Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kokubun, Yuji; Hosomi, Kenji; Seya, Natsumi; Nagaoka, Mika; Inoue, Kazumi; Koike, Yuko; Hasegawa, Ryo; Kubota, Tomohiro; Hirao, Moe; Iizawa, Shogo; et al.
JAEA-Review 2024-053, 116 Pages, 2025/03
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai Reprocessing Plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution prevention act, and by law of Ibaraki Prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2023. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
 -ray fields
-ray fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Kamada, Kei*; Ishii, Junya*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Manabe, Seiya*; Masuda, Akihiko*; Harano, Hideki*; Kato, Masahiro*; Shimazoe, Kenji*
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 19(11), p.P11019_1 - P11019_16, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation) 10
10 W/cm
W/cm
Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Ryazantsev, S. N.*; Kulikov, R. K.*; Sedov, M. V.*; Filippov, E. D.*; Pikuz, S. A.*; Asai, Takafumi*; Kanasaki, Masato*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Jinno, Satoshi; et al.
Photonics (Internet), 10(11), p.1250_1 - 1250_11, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:18.07(Optics)It is challenging to clearly distinguish the impacts of the optical field and collisional ionization in the evolution of the charge state of a plasma produced when matter interacts with high-intensity laser pulses. In this work, time-dependent calculations of plasma kinetics are used to show that it is possible only when low-density gaseous targets with sufficiently small clusters are used. In the case of Ar plasma, the upper limit of the cluster radius was estimated to be 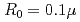 m.
m.
Watakabe, Tomoyoshi; Takahashi, Hideki*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 145(5), p.051502_1 - 051502_11, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Mechanical)To ensure the seismic integrity of Sodium Cooled Fast Reactors, both confirming the ultimate strength under a high-level earthquake beyond the design condition and clarifying the design safety margin up to ultimate strength have been focused as important issues. In this study, a series of dynamic failure tests of a thin wall tee for Sodium-Cooled Fast Reactors was conducted. Some discussions related to the thin wall tee are provided on the failure mode under seismic load, dynamic response behavior, accuracy of fatigue prediction by dynamic elastic-plastic analysis, and a safety margin of fatigue evaluation which is included in conventional design rule.
Okuda, Takahiro; Takahashi, Hideki*; Watakabe, Tomoyoshi
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 10(4), p.23-00075_1 - 23-00075_9, 2023/08
In recent years, to make the seismic design more rational for the piping systems in nuclear power plants, it has been expected to develop a design method considering plastic deformation and the accompanying energy dissipation of the piping itself. In this study, an extensive series of seismic response analyses was conducted to investigate the degree of influence of the plastic deformation of the pipe support structures on the seismic response of the entire piping system. The analyses include; plasticity is considered for (1) none, (2) the piping only, (3) the support structure only, and (4) both the piping and the support structure.
Kitamura, Akihisa*; Okazaki, Sota*; Kondo, Mitsuru*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Nakanishi, Toshimichi*; Hori, Rie*; Ikeda, Masayuki*; Ichimura, Koji*; Nakagawa, Yuki*; Mori, Hideki*
Shizuoka Daigaku Chikyu Kagaku Kenkyu Hokoku, (49), p.73 - 86, 2022/07
On July 3 2021, a debris flow caused by a landslide from a landfill occurred along the Aizome River in the Izusan area of Atami City, Shizuoka. In this study, debris flow deposits and soil samples were characterized in terms of their sedimentology and geochemically analyzed.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
 -clustering in atomic nuclei from first principles with statistical learning and the Hoyle state character
-clustering in atomic nuclei from first principles with statistical learning and the Hoyle state characterOtsuka, Takaharu; Abe, Takashi*; Yoshida, Toru*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Itagaki, Naoyuki*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Vary, J. P.*; Maris, P.*; Ueno, Hideki*
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.2234_1 - 2234_10, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:96.78(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Kosaka, Wataru; Uchibori, Akihiro; Takata, Takashi; Yanagisawa, Hideki*; Watanabe, Akira*; Jang, S.*
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2022/03
