Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
土屋 晴文; 藤 暢輔; 大図 章; 古高 和禎; 北谷 文人; 前田 亮; 米田 政夫
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1301 - 1312, 2023/11
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)An integrated active neutron non-destructive analysis (NDA) system, Active-N, was developed to gain knowledge of active neutron NDA techniques that are applicable to measurements of nuclear materials in highly radioactive nuclear fuels. Active-N, equipped with a D-T neutron generator, combines three complementary active neutron NDA techniques: Differential Die-away Analysis (DDA), Prompt Gamma-ray Analysis (PGA), and Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA). In this paper, we provide an overview of Active-N and then demonstrate that the compact NRTA system in Active-N can quantify nuclear materials. Monte Carlo simulations were conducted to determine the design of the compact NRTA system including a moderator, flight tubes, and a detector shield. To investigate how accurately the compact NRTA system determines areal densities in a sample, measurements were performed with a Pu pellet-type sample as well as metallic plate samples of In and Ag. The experimental areal densities of  Pu,
Pu,  In and
In and  Ag were consistent with those calculated for the individual nuclei. These results show that it is feasible to develop a compact NRTA system capable of determining the contents of nuclear materials in nuclear fuels. This research was implemented under the subsidy for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
Ag were consistent with those calculated for the individual nuclei. These results show that it is feasible to develop a compact NRTA system capable of determining the contents of nuclear materials in nuclear fuels. This research was implemented under the subsidy for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
藤 暢輔; 大図 章; 土屋 晴文; 古高 和禎; 北谷 文人; 米田 政夫; 前田 亮; 小泉 光生
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Virtual Annual Meeting (Internet), 8 Pages, 2021/08
Since neutrons have exceptional ability to penetrate high-density materials and can induce fission, they are used in non-destructive analysis such as, Differential Die-Away Analysis (DDA), Prompt Gamma-ray Analysis (PGA) and Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA). The different analytical methods give us complementary information, which are particularly useful for the quantification of Special Nuclear Materials in highly radioactive nuclear materials, including spent fuel. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and the Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Commission are collaborating to develop an active neutron NDA system for nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security. In the second phase of the project, an integrated active neutron NDA system: Active-N which enables the simultaneous measurements of DDA, PGA and NRTA has been developed. The DDA detects fission neutrons, and it can determine small amounts of the fissile mass. PGA is utilized for the quantification of neutron absorber and particularly useful for the detection of explosives. NRTA can be used to quantify almost all medium and high-Z elements and considered as one of the most accurate NDA. In this presentation, we will provide an overview of Active-N and report the recent experimental results. This research was implemented under the subsidy for nuclear security promotion of MEXT: Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
 S
S郷 慎太郎*; 井手口 栄治*; 横山 輪*; 青井 考*; Azaiez, F.*; 古高 和禎; 初川 雄一; 木村 敦; 木佐森 慶一*; 小林 幹*; et al.
Physical Review C, 103(3), p.034327_1 - 034327_8, 2021/03
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:57.13(Physics, Nuclear)Excited states in  S were investigated by in-beam
S were investigated by in-beam  -ray spectroscopy using the
-ray spectroscopy using the  Mg(
Mg( O, 2
O, 2 1
1 ) fusion-evaporation reaction. The de-exciting
) fusion-evaporation reaction. The de-exciting  -rays were measured with germanium detector arrays along with the measurement of evaporated charged particles in a
-rays were measured with germanium detector arrays along with the measurement of evaporated charged particles in a 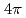 segmented Si detector array. The level scheme was extended up to 12470 keV. The obtained level structure is compared with the large-scale shell-model calculations. The possibility of isoscalar-pair excited states is discussed for
segmented Si detector array. The level scheme was extended up to 12470 keV. The obtained level structure is compared with the large-scale shell-model calculations. The possibility of isoscalar-pair excited states is discussed for 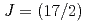 states with comparison between the experimental and theoretical results.
states with comparison between the experimental and theoretical results.
