Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tang, P.*; 北 和之*; 五十嵐 康人*; 佐藤 志彦; 畑中 恒太郎*; 足立 光司*; 木名瀬 健*; 二宮 和彦*; 篠原 厚*
Progress in Earth and Planetary Science (Internet), 9(1), p.17_1 - 17_15, 2022/03
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:69.58(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The deposition of insoluble radiocesium bearing microparticles (CsMPs), which were released from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (F1NPP) accident in March 2011, has resulted in the widespread contamination of eastern Japan. Obviously, these deposited insoluble CsMPs may become the secondary contamination sources by atmospheric migration or other environmental transferring process, however, the understanding of the transport mechanism remains non-elucidation, and the relevant evidence has not been directly provided. This study, for the first time, provides the direct evidence for the resuspension of these insoluble CsMPs to the atmosphere from (1) proximity of  Cs radioactivity and resemblance of the morphology and the elemental compositions of CsMPs in the samples of soil and aerosol derived from the same sampling site, (2) the special characteristics of the resuspended CsMPs of which the ratios of Na/Si, K/Si and/or Cs/Si were smaller than those from the initially released CsMPs collected at either long distance or near F1NPP, which can be ascribed to the slowly natural corrosion of CsMPs by the loss of the small amount of soluble contents in CsMPs, and (3) high CsMPs concentration of 10 granules/gram in the surface soil of our sampling site, and high resuspension frequency of CsMPs in spring when predominant suspended particles were soil dust.
Cs radioactivity and resemblance of the morphology and the elemental compositions of CsMPs in the samples of soil and aerosol derived from the same sampling site, (2) the special characteristics of the resuspended CsMPs of which the ratios of Na/Si, K/Si and/or Cs/Si were smaller than those from the initially released CsMPs collected at either long distance or near F1NPP, which can be ascribed to the slowly natural corrosion of CsMPs by the loss of the small amount of soluble contents in CsMPs, and (3) high CsMPs concentration of 10 granules/gram in the surface soil of our sampling site, and high resuspension frequency of CsMPs in spring when predominant suspended particles were soil dust.
梶野 瑞王*; 足立 光司*; 五十嵐 康人*; 佐藤 志彦; 澤田 壮弘*; 関山 剛*; 財前 祐二*; 佐谷 茜*; 鶴田 治雄*; 森口 祐一*
Journal of Geophysical Research; Atmospheres, 126(1), p.e2020JD033460_1 - e2020JD033460_23, 2021/01
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:72.21(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)The dispersion and deposition of radio-cesium ( Cs) carried by the two types (type A and type B) of water-insoluble Cs-bearing solid microparticles (CsMPs) released due to the Fukushima nuclear accident were simulated for the first time. The presence of type B CsMPs (70-400
Cs) carried by the two types (type A and type B) of water-insoluble Cs-bearing solid microparticles (CsMPs) released due to the Fukushima nuclear accident were simulated for the first time. The presence of type B CsMPs (70-400  m found in soil and 1-5
m found in soil and 1-5  m found in air), associated with the hydrogen explosion of Unit 1 in the afternoon of March 12, could partly explain the simulated underestimation of total deposition over land by assuming that 100% of the Cs carriers were water-soluble submicron particles (WSPs). Type A CsMPs (0.1-10
m found in air), associated with the hydrogen explosion of Unit 1 in the afternoon of March 12, could partly explain the simulated underestimation of total deposition over land by assuming that 100% of the Cs carriers were water-soluble submicron particles (WSPs). Type A CsMPs (0.1-10  m), released from Units 2 or 3 in the midnight between March 14 and 15, travelled over the Kanto Plain, the most populated plain in Japan. Differences in the size distribution of type A CsMPs altered the surface air concentration over Kanto substantially, by up to more than one order of magnitude. The major deposition mechanisms varied among dry, wet, and fog depositions depending on the size distribution. The simulated activity fractions due to the CsMPs in the total deposition were compared to those observed in surface soil for the first time. The observations could be explained by the simulations for the locations under the influence of type B CsMPs. However, the simulations were substantially underestimated for the locations influenced by type A CsMPs. There could be more fractions of type A CsMPs emission in the source term and/or the simulated deposition rates of type A CsMPs were underestimated.
m), released from Units 2 or 3 in the midnight between March 14 and 15, travelled over the Kanto Plain, the most populated plain in Japan. Differences in the size distribution of type A CsMPs altered the surface air concentration over Kanto substantially, by up to more than one order of magnitude. The major deposition mechanisms varied among dry, wet, and fog depositions depending on the size distribution. The simulated activity fractions due to the CsMPs in the total deposition were compared to those observed in surface soil for the first time. The observations could be explained by the simulations for the locations under the influence of type B CsMPs. However, the simulations were substantially underestimated for the locations influenced by type A CsMPs. There could be more fractions of type A CsMPs emission in the source term and/or the simulated deposition rates of type A CsMPs were underestimated.
