Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Cs concentrations in coastal sediments off Fukushima
Cs concentrations in coastal sediments off Fukushima鈴木 翔太郎*; 天野 洋典*; 榎本 昌宏*; 松本 陽*; 守岡 良晃*; 佐久間 一幸; 鶴田 忠彦; 帰山 秀樹*; 三浦 輝*; 津旨 大輔*; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 831, p.154670_1 - 154670_15, 2022/07
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:29.93(Environmental Sciences)The monthly monitoring data (total 3647 samples) between May. 2011 and Mar. 2020 were analyzed to describe temporal variability of  Cs concentration in coastal sediments off Fukushima.
Cs concentration in coastal sediments off Fukushima.  Cs concentration of sediment had decreasing trend, but non-linear model fitting suggested that this decreasing trend showed slower. Additionally,
Cs concentration of sediment had decreasing trend, but non-linear model fitting suggested that this decreasing trend showed slower. Additionally,  Cs concentration were up to 4.08 times greater in shallow sampling sites (7, 10, 20 m depth) following heavy rainfall events (before five months vs. after five months), such as typhoons. These were consistent with increasing particulate
Cs concentration were up to 4.08 times greater in shallow sampling sites (7, 10, 20 m depth) following heavy rainfall events (before five months vs. after five months), such as typhoons. These were consistent with increasing particulate  Cs (P-
Cs (P- Cs) fluxes from river and increasing dissolved
Cs) fluxes from river and increasing dissolved  Cs (D-
Cs (D- Cs) concentration in seawater. Finally, the numerical experiment was conducted and revealed that riverine
Cs) concentration in seawater. Finally, the numerical experiment was conducted and revealed that riverine  Cs input could preserve
Cs input could preserve  Cs concentration in coastal sediment. These results indicate that riverine
Cs concentration in coastal sediment. These results indicate that riverine  Cs input via heavy rainfall events is one of the main factors for preserving
Cs input via heavy rainfall events is one of the main factors for preserving  Cs concentration in coastal sediment off Fukushima.
Cs concentration in coastal sediment off Fukushima.
高田 兵衛*; 久万 健志*; 磯田 豊*; 乙坂 重嘉; 千手 智晴*; 皆川 昌幸*
Geophysical Research Letters, 35(2), p.L02606_1 - L02606_5, 2008/01
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:44.27(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)日本海の2つの海盆(大和海盆及び日本海盆)で採取した海水中の鉄(溶存鉄と可溶性鉄)濃度から、両海盆での鉄の挙動について考察した。孔径0.22 mのフィルターで濾過し、緩衝液でpH=3.2に調整した海水に含まれる鉄を溶存鉄、濾過せずにpH調整のみを行った海水に含まれる鉄を可溶性鉄とした。表層(0
mのフィルターで濾過し、緩衝液でpH=3.2に調整した海水に含まれる鉄を溶存鉄、濾過せずにpH調整のみを行った海水に含まれる鉄を可溶性鉄とした。表層(0 200m深)における可溶性鉄存在量は、いずれの海域でも300
200m深)における可溶性鉄存在量は、いずれの海域でも300 350
350 mol m
mol m で、北太平洋の外洋域に比べて5
で、北太平洋の外洋域に比べて5 9倍大きく、アジア大陸から日本海への大気経由での物質輸送が鉄の存在量に大きく影響していると推測された。日本海における溶存鉄濃度は、水深1
9倍大きく、アジア大陸から日本海への大気経由での物質輸送が鉄の存在量に大きく影響していると推測された。日本海における溶存鉄濃度は、水深1 2kmで極大を示した。この結果は、表層で生物に取り込まれた鉄が、中・深層で分解され滞留したためであると考えられる。鉄は、海洋における生物生産を制限する重要な因子であることが指摘されているが、日本海における鉄濃度分布から、海洋における鉄の供給源と挙動について理解することが可能となった。
