Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
小野田 忍; 阿部 浩之; 山本 卓; 大島 武; 磯谷 順一*; 寺地 徳之*; 渡邊 賢司*
Proceedings of 10th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Applications (RASEDA-10) (Internet), p.93 - 96, 2012/12
We have developed two systems to acquire two-dimensional maps of Single Event Effects (SEEs) by using focused microbeams. While the microbeam has many advantages for SEE testing, the transport and optimization of the microbeam requires much time and effort, especially for high energy heavy ions. Therefore the mapping system with less effort is required, and we are developing the Ion Photon Emission Microscopy (IPEM). Since the spatial resolution is determined by the spot size and the intensity of luminescence, the scintillator is one of the most important parts of IPEM. We propose that the diamond containing Nitrogen Vacancy (NV) centers can be used as a scintillator. For both diamond and YAG:Ce proposed by Sandia National Laboratories, the minimum spot size is a few micrometers. IBIL intensity from diamond is four times higher than that from YAG:Ce. Therefore, we propose that the diamond containing NV centers is a rival candidate of YAG:Ce for IPEM.
小野田 忍; 山本 卓; 大島 武; 磯谷 順一*; 寺地 徳之*; 渡邊 賢司*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 37(2), p.241 - 244, 2012/06
To develop the single ion detection system with high spatial resolution, the ion induced luminescence was evaluated. By capturing the ion induced luminescence from a diamond by using Charge Coupled Device (CCD) Camera, the spot size and location of ion induced luminescence were evaluated. It was found that the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of spot is about 4  m. The position where ion hits the sample can be calculated from the center of mass of each spot. We performed the same experiment by using YAG which is proposed by previous studies. We found that the diamond is comparable to YAG from the point of view of spatial resolution. In addition, the intensity of luminescence from diamond was slightly higher than that from YAG. According to these results, we suggest that both diamond and YAG:Ce are suitable for single ion detection with high spatial resolution.
m. The position where ion hits the sample can be calculated from the center of mass of each spot. We performed the same experiment by using YAG which is proposed by previous studies. We found that the diamond is comparable to YAG from the point of view of spatial resolution. In addition, the intensity of luminescence from diamond was slightly higher than that from YAG. According to these results, we suggest that both diamond and YAG:Ce are suitable for single ion detection with high spatial resolution.
山本 卓; 小野田 忍; 大島 武; Naydenov, B.*; Dolde, F.*; Fedder, H.*; Honert, J.*; Jelezko, F.*; Wrachtrup, J.*; 寺地 徳之*; et al.
no journal, ,
ダイヤモンド結晶中の負に帯電した窒素空孔センター(NV)は、室温で動作可能な量子ビットとして最も有力な材料の一つであるが、応用的観点からはNVセンターを効率よく人工的に生成する必要がある。本研究では、イオン照射条件,熱処理条件,試料の品質の違い(欠陥量、おもに窒素濃度)で、NVセンターの生成にどのような影響があるかを系統的に調べた。その結果、NV生成の収率は照射量が多くなると下がる傾向にあり、照射エネルギーが高い方が収率が上がることがわかった。一方、マイクロビームによる局所的照射試料における収率は25%から数百%であり、ブロードビーム照射試料(例えば、照射量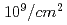 試料では4%)と比較すると収率が飛躍的に改善することがわかった。マイクロビーム照射試料において、収率がそれぞれの試料で異なることから、ダイヤモンド試料基板の質の違いがNV生成に重要な要素であることが示唆される。
試料では4%)と比較すると収率が飛躍的に改善することがわかった。マイクロビーム照射試料において、収率がそれぞれの試料で異なることから、ダイヤモンド試料基板の質の違いがNV生成に重要な要素であることが示唆される。
寺地 徳之*; 谷口 尚*; 渡邊 賢司*; 小泉 聡*; 小野田 忍; 大島 武; 磯谷 順一*
no journal, ,
Homoepitaxial single crystal diamond films and polycrystalline diamond free-standing films were grown by means of microwave-assisted chemical vapour deposition (MPCVD). Methane that is isotopically controlled into  C depleted gas was used as a source gas. In order to fulfil both the higher quality and higher growth rate, diamond films were grown under the high power MPCVD condition. It was found that the free exciton emission was intensively observed from the homoepitaxial diamond (100) films. This fact indicates the high quality of diamond films was obtained by this method. The free exciton emission was also detected from polycrystalline free-standing diamond, although the intensity was weaker than those of homoepitaxial film. These enriched diamond crystals are attracted for improving thermal conductivity and coherence time of nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers.
