Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
山口 正剛; 海老原 健一; 都留 智仁; 板倉 充洋
Materials Transactions, 64(11), p.2553 - 2559, 2023/11
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)アルミニウム合金中のMgZn 析出物とMg
析出物とMg Si晶出物の非整合界面における水素トラップエネルギーを第一原理計算から計算することを試みた。非整合界面を含む単位胞は周期境界条件を満たさず、結晶ブロックが不連続になるため、不連続領域(真空領域)から離れた領域で水素トラップエネルギーを計算した。その結果、この原子論的配置を仮定した非整合界面では、水素原子のトラップエネルギーがかなり大きいことがわかった。また、アルミニウム母相中のMg
Si晶出物の非整合界面における水素トラップエネルギーを第一原理計算から計算することを試みた。非整合界面を含む単位胞は周期境界条件を満たさず、結晶ブロックが不連続になるため、不連続領域(真空領域)から離れた領域で水素トラップエネルギーを計算した。その結果、この原子論的配置を仮定した非整合界面では、水素原子のトラップエネルギーがかなり大きいことがわかった。また、アルミニウム母相中のMg Siの非整合界面における水素トラップによる凝集エネルギーの減少についても予備的計算を行った。
Siの非整合界面における水素トラップによる凝集エネルギーの減少についても予備的計算を行った。
小林 恵太; 奥村 雅彦; 中村 博樹; 板倉 充洋; 町田 昌彦; 浦田 新吾*; 鈴谷 賢太郎
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.18721_1 - 18721_12, 2023/11
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0(Multidisciplinary Sciences)非晶質物質の構造因子に現れる鋭い第一ピークはFSDPと呼ばれ、非晶質物質中の中距離秩序構造を反映したものであると考えられているが、その構造的起源に関しては現在まで議論が続いている。今回、第一原理計算と同等の精度を持つ機械学習分子動力学を用いることにより、高密度シリカガラスにおけるFSDPの構造起源を解析した。まず、機械学習分子動力学を用いることにより、高密度シリカガラスの様々な実験データの再現に成功した。また、高密度シリカガラスにおけるFSDPの発達(減少)は、ガラス構造の圧縮に伴う、Si-O共有結合ネットワーク中のリング構造の変形挙動によって特徴付けられることを明らかにした。
山本 耀二郎*; 早川 頌*; 沖田 泰良*; 板倉 充洋
Computational Materials Science, 229, p.112389_1 - 112389_9, 2023/10
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:52.07(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)ヘリウムバブルは、核融合炉条件下で生成する特有の微細構造である。これらのバブルは、自らの移動によって接近・融合し、微細構造や材料特性に大きな影響を与える。しかし複数の金属原子の移動が含まれるこれらのプロセスは、分子動力学(MD)では時間スケールの制約から扱うことができない。この研究では、自己発展原子論的キネティックモンテカルロ(SEAKMC)法により時間スケールを拡張し、Fe中のバブルの融合過程を再現した。He原子の微小な振動やFe原子の短距離変位など、活性化エネルギーが極めて低い些細なイベントを避けるため、SEAKMCに2つのアルゴリズムを導入した。He原子の微小な振動を回避するために二段階のサドルポイント検索を行い、Fe原子の短距離変位を避けるためにFe原子の変位距離に対する閾値を設定した。さらに、活性化エネルギーの上限を設定する別のアルゴリズムを追加することで、非現実的に高い活性化エネルギーを持つイベントの選択を防ぎ、MDの時間尺度よりも8桁長い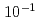 秒までのシミュレーション時間において、ダンベルから楕円形への構造の変化を再現することに成功した。開発された手法は、軽元素を含む金属材料の微細構造を分析するのに効果的であり、実験と比較可能な時間スケールに到達できる唯一の手法である。
秒までのシミュレーション時間において、ダンベルから楕円形への構造の変化を再現することに成功した。開発された手法は、軽元素を含む金属材料の微細構造を分析するのに効果的であり、実験と比較可能な時間スケールに到達できる唯一の手法である。
 Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy宮崎 秀俊*; 赤塚 達吉*; 木村 耕治*; 江草 大佑*; 佐藤 庸平*; 板倉 充洋; 高木 康多*; 保井 晃*; 小澤 健一*; 間瀬 一彦*; et al.