Ma, F.; Kopecky, S.*; Alaerts, G.*; 原田 秀郎; Heyse, J.*; 北谷 文人; Noguere, G.*; Paradela, C.*;  alamon, L.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
alamon, L.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 35(3), p.478 - 488, 2020/03
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:22.14(Chemistry, Analytical)The use of Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis to characterize homogeneous samples not fulfilling good transmission geometry conditions is discussed. Analytical expressions for such samples have been derived and implemented in the resonance shape analysis code REFIT. They were validated by experiments at the time-of-flight facility GELINA using a set of metallic natural copper samples. The expressions were used to derive sample characteristics by a least squares adjustment to experimental transmission data. In addition, the resonance parameters of Cu for energies below 6 keV, which are reported in the literature and recommended in evaluated data libraries, were verified. This research was implemented under the subsidiary for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
 scintillation detector equipped with specially-designed shield for neutron resonance capture analysis
scintillation detector equipped with specially-designed shield for neutron resonance capture analysis土屋 晴文; 小泉 光生; 北谷 文人; 原田 秀郎
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 932, p.16 - 26, 2019/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)A large-volume ( 12.0 cm
12.0 cm 12.7 cm) LaBr
12.7 cm) LaBr scintillation detector equipped with a specially-designed radiation shield was evaluated for neutron resonance capture analysis at the neutron time-of-flight (TOF) facility GELINA. By using the LaBr
scintillation detector equipped with a specially-designed radiation shield was evaluated for neutron resonance capture analysis at the neutron time-of-flight (TOF) facility GELINA. By using the LaBr detector with and without the shield, measurements were carried out at a 13-m TOF station with three metallic samples, namely, Ni, Cr, and Fe. In addition, Monte Carlo simulations with Geant4 were performed, and the results were compared with the measurements to analyze the observed energy spectra and TOF spectra. Energy spectra obtained with the shield showed that prompt
detector with and without the shield, measurements were carried out at a 13-m TOF station with three metallic samples, namely, Ni, Cr, and Fe. In addition, Monte Carlo simulations with Geant4 were performed, and the results were compared with the measurements to analyze the observed energy spectra and TOF spectra. Energy spectra obtained with the shield showed that prompt  -ray peaks emitted from each sample can be used to identify the isotopes. Moreover, the signal-to-noise ratios of resonance peaks in a TOF spectrum with the shield were enhanced 1.5-2.5 in comparison with those without the shield. Furthermore, simultaneous measurements conducted using the three samples demonstrated that the shield employed herein was indispensable for identifying impurities in a composite sample such as particle-like fuel debris.
-ray peaks emitted from each sample can be used to identify the isotopes. Moreover, the signal-to-noise ratios of resonance peaks in a TOF spectrum with the shield were enhanced 1.5-2.5 in comparison with those without the shield. Furthermore, simultaneous measurements conducted using the three samples demonstrated that the shield employed herein was indispensable for identifying impurities in a composite sample such as particle-like fuel debris.
