Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wang, Z.; 松本 俊慶; 柴本 泰照; Duan, G.*
Journal of Computational Physics, 537, p.114072_1 - 114072_29, 2025/09
被引用回数:0In this study, we develop a novel sharp surface tension (SST) model for multiphase particle methods. Our approach integrates surface tension directly into pressure computation, enabling precise representation of pressure discontinuities across interfaces and effectively mitigating parasitic currents. In addition, to improve curvature accuracy, particularly in scenarios involving topological changes, a co-directional scheme is proposed to faithfully consider interfacial normal vectors. Furthermore, we reconstruct the interfacial particle shifting scheme to separately address tangential, normal, and repulsive components, effectively suppressing the common problem of interface particle mixing in multiphase particle methods. The effectiveness and reliability are rigorously validated through a series of numerical tests, including the Rayleigh-Taylor instability, curvature verification, droplet deformation and coalescence, as well as bubble rising and coalescence. The results demonstrate the superior accuracy and robustness of the proposed method, marking a significant advancement in simulations of multiphase flow with surface tension.
Sahboun, N. F.; 松本 俊慶; 岩澤 譲; Wang, Z.; 杉山 智之
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 195, p.110145_1 - 110145_12, 2024/01
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:43.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)Relocated corium into the Primary Containment Vessel needs to be properly cooled to avoid or mitigate molten core concrete interactions in the PCV in order to maintain its supporting capability for the reactor pressure vessel and to suppress combustible or non-condensable gas releases. To know how effective the cooling is, it became important to know the geometry of the relocated corium. The present study chooses to focus on the "Wet Cavity" strategy and to build a reliable tool to evaluate the corium coolability in such a case. To achieve this goal, a previously developed formulation built to predict the corium geometry under the "Dry Cavity" strategy was extended to the conditions used in the "Wet Cavity" strategy. This extension includes the effect of solidification and cooling from the water by using a newly developed expression for the dimensionless thickness s, the water subcooling, and the melts super heat. After the validation of the extended formulation was confirmed, potential restrictions and limitations were investigated.
Wang, Z.
Computational Particle Mechanics, 15 Pages, 2024/00
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Mathematics, Interdisciplinary Applications)Particle methods, benefiting from the Lagrangian meshfree framework, have gained widespread application in free-surface flow simulations. Nonetheless, accurately modeling high-viscosity fluids remains a persistent challenge. In this study, we propose a new implicit moving particle simulation (IMPS) method specifically designed to address the complexities associated with high-viscous free-surface flows, tackling two main issues. Firstly, unlike the traditional Laplacian model, where orthogonal velocity components are treated as independent variables, this method enforces the velocity divergence-free constraint when discretizing the viscous term, effectively coupling the velocity components. This coupling is crucial for conserving angular momentum, especially in high-viscosity scenarios. Secondly, to overcome the time step restrictions imposed by high viscosity, a novel implicit calculation algorithm has been developed. This algorithm enables the simultaneous and implicit solution of pressure and velocity, ensuring the precise application of both free-surface and wall boundary conditions. The effectiveness of the IMPS method is rigorously verified through simulations, including a rotational flow in a circular pipe and a square fluid dropping from a platform. The results indicate that the developed method successfully captures the dynamics of high-viscous free-surface flows, demonstrating its potential for broader applications.
Zhang, A.*; Deng, K.*; Sheng, J.*; Liu, P.*; Kumar, S.*; 島田 賢也*; Jiang, Z.*; Liu, Z.*; Shen, D.*; Li, J.*; et al.