For the safety assessment of a steam generator (SG) in a sodium-cooled fast reactor, the analysis code LEAP-III can evaluate the water leak rate during the long-term event progress including the tube failure propagation triggered by an occurrence of a small water leak in a failed heat transfer tube in SG. The LEAP-III has the advantage in completing the calculation with low computational cost since it consists of semi-empirical formulae and one-dimensional equations of conservation. However, an evaluation model of temperature distribution by the reacting jet provides wider high temperature region than the experimental data. As a result, LEAP-III shows excessive conservativeness in some case. A Lagrangian particle method code based on engineering approaches has been developed in order to improve this model to get more realistic temperature distribution. In this method, the jet behavior and chemical reaction are simulated using Newton's equation of motion with several engineering approximations instead of solving multi-dimension multiphase thermal hydraulic equations with sodium-water reaction. In this study, interparticle interaction force model was added, and also the chemical reaction and gas-liquid heat transfer evaluation models were improved. We conducted a test analysis, and compared the results by this particle method with the ones by SERAPHIM, that is a mechanistic analysis code for multi-dimensional multiphase flow considering compressibility and sodium-water reaction. Through this test analysis, it confirmed that this particle method has the basic capability to get a realistic temperature distribution with low computational cost, and also to predict tube failure occurrence by coupled with LEAP-III.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Satou, Yukihiko; Wakaida, Ikuo; Terabayashi, Ryohei*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Tomita, Hideki*; Zhao, Y.*; Sakamoto, Tetsuo*
Journal of Physics B; Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 54(14), p.145003_1 - 145003_8, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.82(Optics)Two-color two-step photoionization optogalvanic spectroscopy was performed using high-repetition-rate titanium sapphire lasers and a uranium hollow cathode lamp to find the two-step resonance ionization schemes of uranium. Many ionization transitions were observed by exciting uranium atoms in a ground state into five, even parity, excited levels with the first-step laser and by scanning the second-step laser wavelengths. By blocking the first-step laser, single-color, two-photon ionization transitions were also identified. From these results, we have found more than 50 odd-parity autoionizing levels of uranium in the energy, ranging from the ionization potential (49958.4 cm ) to 51150 cm
) to 51150 cm . The determined energy levels are within 1 cm
. The determined energy levels are within 1 cm of previously reported values.
of previously reported values.
Shibano, Koya; Abe, Katsuo; Tsukasa, Kazuo*; Hosogane, Tatsuya; Kayano, Masashi; Sumi, Mika; Fujiwara, Hideki*; Yamaguchi, Kazuya*; Motoki, Chika*
Dai-41-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2020/11
Large-sized dried spikes, called LSD spike, are used as reference material for accountancy analysis for Plutonium and Uranium by Isotope Dilution Mass Spectrometry. LSD spikes preparation is performed each steps as followed (1) Preparing Plutonium and Uranium mix solution, (2) Aliquoting mix solution to vials, and (3) Drying. J-MOX have planned prepared in-house LSD spike and utilized it for accountancy analysis. If LSD spikes are stored for long term, dried material peel off from bottom of vial and it may affect analytical results. In this study, LSD spikes, which have composition suitable for accountancy analysis in J-MOX, had been stored for about 2 years, then long-term stability of LSD spikes had been evaluated.
Negishi, Hitoshi; Kamide, Hideki; Maeda, Seiichiro; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Abe, Tomoyuki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 62(8), p.438 - 441, 2020/08
, 62(8), p.438 - 441, 2020/08
Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor, Monju, was under decommission since April, 2018. It is the first time for Japan to make a sodium cooled reactor into decommission. It is significant work and will take 30 years. The Monju has provided wide spectrum and huge amount of findings and knowledge, e.g., design, R&D, manufacturing, construction, and operation up to 40% of full power over 50 years of development history. It is significant to utilize such findings and knowledge for the development and commercialization of a fast rector in Japan.
Satou, Yukihiko; Sueki, Keisuke*; Sasa, Kimikazu*; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Nakama, Shigeo; Minowa, Haruka*; Abe, Yoshinari*; Nakai, Izumi*; Ono, Takahiro*; Adachi, Koji*; et al.
