Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Rizaal, M.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Suzuki, Eriko; Miwa, Shuhei
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 218, p.111433_1 - 111433_10, 2025/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Aoyama, Takahito; Choudhary, S.*; Pandaleon, A.*; Burns, J. T.*; Kokaly, M.*; Restis, J.*; Ross, J.*; Kelly, R. G.*
Corrosion, 81(6), p.609 - 621, 2025/06
Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2024, P. 31, 2025/06
no abstracts in English
 Co
Co )Sn studied by
)Sn studied by  SR
SRCai, Y.*; Yoon, S.*; Sheng, Q.*; Zhao, G.*; Seewald, E. F.*; Ghosh, S.*; Ingham, J.*; Pasupathy, A. N.*; Queiroz, R.*; Lei, H.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 111(21), p.214412_1 - 214412_17, 2025/06
Auh, Y. H.*; Neal, N. N.*; Arole, K.*; Regis, N. A.*; Nguyen, T.*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Radovic, M.*; Green, M. J.*; et al.
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 17(21), p.31392 - 31402, 2025/05
 under pressure
under pressureKnafo, W.*; Thebault, T.*; Raymond, S.*; Manuel, P.*; Khalyavin, D. D.*; Orlandi, F.*; Ressouche, E.*; Beauvois, K.*; Lapertot, G.*; Kaneko, Koji; et al.
Physical Review X, 15(2), p.021075_1 - 021075_16, 2025/05
 hydridosilicate at high pressures; A Bridge to BaSiH
hydridosilicate at high pressures; A Bridge to BaSiH polyhydride
polyhydrideBeyer, D. C.*; Spektor, K.*; Vekilova, O. Y.*; Grins, J.*; Barros Brant Carvalho, P. H.*; Leinbach, L. J.*; Sannemo-Targama, M.*; Bhat, S.*; Baran, V.*; Etter, M.*; et al.
ACS Omega (Internet), 10(15), p.15029 - 15035, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Hydridosilicates featuring SiH octahedral moieties represent a rather new class of compounds with potential properties relating to hydrogen storage and hydride ion conductivity. Here, we report on the new representative BaSiH
octahedral moieties represent a rather new class of compounds with potential properties relating to hydrogen storage and hydride ion conductivity. Here, we report on the new representative BaSiH obtained from reacting the Zintl phase hydride BaSiH
obtained from reacting the Zintl phase hydride BaSiH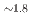 with H
with H fluid at pressures above 4 GPa and subsequent decompression to ambient pressure. It consists of complex SiH
fluid at pressures above 4 GPa and subsequent decompression to ambient pressure. It consists of complex SiH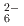 ions, which are octahedrally coordinated by Ba
ions, which are octahedrally coordinated by Ba counterions. The arrangement of Ba and Si atoms deviates only slightly from an ideal fcc NaCl structure. IR and Raman spectroscopy showed SiH
counterions. The arrangement of Ba and Si atoms deviates only slightly from an ideal fcc NaCl structure. IR and Raman spectroscopy showed SiH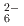 bending and stretching modes in the ranges 800-1200 and 1400-1800 cm
bending and stretching modes in the ranges 800-1200 and 1400-1800 cm , respectively. BaSiH
, respectively. BaSiH is thermally stable up to 95
is thermally stable up to 95 C above which decomposition into BaH
C above which decomposition into BaH and Si takes place. DFT calculations indicated a direct band gap of 2.5 eV. The discovery of BaSiH
and Si takes place. DFT calculations indicated a direct band gap of 2.5 eV. The discovery of BaSiH consolidates the compound class of hydridosilicates, accessible from hydrogenations of silicides at gigapascal pressures (
consolidates the compound class of hydridosilicates, accessible from hydrogenations of silicides at gigapascal pressures (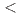 10 GPa). The structural properties of BaSiH
10 GPa). The structural properties of BaSiH suggest that it presents an intermediate (or precursor) for further hydrogenation at considerably higher pressures to the predicted superconducting polyhydride BaSiH
suggest that it presents an intermediate (or precursor) for further hydrogenation at considerably higher pressures to the predicted superconducting polyhydride BaSiH .