Chinese Physics Letters, 40(12), p.126101_1 - 126101_8, 2023/12
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:85.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In a Dirac semimetal, the massless Dirac fermion has zero chirality, leading to surface states connected adiabatically to a topologically trivial surface state as well as vanishing anomalous Hall effect. Recently, itis predicted that in the nonrelativistic limit of certain collinear antiferromagnets, there exists a type of chiral "Dirac-like" fermion, whose dispersion manifests four-fold degenerate crossing points formed by spin-degenerate linear bands, with topologically protected Fermi arcs. Here, by combining with neutron diffraction and first-principles calculations, we suggest a multidomain collinear antiferromagnetic configuration, rendering the existence of the Fermi-arc surface states induced by chiral Dirac-like fermions.
Wang, Z.; 松本 俊慶; Duan, G.*; 松永 拓也*
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 414, p.116168_1 - 116168_49, 2023/09
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:89.36(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)Recently, consistent meshfree particle methods have been intensively studied. It has been pointed out that numerical inaccuracy or instability could easily occur with incomplete or biased neighbor support. This study proposes a new meshfree particle method called the compact moving particle semi-implicit (CMPS) method to decrease the condition number. In the proposed CMPS, the first-order and second-order derivatives are discretized separately, enhancing the numerical stability significantly. By adopting a small dilation parameter of the compact support, the CMPS can remarkably improve accuracy and reduce computational costs. Formulations for zeroth-order, first-order, and second-order derivatives are derived, and various boundary conditions, e.g., Dirichlet and Neumann, are discussed. In order to better deal with complex free-surface flows using the CMPS, some new numerical techniques, i.e., optimized regularization and reconstructed particle shifting schemes, are also developed. Furthermore, the surface fitting method is extended to address the surface tension. A convergence study is conducted in complex geometry to verify the stability, accuracy, and efficiency of the CMPS. Then, second-order accuracy is confirmed using the Taylor-Green vortex problem. After that, numerical examples concerning various free-surface flows, including square patch, hydrostatic pressure, dam break, droplet oscillation, and droplet coalescence, are calculated to demonstrate the potential of the CMPS.
Bao, S.*; Gu, Z.-L.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, B.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Wang, W.*; 梶本 亮一; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.6093_1 - 6093_9, 2023/09
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:92.84(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Magnon polarons are novel elementary excitations possessing hybrid magnonic and phononic signatures, and are responsible for many exotic spintronic and magnonic phenomena. Despite long-term sustained experimental efforts in chasing for magnon polarons, direct spectroscopic evidence of their existence is hardly observed. Here, we report the direct observation of magnon polarons using neutron spectroscopy on a multiferroic Fe Mo
Mo O
O possessing strong magnon-phonon coupling. Specifically, below the magnetic ordering temperature, a gap opens at the nominal intersection of the original magnon and phonon bands, leading to two separated magnon-polaron bands. Each of the bands undergoes mixing, interconverting and reversing between its magnonic and phononic components. We attribute the formation of magnon polarons to the strong magnon-phonon coupling induced by Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction. Intriguingly, we find that the band-inverted magnon polarons are topologically nontrivial. These results uncover exotic elementary excitations arising from the magnon-phonon coupling, and offer a new route to topological states by considering hybridizations between different types of fundamental excitations.
possessing strong magnon-phonon coupling. Specifically, below the magnetic ordering temperature, a gap opens at the nominal intersection of the original magnon and phonon bands, leading to two separated magnon-polaron bands. Each of the bands undergoes mixing, interconverting and reversing between its magnonic and phononic components. We attribute the formation of magnon polarons to the strong magnon-phonon coupling induced by Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction. Intriguingly, we find that the band-inverted magnon polarons are topologically nontrivial. These results uncover exotic elementary excitations arising from the magnon-phonon coupling, and offer a new route to topological states by considering hybridizations between different types of fundamental excitations.
 SnSe
SnSe
Ren, Q.*; Gupta, M. K.*; Jin, M.*; Ding, J.*; Wu, J.*; Chen, Z.*; Lin, S.*; Fabelo, O.*; Rodriguez-Velamazan, J. A.*; 古府 麻衣子; et al.