藤 暢輔; 大図 章; 土屋 晴文; 古高 和禎; 北谷 文人; 米田 政夫; 前田 亮; 小泉 光生
Proceedings of INMM 60th Annual Meeting (Internet), 7 Pages, 2019/07
Nuclear material accountancy plays a key role in nuclear safeguards and security. The collaboration between the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and the Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Commission aims to develop an active neutron NDA system for Special Nuclear Materials (SNM) and Minor Actinides (MA) in highly radioactive nuclear materials. Several active neutron NDA techniques, namely Differential Die-Away Analysis (DDA), Prompt Gamma-ray Analysis (PGA), Neutron Resonance Capture Analysis (NRCA), Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) and Delayed Gamma-ray Analysis (DGA) have been developed. The different methods can provide complementary information. In the first phase of the project, we developed a combined NDA system, which enables the simultaneous measurements of DDA and PGA. The DDA technique can determine very small amounts of the fissile mass. PGA is valuable for the measurement of light elements. In the second phase, we will continue to conduct additional research to improve the methodology and develop a new integrated NDA system which can use for NRTA as well as DDA and PGA. In this presentation, we will provide an overview of the project and report the recent results, especially the design of new integrated NDA system. This research was implemented under the subsidiary for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
中村 詔司; 北谷 文人; 木村 敦; 上原 章寛*; 藤井 俊行*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(6), p.493 - 502, 2019/06
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:48.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)放射化法により Np(n,
Np(n, )
) Np反応の熱中性子捕獲断面積(
Np反応の熱中性子捕獲断面積( )及び共鳴積分(I
)及び共鳴積分(I )を測定した。
)を測定した。 Npの0.489eVにある第一共鳴に注意を払い、カドミウム差法において、ガドリニウムフィルタを用いて、カットオフエネルギーを0.133eVに設定して
Npの0.489eVにある第一共鳴に注意を払い、カドミウム差法において、ガドリニウムフィルタを用いて、カットオフエネルギーを0.133eVに設定して を測定した。ネプツニウム237試料を、京都大学複合原子力科学研究所の研究炉にて照射した。照射位置における熱中性子束、及び熱外ウェストコット因子を決定するために、金合金線モニタ、及びコバルト合金線モニタも一緒に照射した。照射したネプツニウム237試料及びモニタ試料の生成放射能を、ガンマ線分光により測定した。ウェストコットの理論に基づき、
を測定した。ネプツニウム237試料を、京都大学複合原子力科学研究所の研究炉にて照射した。照射位置における熱中性子束、及び熱外ウェストコット因子を決定するために、金合金線モニタ、及びコバルト合金線モニタも一緒に照射した。照射したネプツニウム237試料及びモニタ試料の生成放射能を、ガンマ線分光により測定した。ウェストコットの理論に基づき、 とI
とI を、それぞれと186.9
を、それぞれと186.9 6.2 barn、及び1009
6.2 barn、及び1009 90 barnと導出した。
90 barnと導出した。
土屋 晴文; Ma, F.; 北谷 文人; Paradella, C.*; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*
Proceedings of 41st ESARDA Annual Meeting (Internet), p.374 - 377, 2019/05
From a viewpoint of nuclear safeguards and nuclear security, non-destructive assay (NDA) techniques are needed to quantify special nuclear materials (SNMs) in nuclear fuels such as spent fuels and fuel debris. Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) is an NDA technique and it measures the amount of U isotopes in a U O
O sample within 1% accuracy and Pu isotopes in a PuO
sample within 1% accuracy and Pu isotopes in a PuO sample within 5% accuracy. However, NRTA measurements done so far were mainly applied to homogeneous samples with a constant thickness. Spent fuel and especially debris have irregular shapes that affect the NRTA measurements. In order to investigate the influence of irregular-shaped samples, NRTA experiments were done with a copper bar sample with different rotation angles with respect to neutron beams, at a neutron Time-Of-Flight (TOF) facility GELINA (Belgium). Analytical models for irregular shaped samples proposed by Harada et al. (JNST, 2015) were applied to the experimental data. It has been found that the experimental data can be well reproduced by the proposed models. In this presentation, we report how analytical models are applied to a real NRTA experiment with a Cu bar sample and discuss a future prospect of a compact NRTA system for SNM quantification. This research was implemented under the subsidiary for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
sample within 5% accuracy. However, NRTA measurements done so far were mainly applied to homogeneous samples with a constant thickness. Spent fuel and especially debris have irregular shapes that affect the NRTA measurements. In order to investigate the influence of irregular-shaped samples, NRTA experiments were done with a copper bar sample with different rotation angles with respect to neutron beams, at a neutron Time-Of-Flight (TOF) facility GELINA (Belgium). Analytical models for irregular shaped samples proposed by Harada et al. (JNST, 2015) were applied to the experimental data. It has been found that the experimental data can be well reproduced by the proposed models. In this presentation, we report how analytical models are applied to a real NRTA experiment with a Cu bar sample and discuss a future prospect of a compact NRTA system for SNM quantification. This research was implemented under the subsidiary for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