.
Niu, X.*; Elakneswaran, Y.*; Li, A.*; Seralathan, S.*; Kikuchi, Ryosuke*; Hiraki, Yoshihisa; Sato, Junya; Osugi, Takeshi; Walkley, B.*
Cement and Concrete Research, 190, p.107814_1 - 107814_17, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Construction & Building Technology)Naeem, M.*; Rehman, A. U.*; Romero Resendiz, L.*; Salamci, E.*; Aydin, H.*; Ansari, P.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Wang, X.-L.*; 3 of others*
Communications Materials (Internet), 6, p.65_1 - 65_13, 2025/04
Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center
JAEA-Review 2024-050, 55 Pages, 2025/03
This report outlines some main research and development activities executed by the Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center in FY2023. The Center was working on the development of the nuclear fuel cycle with a focus on its frontend (i.e., uranium exploration, mining, refining, conversion, and enrichment) until 2001, and is now dismantling and removing the facilities and equipment used in the past. In addition, based on the concept of "Uranium and environmental research platform" announced in 2016, we are also working on research and development for the safe processing and disposal of uranium wastes. This research and development can be mainly divided into "Environmental research" and "Uranium waste engineering research"; the former takes advantage of the characteristics of the natural environment in Ningyo-toge, and the latter utilizes our facilities and potentials. Some works are also made on safety and its management as well as radiation effect research in terms of health physics and radiobiology. Regarding the environmental research and environmental conservation, this report describes research on the heterogeneity of groundwater in granitic mountains and the fundamentals and applications of the partitioning of trace elements into minerals. As for the uranium waste engineering research, the laser-based decontamination technique and the corrosion resistance suitable for waste package material are reported. Further, the progress of safeguards activities at the uranium enrichment facility, the construction of safety measures at the mill tailings ponds, and the risk and biological effects of radon are also reported. The achievements of those works have been widely presented through research papers etc.
Scaria, J.*; P drot, M.*; Fablet, L.*; Yomogida, Takumi; Nguyen, T. T.*; Sivry, Y.*; Catrouillet, C.*; Pradas del Real, A. E.*; Choueikani, F.*; Vantelon, D.*; et al.
drot, M.*; Fablet, L.*; Yomogida, Takumi; Nguyen, T. T.*; Sivry, Y.*; Catrouillet, C.*; Pradas del Real, A. E.*; Choueikani, F.*; Vantelon, D.*; et al.
Environmental Science & Technology, 59(11), p.5747 - 5755, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Environmental)Understanding and predicting the interaction mechanisms between chromium and magnetite is of particular interest to elucidate the biogeochemical behavior of Cr in the environment and to develop optimal soil remediation and water treatment strategies. However, while the elimination of the most toxic form of (Cr(VI)) by its reduction to Cr(III) has widely been documented, elucidating the exact mechanism involved in Cr(III) sorption to magnetite has attracted less attention. This study examined the interaction of Cr(III) solution with 10 nm-sized magnetites, whose stoichiometries were carefully defined and preserved in anaerobic conditions. This study reveals the joint effects of pH and magnetite stoichiometry on Cr(III) sorption mechanism, and that Cr(III)-(hydr)oxide precipitation is not necessarily the driving process of Cr(III) elimination from solutions. These results will help predict the fate and transport of chromium, as well as developing magnetite-based chromium remediation processes.
 Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe
FeNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(3), p.300 - 307, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Morishita, Yuki; Miyamura, Hiroko; Sato, Yuki; Matsubara, Jun*; Sumali, B.*; Mitsukura, Yasue*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, p.170368_1 - 170368_16, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Decommissioning nuclear reactor sites presents challenges due to the presence of various radionuclides, including alpha emitters (e.g., Pu, Am, Cm) and beta emitters (e.g.,  Cs,
Cs,  Sr-
Sr- Y), which pose significant internal exposure risks to workers. Traditional measurement methods require multiple instruments and are time-consuming, particularly in high gamma-ray environments. To address these issues, we developed a remote alpha and beta discrimination measurement system that integrates a stilbene scintillator detector with a silicon photomultiplier, enabling simultaneous detection of both alpha and beta particles. This study further incorporates machine learning techniques, specifically Support Vector Machines (SVM), for automatic discrimination, eliminating the need for user-defined thresholds and ensuring consistent operational conditions. The system was tested with known radiation sources, demonstrating over 96% classification accuracy for alpha and beta particles. Measurements conducted in motion effectively identified contamination sources, confirming the system's capability for real-time analysis. This innovative approach enhances radiation safety and efficiency in nuclear decommissioning operations, making it particularly beneficial in environments where human access is limited.