Nature Materials, 22(8), p.999 - 1006, 2023/08
被引用回数:78 パーセンタイル:99.19(Chemistry, Physical)Ultralow thermal conductivity and fast ionic diffusion endow superionic materials with excellent performance both as thermoelectric converters and as solid-state electrolytes. Yet the correlation and interdependence between these two features remain unclear owing to a limited understanding of their complex atomic dynamics. Here we investigate ionic diffusion and lattice dynamics in argyrodite Ag SnSe
SnSe using synchrotron X-ray and neutron scattering techniques along with machine-learned molecular dynamics. We identify a critical interplay of the vibrational dynamics of mobile Ag and a host framework that controls the overdamping of low-energy Ag-dominated phonons into a quasi-elastic response, enabling superionicity. Concomitantly, the persistence of long-wavelength transverse acoustic phonons across the superionic transition challenges a proposed 'liquid-like thermal conduction' picture. Rather, a striking thermal broadening of low-energy phonons, starting even below 50 K, reveals extreme phonon anharmonicity and weak bonding as underlying features of the potential energy surface responsible for the ultralow thermal conductivity (
using synchrotron X-ray and neutron scattering techniques along with machine-learned molecular dynamics. We identify a critical interplay of the vibrational dynamics of mobile Ag and a host framework that controls the overdamping of low-energy Ag-dominated phonons into a quasi-elastic response, enabling superionicity. Concomitantly, the persistence of long-wavelength transverse acoustic phonons across the superionic transition challenges a proposed 'liquid-like thermal conduction' picture. Rather, a striking thermal broadening of low-energy phonons, starting even below 50 K, reveals extreme phonon anharmonicity and weak bonding as underlying features of the potential energy surface responsible for the ultralow thermal conductivity ( 0.5 Wm
0.5 Wm K
K ) and fast diffusion. Our results provide fundamental insights into the complex atomic dynamics in superionic materials for energy conversion and storage.
) and fast diffusion. Our results provide fundamental insights into the complex atomic dynamics in superionic materials for energy conversion and storage.
 neutron diffraction study on the deformation behavior of the plastic inorganic semiconductor Ag
neutron diffraction study on the deformation behavior of the plastic inorganic semiconductor Ag S
SWang, Y.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; Zhang, K.*; Zhang, Z. D.*; Li, B.*
Applied Physics Letters, 123(1), p.011903_1 - 011903_6, 2023/07
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:47.87(Physics, Applied)Bulk Ag S is a plastic inorganic semiconductor at room temperature. It exhibits a compressive strain greater than 50%, which is highly different from brittle conventional counterparts, such as silicon. Here, we present the experimental investigation of the deformation behavior in a plastic inorganic semiconductor Ag
S is a plastic inorganic semiconductor at room temperature. It exhibits a compressive strain greater than 50%, which is highly different from brittle conventional counterparts, such as silicon. Here, we present the experimental investigation of the deformation behavior in a plastic inorganic semiconductor Ag S using
S using  neutron diffraction during compressive deformation at room and elevated temperatures. At room temperature, the lattice strain partitioning among
neutron diffraction during compressive deformation at room and elevated temperatures. At room temperature, the lattice strain partitioning among 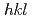 -orientated grain families could be responsible for the significant work-hardening behavior in the bulk Ag
-orientated grain families could be responsible for the significant work-hardening behavior in the bulk Ag S with a monoclinic structure. The rapid accumulation of lattice defects and remarkable development of the deformation texture suggest that dislocation slip promotes plasticity. At 453 K, a monoclinic phase transforms into a body-centered cubic phase. A stress plateau appears at
S with a monoclinic structure. The rapid accumulation of lattice defects and remarkable development of the deformation texture suggest that dislocation slip promotes plasticity. At 453 K, a monoclinic phase transforms into a body-centered cubic phase. A stress plateau appears at  -4.8 MPa, followed by a rehardening state. The deformation mode of bulk Ag
-4.8 MPa, followed by a rehardening state. The deformation mode of bulk Ag S at the initial stage is likely attributable to the migration of silver ions, and as strain increases, it is closer to that of room temperature, leading to rehardening.