Materials Transactions, 64(6), p.1194 - 1198, 2023/06
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:54.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)硬X線およびソフトX線光電子分光法、およびバンド構造計算を用いて、Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y 合金の電子構造を調査し、この材料の相安定性のメカニズムを調べた。Mg
合金の電子構造を調査し、この材料の相安定性のメカニズムを調べた。Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y 合金の電子構造は、フェルミエネルギー近傍に疑ギャップを持つ半金属的な電子構造を示した。Mg
合金の電子構造は、フェルミエネルギー近傍に疑ギャップを持つ半金属的な電子構造を示した。Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y 合金の観察された電子構造は、疑ギャップ構造が相安定性に寄与していることを示唆する。
合金の観察された電子構造は、疑ギャップ構造が相安定性に寄与していることを示唆する。
森 英喜*; 都留 智仁; 奥村 雅彦; 松中 大介*; 椎原 良典*; 板倉 充洋
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(6), p.063605_1 - 063605_8, 2023/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)析出物などの障害物を導入して転位の動きを制御することは、金属の機械的強度を設計するための有力な方法である。転位コアのサイズは1nm以下とナノスケールであるため、転位と障害物の相互作用を調べるには、原子レベルのモデリングが必要である。しかし、従来の経験的ポテンシャルでは十分な精度が得られなかったため、転位と障害物の相互作用の原子レベルでの詳細が解明されていない。そこで、本研究では、人工ニューラルネットワーク(ANN)の枠組みを用い、第一原理計算の高精度を生かした原子ポテンシャルを構築した。構築したANNポテンシャルを用いて、BCC鉄における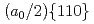 刃状転位と障害物の動的相互作用を調査した。転位が空隙を横切ると、Bow-out転位では超平滑で対称的な半ループが観察された。らせん転位を除き、ANNを用いて予測されたすべての転位のパイエルス応力は100MPa以下であった。さらに重要なことは、剛体球と転位の相互作用において、オロワンループが形成されることを確認したことである。さらに、オロワンループが剛体球と転位の相互作用の中で、2つの小さなループに分解する現象を発見した。
刃状転位と障害物の動的相互作用を調査した。転位が空隙を横切ると、Bow-out転位では超平滑で対称的な半ループが観察された。らせん転位を除き、ANNを用いて予測されたすべての転位のパイエルス応力は100MPa以下であった。さらに重要なことは、剛体球と転位の相互作用において、オロワンループが形成されることを確認したことである。さらに、オロワンループが剛体球と転位の相互作用の中で、2つの小さなループに分解する現象を発見した。
浦川 裕翔*; 江草 大佑*; 板倉 充洋; 阿部 英司*
Materials Transactions, 64(5), p.1065 - 1071, 2023/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have evaluated local elastic properties at kink boundaries in dilute Mg-Zn-Y alloys based on scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM), first-principles calculations, and geometrical phase analysis (GPA) by measuring atomic-scale strain fields around dislocation cores. STEM observations showed that dislocations constituting kink boundaries are extended into Shockley partial dislocations by accompanying solute-enriched stacking faults (SESF). Using GPA analysis, we found that strain distributions around the partial dislocation cores are asymmetric across the Mg matrix and the SESF, showing local elastic heterogeneity. Comparison with the calculated strain field model, it is indicated that the observed asymmetric strain profiles are essentially caused by a softening of the Mg matrix. This anomalous elastic softening can be interpreted as a change in strain energy of dislocations at the kink boundary, which may contribute to the unique deformation mechanism of kink in dilute Mg alloys.