佐藤 志彦; 末木 啓介*; 笹 公和*; 吉川 英樹; 中間 茂雄; 箕輪 はるか*; 阿部 善也*; 中井 泉*; 小野 貴大*; 足立 光司*; et al.
Geochemical Journal, 52(2), p.137 - 143, 2018/00
被引用回数:68 パーセンタイル:97.15(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Two types of radioactive particles have been isolated from environmental samples collected at various distances from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station. "Type A" particles are 2-10  m in diameter and display characteristic Cs X-ray emissions when analysed by energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDS). "Type B" particles are considerably larger, up to 400
m in diameter and display characteristic Cs X-ray emissions when analysed by energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDS). "Type B" particles are considerably larger, up to 400  m in diameter, with Cs concentrations too low to be detectable by EDS. These larger particles were isolated from the region to the north of the nuclear reactor site, which was contaminated on March 12, 2011. The specific activity of Type B particles is much lower than Type A, and the mean
m in diameter, with Cs concentrations too low to be detectable by EDS. These larger particles were isolated from the region to the north of the nuclear reactor site, which was contaminated on March 12, 2011. The specific activity of Type B particles is much lower than Type A, and the mean  Cs
Cs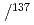 Cs ratios are
Cs ratios are  0.93 and 1.04, respectively. The Type B ratio indicates power station Unit 1 as the source, implying that these larger radioactive particles were discharged on March 12. This study found that different type of radioactive particle was released not only on March 15 but also on March 12.
0.93 and 1.04, respectively. The Type B ratio indicates power station Unit 1 as the source, implying that these larger radioactive particles were discharged on March 12. This study found that different type of radioactive particle was released not only on March 15 but also on March 12.
小野 貴大*; 飯澤 勇信*; 阿部 善也*; 中井 泉*; 寺田 靖子*; 佐藤 志彦; 末木 啓介*; 足立 光司*; 五十嵐 康人*
分析化学, 66(4), p.251 - 261, 2017/04
被引用回数:32 パーセンタイル:79.03(Chemistry, Analytical)2011年3月の福島第一原子力発電所事故により、1号機由来の放射性物質が飛来したと考えられる原子力発電所北西地域の土壌から、強放射性の粒子を7点分離した。分離された粒子は100um前後の大きさで歪な形状のものが多く、2号機から放出されたとされる直径数umの球形粒子(Csボール)とは明らかに異なる物理性状を有していた。これらの粒子に対して、大型放射光施設SPring-8において放射光マイクロビームX線を用いた蛍光X線分析、X線吸収端近傍構造分析、X線回折分析を非破壊で適用し、詳細な化学性状を解明した。1号機由来の粒子はCsボールに比べて含有する重金属の種類に富み、特にSrやBaといった還元雰囲気で揮発性が高くなる元素が特徴的に検出され、粒子内で明確な元素の不均一性が見られた。粒子本体はCsボールと同様にケイ酸塩ガラスであったが、Feなど一部の金属元素が濃集した数um程度の結晶性物質を含有していた。これらの粒子は3月12 13日に大気中に放出されたものであると考えられ、核燃料と格納容器との熔融がかなり早い段階で進行していたことが示唆された。さらに放出源の推定において、放射性物質自体の化学組成情報が放射能比に代わる新たな指標となることが実証された。
13日に大気中に放出されたものであると考えられ、核燃料と格納容器との熔融がかなり早い段階で進行していたことが示唆された。さらに放出源の推定において、放射性物質自体の化学組成情報が放射能比に代わる新たな指標となることが実証された。
佐藤 志彦*; 末木 啓介*; 笹 公和*; 箕輪 はるか*; 吉川 英樹; 藤原 健壮; 中間 茂雄; 足立 光司*; 五十嵐 康人*
no journal, ,