S at the initial stage is likely attributable to the migration of silver ions, and as strain increases, it is closer to that of room temperature, leading to rehardening.
 ; Bandgap narrowing, metallization, and remarkable enhancement of photoelectric activity
; Bandgap narrowing, metallization, and remarkable enhancement of photoelectric activityFang, Y.*; Kong, L.*; Wang, R.*; Zhang, Z.*; Li, Z.*; Wu, Y.*; Bu, K.*; Liu, X.*; Yan, S.*; 服部 高典; et al.
Materials Today Physics (Internet), 34, p.101083_1 - 101083_7, 2023/05
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:72.60(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)層状ファンデルワールスハライドは、外部圧力に対して特に敏感であるため、目的とする性質を持つ構造にチューンすることが可能となる。一方で、圧力に非常に敏感であるという特性は、同時に目的とする機能の実現に有害な相転移や格子歪みを引き起こす可能性があるためその操作は依然として困難である。この研究では、層状RhI 結晶が持つ極めて弱い層間結合と高い機能可変性を観察した。5GPaという適度な圧力をかけると圧力誘起相転移が起こり、積層構造に変化が現れた。驚くべきことに、この相転移は、圧力に対してほぼ直線的なバンドギャップ減少という傾向に影響を与えなかった。また、より高い圧力では、1.3eVの赤方偏移というかなり大きな調整幅を伴う金属相が観測された。さらに、RhI
結晶が持つ極めて弱い層間結合と高い機能可変性を観察した。5GPaという適度な圧力をかけると圧力誘起相転移が起こり、積層構造に変化が現れた。驚くべきことに、この相転移は、圧力に対してほぼ直線的なバンドギャップ減少という傾向に影響を与えなかった。また、より高い圧力では、1.3eVの赤方偏移というかなり大きな調整幅を伴う金属相が観測された。さらに、RhI のキャリア濃度は30GPaで4桁増加し、光電流は7.8GPaで5桁増加することが確認された。これらの結果は、ファンデルワールスハライドの層状構造という特異な特徴を生かした探索、調整、理解のための新たな機会を創出し、原子レベルの薄さを持つマテリアルバイデザインに基づく将来のデバイスとして有望である。
のキャリア濃度は30GPaで4桁増加し、光電流は7.8GPaで5桁増加することが確認された。これらの結果は、ファンデルワールスハライドの層状構造という特異な特徴を生かした探索、調整、理解のための新たな機会を創出し、原子レベルの薄さを持つマテリアルバイデザインに基づく将来のデバイスとして有望である。
 -wave
-wave 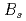 states combining quark model and lattice QCD in the coupled channel framework
states combining quark model and lattice QCD in the coupled channel frameworkYang, Z.*; Wang, G.-J.*; Wu, J.-J.*; 岡 眞; Zhu, S.-L.*
Journal of High Energy Physics (Internet), 2023(1), p.058_1 - 058_19, 2023/01
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:76.22(Physics, Particles & Fields)ハミルトニアン有効理論にクォーク模型、クォークペア生成、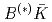 相互作用の情報を含むベアな状態と散乱状態の結合を取り入れた形式を用いて、しきい値近傍の
相互作用の情報を含むベアな状態と散乱状態の結合を取り入れた形式を用いて、しきい値近傍の 波の4個の
波の4個の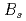 状態のスペクトルを研究した。
状態のスペクトルを研究した。
Li, G.*; Duan, G.*; Liu, X.*; Wang, Z.