2kmで極大を示した。この結果は、表層で生物に取り込まれた鉄が、中・深層で分解され滞留したためであると考えられる。鉄は、海洋における生物生産を制限する重要な因子であることが指摘されているが、日本海における鉄濃度分布から、海洋における鉄の供給源と挙動について理解することが可能となった。
高田 兵衛*; 久万 健志*; 磯田 豊*; 西岡 純*; 乙坂 重嘉; 千木良 充*; 高木 省吾*; 亀井 佳彦*; 坂岡 桂一郎*
no journal, ,
日本海の2つの海盆(大和海盆及び日本海盆)で採取した海水中の鉄(溶存鉄と可溶性鉄)及び、栄養塩濃度を分析し、両海盆間での鉄の挙動の違いについて考察した。孔径0.22マイクロメートルのフィルターで濾過し、緩衝液でpH=3.2に調整した海水に含まれる鉄を溶存鉄、濾過せずにpH調整のみを行った海水に含まれる鉄を可溶性鉄とした。表層における可溶性鉄濃度は、いずれの海盆でも1.0nM程度で、海域による有意な差はみられなかった。日本海盆における可溶性鉄濃度は、深層(1 2km層)で4.5nM程度まで増加し、それ以深で4nM程度まで減少した。大和海盆では、深層で5.5nMと日本海盆に比べて有意に高く、底層で6.0nMまで増加した。両海盆における可溶性鉄の分布の違いは、日本海深層における親生物元素の輸送過程の違いを示唆している。
2km層)で4.5nM程度まで増加し、それ以深で4nM程度まで減少した。大和海盆では、深層で5.5nMと日本海盆に比べて有意に高く、底層で6.0nMまで増加した。両海盆における可溶性鉄の分布の違いは、日本海深層における親生物元素の輸送過程の違いを示唆している。
 Cs from rivers to
Cs from rivers to  Cs concentrations in coastal sediment off Fukushima
Cs concentrations in coastal sediment off Fukushima鈴木 翔太郎*; 佐久間 一幸; 鶴田 忠彦; 松本 陽*; 天野 洋典*; 榎本 昌宏*; 守岡 良晃*; 神山 享一*; 高田 兵衛*
no journal, ,
To evaluate contribution of riverine particulate  Cs input, we estimated
Cs input, we estimated  Cs concentration coastal sediment (7-20 m depth) with particulate
Cs concentration coastal sediment (7-20 m depth) with particulate  Cs flux of the total 13 rivers (Uda, Mano, Niida, Ohta, Odaka, Ukedo(+Takase), Maeda, Kuma, Tomioka, Ide, Kido, Natsui, Same) calculated by tank model for water discharge and empirical equations for suspended solids fluxes and
Cs flux of the total 13 rivers (Uda, Mano, Niida, Ohta, Odaka, Ukedo(+Takase), Maeda, Kuma, Tomioka, Ide, Kido, Natsui, Same) calculated by tank model for water discharge and empirical equations for suspended solids fluxes and  Cs discharge between May 2011 and March 2020. Calculated particulate
Cs discharge between May 2011 and March 2020. Calculated particulate  Cs flux from the river were ranged from 2.11
Cs flux from the river were ranged from 2.11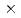 10
10 to 4979
to 4979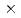 10
10 Bq/month. Estimated
Bq/month. Estimated  Cs concentration including particulate
Cs concentration including particulate  Cs via deposition kept concentration level more than minimum 0.351 Bq/kg-dry when initial
Cs via deposition kept concentration level more than minimum 0.351 Bq/kg-dry when initial  Cs concentration, variation rate and deposition ratio were set 300 Bq/kg-dry, -95% and 0.1, respectively.
Cs concentration, variation rate and deposition ratio were set 300 Bq/kg-dry, -95% and 0.1, respectively.
青野 辰雄*; 西川 淳*; 乙坂 重嘉*; 高田 兵衛*; 御園生 敏治; 中西 貴宏; 三浦 輝*; 神林 翔太*; 福田 美保*; 櫻田 正宣*; et al.
no journal, ,
2016年から2020年に東北海洋生態系調査研究船「新青丸」による福島周辺の放射性核種の動態と生物利用性等の調査航海が4回実施され、福島第一原子力発電所(FDNPS)周辺海域を中心に、海水,堆積物や生物等の採取が行われた。調査航海の目的はFDNPS事故によって海洋に放出された放射性核種の沿岸域における放射性核種のフラックスの観測や放射性核種の生物利用性の把握等である。海洋環境の状況を把握するために、福島沖の海水と堆積物中の放射性セシウム(Cs)濃度を調査した。その結果、2016年から2018年のFDNPS近傍の表層海水中の溶存態Cs-137濃度範囲は10-23mBq/Lであったが、2020年には7mBq/Lに減少し、その他の観測点でも年々溶存態Cs-137濃度が減少する傾向にあった。一方、堆積物では2016年から2017年ではCs-137濃度は、表層(0-2cm)が高く、深さと共に減少する傾向にあったが、2018年以降は表層よりもその下層でCs-137濃度が高くなる傾向が観測されたが、堆積物中のCs-137濃度も年々減少する傾向にあった。本報では、福島沖における海水と堆積物中の放射性Csの濃度変動やその特性について報告する。
青野 辰雄*; 西川 淳*; 乙坂 重嘉*; 高田 兵衛*; 御園生 敏治; 中西 貴宏; 三浦 輝*; 福田 美保*; 神林 翔太*; 櫻田 正宣*; et al.
