analysis revealed an anomalous response of dislocation evolution with the strain.
Wang, Y.*; Gong, W.; Su, Y. H.; Li, B.*
Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 60(8), p.1001 - 1016, 2024/08
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:41.92(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)The correlation between the atomic structure, microstructure, and macroscopic properties of structural materials remains a core issue in materials research. In recent years, substantial progress has been achieved in constructing accelerator-based neutron sources and related experimental techniques, offering a robust platform for an in-depth understanding of the aforementioned correlation under real-time and in situ conditions. This article reviews the latest advancements in the application of major neutron characterization techniques, including neutron diffraction, Bragg-edge imaging, small-angle neutron scattering, pair distribution function analysis, and quasi-elastic/inelastic neutron scattering, in structural materials. Furthermore, it particularly highlights the origins and evolution of internal stresses during the phase transformations of steels, deformation mechanisms in light metals such as magnesium alloys, and microstructure and residual stress analyses using Bragg-edge imaging. Finally, a brief outlook on future development trends is provided.
Wang, Y. W.*; 徐 平光; Su, Y. H.; Ma, Y. L.*; Wang, H. H.*
Physics Examination and Testing, 42(4), p.32 - 41, 2024/08
With the rapid technological development of large spallation neutron source facilities, the neutron beam flux obtained has been greatly improved and neutron imaging techniques have been further developed. Due to the limitation of neutron beam flux, conventional neutron imaging techniques require neutron beams with a wide wavelength range to obtain relatively high neutron beam flux conditions. Recently, spallation neutron sources using large proton accelerators have made it possible to obtain high-flux pulsed neutron beams. Energy (wavelength) resolved neutron imaging technique based on the Bragg edge effect (neutron Bragg edge transmission imaging technique) is expected to have a wide range of applications because of its high energy resolution, high spatial resolution, and ability to detect crystallographic information. The basic principle of this technique is briefly introduced. Several applications in the evaluation of residual strain, phase composition, dislocation density, and oriented structure are also reviewed to play an active role in promoting the wider applications of related technique.
Wang, S.*; Wang, J.*; Zhang, S.*; Wei, D.*; Chen, Y.*; Rong, X.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Liu, X.*; Jiao, Z.*; et al.
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 185, p.245 - 258, 2024/06
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:97.90(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nanoprecipitates and nanoscale retained austenite (RA) with suitable stability play crucial roles in determining the yield strength (YS) and ductility of ultrahigh strength steels (UHSSs). However, owing to the kinetics incompatibility between nanoprecipitation and austenite reversion, it is highly challenging to simultaneously introduce high-density nanoprecipitates and optimized RA in UHSSs. In this work, through the combination of austenite reversion treatment (ART) and subsequent flash austenitizing (FA), nanoscale chemical heterogeneity was successfully introduced into a low-cost UHSS prior to the aging process. This chemical heterogeneity involved the enrichment of Mn and Ni in the austenite phase. The resulting UHSS exhibited dual-nanoprecipitation of Ni(Al,Mn) and (Mo,Cr) C and nanoscale austenite stabilized via Mn and Ni enrichment. The hard martensitic matrix strengthened by high-density dual-nanoprecipitates constrains the plastic deformation of soft RA with a relatively low fraction, and the presence of relatively stable nanoscale RA with adequate Mn and Ni enrichment leads to a marginal loss in YS but keeps a persistent transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect. As a result, the newly-developed UHSS exhibits an ultrahigh YS of 1.7 GPa, an ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 1.8 GPa, a large uniform elongation (UE) of 8.5 percent, and a total elongation (TE) of 13 percent. The strategy of presetting chemical heterogeneity to introduce proper metastable phases before aging can be extended to other UHSSs and precipitation-hardened alloys.
C and nanoscale austenite stabilized via Mn and Ni enrichment. The hard martensitic matrix strengthened by high-density dual-nanoprecipitates constrains the plastic deformation of soft RA with a relatively low fraction, and the presence of relatively stable nanoscale RA with adequate Mn and Ni enrichment leads to a marginal loss in YS but keeps a persistent transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect. As a result, the newly-developed UHSS exhibits an ultrahigh YS of 1.7 GPa, an ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 1.8 GPa, a large uniform elongation (UE) of 8.5 percent, and a total elongation (TE) of 13 percent. The strategy of presetting chemical heterogeneity to introduce proper metastable phases before aging can be extended to other UHSSs and precipitation-hardened alloys.