C depleted gas was used as a source gas. In order to fulfil both the higher quality and higher growth rate, diamond films were grown under the high power MPCVD condition. It was found that the free exciton emission was intensively observed from the homoepitaxial diamond (100) films. This fact indicates the high quality of diamond films was obtained by this method. The free exciton emission was also detected from polycrystalline free-standing diamond, although the intensity was weaker than those of homoepitaxial film. These enriched diamond crystals are attracted for improving thermal conductivity and coherence time of nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers.
小野田 忍; 山本 卓; 阿部 浩之; 花屋 博秋; 大島 武; 谷口 尚*; 寺地 徳之*; 渡邊 賢司*; 小泉 聡*; 神田 久生*; et al.
no journal, ,
量子情報素子や磁気センサーへの応用,超伝導キュービットとのハイブリッド系が注目されている窒素-空孔(NV)センターでは、電子スピンを持つ不純物窒素や欠陥による双極子場, C核スピンの双極子場,他のNVセンターの双極子場など、コヒーレンス時間を短くする要因をできるだけ排除して、最適の濃度あるいは配列を作成するエンジニアリングが求められる。窒素濃度,同位体濃度の異なる結晶にイオン照射や熱処理,高温電子線照射を行い、それぞれの応用に対して最適のものを求める試みを行った。熱処理を800から1200
C核スピンの双極子場,他のNVセンターの双極子場など、コヒーレンス時間を短くする要因をできるだけ排除して、最適の濃度あるいは配列を作成するエンジニアリングが求められる。窒素濃度,同位体濃度の異なる結晶にイオン照射や熱処理,高温電子線照射を行い、それぞれの応用に対して最適のものを求める試みを行った。熱処理を800から1200 Cまで変化させてNVセンターやそれ以外の欠陥を調べた結果、1000
Cまで変化させてNVセンターやそれ以外の欠陥を調べた結果、1000 Cの熱処理が最も優れていることを明らかにできた。また、マイクロビームとシングルイオンヒット技術を利用して、量子情報素子の最も基本的なNVセンターのペアを作成することに成功した。さらに、空孔が格子中を動き回るような高温(700
Cの熱処理が最も優れていることを明らかにできた。また、マイクロビームとシングルイオンヒット技術を利用して、量子情報素子の最も基本的なNVセンターのペアを作成することに成功した。さらに、空孔が格子中を動き回るような高温(700 C)の電子線照射を用いることにより、NVセンターの広い濃度領域(2
C)の電子線照射を用いることにより、NVセンターの広い濃度領域(2 30ppm)に渡って、コヒーレンス時間が、残存する窒素の双極子場の搖動ではなく、NVセンター同士の双極子双極子相互作用で決まるような作成法に成功した。
30ppm)に渡って、コヒーレンス時間が、残存する窒素の双極子場の搖動ではなく、NVセンター同士の双極子双極子相互作用で決まるような作成法に成功した。
小野田 忍; 阿部 浩之; 山本 卓; 大島 武; 磯谷 順一*; 寺地 徳之*; 渡邊 賢司*
no journal, ,
高エネルギー重イオン1個が半導体に誘起するシングルイベント効果(Single Event Effect: SEE)を評価するために、ブロードビームと位置検出技術を組合せてマイクロビーム照射実験と同等の実験、つまりイオン誘起電荷のマッピング像を測定することができる装置の開発に取り組んでいる。不純物として窒素を多く含む単結晶ダイヤモンド基板に対して、室温で2MeVの電子線を照射し、空孔を導入した。熱処理を施すことで、窒素と空孔を結合させ、Nitrogen Vacancy (NV)センターを多量に含むダイヤモンドを作成した。フォトルミネッセンス測定により、NVセンターが含まれていることを確認した。この試料に対し、イオン照射を行った結果、単一イオン検出が可能であることがわかり、NVセンターを含むダイヤモンドが発光体として有望であることがわかった。
小野田 忍; 阿部 浩之; 山本 卓; 大島 武; 磯谷 順一*; 寺地 徳之*; 渡邊 賢司*
no journal, ,
The Ion Photon Emission Microscopy (IPEM) gives us two-dimensional maps of Single Event Effects (SEEs). To observe the map, the position where the single ion strikes a scintillator placed over a microelectronics circuit is recorded together with SEE signal. Since the spatial resolution is determined by the spot size and the intensity of the Ion Beam Induced Luminescence (IBIL), the scintillator is one of the most important parts of IPEM. In this study, we propose that the diamond containing Nitrogen Vacancy (NV) centers can be used as a scintillator. The results obtained from diamond were compared to those of YAG:Ce. For both cases, the averaged spot size of a few micrometers is observed. The IBIL intensity from diamond is 4 times higher than that from YAG:Ce. According to these results, we suggest that diamond containing NV centers is a rival candidate of YAG:Ce from the point of view of single ion detection with high spatial resolution.