Geochemical Journal, 52(2), p.137 - 143, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:73 Percentile:96.10(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Jung, K.; Iimura, Hideki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Kato, Masaaki; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Khumaeni, A.*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 134, p.42 - 51, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:91.41(Spectroscopy)Spectroscopic properties of atomic species of plutonium were investigated by combining laser ablation and resonance absorption techniques for the analysis of a plutonium oxide sample. For 17 transitions of Pu atoms and ions, the absorbance, isotope shift, and hyperfine splitting were determined via Voigt profile fitting of the recorded absorption spectra. Three transitions were selected as candidates for analytical use. Using these transitions, we investigated the analytical performance that was attainable and determined a correlation coefficient R2 between the absorbance and plutonium concentration of 0.9999, a limit of detection of 30-130 ppm, and a relative standard deviation of approximately 6% for an abundance of  Pu of 2.4%. These results demonstrate that laser ablation absorption spectroscopy is applicable to the remote isotopic analysis of highly radioactive nuclear fuels and waste materials containing multiple actinide elements.
Pu of 2.4%. These results demonstrate that laser ablation absorption spectroscopy is applicable to the remote isotopic analysis of highly radioactive nuclear fuels and waste materials containing multiple actinide elements.
 and their Zr-O surface modified electrodes
and their Zr-O surface modified electrodesAbe, Machiko*; Iba, Hideki*; Suzuki, Kota*; Minamishima, Hiroaki*; Hirayama, Masaaki*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Mizuki, Junichiro*; Saito, Tomohiro*; Ikuhara, Yuichi*; Kanno, Ryoji*
Journal of Power Sources, 345, p.108 - 119, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:37.37(Chemistry, Physical)The surface structure of the Li(Ni, Co, Mn)O electrode was studied during charge/discharge process using electrochemical methods and X-ray/Neutron scattering techniques. It was found that during charge/discharge process the coverage of spinel structure increased. The spinel structure has low electrochemical activity and is not involved in Li insertion/extraction. After the surface modification, it was found that the coverage of the spinel structure did not increase. Further, it was also found out that the Li concentration at the electrode/electrolyte interface increased.
electrode was studied during charge/discharge process using electrochemical methods and X-ray/Neutron scattering techniques. It was found that during charge/discharge process the coverage of spinel structure increased. The spinel structure has low electrochemical activity and is not involved in Li insertion/extraction. After the surface modification, it was found that the coverage of the spinel structure did not increase. Further, it was also found out that the Li concentration at the electrode/electrolyte interface increased.
Doda, Norihiro; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Kamide, Hideki; Watanabe, Osamu*
Proceedings of 10th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-10) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2016/11
A natural circulation decay heat removal system is adopted in the design of an advanced loop type fast reactor in Japan. For the core structural integrity, we have developed a new evaluation method for the core hot spot temperature during natural circulation decay heat removal operations. In the method, safety analyses are performed with the plant dynamics models that can consider characteristic thermal-hydraulic phenomena under natural circulation conditions. In addition, the core hot spot temperature is estimated with its uncertainty quantified in the statistical manner. This paper describes the evaluation method and also the application results to a loss of offsite power event.
Ono, Ayako; Kamide, Hideki; Kobayashi, Jun; Doda, Norihiro; Watanabe, Osamu*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(9), p.1385 - 1396, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:67.39(Nuclear Science & Technology)Decay heat removal by natural circulation is a significant passive safety measure of a fast reactor against station blackout. The decay heat removal system (DHRS) of the loop type sodium fast reactor being designed in Japan comprises a direct reactor auxiliary cooling system and primary reactor auxiliary cooling system (PRACS). The thermal hydraulic phenomena in the plant under natural circulation conditions need to be understood for establishing a reliable natural circulation driven DHRS. In this study, sodium experiments were conducted using a plant dynamic test loop to understand the thermal-hydraulic phenomena considering natural circulation in the plant. The experiments simulating the scram transient confirmed that PRACS started up smoothly under natural circulation, and the simulated core was stably cooled after the scram. Moreover, the experiments varying the pressure loss coefficients of the loop as the experimental parameters showed robustness of the PRACS.
 Li
LiIshiyama, Hironobu*; Jeong, S.-C.*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Jung, H. S.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Oyaizu, Mitsuhiro*; Osa, Akihiko; Otokawa, Yoshinori; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 376, p.379 - 381, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:55.98(Instruments & Instrumentation)Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Inoue, Kazumi; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; Kikuchi, Masaaki*; Sakauchi, Nobuyuki*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-030, 115 Pages, 2015/12
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and bylaw of Ibaraki prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2014. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.