Y), which pose significant internal exposure risks to workers. Traditional measurement methods require multiple instruments and are time-consuming, particularly in high gamma-ray environments. To address these issues, we developed a remote alpha and beta discrimination measurement system that integrates a stilbene scintillator detector with a silicon photomultiplier, enabling simultaneous detection of both alpha and beta particles. This study further incorporates machine learning techniques, specifically Support Vector Machines (SVM), for automatic discrimination, eliminating the need for user-defined thresholds and ensuring consistent operational conditions. The system was tested with known radiation sources, demonstrating over 96% classification accuracy for alpha and beta particles. Measurements conducted in motion effectively identified contamination sources, confirming the system's capability for real-time analysis. This innovative approach enhances radiation safety and efficiency in nuclear decommissioning operations, making it particularly beneficial in environments where human access is limited.
Ulanowski, A.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Petoussi-Henss, N.*; Balonov, M.*
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 64(1), p.105 - 115, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:92.14(Biology)Papadopoulos, A.*; Kyriakou, I.*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Cort s-Giraldo, M. A.*; Galocha-Oliva, M.*; Plante, I.*; Steward, R. D.*; Tran, N. H.*; Li, W.*; Daglis, I. A.*; et al.
s-Giraldo, M. A.*; Galocha-Oliva, M.*; Plante, I.*; Steward, R. D.*; Tran, N. H.*; Li, W.*; Daglis, I. A.*; et al.
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 64(1), p.117 - 135, 2025/03
Radiation quality for determining biological effects is commonly linked to the microdosimetric quantity, especially dose-mean lineal energy y . Calculations of y
. Calculations of y can be performed by sophisticated Monte Carlo track structure (MCTS) codes. The y
can be performed by sophisticated Monte Carlo track structure (MCTS) codes. The y estimate depends on the type of the MCTS code and analysis model. This study focused on proton beams with 1 MeV-1 GeV, which are important in radiation protection, space applications, radiation therapy, etc., and compared the estimates of the y
estimate depends on the type of the MCTS code and analysis model. This study focused on proton beams with 1 MeV-1 GeV, which are important in radiation protection, space applications, radiation therapy, etc., and compared the estimates of the y in liquid water by various MCTS codes (PHITS, RITRACK, and Geant4-DNA) and analysis models (refined Xapsos model). The comparison results showed that good agreement with the refined Xapsos model and various MCTS codes can be attained at less than 10-20% level, and Q values by the analytic model are also in better agreement with MCTS simulation data. These findings conclude that the refined analytic model might be used as an alternative to time- and CPU-intensive MCTS simulations and advance practical calculations of radiation qualities and risk assessment.
in liquid water by various MCTS codes (PHITS, RITRACK, and Geant4-DNA) and analysis models (refined Xapsos model). The comparison results showed that good agreement with the refined Xapsos model and various MCTS codes can be attained at less than 10-20% level, and Q values by the analytic model are also in better agreement with MCTS simulation data. These findings conclude that the refined analytic model might be used as an alternative to time- and CPU-intensive MCTS simulations and advance practical calculations of radiation qualities and risk assessment.