大島 武; 山本 卓; 小野田 忍; 阿部 浩之; 佐藤 真一郎; Jahnke, K.*; Heller, P.*; Gerstmayr, A.*; H ussler, A.*; Naydenov, B.*; et al.
ussler, A.*; Naydenov, B.*; et al.
no journal, ,
ダイヤモンド中のマイナスに帯電した窒素-空孔(NV )中心はスピンを利用した量子計算の観点から注目されている。高純度IIaダイヤモンドに窒素(N)イオンを注入することでNV
)中心はスピンを利用した量子計算の観点から注目されている。高純度IIaダイヤモンドに窒素(N)イオンを注入することでNV の形成を試みた。本研究では、長いスピン緩和時間(T
の形成を試みた。本研究では、長いスピン緩和時間(T )を達成することを目的とし、スピン散乱の原因となる
)を達成することを目的とし、スピン散乱の原因となる Cを減少させた高濃度
Cを減少させた高濃度 C (99.99%)のダイヤモンドを化学気相法を用いて成長した。Nイオンは、打ち込んだNと試料にもともと残留していたNを区別するため、
C (99.99%)のダイヤモンドを化学気相法を用いて成長した。Nイオンは、打ち込んだNと試料にもともと残留していたNを区別するため、 Nイオンを用い、10MeVのエネルギーでのマイクロビーム照射を行った。Nを打ち込んだ領域を共焦点顕微鏡及びODMR(optically detected magnetic resonance)で評価したところ、
Nイオンを用い、10MeVのエネルギーでのマイクロビーム照射を行った。Nを打ち込んだ領域を共焦点顕微鏡及びODMR(optically detected magnetic resonance)で評価したところ、 N由来のNV
N由来のNV と
と N由来のNV
N由来のNV の両者が形成されることが見いだされた。T
の両者が形成されることが見いだされた。T を測定した結果、両者のNV
を測定した結果、両者のNV とも2msであり、イオン注入を用いて形成したNV
とも2msであり、イオン注入を用いて形成したNV のこれまでの報告値より10倍程度長い値であることが判明した。
のこれまでの報告値より10倍程度長い値であることが判明した。
山本 卓; 小野田 忍; 大島 武; 磯谷 順一*; 寺地 徳之*; 谷口 尚*; 渡邊 賢司*; 小泉 聡*; 梅田 享英*; Jelezko, F.*; et al.
no journal, ,
 Nイオン照射で生成した高純度
Nイオン照射で生成した高純度 C濃縮ダイヤモンド中のNV中心について、単一スピンの光学的検出磁気共鳴を測定した。詳細な光学的検出磁気共鳴測定から、
C濃縮ダイヤモンド中のNV中心について、単一スピンの光学的検出磁気共鳴を測定した。詳細な光学的検出磁気共鳴測定から、 Nイオン照射によって
Nイオン照射によって NVと
NVと NVが[
NVが[ NV]/[
NV]/[ NV]
NV]  1の比で生成され、収率(イオン照射量に対する生成したNV中心の割合)は70-100%であることがわかった。スピンコヒーレンス時間は室温で2msと長く、これまで報告されているイオン照射試料の中で最も長いことがわかった。これらの結果は、イオン照射で生成したNVスピンを用いた応用が十分期待できると結論できた。
1の比で生成され、収率(イオン照射量に対する生成したNV中心の割合)は70-100%であることがわかった。スピンコヒーレンス時間は室温で2msと長く、これまで報告されているイオン照射試料の中で最も長いことがわかった。これらの結果は、イオン照射で生成したNVスピンを用いた応用が十分期待できると結論できた。
山本 卓; 小野田 忍; 大島 武; 寺地 徳之*; 渡邊 賢司*; 谷口 尚*; 小泉 聡*; 梅田 享英*; 磯谷 順一*; McGuinness, L.*; et al.