Moving Particle Semi-implicit Method; Recent Developments and Applications, 266 Pages, 2023/00
Moving Particle Semi-implicit (MPS) method has experienced decades of research and development since it was firstly proposed in 1996. The advanced numerical models have been developed. As the MPS method is becoming mature and stable, more and more researchers are engaging in its development and applying it to the simulations of complex multicomponent and multiphase flow in engineering. This book provides a comprehensive overview of the advanced numerical models of MPS method, including the improved discretization scheme, stabilization method, boundary condition, multiphase flow and fluid-structure interaction. The applications in the fields of nuclear engineering and ocean engineering are summarized as well. It promotes a deep understanding of the current challenges and the future development directions of the MPS method. This book is a valuable reference resource for the researchers, engineers and postgraduates with an interest in computational fluid dynamics and meshless particle methods.
Wang, Z.; 杉山 智之
Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 144, p.279 - 300, 2022/11
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:57.79(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)Numerical simulation of gas bubbles rising in liquid is challenging due to high density and viscosity ratios. This study proposes to separately model the liquid and gas phases by the incompressible Moving Particle Semi-implicit (MPS) method and the Weakly Compressible MPS (WCMPS) method. The liquid-gas phase interface is explicitly represented by a series of discrete nodes. By adequately enforcing the stress balance equation on these moving interface nodes, the MPS and WCMPS methods are coupled. Rather than being treated as the volume force, the surface tension is considered as a pressure jump at the interface. Without applying any smoothing or averaging scheme, the density, viscosity and pressure are discontinuous across the interface. The axisymmetric formulation is directly introduced based on the least squares scheme to save computational cost. In addition, a multi-time step algorithm is proposed so that independent time increments can be adopted for different phases. Furthermore, the particle shifting technique is extended to control the multi-spatial resolution dynamically and maintain the particle distribution quasi-isotropic. Several numerical tests, including hydrostatic pressure problems, droplet deformation and bubble rising benchmark are conducted to show the accuracy, efficiency and stability. Finally, validations are performed using experimental results with wide ranges of Reynolds number and Bond number, which dominate the bubble shape.
Wang, Z.; 杉山 智之; 松永 拓也*; 越塚 誠一*
Computers & Fluids, 247, p.105646_1 - 105646_21, 2022/10
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:46.25(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)This paper develops a highly accurate, multi-resolution particle method to simulate solid-liquid phase change coupled with the thermal flow. Instead of including the latent heat in the governing equation, the heat equations for solid and liquid phases are solved separately. A sharp interface model is proposed to represent the solid-liquid interface explicitly. The sharp interface, represented by discrete nodes, provides the Neumann boundary condition for pressure and the Dirichlet boundary condition for velocity/temperature, respectively. Based on temperature gradients in the solid and liquid phases, the positions of these interface nodes are updated every time step. The Eulerian-based formulation, rather than the conventional Lagrangian-based one, is utilized to minimize time step-dependent error. Up to 4th order spatial discretization scheme is adopted based on the Least Square Moving Particle Semi-implicit (LSMPS) scheme. Moreover, a geometry-based multi-resolution scheme is introduced to dynamically refine the spatial resolution near the interface for saving computational cost. The 1-D Stefan problem is firstly simulated to verify the accuracy of the proposed sharp interface model. Then, the consistency of the multi-resolution scheme is investigated by a convergence study of the Taylor-Green vortex problem. After that, numerical simulations of natural convection in a cavity are performed with different spatial resolutions and high order schemes. Resulted computational costs are compared and discussed. Finally, the problems of melting by natural convection with different Rayleigh numbers are investigated. The results achieved so far indicate that the multi-resolution and high order schemes have great potential to save computational cost.