北谷 文人; 土屋 晴文; 藤 暢輔; 堀 順一*; 佐野 忠史*; 高橋 佳之*; 中島 健*
KURRI Progress Report 2017, P. 99, 2018/08
As a non-destructive analytical technique for nuclear material in the field of nuclear security and nuclear nonproliferation, a neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) attracts attention of researchers. It is important to downsize a NRTA system when it is deployed at various facilities. For this aim, we have developed a compact NRTA system which utilizes a D-T neutron generator. Its pulse width of 10 s is much longer than that of a large electron beam accelerator. It is necessary to understand the influence of pulse widths on the NRTA measurement. Therefore, we conducted the experiments of the simulated nuclear fuel pin samples to evaluate how the NRTA measurement is influenced by the pulse width of neutron beam. Experiments were performed in Kyoto University. The simulated fuel pellet sample was made from metallic powders of Ag (around 1%) and Al (around 99%). The energy of the irradiation neutron is determined by a Time of Flight technique. We used three pulse widths of the neutron beam of 0.1, 1 and 4
s is much longer than that of a large electron beam accelerator. It is necessary to understand the influence of pulse widths on the NRTA measurement. Therefore, we conducted the experiments of the simulated nuclear fuel pin samples to evaluate how the NRTA measurement is influenced by the pulse width of neutron beam. Experiments were performed in Kyoto University. The simulated fuel pellet sample was made from metallic powders of Ag (around 1%) and Al (around 99%). The energy of the irradiation neutron is determined by a Time of Flight technique. We used three pulse widths of the neutron beam of 0.1, 1 and 4  s. A resonance dip of
s. A resonance dip of 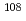 Ag at 5.19 eV is observed in the all spectra. And the dip of the TOF spectrum shifts towards low energy, with pulse width changed to a longer one. In this work, we confirmed that neutron pulse width affected the NRTA measurement of the fuel pin sample. On the basis of this work, we will be able to quantify the effects of long-pulse width in a resonance analysis.
Ag at 5.19 eV is observed in the all spectra. And the dip of the TOF spectrum shifts towards low energy, with pulse width changed to a longer one. In this work, we confirmed that neutron pulse width affected the NRTA measurement of the fuel pin sample. On the basis of this work, we will be able to quantify the effects of long-pulse width in a resonance analysis.
土屋 晴文; 北谷 文人; 藤 暢輔; Paradela, C.*; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*
Proceedings of INMM 59th Annual Meeting (Internet), 6 Pages, 2018/07
In fields of nuclear safeguards and nuclear security, non-destructive assay (NDA) techniques are needed in order to quantify special nuclear materials (SNMs) in nuclear fuels. Among those techniques, active NDA ones would be preferable to passive ones. One candidate of active NDA techniques is neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA). In fact, experiments done at GELINA have shown that NRTA has high potential enough to quantify SNMs in complex materials. Currently, such a NRTA system requires a large electron accelerator facility to generate intense neutron sources. In other words, it is very difficult to perform NRTA at various facilities that need to measure SNMs. Thus, downsizing a NRTA system would be one solution of its difficulty. In order to realize a compact NRTA system, we develop a prototype with a D-T neutron generator that has a pulse width of 10  s. For this aim, numerical calculations to optimize the compact NRTA system were done. In addition, NRTA measurements with simulated fuel pins were made at neutron time-of-flight facilities such as GELINA. In this presentation, we present results of the numerical calculations and the experimental results. On the basis of those results we discuss a future prospect of a compact NRTA system that would be applicable to SNM quantification. This research was implemented under the subsidiary for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