福島第一原子力発電所事故では、Csを高濃度に濃縮した放射性粒子が放出したことが確認されている。本研究では原子力発電所周辺の特に線量が高いエリアにおいて土壌等を採取し、放射性粒子の分布およびその特徴を分析した。その結果、土壌試料から、複数の放射性粒子が確認された。特に原子力発電所から北北西方向約7kmの地点では数百 mに達する放射性粒子が複数見つかった。見つかった放射性粒子は、先行研究において、原子力発電所から20km北西に離れた地点、およびつくば市で見つかった粒子と元素組成、並びに粒子の表面状態が類似していた。
mに達する放射性粒子が複数見つかった。見つかった放射性粒子は、先行研究において、原子力発電所から20km北西に離れた地点、およびつくば市で見つかった粒子と元素組成、並びに粒子の表面状態が類似していた。
梶野 瑞王*; 関山 剛*; 五十嵐 康人*; 足立 光司*; 財前 祐二*; 澤田 壮弘*; 佐藤 志彦; 森口 祐一*
no journal, ,
A great number of atmospheric simulations have been conducted to understand the consequences of FDNPP accident. We came to know wet deposition is important but don't know to what extent. We know simulations vary but we don't know why. Meteorological model comparison with a single dispersion model was conducted to evaluate the magnitude of uncertainty in meteorological simulations. Among the deposition processes, rainout by liquid precipitation was the most important process. The fog deposition was the next, which was not considered in any other models but Katata et al., ACP (2015) and this study. Fog deposition is the main cause for the deposition in Gunma and Tochigi prefecture. All the simulation underestimated the airborne observation of Cs deposition, which amounted to 2.6 PBq. The underestimation is approximately 1.5 PBq (1 PBq in Hamadori and 0.4 PBq in Nakadori). It is due to underestimation of deposition process, which is the main finding of the meteorological model ensemble study: Some model overestimated while others underestimated both the precipitation and surface concentration, and therefore the precipitation and source term estimation should be reasonable and not be the cause of underestimation. By considering the A-type (Adachi et al., Sci. Rep., 2014) and S-type (Satou et al., Anthropocene, 2016) of Cs-ball particles, associated with the SRV opening of Unit 2 and Hydrogen explosion of Unit 1, respectively, the underestimation of simulated Cs deposition could be significantly improved. The maximum estimation of the additional deposition due to Cs-ball amounted approximately 1 PBq.
石井 達也*; 末木 啓介*; 松尾 一樹*; 黒澤 正紀*; 佐藤 志彦; 小畠 雅明; 福田 竜生; 吉井 賢資; 谷田 肇; 岡根 哲夫; et al.
no journal, ,
2011年3月、福島第一原子力発電所事故によって、放射性セシウムを高濃度に含む不溶性の放射性粒子が放出された。放射性粒子の物理的, 化学的な性質を調べることは、事故発生時の原子炉内部の情報を理解することにつながると考えられている。放射性粒子はType-A(2, 3号機由来)とType-B(1号機由来)に大別される。Type-BはType-Aとは異なり、大きさが数百 mと大きく、不定形であり、元素分布は不均一である。そのため、生成過程や生成環境も異なると考えられる。そこで、放射性粒子の原料や元素の化学状態等について議論し、Type-Bの放射性粒子の生成過程を検討した。放射性粒子は、福島第一原子力発電所から北北西に2km地点にある工場敷地内のダスト試料から取り出した。Type-Bの放射性粒子2個を断面加工し、母材部分や重元素部分について、SEM-EDS分析をした。また大型放射光施設SPring-8 BL22XUにて、硬X線光電子分光(HAXPES)を行い、放射性粒子表面の元素の化学状態を分析した。そしてこれらによりType-Bの放射性粒子の原料とCsの化学状態を考えることで、どのように粒子が形成され、高放射能を持つようになったかを推察する手掛かりが得られた。
mと大きく、不定形であり、元素分布は不均一である。そのため、生成過程や生成環境も異なると考えられる。そこで、放射性粒子の原料や元素の化学状態等について議論し、Type-Bの放射性粒子の生成過程を検討した。放射性粒子は、福島第一原子力発電所から北北西に2km地点にある工場敷地内のダスト試料から取り出した。Type-Bの放射性粒子2個を断面加工し、母材部分や重元素部分について、SEM-EDS分析をした。また大型放射光施設SPring-8 BL22XUにて、硬X線光電子分光(HAXPES)を行い、放射性粒子表面の元素の化学状態を分析した。そしてこれらによりType-Bの放射性粒子の原料とCsの化学状態を考えることで、どのように粒子が形成され、高放射能を持つようになったかを推察する手掛かりが得られた。
山澤 弘実*; 佐藤 陽祐*; 大浦 泰嗣*; 森口 祐一*; 寺田 宏明; 古野 朗子; 都築 克紀; 門脇 正尚; 関山 剛*; 足立 光司*; et al.