佐藤 庸平*; 江草 大佑*; 宮崎 秀俊*; 木村 耕治*; 板倉 充洋; 寺内 正己*; 阿部 英司*
Materials Transactions, 64(5), p.950 - 954, 2023/05
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:54.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)ミルフィーユ構造(MFS)を持つ希釈Mg-Zn-Y合金は、キンク変形を介して長周期積層順序(LPSO)構造を持つMg-Zn-Y合金と同等の機械強度を示す。MFSタイプのMg合金の熱安定性をより深く理解するためには、溶質濃化積層欠陥(SESFs)中のZnおよびYからなる溶質クラスター構造を明確にする必要がある。走査透過型電子顕微鏡(STEM-EELS/EDS)に基づく電子エネルギー損失およびエネルギー分散X線分光法で、MFS-Mg合金のSESFs中のZnおよびYの電子構造と組成を調べた。Zn-L2,3スペクトルは、希釈Mg合金中のZnの価電子電荷がLPSO型Mg-Zn-Y合金と異なることを示した。さらに、希釈MFS-Mg合金のY-L2,3スペクトルのL3/L2の強度比は、LPSO-Mg合金よりも大きく、これはY原子の4d3/2および4d5/2軌道の電子占有がLPSO-Mg合金と異なることを反映している。希釈MFS-Mg合金のSESF組成のSTEM-EELS解析は、Zn/Y比がLPSO-Mg合金よりも低いはずであることを示し、これはSTEM-EDS測定によっても確認された。これらの結果は、希釈MFS-Mg合金のSESFs中のクラスター構造が、LPSO型Mg-Zn-Y合金の理想的なZn6Y8クラスターとは異なるはずであることを示している。
板倉 充洋; 山口 正剛; 江草 大佑*; 阿部 英司*
Materials Transactions, 64(4), p.813 - 816, 2023/04
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:54.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kink boundaries formed in Mg-based long period stacking order (LPSO) alloys play a key role in strengthening of these materials. As the kink structure grows, many high-angle kink boundaries are eventually formed which has inclination angle close to 34 degrees. We show that this peculiar structure is a result of irreversible structural transformation and is energetically stable. We also calculate segregation energies of alloying elements Y and Zn to this boundary. Finally, the critical resolved shear stress for the migration of kink boundary is estimated for a pure-Mg kink and that with saturated with segregation. We show that segregated kink boundary requires very high shear stress about 700 MPa for migration.
小林 恵太; 中村 博樹; 板倉 充洋; 町田 昌彦; 奥村 雅彦
まてりあ, 62(3), p.175 - 181, 2023/03
核燃料の研究開発において、原子炉運転時からシビアアクシデント時の融点付近に至る温度領域まで、核燃料物質の高温物性を把握することが必須となるが、その取扱いの困難さから、実験研究を行うことは容易ではない。一方、シミュレーション研究は安全に実施可能であるが、高温物性評価のために必要である、高精度な大規模構造の長時間シミュレーションは、従来のシミュレーション手法では、実施が難しかった。我々は、最近開発された機械学習技術を応用して高精度な大規模構造の長時間シミュレーションが実施可能な「機械学習分子動力学法」を用いて、酸化トリウムの高温熱物性評価に成功した。本稿は、機械学習分子動力学法と我々の研究成果について概説する。
Lobzenko, I.; Wei, D.*; 板倉 充洋; 椎原 良典*; 都留 智仁
Results in Materials (Internet), 17, p.100364_1 - 100364_7, 2023/03
ハイエントロピー合金(HEA)は、その優れた機械的・熱力学的特性から注目されている。最近の研究では、Coフリーの面心立方HEAは、原子力材料として重要な強度・延性を向上させる可能性があることが明らかになった。本研究では、第一原理計算を用いて、CoフリーHEAの機械的特性向上の基本的なメカニズムについて検討を行った。その結果、CoフリーHEAの局所格子歪みは、よく知られたCantor合金のそれよりも顕著であることを見いだした。また、CoフリーHEAの短距離秩序形成により、積層欠陥エネルギーが大きく変動していることがわかった。このように、CoフリーHEAでは著しい局所格子歪みと、低積層欠陥領域と高積層欠陥領域からなる不均一な固溶体状態が、強度・延性の向上に寄与していることがわかった。
早川 頌*; 山本 耀二郎*; 沖田 泰良*; 板倉 充洋; 鈴木 克幸*
Computational Materials Science, 218, p.111987_1 - 111987_10, 2023/02
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:14.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)On-the-fly kinetic Monte Carlo (kMC), a computational technique for atomistic simulations, has attracted attention because it increases the simulation timescale beyond that of molecular dynamics (MD) simulations while maintaining atomistic fidelity. However, for most kMC methods, when events with high and low activation energies coexist in the event list, trivial events with extremely low activation energies that do not essentially affect the phenomena of interest, so-called flicker events, are frequently selected, making it challenging to observe the key dynamics. In this study, we use Self-Evolving Atomistic kMC (SEAKMC), one of the on-the-fly kMC methods, to model the