s. For this aim, numerical calculations to optimize the compact NRTA system were done. In addition, NRTA measurements with simulated fuel pins were made at neutron time-of-flight facilities such as GELINA. In this presentation, we present results of the numerical calculations and the experimental results. On the basis of those results we discuss a future prospect of a compact NRTA system that would be applicable to SNM quantification. This research was implemented under the subsidiary for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
藤 暢輔; 大図 章; 土屋 晴文; 古高 和禎; 北谷 文人; 米田 政夫; 前田 亮; 小泉 光生; Heyse, J.*; Paradela, C.*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 59th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2018/07
Nuclear material accountancy is of fundamental importance for nuclear safeguards and security. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no established technique that enables us to accurately determine the amount of Special Nuclear Materials (SNM) and Minor Actinides (MA) in high radioactive nuclear materials. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and the Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Commission Collaboration Action Sheet-7 started in 2015. The purpose of this project is to develop an innovative non-destructive analysis (NDA) system using a D-T pulsed neutron source. Active neutron NDA techniques, namely Differential Die-Away Analysis (DDA), Prompt Gamma-ray Analysis (PGA), Neutron Resonance Capture Analysis (NRCA), Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) and Delayed Gamma-ray Analysis (DGA) have been studied and developed. The different methods can provide complementary information which is particularly useful for quantification of SNM and MA in high radioactive nuclear materials. The second phase of the project has started. In the second phase, we will continue to conduct additional research to improve the methodology and develop an integrated NDA system. This presentation gives an overview of the project and the NDA system and reports the recent results. This research was implemented under the subsidiary for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
土屋 晴文; 北谷 文人; 前田 亮; 藤 暢輔; 呉田 昌俊
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 13(Sp.1), p.2406004_1 - 2406004_4, 2018/02
近年、核セキュリティや核不拡散の分野において核燃料中の核物質を非破壊で測定する重要性が増している。その目的に叶う技術として、中性子共鳴透過分析法(NRTA)がある。NRTAは、パルス中性子ビームを測定試料に照射し、試料から透過してくる中性子を計測することにより、試料の分析を行う。NRTAの基となっている測定技術は、高い精度が要求される核データの測定に長年使われており、確立された技術である。しかし、現状のNRTA測定システムは、強力な中性子ビームを生み出すために規模の大きな電子線加速器を用いなければならず、核燃料の測定が必要とされる施設に組み込むことは容易ではない。この問題を解く一つの鍵は、NRTAシステムに組み込まれる中性子発生源をできるだけ小さくし、NRTAシステムを小型化することである。そこで我々は2つのタイプの小型中性子源を考えている。一つは、10 secの中性子パルス幅を有するD-T中性子発生管を使うもので、もう一つは1
secの中性子パルス幅を有するD-T中性子発生管を使うもので、もう一つは1 secという短いパルス幅を持つ小型電子線加速器を用いるものである。本発表では、NRTA測定の原理や小型NRTAシステムの概要を紹介するとともに、DT中性子発生管と小型電子線加速器を用いた場合について、NRTA測定で得られる透過中性子スペクトルを数値計算により導出し、比較する。その比較を基に、核燃料中の核物質の測定に中性子ビームのパルス幅がどのように影響を与えるのかについて議論する。
secという短いパルス幅を持つ小型電子線加速器を用いるものである。本発表では、NRTA測定の原理や小型NRTAシステムの概要を紹介するとともに、DT中性子発生管と小型電子線加速器を用いた場合について、NRTA測定で得られる透過中性子スペクトルを数値計算により導出し、比較する。その比較を基に、核燃料中の核物質の測定に中性子ビームのパルス幅がどのように影響を与えるのかについて議論する。
Paradela, C.*; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; 原田 秀郎; 北谷 文人; 小泉 光生; 土屋 晴文
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.09002_1 - 09002_4, 2017/09
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:97.81(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutron-induced reactions can be used to study the properties of nuclear materials in the field of nuclear safeguards and security. The elemental and isotopic composition of these materials can be determined by using the presence of resonance structures in the reaction cross sections as fingerprints. This idea is the basis of two non-destructive analytical techniques which have been developed at the GELINA neutron time-of-flight facility of the JRC-IRMM: Neutron Resonance Capture Analysis (NRCA) and Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA). A full quantitative validation of the NRTA technique was obtained by determining the areal densities of enriched reference samples used for safeguards applications with an accuracy better than 1%. Moreover, a combination of NRTA and NRCA has been proposed for the characterisation of particle-like debris of melted fuel formed in severe nuclear accidents. In order to deal with the problems due to the diversity in shape and size of these samples and the presence of strong absorbing matrix materials, new capabilities have been implemented in the resonance shape analysis code REFIT. They have been validated by performing a blind test in which the elemental abundance of a combined sample composed of unknown quantities of materials such as cobalt, tungsten, rhodium or gold was determined with accuracies better than 2%.