no journal, ,
窒素イオン注入と熱処理によって生成した同位体濃縮ダイヤモンド単結晶中の窒素空孔発光中心(NV)のスピン特性を、共焦点顕微鏡による光学的検出磁気共鳴法を用いて詳細に測定した。スピンエコー測定の結果、電子スピンコヒーレンス時間は、イオン照射したNVとしては最長の2ミリ秒、表面付近(15ナノメートルの深さ)でも500マイクロ秒以上と非常に長いことがわかった。これらの結果は、良質な同位体濃縮結晶の結晶性と不純物スピンの低減、及び、熱処理による十分な照射損傷の回復を反映している。また、窒素分子イオン照射による近接するNVペアの作製に成功し、2つのNVスピン間の磁気的結合にも成功した。これらの単一NVのスピン特性は、室温で動作可能なナノマグネトメトリーや量子情報処理への応用が期待できる。
 C同位体濃縮ダイヤモンドのホモエピタキシャル合成
C同位体濃縮ダイヤモンドのホモエピタキシャル合成寺地 徳之*; 山本 卓*; 小泉 聡*; 渡邊 賢司*; 谷口 尚*; 小野田 忍; 大島 武; Naydenov, B.*; Jelezko, F.*; 磯谷 順一*
no journal, ,
本研究では、 C炭素同位体比が天然存在比より約3桁高い同位体濃縮メタンガスを用いてダイヤモンド薄膜を合成し、その発光特性を評価した。発光特性の評価には、窒素イオンを照射することで作製した窒素-空孔欠陥(NVセンター)からの発光を利用した。測定の結果、照射領域からはNVセンター固有の発光スペクトルが観測された。NVセンターに加えて、シリコン-空孔欠陥(SiVセンター)が、0.01ppb以下の密度ではあるが、照射領域近傍で観測された。一方、照射領域以外からは余分な発光が検出されることはなく、良質のダイヤモンドホモエピタキシャル膜が作製できたといえる。
C炭素同位体比が天然存在比より約3桁高い同位体濃縮メタンガスを用いてダイヤモンド薄膜を合成し、その発光特性を評価した。発光特性の評価には、窒素イオンを照射することで作製した窒素-空孔欠陥(NVセンター)からの発光を利用した。測定の結果、照射領域からはNVセンター固有の発光スペクトルが観測された。NVセンターに加えて、シリコン-空孔欠陥(SiVセンター)が、0.01ppb以下の密度ではあるが、照射領域近傍で観測された。一方、照射領域以外からは余分な発光が検出されることはなく、良質のダイヤモンドホモエピタキシャル膜が作製できたといえる。
磯谷 順一*; 寺地 徳之*; 山本 卓*; 谷口 尚*; 渡邊 賢司*; 小泉 聡*; 小野田 忍; 阿部 浩之; 大島 武; 梅田 享英*; et al.
no journal, ,
炭化ケイ素(SiC)やダイヤモンドはパワー半導体素子としてだけでなく、単一欠陥を利用した量子ビットとしての応用も期待されている。本講演では、SiC及びダイヤモンド中の欠陥についてレビューする。特に、SiCに比べて量子ビット応用が進んでいるダイヤモンドについては、光検出磁気共鳴(ODMR)やフォトルミネッセンス(PL)測定から得られた最近の結果について述べる。ダイヤモンド中の窒素-空孔(NV)センターは、たった1個しかなくてもODMRやPLによって検出することが可能である。この特徴を活かして、本研究では、極低温下において光の波長を変えながらPLを測定し、NVセンター周囲の結晶格子の歪みを検出することに成功した。また、ODMRによってダイヤモンド中の NVと
NVと NVを区別して測定し、イオン注入によって形成されたNVセンターの生成収率を得ることにも成功した。以上のように、単一のNVセンターを検出できる特徴を利用し、ダイヤモンド結晶格子の状態を観察できることを示した。
NVを区別して測定し、イオン注入によって形成されたNVセンターの生成収率を得ることにも成功した。以上のように、単一のNVセンターを検出できる特徴を利用し、ダイヤモンド結晶格子の状態を観察できることを示した。