unstable-to-stable transformations of irregular three-dimensional self-interstitial-atom (SIA) clusters in Cu generated through collision cascade. By setting an activation energy threshold once every five steps, transformations into stable configurations are enhanced. The algorithm renders the simulation timescales one or two orders of magnitude longer than those possible with MD simulations. Further, the probability of transformations into stable configurations is increased by 40 times compared to that of the original SEAKMC method. In addition, we find that the stable configurations obtained by the transformation of the SIA clusters are mostly Frank loops. In summary, this new algorithm for the SEAKMC method helps to resolve the inefficiency of kMC methods resulting from the selection of flicker events and will aid the study of meso-timescale atomistic dynamics.
津川 聖人*; 早川 頌*; 沖田 泰良*; 愛知 正温*; 板倉 充洋; 鈴木 克幸*
Computational Materials Science, 215, p.111806_1 - 111806_8, 2022/12
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:29.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Molecular dynamics simulations were conducted to evaluate the interactions between an edge dislocation and a rigid, impenetrable precipitate in Cu by changing the distance between the glide plane of the dislocation and the center of the precipitate ( ). In these calculations, the precipitate was introduced as a super particle that moved according to the total force exerted by the matrix atoms on the precipitate atoms. When the center of the precipitate was close to the glide plane, an Orowan loop was formed around the precipitate after the dislocation detached, and the critical resolved shear stress (CRSS) was similar to the value evaluated by the results at
). In these calculations, the precipitate was introduced as a super particle that moved according to the total force exerted by the matrix atoms on the precipitate atoms. When the center of the precipitate was close to the glide plane, an Orowan loop was formed around the precipitate after the dislocation detached, and the critical resolved shear stress (CRSS) was similar to the value evaluated by the results at 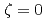 . However, when the glide plane was far from the center of the precipitate, either a vacancy loop or loops generated through the Hirsch mechanism were formed, depending on whether the center of the precipitate was below or above the glide plane. The magnitude of the CRSS was not symmetric about
. However, when the glide plane was far from the center of the precipitate, either a vacancy loop or loops generated through the Hirsch mechanism were formed, depending on whether the center of the precipitate was below or above the glide plane. The magnitude of the CRSS was not symmetric about 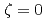 . This study confirmed that it is necessary to analyze the CRSS by changing
. This study confirmed that it is necessary to analyze the CRSS by changing  to construct a predictive model for the hardening caused by the formation of lattice defects, and that precipitate hardening appears to be smaller than the value estimated using the results at
to construct a predictive model for the hardening caused by the formation of lattice defects, and that precipitate hardening appears to be smaller than the value estimated using the results at 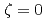 .
.