no journal, ,
2016年から2020年にかけて、福島周辺海域の放射性物質の動態を調査する航海が4回実施された。福島第一原子力発電所(FDNPS)沖の海域で、海水や堆積物等の採取が行われた。海洋環境の状況を把握するために、福島沖の海水と堆積物中の放射性セシウム(Cs)濃度を調査した。その結果、海水,堆積物ともに2016年から2020年にかけて大きな変動はみられなかった。
高田 兵衛*; 大槻 あずさ*; 佐藤 俊*; 乙坂 重嘉*; 戸田 亮二*; 西川 淳*; 剣持 瑛行*; 石倉 明依*; 山田 萌々加*; 新開 祐介*; et al.
no journal, ,
2021年10月7日から10月17日までの11日間ならびに2022年10月2日から13日の12日間の日程で、新青丸による福島沿岸海域において、研究航海を実施したので、その航海概要を報告する。この航海では2011年3月に起きた福島第一原子力発電所事故以降のフォローモニタリングという位置づけに加え、放射性核種の海洋における動態や生態系の環境応答に対する科学的理解を深めることの二点を目的としている。
青野 辰雄*; 福田 美保*; 櫻田 正宣*; 高橋 博路*; 山崎 慎之介*; 神林 翔太*; 御園生 敏治; 中西 貴宏; 三浦 輝*; 西川 淳*; et al.
no journal, ,
2016年から2020年に東北海洋生態系調査研究船新青丸による福島周辺海域の放射性核種の動態と生物利用性等の調査航海が4回実施され、福島第一原子力発電所(FDNPS)周辺海域を中心に、海水,堆積物や生物等の採取が行われた。調査航海の目的はFDNPS事故によって海域に放出された放射性核種の沿岸域における放射性核種のフラックスの観測や放射性核種の生物利用性の把握等である。海洋環境の状況を把握するために、福島沖の海水と堆積物中の放射性セシウム濃度を調査した。今回は、FDNPS近傍の海水と堆積物中の放射性セシウムの濃度分布や変動について報告する。
Chaboche, P.-A.*; 脇山 義史*; 高田 兵衛*; 和田 敏裕*; Evrard, O.*; 御園生 敏治; 尻引 武彦; 舟木 泰智
no journal, ,
Following the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident in March 2011, large quantities of radionuclides in general, and radiocaesium (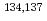 Cs) in particular, were emitted in terrestrial and marine environments of Fukushima Prefecture. Although
Cs) in particular, were emitted in terrestrial and marine environments of Fukushima Prefecture. Although  Cs activity in these environments has decreased since the accident, the secondary inputs via the rivers draining and eroding the main terrestrial radioactive plume were shown to sustain high level of
Cs activity in these environments has decreased since the accident, the secondary inputs via the rivers draining and eroding the main terrestrial radioactive plume were shown to sustain high level of  Cs in riverine and coastal sediments, which are likely deposited off the coasts of the Prefecture. Accordingly, quantifying the riverine sources of sediment deposited along the coast and characterizing its spatial and depth distribution, as well as its physico-chemical properties, is of the utmost importance to ensure the safety of fishery products and anticipate the environmental fate of radiocaesium. To conduct this project, coastal sediment cores (n=6) from 26 to 60cm depth were collected during cruise campaigns between July and September 2022 at the Ota, Niida and Ukedo river mouths. In this presentation, we report preliminary results regarding the spatial and depth distribution of radiocaesium activities in these sediment cores. Finally, we will discuss the main challenges identified so far to design and implement a sediment tracing method along the coast of the Fukushima Prefecture.