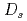 states
statesYang, Z.*; Wang, G.-J.*; Wu, J.-J.*; 岡 眞; Zhu, S.-L.*
Physical Review Letters, 128(11), p.112001_1 - 112001_6, 2022/03
被引用回数:40 パーセンタイル:95.41(Physics, Multidisciplinary)閾値近傍のハドロン共鳴を有限サイズの格子QCDのデータを用いて解析する新しい手法を提案し、正パリティの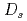 メソンのスペクトルに応用した。ハミルトニアン有効理論にクォーク模型,クォークペア生成,DK相互作用の情報を入れてベアな状態と散乱状態の結合を取り入れた。4個の
メソンのスペクトルに応用した。ハミルトニアン有効理論にクォーク模型,クォークペア生成,DK相互作用の情報を入れてベアな状態と散乱状態の結合を取り入れた。4個の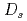 状態のうち、
状態のうち、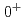 と
と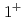 の状態は散乱状態と強く混合する。一方で、
の状態は散乱状態と強く混合する。一方で、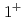 と
と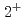 はほとんどベアなクォーク模型状態で記述できる。有限格子サイズでのレベル交差が再現されることを示した。
はほとんどベアなクォーク模型状態で記述できる。有限格子サイズでのレベル交差が再現されることを示した。
Wang, Z.; 杉山 智之
Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 135, p.266 - 283, 2022/02
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:47.19(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)The moving particle semi-implicit (MPS) method has great potential in dealing with free surface flow due to its Lagrangian nature. In most cases, the free surface boundary is simply served as the pressure boundary condition. In this paper, an improved MPS method is presented for thermocapillary driven free surface flow. A series of surface nodes explicitly represent the free surface boundary. The normal stress on the free surface provides the Dirichlet pressure boundary condition, while the velocity boundary condition, i.e., Marangoni stress, is enforced through the Taylor series expansion and least squares method. Meanwhile, a quasi-Lagrangian formulation is introduced to avoid particle clustering and the corresponding numerical instability by slightly modifying the advection velocity. The upwind scheme is employed for the convection term to obtain accurate and stable results. A novel constraint scheme with the divergence of provisional velocity is developed for the pressure gradient to enhance stability further. The consistency of the derived generalized boundary condition is firstly verified with a simple convergence test. Then, several numerical tests, including square patch rotation, lid-driven and square droplet oscillation, are simulated to show the improvements. Finally, thermocapillary driven flows in an open cavity without and with buoyancy effect are studied. Good agreements are obtained by comparing with reference simulations taken from literature. Heat transfer characteristics are further investigated for different dimensionless numbers, including the Rayleigh number and Marangoni number.
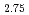 GeTe
GeTe
Bao, S.*; Wang, W.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Cai, Z.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Si, W.*; Ma, Z.*; 梶本 亮一; 池内 和彦*; et al.
Physical Review X, 12(1), p.011022_1 - 011022_15, 2022/02
被引用回数:35 パーセンタイル:95.19(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In the local or itinerant extreme, magnetic excitations can be described by the Heisenberg model which treats electron spins as localized moments, or by the itinerant-electron model where the exchange interaction between electrons leads to unequal numbers of electrons with up and down spins. However, the nature of the magnetic excitations has been elusive when both local moments and itinerant electrons are present in the intermediate range. Using inelastic neutron scattering, we provide direct spectroscopic evidence on the coexistence of and interplay between local moments and itinerant electrons in a van der Waals metallic ferromagnet Fe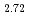 GeTe
GeTe , which can sustain tunable room-temperature ferromagnetism down to the monolayer limit. We find that there exist ferromagnetic spin-wave excitations dispersing from the zone center at low energies resulting from local moments and a columnlike broad continuum at the zone boundary at high energies up to over 100 meV resulting from itinerant electrons. Unlike the two-dimensional crystal structure, the low-energy mode exhibits a three-dimensional nature, and the high-energy mode also has an out-of-plane dependence. Both modes persist well above the Curie temperature of 160 K. Our neutron spectroscopic data reveal that the low-energy spin waves at 100 K are more coherent than those at 4 K, which is evidence of the weakening of the Kondo screening at high temperatures. These results unambiguously demonstrate the coexistence of local moments and itinerant electrons and the Kondo effect between these two components in Fe
, which can sustain tunable room-temperature ferromagnetism down to the monolayer limit. We find that there exist ferromagnetic spin-wave excitations dispersing from the zone center at low energies resulting from local moments and a columnlike broad continuum at the zone boundary at high energies up to over 100 meV resulting from itinerant electrons. Unlike the two-dimensional crystal structure, the low-energy mode exhibits a three-dimensional nature, and the high-energy mode also has an out-of-plane dependence. Both modes persist well above the Curie temperature of 160 K. Our neutron spectroscopic data reveal that the low-energy spin waves at 100 K are more coherent than those at 4 K, which is evidence of the weakening of the Kondo screening at high temperatures. These results unambiguously demonstrate the coexistence of local moments and itinerant electrons and the Kondo effect between these two components in Fe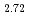 GeTe
GeTe . Such behaviors are generally expected in heavy-fermion systems with heavy
. Such behaviors are generally expected in heavy-fermion systems with heavy  electrons but are rarely clearly observed in materials with light
electrons but are rarely clearly observed in materials with light  electrons. These findings shed light on the understanding of magnetism in transition-metal compounds.