北谷 文人; 土屋 晴文; 小泉 光生; 高峰 潤; 堀 順一*; 佐野 忠史*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.09032_1 - 09032_3, 2017/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)The use of a short flight path is effective in the neutron resonance analysis. On the other hand, such a short path would reduce a time resolution in Time-Of-Flight (TOF) measurements. In order to investigate the effect of neutron flight-path length, we carried out Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) experiments with a short neutron flight path at the Kyoto University Research Reactor Institute - Linear Accelerator (KURRI-LINAC). In measurements of Neutron Resonance Densitometry, the quantity of nuclear materials is determined from TOF spectra obtained in the neutron energy range below 30 eV. Performing NRTA experiments with a 7-m flight path at KURRI-LINAC, we examined effects of flight path and pulse width on a TOF spectrum. A resonance dip of 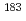 W at 27 eV in a TOF spectrum was successfully observed with an electron pulse width less than 2
W at 27 eV in a TOF spectrum was successfully observed with an electron pulse width less than 2  s. In this presentation, we will discuss importance of the pulse width and short flight path to study design of a compact TOF facility to quantify nuclear materials.
s. In this presentation, we will discuss importance of the pulse width and short flight path to study design of a compact TOF facility to quantify nuclear materials.
藤 暢輔; 大図 章; 土屋 晴文; 古高 和禎; 北谷 文人; 米田 政夫; 前田 亮; 呉田 昌俊; 小泉 光生; 瀬谷 道夫; et al.
EUR-28795-EN (Internet), p.684 - 693, 2017/00
In 2015, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and the Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Commission collaboration started to develop an active neutron non-destructive assay system for nuclear nonproliferation and nuclear security. To the best of our knowledge, no adequate technique exists that allows us to determine the amount of special nuclear materials and minor actinides in high radioactive nuclear materials, such as spent fuel, transuranic waste, etc. The collaboration aims at contributing to the establishment of an innovative NDA system using a D-T pulsed neutron source for various applications. We utilize several active neutron NDA techniques, namely Differential Die-Away Analysis (DDA), Prompt Gamma-ray Analysis (PGA), Neutron Resonance Capture Analysis (NRCA), Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) and Delayed Gamma Spectroscopy (DGS). All of these techniques have advantages and disadvantages. The different methods can provide complementary information which is particularly useful for nuclear nonproliferation and nuclear security. In this project, we have developed a combined NDA system, which enables the measurements of DDA and PGA, at NUclear fuel Cycle safety Engineering research Facility (NUCEF) in JAEA. In this presentation, we will introduce our project and report the recent progress of developments, especially in NRTA, DDA and PGA.

 -ray spectrometer for detecting
-ray spectrometer for detecting  B in debris of melted nuclear fuel
B in debris of melted nuclear fuel小泉 光生; 土屋 晴文; 北谷 文人; 原田 秀郎; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Mondelaers, W.*; Paradela, C.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 837, p.153 - 160, 2016/11
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:19.71(Instruments & Instrumentation)Neutron Resonance Densitometry (NRD) has been proposed as a non-destructive analytical method for quantifying Special Nuclear Material (SNM) in the rock- and particle-like debris that is to be removed from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. The method is based on Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) and Neutron Resonance Capture Analysis combined with Prompt Gamma Ray Analysis (NRCA/PGA). Although quantification of SNM will predominantly rely on NRTA, this will be hampered by the presence of strong neutron-absorbing matrix materials, in particular  B. Results obtained with NRCA/PGA are used to improve the interpretation of NRTA data. Prompt
B. Results obtained with NRCA/PGA are used to improve the interpretation of NRTA data. Prompt  -rays originating from the
-rays originating from the  B(n,
B(n, 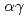 ) reaction are used to assess the amount of
) reaction are used to assess the amount of  B. The 478 keV
B. The 478 keV  -rays from
-rays from  B, however, need to be measured under a high-radiation environment, especially from
B, however, need to be measured under a high-radiation environment, especially from  Cs. In order to meet this requirement, we have developed a well-shaped
Cs. In order to meet this requirement, we have developed a well-shaped  -ray spectrometer consisting of a cylindrical and four rectangular cuboid LaBr
-ray spectrometer consisting of a cylindrical and four rectangular cuboid LaBr scintillators, and a fast data acquisition system.