津川 聖人*; 早川 頌*; 岩瀬 祐樹*; 沖田 泰良*; 鈴木 克幸*; 板倉 充洋; 愛知 正温*
Computational Materials Science, 210, p.111450_1 - 111450_9, 2022/07
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:75.5(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Precipitation strengthening has been utilized to improve the properties of metallic materials so far. Since interactions between precipitates and dislocations are micro-mechanisms responsible for this phenomenon, a molecular dynamics (MD) simulation is a powerful tool for quantifying this phenomenon. In this study, we introduced a method to simulate a rigid and impenetrable precipitate against a direct contact with a dislocation using a single interatomic potential representing the bulk material. The total force exerted on all atoms in the precipitate region was divided by the number of atoms in the region. This average force was then applied to each atom in the region to simulate one super particle that moved depending on the total force exerted by the matrix atoms on the precipitate atoms. We used MD simulations to quantify the interaction of a precipitate with an edge dislocation. After the dislocation overcame the precipitate, an Orowan loop was formed along the outer circumference of the precipitate. The energy of the loop was 2.1  0.1 eV/b, which was higher than that obtained using the elasticity. The hardening caused by the precipitate was larger than that caused by voids of the same size. The proposed method can be applied to simulate interactions of precipitates with dislocations in any type of metallic material, especially when a dislocation bypasses a precipitate without changing its structure, except when a strong repulsive force acts between them.
0.1 eV/b, which was higher than that obtained using the elasticity. The hardening caused by the precipitate was larger than that caused by voids of the same size. The proposed method can be applied to simulate interactions of precipitates with dislocations in any type of metallic material, especially when a dislocation bypasses a precipitate without changing its structure, except when a strong repulsive force acts between them.
山口 正剛; 都留 智仁; 板倉 充洋; 阿部 英司*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12(1), p.10886_1 - 10886_7, 2022/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Multidisciplinary Sciences)液体金属脆化は特定の固体金属-液体金属のペアにおいて顕著に発生することが知られているが、そのメカニズムは理解されていない。ここで我々は、第一原理計算とサーベイランス試験との比較から、粒界吸着エネルギーや格子溶解エネルギーがゼロ付近になるペアにおいて脆化が発生するという相関関係を発見した。一方で、亀裂先端における原子間結合切断に寄与する表面吸着エネルギーはすべてのペアにおいて大きいが、元素選択性とは相関しないことが分かった。これらの結果から、亀裂先端において結合切断に先立って原子の侵入が生じることが、液体金属脆化の元素選択性を決定している要因であることが示唆される。
小林 恵太; 奥村 雅彦; 中村 博樹; 板倉 充洋; 町田 昌彦; Cooper, M. W. D.*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12(1), p.9808_1 - 9808_11, 2022/06
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:71.37(Multidisciplinary Sciences)核燃料の一つであるトリウム酸化物に対し、機械学習分子動力学法を用い、その高温物性を調査した。様々な交換汎関数により第一原理計算を実施し、ニューラルネットによりその結果を学習することにより機械学習力場を構築した。特にSCANと呼ばれる交換汎関数を用いた第一原理計算結果を学習することにより得られた機械学習力場は、ラムダ転移温度や融点を含め、比較可能な実験データの多くに対し高精度な結果を示した。
森 承宇*; 松田 那由多*; 沖田 泰良*; 愛知 正温*; 板倉 充洋; 鈴木 克幸*
Materialia, 21, p.101371_1 - 101371_6, 2022/03
The nonlinear ultrasonic (NLU) technique is a nondestructive method for detecting nanostructure in crystalline materials. In this study, a method was developed to quantify the changes in NLU signals associated with nanostructure using molecular dynamics (MD). A nonreflective boundary, which reduces the computational cost to the first power of the wavelength, was used to achieve this. This method is distinct from previous studies using a conventional MD, for which the computational cost is proportional to the square of the wavelength. The nonreflective boundary eliminates the influence of reflected waves at the detection position by setting a buffer region at the end of the simulation cell opposite from the wave source, and periodically resetting the displacements and velocities of all atoms in this region. This method allows the introduction of elastic waves with wavelengths longer than the cell size, and only an extension of time is required, according to the extension of the wavelength, without increasing the cell size. Hence, it is possible to extend the NLU wavelength by approximately four orders of magnitude, which approaches the wavelengths used for inspections and, thus, to use MD to simulate the changes in the NLU signals induced by nanostructure. The NLU signal values obtained by the two methods were in good agreement for a perfect Fe crystal and a Fe crystal containing 1% monovacancies. No significant frequency dependence of the acoustic nonlinearity parameter was found at 0 K. This method will contribute to the development of an inspection technique based on scientific principles.