Brumm, S.*; Gabrielli, F.*; Sanchez Espinoza, V.*; Stakhanova, A.*; Groudev, P.*; Petrova, P.*; Vryashkova, P.*; Ou, P.*; Zhang, W.*; Malkhasyan, A.*; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 211, p.110962_1 - 110962_16, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:93.24(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yoshida, M.*; McDermott, R. M.*; Angioni, C.*; Camenen, Y.*; Citrin, J.*; Jakubowski, M.*; Hughes, J. W.*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Mantica, P.*; Mariani, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 65(3), p.033001_1 - 033001_132, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:89.66(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Progress in physics understanding and theoretical model development of plasma transport and confinement in the ITPA Transport and Confinement Topical Group since the publication of the ITER Physics Basis was summarized focusing on the contributions to ITER and burning plasma prediction and control. This paper provides a general and streamlined overview on the advances that were mainly led by the ITPA TC joint experiments and joint activities for the last 15 years. This paper starts with the scientific strategy and scope of the ITPA TC Topical group and overall picture of the major progress, followed by the progress of each research field: particle transport, impurity transport, ion and electron thermal turbulent transport, momentum transport, impact of 3D magnetic fields on transport, confinement mode transitions, global confinement, and reduced transport modeling.
HPC Technology Promotion Office, Center for Computational Science & e-Systems
JAEA-Review 2024-044, 121 Pages, 2025/01
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) conducts research and development (R&D) in various fields related to nuclear power as a comprehensive institution of nuclear energy R&Ds, and utilizes computational science and technology in many activities. Over the past 10 years or so, the publication of papers utilizing computational science and technology at JAEA has accounted for about 20 percent of the total publications each fiscal year. The supercomputer system of JAEA has become an important infrastructure to support computational science and technology. In FY2023, the system was utilized in R&D activities that were prioritized in the Fourth Medium- to Long-Term Plan, including contributing to carbon neutrality through the development of innovative technologies such as improving safety, creating innovation by promoting diverse R&D related to nuclear science and technology, promoting R&D in response to the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, steadily implementing technological developments for the treatment and disposal of high-level radioactive waste, and supporting nuclear safety regulatory administration and nuclear disaster prevention by promoting safety research for these purposes. This report presents a great number of R&D results accomplished by using the system in FY2023, as well as user support, operational records and overviews of the system, and so on.
Calabrese, R.*; Hirooka, Shun
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 178, p.105516_1 - 105516_11, 2025/01
Thermal creep is one of the key properties of mixed oxide (MOX) fuel for innovative fast reactors. Thermal creep of fuel affects markedly the interaction between the fuel and the cladding. A review of correlations available in the literature is presented. The effect of porosity, plutonium concentration, and stoichiometry are discussed also in the light of recent numerical results. Our analysis pointed out some inconsistencies concerning the modelling of the effect of porosity on diffusional creep and a re-evaluation of the effect of plutonium concentration. The discussion suggested that Evans's findings on the effect of stoichiometry should be better assessed as well as the level of increase in creep moving towards stoichiometry. Typical operating conditions of fast breeder reactors confirmed the need for an extension of porosity and temperature correlations' domains. Besides this, a new correlation based on a separate-effect approach has been proposed for fuel performance codes.
Metcalfe, R.*; Benbow, S. J.*; Kawama, Daisuke*; Tachi, Yukio
Science of the Total Environment, 958, p.177690_1 - 177690_17, 2025/01
Uplifting fractured granitic rocks occur in substantial areas of countries such as Japan. A repository site would be selected in such an area only if it is possible to make a safety case, accounting for the changing conditions during uplift. The safety case must include robust arguments that chemical processes in the rocks around the repository will contribute sufficiently to minimise radiological doses to biosphere receptors. To provide confidence in the safety arguments, numerical models need to be sufficiently realistic, but also parameterised conservatively (pessimistically). However, model development is challenging because uplift involves many complex couplings between groundwater flow, chemical reactions between water and rock, and changing rock properties. The couplings would affect radionuclide mobilisation and retardation, by influencing diffusive radionuclide fluxes between groundwater flowing in fractures and effectively immobile porewater in the rock matrix and radionuclide partitioning between water and solid phases, via: (i) mineral precipitation/dissolution; (ii) mineral alteration; and (iii) sorption/desorption. It is difficult to represent all this complexity in numerical models while showing that they are parameterised conservatively. Here we present a modelling approach, illustrated by simulation cases for some exemplar radioelements, to identify realistically conservative process conceptualisations and model parameterisations.