scintillators, and a fast data acquisition system.
国枝 賢; 岩本 修; 岩本 信之; 湊 太志; 岡本 力; 佐藤 達彦; 中島 宏; 岩元 洋介; 岩元 大樹; 北谷 文人; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, p.41 - 46, 2016/09
加速器を用いた種々のアプリケーションを開発・設計するための基礎データとして、中性子や陽子入射の高エネルギー核データを整備する必要がある。本研究では、光学モデルや前平衡モデル計算における最新の知見を投入してJENDL/HE-2007の見直しを行うと共に、特に医療分野で需要の高い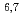 Liや
Liや Be等の核種を新たに加えて、約130核種に対する200MeVまでの中性子・陽子核データライブラリJENDL-4.0/HEを完成させた。本発表においては、ライブラリの概要を説明すると共に、粒子輸送計算コードPHITSやMCNPXを用いた中性子透過計算等における積分検証結果を中心に報告する。
Be等の核種を新たに加えて、約130核種に対する200MeVまでの中性子・陽子核データライブラリJENDL-4.0/HEを完成させた。本発表においては、ライブラリの概要を説明すると共に、粒子輸送計算コードPHITSやMCNPXを用いた中性子透過計算等における積分検証結果を中心に報告する。
土屋 晴文; 北谷 文人; 前田 亮; 呉田 昌俊
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 6 Pages, 2016/07
近年、核保障措置や核セキュリティの観点から、使用済み燃料や次世代のMA-Pu燃料、燃料デブリ中の核物質を非破壊により測定する重要性が増している。その重要性に叶う非破壊分析技術の一つに中性子共鳴透過分析法[Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis(NRTA)]がある。NRTAは中性子飛行時間測定技術に立脚した技術で、精密さが要求される核データ測定に長年、使われている。実際、核物質の定量にNRTAが有効であることは、これまでの原子力機構とJRCとの共同実験により示されている。ゆえに、NRTAは現在の核不拡散・核セキュリティ分野の必要性にまさに叶うと考えている。しかしながら、今までのNRTA装置は大型の電子線加速器施設を利用しているため、汎用性に欠ける一面があった。そこで、われわれはD-T管(パルス幅10マイクロ秒、平均最大強度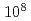 から
から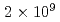 n/s)を利用した小型NRTA装置のプロトタイプの開発に着手した。本発表では、プロトタイプ装置の概要と、プロトタイプ装置の使用済み核燃料やMA-Pu燃料に対する適用性を数値計算により評価した結果を報告する。また、将来的には小型電子線加速器を用いたNRTA装置を開発することを視野に入れており、小型電子線加速器を用いたNRTA装置の性能についても議論する。
n/s)を利用した小型NRTA装置のプロトタイプの開発に着手した。本発表では、プロトタイプ装置の概要と、プロトタイプ装置の使用済み核燃料やMA-Pu燃料に対する適用性を数値計算により評価した結果を報告する。また、将来的には小型電子線加速器を用いたNRTA装置を開発することを視野に入れており、小型電子線加速器を用いたNRTA装置の性能についても議論する。
 Se(
Se( ,n)断面積測定と
,n)断面積測定と Se(n,
Se(n, )断面積の不確かさ評価
)断面積の不確かさ評価北谷 文人
核データニュース(インターネット), (114), p.44 - 49, 2016/06
 Seは長寿命核分裂生成物(LLFP)の一つで、地層処分負荷軽減のために、短寿命核種・安定核種への核変換の対象である。この中性子捕獲反応断面積について不確かさを考慮したものを算出するために実施した研究についてレビューする。現時点では
Seは長寿命核分裂生成物(LLFP)の一つで、地層処分負荷軽減のために、短寿命核種・安定核種への核変換の対象である。この中性子捕獲反応断面積について不確かさを考慮したものを算出するために実施した研究についてレビューする。現時点では Seは、測定用試料の入手が困難で、断面積の直接測定ができない。そのため、この断面積は統計モデル計算等を用いて見積られている。しかし、現状では、計算値には不確かさが付与されていない不十分なものである。
Seは、測定用試料の入手が困難で、断面積の直接測定ができない。そのため、この断面積は統計モデル計算等を用いて見積られている。しかし、現状では、計算値には不確かさが付与されていない不十分なものである。 線強度関数(
線強度関数( SF)法を利用して不確かさを明らかにした
SF)法を利用して不確かさを明らかにした Seの(n,
Seの(n, )断面積データを導出するため、
)断面積データを導出するため、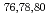 Seの光核反応断面積に加え
Seの光核反応断面積に加え Seの光核反応断面積の測定を(
Seの光核反応断面積の測定を( ,n)反応のしきい値から(