都留 智仁; 板倉 充洋; 山口 正剛; 渡邊 千尋*; 三浦 博己*
Computational Materials Science, 203, p.111081_1 - 111081_9, 2022/02
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:64.95(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)六方晶構造を有する材料は、結晶構造の異方性によって塑性変形の異方性が存在し、合金化によってその特性が大きく変化をすることが知られている。純チタンでは一般に柱面転位を主すべり系として塑性変形するが、広く用いられるAlやVを添加したTi64合金の疲労破壊は 相の底面で生じる。純Tiと異なり底面すべりが生じていることが実験観察によって確認されているが、その要因は知られていない。近年、第一原理計算に基づく原子モデルを用いた転位の解析が行われるようになり、詳細なメカニズムの解明が進んでいる。本研究では、HCP構造を持つチタンを対象に、合金元素の転位運動への影響を詳細に検討した。その結果、転位のすべりのPeierlsポテンシャルは柱面と底面で大きな違いがないが、AlやVの添加によって転位芯構造の安定性が変化し、すべり変形のモードが変化することを明らかにした。
相の底面で生じる。純Tiと異なり底面すべりが生じていることが実験観察によって確認されているが、その要因は知られていない。近年、第一原理計算に基づく原子モデルを用いた転位の解析が行われるようになり、詳細なメカニズムの解明が進んでいる。本研究では、HCP構造を持つチタンを対象に、合金元素の転位運動への影響を詳細に検討した。その結果、転位のすべりのPeierlsポテンシャルは柱面と底面で大きな違いがないが、AlやVの添加によって転位芯構造の安定性が変化し、すべり変形のモードが変化することを明らかにした。
沖田 泰良*; 寺山 怜志*; 津川 聖人*; 小林 恵太; 奥村 雅彦; 板倉 充洋; 鈴木 克幸*
Computational Materials Science, 202, p.110865_1 - 110865_9, 2022/02
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:48.44(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, a Neural Network Potential (NNP) using an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) was developed for Zr, which is used as fuel cladding material in light water reactors. The reference data were obtained through first-principles calculations of various quantities, such as strained hexagonal-closed-packed (hcp) cells, strained face-centered cubic cells, cells containing a vacancy, several vacancies, and surfaces and  -surface energy on all five slip planes in the hcp structures. These data were converted to training data for the ANN, which were invariant to the rotation and translation of the atoms and independent of the number of atoms in the cells. The ANN was defined as a three-layer structure and the number of the nodes was set to 26-12-18-1. The NNP reproduced the first-principles calculations, particularly for the shear deformation, vacancy formation energy, surface energy, and
-surface energy on all five slip planes in the hcp structures. These data were converted to training data for the ANN, which were invariant to the rotation and translation of the atoms and independent of the number of atoms in the cells. The ANN was defined as a three-layer structure and the number of the nodes was set to 26-12-18-1. The NNP reproduced the first-principles calculations, particularly for the shear deformation, vacancy formation energy, surface energy, and  -surface energy, with much higher accuracy than any of the existing potentials that have been developed for classical molecular dynamics simulations. The NNP was applied to identify the formation process of c-type dislocation loops in Zr, which is a key microstructure responsible for abrupt increases in hydrogen absorption. The formation process was determined by the balance of the vacancy formation energy, surface energy and the
-surface energy, with much higher accuracy than any of the existing potentials that have been developed for classical molecular dynamics simulations. The NNP was applied to identify the formation process of c-type dislocation loops in Zr, which is a key microstructure responsible for abrupt increases in hydrogen absorption. The formation process was determined by the balance of the vacancy formation energy, surface energy and the  -surface energy on the basal plane, both of which were precisely reproduced only by the NNP developed in this study. The formation process was identified based on the atomistic behavior of the NNP.