no journal, ,
環境研究総合推進費: 課題番号1-1802「原子力事故データの総合解析による事故時の有害物質大気中動態評価法の高度化」(2018 2020年)では、東京電力福島第一原子力発電所(1F)事故を題材として、有害物質放出事故時の数百km範囲での大気中動態を評価するために必要な要素技術の高度化に取り組んでいる。本研究は、(1)1F事故大気中濃度データの整備と解析、(2)放出源情報推定法の改良、(3)気象場再現法及び大気拡散数値モデルの高度化、(4)大気中濃度解析結果を参照データとするモデル比較試験及び防災利用での計算結果提示法のプロトタイプ構築、の研究テーマにより構成されている。本発表では、各研究テーマによるこれまでに得られた主要な成果の概要を紹介する。
2020年)では、東京電力福島第一原子力発電所(1F)事故を題材として、有害物質放出事故時の数百km範囲での大気中動態を評価するために必要な要素技術の高度化に取り組んでいる。本研究は、(1)1F事故大気中濃度データの整備と解析、(2)放出源情報推定法の改良、(3)気象場再現法及び大気拡散数値モデルの高度化、(4)大気中濃度解析結果を参照データとするモデル比較試験及び防災利用での計算結果提示法のプロトタイプ構築、の研究テーマにより構成されている。本発表では、各研究テーマによるこれまでに得られた主要な成果の概要を紹介する。
北 和之*; 林 奈穂; 五十嵐 康人*; 濱 賢三*; 財前 祐二*; 関山 剛*; 足立 光司*; 吉田 尚弘*; 豊田 栄*; 保坂 健太郎*; et al.
no journal, ,
大気バイオエアロゾルは、東京電力福島第一原子力発電所事故で環境中に放出され土壌・植生に沈着した放射性セシウムが、大気中に再浮遊(再飛散,再放出)される現象に重要な役割を果たしていることが近年の研究で明らかになっている。しかし、どのようなバイオエアロゾルが再浮遊にどれだけ寄与しているかはまだ明らかになっていない。今回、セシウムを吸収・濃縮することが知られている真菌胞子に着目し、主な再浮遊担体となっているかを検討した。福島県浪江町で行ったエアロゾル粒径別サンプリングの結果、粒径2.1 10.2
10.2 mの範囲に大気放射性セシウムの約70%と大部分が存在していることが分かった。この粒径範囲は真菌胞子と一致する。大気セシウム放射能濃度とバイオエアロゾルの粒径別濃度は正相関を示し、特に粒径3
mの範囲に大気放射性セシウムの約70%と大部分が存在していることが分かった。この粒径範囲は真菌胞子と一致する。大気セシウム放射能濃度とバイオエアロゾルの粒径別濃度は正相関を示し、特に粒径3 15
15 mの範囲で高い相関を示した。更に放射性セシウム沈着が多い林地において数種類のキノコ胞子のセシウム放射能を測定した。キノコ胞子の1個あたり放射能の中央値は、1.7
mの範囲で高い相関を示した。更に放射性セシウム沈着が多い林地において数種類のキノコ胞子のセシウム放射能を測定した。キノコ胞子の1個あたり放射能の中央値は、1.7 10
10 Bqであり、それを大気中の粒径3
Bqであり、それを大気中の粒径3 15
15 mのバイオエアロゾル数濃度にかけ算して求めた大気セシウム放射能濃度は、実際の測定値を大きく上回る。他の地域から運ばれた胞子もあることを考えると、この胞子によって大気中の放射性セシウム濃度が充分説明できることが分かる。
mのバイオエアロゾル数濃度にかけ算して求めた大気セシウム放射能濃度は、実際の測定値を大きく上回る。他の地域から運ばれた胞子もあることを考えると、この胞子によって大気中の放射性セシウム濃度が充分説明できることが分かる。