 C
CNguyen, B. V. C.*; 村上 健太*; Chena, L.*; Phongsakorn, P. T.*; Chen, X.*; 橋本 貴司; Hwang, T.*; 古澤 彰憲; 鈴木 達也*
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 39, p.101639_1 - 101639_9, 2024/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)In reactor pressure vessel materials, the formation of Mn- and Ni-rich nanoclusters is a major cause of neutron irradiation embrittlement. The segregation of these solute atoms into dislocation loops has attracted attention as a mechanism to accelerate solute clustering. In this study, the behaviors of solute Mn and Ni atoms in Fe-0.6wt.%Ni, Fe-1.4wt.%Mn, and Fe-1.4wt.%Mn-0.6wt.%Ni alloys irradiated at 400  C up to 3 dpa were analyzed using three-dimensional atom probe tomography. Solute atom clusters were observed in all materials, and their shapes were spherical, flat, and torus in FeNi, FeMn, and FeMnNi, respectively. In ternary alloy FeMnNi, Mn and Ni atoms were concentrated in the sample in the form of arcs, and the orientation of the plane containing the arcs was estimated by comparing field desorption images. The size, number density, and orientation of this structure were found to be in good agreement with those of both types of dislocation loops, namely, b = 1/2
C up to 3 dpa were analyzed using three-dimensional atom probe tomography. Solute atom clusters were observed in all materials, and their shapes were spherical, flat, and torus in FeNi, FeMn, and FeMnNi, respectively. In ternary alloy FeMnNi, Mn and Ni atoms were concentrated in the sample in the form of arcs, and the orientation of the plane containing the arcs was estimated by comparing field desorption images. The size, number density, and orientation of this structure were found to be in good agreement with those of both types of dislocation loops, namely, b = 1/2  111
111 and b =
and b =  100
100 , identified in a previous study using the same material. The positions of Ni and Mn enrichment did not fully overlap. Ni atoms tended to be concentrated more in the inner part of the loop than the Mn atoms. Mn atoms were enriched only in the vicinity of the dislocation loops, whereas Ni atoms showed a higher concentration inside the dislocation loops than in the bulk.
, identified in a previous study using the same material. The positions of Ni and Mn enrichment did not fully overlap. Ni atoms tended to be concentrated more in the inner part of the loop than the Mn atoms. Mn atoms were enriched only in the vicinity of the dislocation loops, whereas Ni atoms showed a higher concentration inside the dislocation loops than in the bulk.
Ma, Y.*; Naeem, M.*; Zhu, L.*; He, H.*; Sun, X.*; Yang, Z.*; He, F.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Wang, X.-L.*
Acta Materialia, 270, p.119822_1 - 119822_13, 2024/05
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:95.42(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report an in situ neutron diffraction study of 316 L that reveals an extraordinary work-hardening rate (WHR) of  7 GPa at 15 K. Detailed analyses show that the major contribution to the excellent strength and ductility comes from the transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect, introduced by the austenite-to-martensite (
7 GPa at 15 K. Detailed analyses show that the major contribution to the excellent strength and ductility comes from the transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect, introduced by the austenite-to-martensite ( -to-
-to- ') phase transition. A dramatic increase in the WHR is observed along with the transformation; the WHR declined when the austenite phase is exhausted. During plastic deformation, the volume-fraction weighted phase stress and stress contribution from the
') phase transition. A dramatic increase in the WHR is observed along with the transformation; the WHR declined when the austenite phase is exhausted. During plastic deformation, the volume-fraction weighted phase stress and stress contribution from the  '-martensite increase significantly. The neutron diffraction data further suggest that the
'-martensite increase significantly. The neutron diffraction data further suggest that the  -to-
-to- ' phase transformation was mediated by the
' phase transformation was mediated by the  -martensite, as evidenced by the concurrent decline of the
-martensite, as evidenced by the concurrent decline of the  phase with the
phase with the  phase.
phase.