-surface energy on the basal plane, both of which were precisely reproduced only by the NNP developed in this study. The formation process was identified based on the atomistic behavior of the NNP.
寺山 怜志*; 岩瀬 祐樹*; 早川 頌*; 沖田 泰良*; 板倉 充洋; 鈴木 克幸*
Computational Materials Science, 195, p.110479_1 - 110479_12, 2021/07
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:57.69(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Austenitic stainless steels, which are used as incore structural materials in light water reactors, are characterized by an extremely low stacking fault energy (SFE) among face-centered cubic (FCC) metals. To evaluate the effects of SFE on defect formation under high-energy particle irradiation, molecular dynamics simulations were performed using the interatomic potential sets for FCC metals with different SFEs and a primary knock-on atom energy (E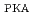 ) of 100 keV at 600 K. The results show that the number of residual defects is independent of the SFE. However, the characteristics of self-interstitial atom (SIA) clusters do depend on the SFE. For clusters smaller than a certain size, the ratio of glissile SIA clusters decreases as the SFE increases, which is similar to the trend observed at the low E
) of 100 keV at 600 K. The results show that the number of residual defects is independent of the SFE. However, the characteristics of self-interstitial atom (SIA) clusters do depend on the SFE. For clusters smaller than a certain size, the ratio of glissile SIA clusters decreases as the SFE increases, which is similar to the trend observed at the low E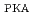 . However, for larger clusters, which can be detected only at a high E
. However, for larger clusters, which can be detected only at a high E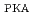 , the ratio of glissile clusters increases. These results correspond to static energy calculations, in which the difference in the formation energy between a Frank loop and perfect loop (
, the ratio of glissile clusters increases. These results correspond to static energy calculations, in which the difference in the formation energy between a Frank loop and perfect loop ( E
E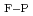 ) for the small clusters decreases as the SFE increases. In contrast, for the larger clusters, the SFE dependence of
) for the small clusters decreases as the SFE increases. In contrast, for the larger clusters, the SFE dependence of  E
E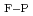 changes due to the shape restrictions of stable perfect loops. At a high temperature of 600 K, large vacancy clusters with stacking faults can be detected at E
changes due to the shape restrictions of stable perfect loops. At a high temperature of 600 K, large vacancy clusters with stacking faults can be detected at E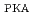 = 100 keV, resulting in the enhanced formation of these clusters at lower SFEs. Furthermore, several of these clusters were similar to perfect loops, with the edges split into two partial dislocations with stacking faults, although the largest clusters detected at low E
= 100 keV, resulting in the enhanced formation of these clusters at lower SFEs. Furthermore, several of these clusters were similar to perfect loops, with the edges split into two partial dislocations with stacking faults, although the largest clusters detected at low E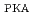 s were similar to stacking fault tetrahedrons.
s were similar to stacking fault tetrahedrons.
小林 恵太; 永井 佑紀; 板倉 充洋; 志賀 基之
Journal of Chemical Physics, 155(3), p.034106_1 - 034106_9, 2021/07
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:44.89(Chemistry, Physical)自己学習ハイブリッドモンテカルロ法は機械学習力場を利用することにより、第一原理計算の高速化を可能にする手法である。今回、自己学習ハイブリッドモンテカルロ法をNPTアンサンブルに適用し、液体シリカの解析を行った。本論文では自己学習ハイブリッドモンテカルロ法を用いることにより、厳密に第一原理計算の精度を保ちながら、高速に液体シリカの配置空間のサンプリングが可能であることを示した。また、液体シリカの構造因子の計算を行い実験データとの比較を行ったところ、両者はよい一致を見せた。