electrons. These findings shed light on the understanding of magnetism in transition-metal compounds.
 Cu
Cu TeO
TeO
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Cai, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Huang, Z.*; Ma, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; 梶本 亮一; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(22), p.224430_1 - 224430_8, 2021/12
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:10.46(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dimerized magnets forming alternating Heisenberg chains exhibit quantum coherence and entanglement and thus can find potential applications in quantum information and computation. However, magnetic systems typically undergo thermal decoherence at finite temperatures. Here, we show inelastic neutron scattering results on an alternating antiferromagnetic-ferromagnetic chain compound Na Cu
Cu TeO
TeO that the excited quasiparticles can counter thermal decoherence and maintain strong correlations at elevated temperatures. At low temperatures, we observe clear dispersive singlet-triplet excitations arising from the dimers formed along the crystalline
that the excited quasiparticles can counter thermal decoherence and maintain strong correlations at elevated temperatures. At low temperatures, we observe clear dispersive singlet-triplet excitations arising from the dimers formed along the crystalline  -axis. The excitation gap is of
-axis. The excitation gap is of  18 meV and the bandwidth is about half of the gap. The band top energy has a weak modulation along the [100] direction, indicative of a small interchain coupling. The gap increases while the bandwidth decreases with increasing temperature, leading to a strong reduction in the available phase space for the triplons. As a result, the Lorentzian-type energy broadening becomes highly asymmetric as the temperature is raised. These results are associated with a strongly correlated state resulting from hard-core constraint and quasiparticle interactions. We consider these results to be not only evidence for strong correlations at finite temperatures in Na
18 meV and the bandwidth is about half of the gap. The band top energy has a weak modulation along the [100] direction, indicative of a small interchain coupling. The gap increases while the bandwidth decreases with increasing temperature, leading to a strong reduction in the available phase space for the triplons. As a result, the Lorentzian-type energy broadening becomes highly asymmetric as the temperature is raised. These results are associated with a strongly correlated state resulting from hard-core constraint and quasiparticle interactions. We consider these results to be not only evidence for strong correlations at finite temperatures in Na Cu
Cu TeO
TeO , but also for the universality of the strongly correlated state in a broad range of quantum magnetic systems.
, but also for the universality of the strongly correlated state in a broad range of quantum magnetic systems.