土屋 晴文; 日比野 欣也*; 川田 和正*; 大西 宗博*; 瀧田 正人*; 宗像 一起*; 加藤 千尋*; 霜田 進*; Shi, Q.*; Wang, S.*; et al.
Progress of Earth and Planetary Science (Internet), 11, p.26_1 - 26_14, 2024/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)From 1998 to 2017, neutron monitors located at an altitude of 4300 m on the Tibetan plateau detected 127 long-duration bursts of high-energy radiation in association with thunderclouds. These bursts typically lasted for 10-40 min, and 89% of them occurred between 10:00 and 24:00 local time. They were also found to be more likely to occur at night, especially during 18:00-06:00 local time period. The observed diurnal and seasonal variations in burst frequency were consistent with the frequencies of lightning and precipitation on the Tibetan plateau. Based on 19 years of data, the present study suggests that an annual variation in burst frequency has a periodicity of  16 years and a lag of
16 years and a lag of  3 years relative to solar activity.
3 years relative to solar activity.
 -MgAgSb
-MgAgSbLi, J.*; Li, X.*; Zhang, Y.*; Zhu, J.*; Zhao, E.*; 古府 麻衣子; 中島 健次; Avdeev, M.*; Liu, P.-F.*; Sui, J.*; et al.
Applied Physics Reviews (Internet), 11(1), p.011406_1 - 011406_8, 2024/03
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:91.57(Physics, Applied)The desire for intrinsically low lattice thermal conductivity (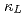 ) in thermoelectrics motivates numerous efforts on understanding the microscopic mechanisms of heat transport in solids. Here, based on theoretical calculations, we demonstrate that
) in thermoelectrics motivates numerous efforts on understanding the microscopic mechanisms of heat transport in solids. Here, based on theoretical calculations, we demonstrate that  -MgAgSb hosts low-energy localized phonon bands and avoided crossing of the rattler modes, which coincides with the inelastic neutron scattering result. Using the two-channel lattice dynamical approach, we find, besides the conventional contribution (
-MgAgSb hosts low-energy localized phonon bands and avoided crossing of the rattler modes, which coincides with the inelastic neutron scattering result. Using the two-channel lattice dynamical approach, we find, besides the conventional contribution ( 70% at 300 K) from particlelike phonons propagating, the coherence contribution dominated by the wavelike tunneling of phonons accounts for
70% at 300 K) from particlelike phonons propagating, the coherence contribution dominated by the wavelike tunneling of phonons accounts for  30% of total
30% of total 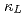 at 300 K. By considering dual contributions, our calculated room-temperature
at 300 K. By considering dual contributions, our calculated room-temperature 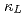 of 0.64 Wm
of 0.64 Wm K
K well agrees with the experimental value of 0.63 Wm
well agrees with the experimental value of 0.63 Wm K
K . More importantly, our computations give a nonstandard
. More importantly, our computations give a nonstandard 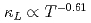 dependence, perfectly explaining the abnormal temperature-trend of
dependence, perfectly explaining the abnormal temperature-trend of 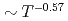 in experiment for
in experiment for  -MgAgSb. By molecular dynamics simulation, we reveal that the structure simultaneously has soft crystalline sublattices with the metavalent bonding and fluctuating liquid-like sublattices with thermally induced large amplitude vibrations. These diverse forms of chemical bonding arouse mixed part-crystal part-liquid state, scatter strongly heat-carrying phonons, and finally produce extremely low
-MgAgSb. By molecular dynamics simulation, we reveal that the structure simultaneously has soft crystalline sublattices with the metavalent bonding and fluctuating liquid-like sublattices with thermally induced large amplitude vibrations. These diverse forms of chemical bonding arouse mixed part-crystal part-liquid state, scatter strongly heat-carrying phonons, and finally produce extremely low 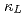 . The fundamental research from this study will accelerate the design of ultralow-
. The fundamental research from this study will accelerate the design of ultralow-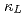 materials for energy-conversion applications.
materials for energy-conversion applications.