Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Liu, P.-F.*; Li, X.*; Li, J.*; Zhu, J.*; Tong, Z.*; 古府 麻衣子*; 楡井 真実; Xu, J.*; Yin, W.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
National Science Review, 11(12), p.nwae216_1 - nwae216_10, 2024/12
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:94.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Crystalline solids exhibiting inherently low lattice thermal conductivity ( ) are of great importance in applications such as thermoelectrics and thermal barrier coatings. However,
) are of great importance in applications such as thermoelectrics and thermal barrier coatings. However,  cannot be arbitrarily low and is limited by the minimum thermal conductivity related to phonon dispersions. In this work, we report the liquid-like thermal transport in a well-ordered crystalline CsAg
cannot be arbitrarily low and is limited by the minimum thermal conductivity related to phonon dispersions. In this work, we report the liquid-like thermal transport in a well-ordered crystalline CsAg Te
Te , which exhibits an extremely low
, which exhibits an extremely low  value of
value of  0.18 Wm
0.18 Wm K
K . On the basis of first-principles calculations and inelastic neutron scattering measurements, we find that there are lots of low-lying optical phonon modes at
. On the basis of first-principles calculations and inelastic neutron scattering measurements, we find that there are lots of low-lying optical phonon modes at  3.1 meV hosting the avoided-crossing behavior with acoustic phonons. These strongly localized modes are accompanied by weakly bound rattling Ag atoms with thermally induced large amplitudes of vibrations. Using the two-channel model, we demonstrate that coupling of the particle-like phonon modes and the heat-carrying wave-like phonons is essential for understanding the low
3.1 meV hosting the avoided-crossing behavior with acoustic phonons. These strongly localized modes are accompanied by weakly bound rattling Ag atoms with thermally induced large amplitudes of vibrations. Using the two-channel model, we demonstrate that coupling of the particle-like phonon modes and the heat-carrying wave-like phonons is essential for understanding the low  , which is heavily deviated from the
, which is heavily deviated from the 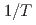 temperature dependence of the standard Peierls theory. In addition, our analysis indicates that the soft structural framework with liquid-like motions of the fluctuating Ag atoms is the underlying cause that leads to the suppression of the heat conduction in CsAg
temperature dependence of the standard Peierls theory. In addition, our analysis indicates that the soft structural framework with liquid-like motions of the fluctuating Ag atoms is the underlying cause that leads to the suppression of the heat conduction in CsAg Te
Te . These factors synergistically account for the ultralow
. These factors synergistically account for the ultralow  value. Our results demonstrate that the liquid-like heat transfer could indeed exist in a well-ordered crystal.
value. Our results demonstrate that the liquid-like heat transfer could indeed exist in a well-ordered crystal.
 Te
Te
Ye, M.*; Li, W.*; Zhu, S.-Y.*; 竹田 幸治; 斎藤 祐児; Wang, J.*; Pan, H.*; Nurmamat, M.*; 角田 一樹*; Ji, F.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 6, p.8913_1 - 8913_7, 2015/11
被引用回数:60 パーセンタイル:90.28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)磁性元素を添加したトポロジカル絶縁体は、量子異常ホール効果や無散逸伝導などの魅力的な現象の発現が予言され、低消費電力スピンデバイスの開発につながっていくものと期待されている。既に、いくつかの磁性添加トポロジカル絶縁体で長距離磁気秩序が確認されている。しかし、量子異常ホール効果の発現は、極低温におけるCrを添加した(Sb,Bi) Te
Te 系に限られており、強磁性の微視的な起源はほとんど分かっていない。そこで、今回、X線磁気円二色性実験による元素選択的研究を行うことにより、本物質系の強磁性は、母体の正孔キャリアーを媒介としたものであり、Crの3d電子とSbやTeのp電子の相互作用が極めて重要であることを明らかにした。この結果は、異常量子ホール素子の実現に向けても重要である。
系に限られており、強磁性の微視的な起源はほとんど分かっていない。そこで、今回、X線磁気円二色性実験による元素選択的研究を行うことにより、本物質系の強磁性は、母体の正孔キャリアーを媒介としたものであり、Crの3d電子とSbやTeのp電子の相互作用が極めて重要であることを明らかにした。この結果は、異常量子ホール素子の実現に向けても重要である。