,n)反応のしきい値から( ,2n)反応のしきい値の領域で行った。これから得られた光核反応断面積を基に統計モデル計算での共通の物理量である
,2n)反応のしきい値の領域で行った。これから得られた光核反応断面積を基に統計モデル計算での共通の物理量である SFを求めた。求めた
SFを求めた。求めた SFを用いて
SFを用いて Seの中性子捕獲反応断面積を統計モデルによって計算した。この結果、不確かさ
Seの中性子捕獲反応断面積を統計モデルによって計算した。この結果、不確かさ 26%を付加した
26%を付加した Seの(n,
Seの(n, )断面積データを得ることができた。得られた
)断面積データを得ることができた。得られた Seの(n,
Seの(n, )断面積は、JENDL-4.0の1/3から1/4と大きく異なる値を得た。
)断面積は、JENDL-4.0の1/3から1/4と大きく異なる値を得た。
 Se(
Se( , n) cross section and uncertainty evaluation of the
, n) cross section and uncertainty evaluation of the  Se(n,
Se(n,  ) cross section
) cross section北谷 文人; 原田 秀郎; 後神 進史*; 岩本 信之; 宇都宮 弘章*; 秋宗 秀俊*; 豊川 弘之*; 山田 家和勝*; 井頭 政之*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(4), p.475 - 485, 2016/04
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:43.41(Nuclear Science & Technology)We precisely measured the ( , n) cross section for
, n) cross section for  Se by developing a spectroscopic method utilizing Laser Compton-Scattering
Se by developing a spectroscopic method utilizing Laser Compton-Scattering  -rays. Moreover, the
-rays. Moreover, the  Se(n,
Se(n,  )
)  Se cross section was deduced using the statistical model calculation code CCONE with
Se cross section was deduced using the statistical model calculation code CCONE with  -ray strength functions adjusted to reproduce the (
-ray strength functions adjusted to reproduce the ( , n) cross sections for
, n) cross sections for  Se and the even Se isotopes
Se and the even Se isotopes  Se,
Se, 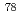 Se and
Se and  Se. The reliability of the
Se. The reliability of the  Se(n,
Se(n,  )
)  Se cross section calculated by CCONE with the adjusted
Se cross section calculated by CCONE with the adjusted  -ray strength function was evaluated by comparing available experimental (n,
-ray strength function was evaluated by comparing available experimental (n,  ) cross sections for stable
) cross sections for stable 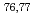 Se isotopes and those calculated by CCONE with the adjusted
Se isotopes and those calculated by CCONE with the adjusted  -ray strength function. The result provides fundamental data for the study of nuclear transmutation for the long-lived fission product of
-ray strength function. The result provides fundamental data for the study of nuclear transmutation for the long-lived fission product of  Se.
Se.