Cs in riverine and coastal sediments, which are likely deposited off the coasts of the Prefecture. Accordingly, quantifying the riverine sources of sediment deposited along the coast and characterizing its spatial and depth distribution, as well as its physico-chemical properties, is of the utmost importance to ensure the safety of fishery products and anticipate the environmental fate of radiocaesium. To conduct this project, coastal sediment cores (n=6) from 26 to 60cm depth were collected during cruise campaigns between July and September 2022 at the Ota, Niida and Ukedo river mouths. In this presentation, we report preliminary results regarding the spatial and depth distribution of radiocaesium activities in these sediment cores. Finally, we will discuss the main challenges identified so far to design and implement a sediment tracing method along the coast of the Fukushima Prefecture.
Chaboche, P.-A.*; 脇山 義史*; 高田 兵衛*; 和田 敏裕*; Evrard, O.*; 御園生 敏治; 尻引 武彦; 舟木 泰智
no journal, ,
The Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident trigged by the Great East Japan Earthquake and subsequent tsunami in March 2011 released large quantities of radionuclides in terrestrial and marine environments of Fukushima Prefecture. Although radiocaesium activity in these environments has decreased since the accident, the secondary inputs via the rivers draining and eroding the main terrestrial radioactive plume were shown to sustain high levels of  Cs in riverine and coastal sediments, which are likely deposited off the coast of the Prefecture. Accordingly, identifying the sources of sediment is required to elucidate the links between terrestrial and marine radiocaesium dynamics and to anticipate the fate of these persistent radionuclides in the environment.
Cs in riverine and coastal sediments, which are likely deposited off the coast of the Prefecture. Accordingly, identifying the sources of sediment is required to elucidate the links between terrestrial and marine radiocaesium dynamics and to anticipate the fate of these persistent radionuclides in the environment.
 Cs in a river-sea system boundary area
Cs in a river-sea system boundary area高田 兵衛*; 和田 敏裕*; 脇山 義史*; 平尾 茂一*; 佐藤 俊*; 青野 辰雄*; 中西 貴宏; 御園生 敏治; 尻引 武彦
no journal, ,
The  Cs sorption behavior on suspended particles was studied in river and coastal seawater, Fukushima Prefecture from June 2019 to October 2021. Although the suspended particle concentration was lower in the river than in seawater, the
Cs sorption behavior on suspended particles was studied in river and coastal seawater, Fukushima Prefecture from June 2019 to October 2021. Although the suspended particle concentration was lower in the river than in seawater, the  Cs activity on suspended particles in the river lager than that in seawater. Proportions of ion-exchangeable, organically bound, and refractory fractions of
Cs activity on suspended particles in the river lager than that in seawater. Proportions of ion-exchangeable, organically bound, and refractory fractions of  Cs on suspended particles were also determined by conducting sequential extraction method. The ion-exchangeable fraction was less than 1% at both areas. The organically bound fraction was a few %, resulting in that the refractory fraction accounted for
Cs on suspended particles were also determined by conducting sequential extraction method. The ion-exchangeable fraction was less than 1% at both areas. The organically bound fraction was a few %, resulting in that the refractory fraction accounted for  90%. Thus, it is indicated that the mobility of
90%. Thus, it is indicated that the mobility of  Cs to marine biota is low in the studied areas.
Cs to marine biota is low in the studied areas.
Chaboche, P.-A.*; 脇山 義史*; 高田 兵衛*; 和田 敏裕*; 御園生 敏治; 尻引 武彦; 舟木 泰智
no journal, ,
2011年3月の東日本大震災とそれに続く津波に端を発した福島第一原子力発電所(FDNPP)事故は、福島県の陸域および海域環境に大量の放射性核種を放出する結果となった。これらの環境中の放射性セシウム(すなわち Csと
Csと Cs)の放射能濃度は事故以来低下しているが、主な陸上放射性プルームを流出・浸食している河川からの継続的な流入が測定されており、福島県の沿岸沖に堆積した河川堆積物や沿岸堆積物中の
Cs)の放射能濃度は事故以来低下しているが、主な陸上放射性プルームを流出・浸食している河川からの継続的な流入が測定されており、福島県の沿岸沖に堆積した河川堆積物や沿岸堆積物中の Csの濃度が高いまま維持されている。したがって、陸域と海域の放射性セシウム動態の関連性を解明し、環境中の残留性放射性核種の運命を予測するためには、堆積物の発生源を特定することが必要である。
Csの濃度が高いまま維持されている。したがって、陸域と海域の放射性セシウム動態の関連性を解明し、環境中の残留性放射性核種の運命を予測するためには、堆積物の発生源を特定することが必要である。