Wang, Z.; Duan, G.*; 越塚 誠一*; 山路 哲史*
Nuclear Power Plant Design and Analysis Codes, p.439 - 461, 2021/00
The Moving Particle Semi-implicit (MPS) method is one kind of particles methods which are based on Lagrangian approach. It has been developed to analyze complex thermal-hydraulic problems, including those in nuclear engineering. Since meshes are no longer used, large deformation of free surfaces or interfaces can be simulated without the problems of mesh distortion. This approach is effective in solving multiphase fluid dynamics which is subject to complex motion of free surfaces or interfaces. Since its development, MPS method has been extensively utilized for wide range of applications in nuclear engineering. In this chapter, the basic theory of the MPS method is firstly explained. Then, some examples of its application in nuclear engineering, including bubble dynamic, vapor explosion, jet breakup, multiphase flow instability, in-vessel phenomenon, molten spreading, molten core concrete interaction (MCCI) and flooding, are presented.
Wang, Z.; Duan, G.*; 松永 拓也*; 杉山 智之
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 157, p.119919_1 - 119919_20, 2020/08
被引用回数:26 パーセンタイル:78.69(Thermodynamics)Enforcing accurate and consistent boundary conditions is a difficult issue for particle methods, due to the lack of information outside boundaries. Recently, consistent Neumann boundary condition enforcement is developed for the least squares moving particle semi-implicit method (LSMPS). However, the Robin boundary cannot be straightforwardly considered by that method because no computational variables are defined on the wall boundary. In this paper, a consistent Robin boundary enforcement for heat transfer problem is proposed. Based on the Taylor series expansion, the Robin boundary condition for temperature is converted to the fitting function of internal rather than boundary particles and incorporated into least squares approach for discretization schemes. Arbitrary geometries can be easily treated due to the use of polygons for wall boundary. A convergence study was firstly carried out to verify the consistency. Then, numerical tests of 1-D and 2-D heat conduction problems subjected to mixed boundary conditions were performed for verification, and good agreements with theoretical solutions were observed. Natural convection problems with different boundary conditions in an annulus were carried out for further validations of heat-fluid coupling. Excellent agreements between the present and literature results were demonstrated.
Wu, P.*; Fan, F.-R.*; 萩原 雅人*; 古府 麻衣子; Peng, K.*; 石川 喜久*; Lee, S.*; 本田 孝志*; 米村 雅雄*; 池田 一貴*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 22(8), p.083083_1 - 083083_9, 2020/08
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:64.36(Physics, Multidisciplinary)熱電材料SnSeは、過去数年間で世界的な関心を呼び、その固有の強い格子非調和性は、その優れた熱電性能の重要な要素と見なされている。一方、SnSeにおける格子非調和性の理解は、特にフォノンダイナミクスがこの動作によってどのように影響を受けるかに関して、依然として不十分である。そのため、中性子全散乱,非弾性中性子散乱,ラマン分光法、および凍結フォノン計算により、Na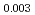 Sn
Sn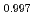 Se
Se S
S の格子力学の包括的な研究を行った。格子非調和性は、対分布関数,非弾性中性子散乱、およびラマン測定によって確かめられた。熱膨張と多重フォノン散乱の影響を分離することにより、後者は高エネルギー光学フォノンモードで非常に重要であることがわかった。フォノンモードの強い温度依存性は、この系の非調和性を示している。さらに、我々のデータは、Sドーピングにより、高エネルギー光学フォノンの線幅が広がることを明らかにした。私たちの研究は、SnSeの熱電性能は、フォノンエンジニアリングを介して格子熱伝導率への高エネルギー光学フォノンモードの寄与を減らすことによってさらに強化できることを示唆する。
の格子力学の包括的な研究を行った。格子非調和性は、対分布関数,非弾性中性子散乱、およびラマン測定によって確かめられた。熱膨張と多重フォノン散乱の影響を分離することにより、後者は高エネルギー光学フォノンモードで非常に重要であることがわかった。フォノンモードの強い温度依存性は、この系の非調和性を示している。さらに、我々のデータは、Sドーピングにより、高エネルギー光学フォノンの線幅が広がることを明らかにした。私たちの研究は、SnSeの熱電性能は、フォノンエンジニアリングを介して格子熱伝導率への高エネルギー光学フォノンモードの寄与を減らすことによってさらに強化できることを示唆する。