Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M
Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M ssbauer and
ssbauer and  SR studies of Sm
SR studies of Sm Ru
Ru Ge
Ge
Tsutsui, Satoshi; Ito, Takashi; Nakamura, Jin*; Yoshida, Mio*; Kobayashi, Yoshio*; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Koda, Akihiro*; Higashinaka, Ryuji*; Aoki, Dai*; et al.
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.55_1 - 55_9, 2024/12
 Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M
Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M ssbauer spectroscopy of Sm-based heavy fermion compounds
ssbauer spectroscopy of Sm-based heavy fermion compoundsTsutsui, Satoshi; Higashinaka, Ryuji*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Kobayashi, Yoshio*; Nakamura, Jin*; Ito, Takashi; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Aoki, Yuji*; Sato, Hideyuki*
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.9_1 - 9_10, 2024/12
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Tanaka, Satoshi*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Iwata, Ayako*; Aoki, Yuto; Aoki, Kazuhisa; Yanagisawa, Kenichi*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (70), p.3 - 22, 2024/09
Inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F), there are many locations with high radiation levels due to contamination by radioactive materials that leaked from the reactor. These pose a significant obstacle to the smooth progress of decommissioning work. To help solve this issue, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), under a subsidy from the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry's decommissioning and contaminated water management project, is conducting research and development on digital technologies to improve the radiation environment inside the decommissioning site. This project, titled "Development of Technology to Improve the Environment Inside Reactor Buildings (Enhancing Digital Technology for Environment and Source Distribution to Reduce Radiation Exposure)," began in April of FY 2023. In this project, the aim is to develop three interconnected systems: FrontEnd, Pro, and BackEnd. The FrontEnd system, based on the previously developed 3D-ADRES-Indoor (prototype) from FY 2021-2022, will be upgraded to a high-speed digital twin technology usable on-site. The Pro system will carry out detailed analysis in rooms such as the new office building at 1F, while the BackEnd system will serve as a database to centrally manage the collected and analyzed data. This report focuses on the FrontEnd system, which will be used on-site. After point cloud measurement, the system will quickly create a 3D mesh model, estimate the radiation source from dose rate measurements, and refine the position and intensity of the estimated source using recalculation techniques (re-observation instructions and re-estimation). The results of verification tests conducted on Unit 5 are also presented. Furthermore, the report briefly discusses the future research and development plans for this project.
Kawabata, Kuniaki; Imabuchi, Takashi; Shirasaki, Norihito*; Suzuki, Soichiro; Ito, Rintaro; Aoki, Yuto; Omori, Takazumi
ROBOMECH Journal (Internet), 11, p.11_1 - 11_11, 2024/09
Uchida, Kazuto*; Masuda, Tsukuru*; Hara, Shintaro*; Matsuo, Yoichi*; Liu, Y.*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Asano, Yoshihiko*; Miyata, Kazuki*; Fukuma, Takeshi*; Ono, Toshiya*; et al.
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 16(30), p.39104 - 39116, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:30.18(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) -phenylmaleimide
-phenylmaleimideYamazaki, Shun*; Kaneko, Naoya*; Kato, Atsuya*; Watanabe, Kohei*; Aoki, Daisuke*; Taniguchi, Tatsuo*; Karatsu, Takashi*; Ueda, Yuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Okura, Koki*; et al.
Polymer, 298, p.126846_1 - 126846_11, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:74.19(Polymer Science) O/H
O/H O vapor generator for contrast-variation neutron scattering
O vapor generator for contrast-variation neutron scatteringArima-Osonoi, Hiroshi*; Takata, Shinichi; Kasai, Satoshi*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Miyata, Noboru*; Miyazaki, Tsukasa*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Iwase, Hiroki*; Hiroi, Kosuke; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 56(6), p.1802 - 1812, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:81.06(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Machida, Masahiko; Shi, W.*; Yamada, Susumu; Miyamura, Hiroko; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji; Aoki, Yuto; Ito, Rintaro; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2023/02
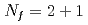 lattice QCD with chiral fermions
lattice QCD with chiral fermionsAoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Kanamori, Issaku*; Kaneko, Takashi*; Nakamura, Yoshifumi*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 396, p.332_1 - 332_7, 2022/07
The axial U(1) anomaly in high-temperature QCD plays an important role to understand the phase diagram of QCD. The previous works by JLQCD Collaboration studied high-temperature QCD using 2-flavor dynamical chiral fermions such as the domain-wall fermion and reweighted overlap fermion. We extend our simulations to QCD with 2+1-flavor dynamical quarks, where the masses of the up, down, and strange quarks are near the physical point, and the temperatures are close to or higher than the pseudocritical temperature. In this talk, we will present the results for the Dirac spectrum, topological susceptibility, axial U(1) susceptibility, and hadronic collelators.
Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Yuta; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Aoki, Takayuki*
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 27, 4 Pages, 2022/06
We have developed a wind simulation code named CityLBM to realize wind digital twins. Mesoscale wind conditions are given as boundary conditions in CityLBM by using a nudging data assimilation method. It is found that conventional approaches with constant nudging coefficients fail to reproduce turbulent intensity in long time simulations, where atmospheric stability conditions change significantly. We propose a dynamic parameter optimization method for the nudging coefficient based on a particle filter. CityLBM was validated against plume dispersion experiments in the complex urban environment of Oklahoma City. The nudging coefficient was updated to reduce the error of the turbulent intensity between the simulation and the observation, and the atmospheric boundary layer was reproduced throughout the day.
 Sm M
Sm M ssbauer and Sm L
ssbauer and Sm L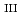 -edge X-ray absorption spectroscopies
-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopiesTsutsui, Satoshi; Higashinaka, Ryuji*; Nakamura, Raito*; Fujiwara, Kosuke*; Nakamura, Jin*; Kobayashi, Yoshio*; Ito, Takashi; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Kato, Kazuo*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 242(1), p.32_1 - 32_10, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:75.14(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Aoki, Hiroyuki; Liu, Y.*; Yamashita, Takashi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.22711_1 - 22711_9, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:63.12(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Asakura, Kazuki; Shimomura, Yusuke; Donomae, Yasushi; Abe, Kazuyuki; Kitamura, Ryoichi; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki; Takamatsu, Misao; Sakamoto, Naoki; Isozaki, Ryosuke; Onishi, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-020, 42 Pages, 2021/10
The disposal of radioactive waste from the research facility need to calculate from the radioactivity concentration that based on variously nuclear fuels and materials. In Japan Atomic Energy Agency Oarai Research and Development Institute, the study on considering disposal is being advanced among the facilities which generate radioactive waste as well as the facilities which process radioactive waste. This report summarizes a study result in FY2020 about the evaluation method to determine the radioactivity concentration in radioactive waste on Oarai Research and Development Institute.
 SR and NMR studies
SR and NMR studiesHiga, Nonoka*; Ito, Takashi; Yogi, Mamoru*; Hattori, Taisuke; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Guguchia, Z.*; Higemoto, Wataru; Nakashima, Miho*; Homma, Yoshiya*; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(4), p.045145_1 - 045145_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:30.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Yuta; Nakayama, Hiromasa; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Aoki, Takayuki*
Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 179(2), p.187 - 208, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:70.48(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)A plume dispersion simulation code named CityLBM enables a real time simulation for several km by applying adaptive mesh refinement (AMR) method on GPU supercomputers. We assess plume dispersion problems in the complex urban environment of Oklahoma City (JU2003). Realistic mesoscale wind boundary conditions of JU2003 produced by a Weather Research and Forecasting Model (WRF), building structures, and a plant canopy model are introduced to CityLBM. Ensemble calculations are performed to reduce turbulence uncertainties. The statistics of the plume dispersion field, mean and max concentrations show that ensemble calculations improve the accuracy of the estimation, and the ensemble-averaged concentration values in the simulations over 4 km areas with 2-m resolution satisfied factor 2 agreements for 70% of 24 target measurement points and periods in JU2003.
Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Yuta; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Aoki, Takayuki*
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 26, 3 Pages, 2021/05
We develop a mixed-precision preconditioner for the pressure Poisson equation in a two-phase flow CFD code JUPITER-AMR. The multi-grid (MG) preconditioner is constructed based on the geometric MG method with a three- stage V-cycle, and a cache-reuse SOR (CR-SOR) method at each stage. The numerical experiments are conducted for two-phase flows in a fuel bundle of a nuclear reactor. The MG-CG solver in single-precision shows the same convergence histories as double-precision, which is about 75% of the computational time in double-precision. In the strong scaling test, the MG-CG solver in single-precision is accelerated by 1.88 times between 32 and 96 GPUs.
 anomaly at high temperature with lattice chiral fermions
anomaly at high temperature with lattice chiral fermionsAoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Cossu, G.*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Kaneko, Takashi*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 103(7), p.074506_1 - 074506_18, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:84.12(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We investigate the axial  anomaly of two-flavor QCD at temperatures 190-330 MeV. In order to preserve precise chiral symmetry on the lattice, we employ the M
anomaly of two-flavor QCD at temperatures 190-330 MeV. In order to preserve precise chiral symmetry on the lattice, we employ the M bius domain-wall fermion action as well as overlap fermion action implemented with a stochastic reweighting technique. Compared to our previous studies, we reduce the lattice spacing to 0.07 fm, simulate larger multiple volumes to estimate finite size effect, and take more than four quark mass points, including one below physical point to investigate the chiral limit. We measure the topological susceptibility, axial
bius domain-wall fermion action as well as overlap fermion action implemented with a stochastic reweighting technique. Compared to our previous studies, we reduce the lattice spacing to 0.07 fm, simulate larger multiple volumes to estimate finite size effect, and take more than four quark mass points, including one below physical point to investigate the chiral limit. We measure the topological susceptibility, axial  susceptibility, and examine the degeneracy of
susceptibility, and examine the degeneracy of  partners in meson/baryon correlators. All the data above the critical temperature indicate that the axial
partners in meson/baryon correlators. All the data above the critical temperature indicate that the axial  violation is consistent with zero within statistical errors. The quark mass dependence suggests disappearance of the
violation is consistent with zero within statistical errors. The quark mass dependence suggests disappearance of the  anomaly at a rate comparable to that of the
anomaly at a rate comparable to that of the 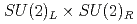 symmetry breaking.
symmetry breaking.
Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Yuta; Yamashita, Susumu; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Aoki, Takayuki*
Proceedings of International Conference on High Performance Computing in Asia-Pacific Region (HPC Asia 2021) (Internet), p.120 - 128, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Computer Science, Hardware & Architecture)We develop a multigrid preconditioned conjugate gradient (MG-CG) solver for the pressure Poisson equation in a two-phase flow CFD code JUPITER. The MG preconditioner is constructed based on the geometric MG method with a three-stage V-cycle, and a RB-SOR smoother and its variant with cache-reuse optimization (CR-SOR) are applied at each stage. The numerical experiments are conducted for two-phase flows in a fuel bundle of a nuclear reactor. The MG-CG solvers with the RB-SOR and CR-SOR smoothers reduce the number of iterations to less than 15% and 9% of the original preconditioned CG method, leading to 3.1- and 5.9-times speedups, respectively. The obtained performance indicates that the MG-CG solver designed for the block-structured grid is highly efficient and enables large-scale simulations of two-phase flows on GPU based supercomputers.
Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Asahi, Yuichi; Hasegawa, Yuta; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Aoki, Takayuki*
Dai-34-Kai Suchi Ryutai Rikigaku Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 2 Pages, 2020/12
We develop a multigrid preconditioned conjugate gradient (MG-CG) solver for the pressure Poisson equation in a two-phase flow CFD code JUPITER. The code is written in C++ and CUDA to keep the portability on multi-platforms. The main kernels of the CG solver achieve reasonable performance as 0.4  0.75 of the roofline performances, and the performances of the MG-preconditioner are also reasonable on NVIDIA GPU and Intel CPU. However, the performance degradation of the SpMV kernel on ARM is significant. It is confirmed that the optimization does not work if any functions are included in the loop.
0.75 of the roofline performances, and the performances of the MG-preconditioner are also reasonable on NVIDIA GPU and Intel CPU. However, the performance degradation of the SpMV kernel on ARM is significant. It is confirmed that the optimization does not work if any functions are included in the loop.
Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ali, Y.*; Yamashita, Susumu; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Aoki, Takayuki*
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications + Monte Carlo 2020 (SNA + MC 2020), p.210 - 215, 2020/10
This paper presents a GPU-based Poisson solver on a block-based adaptive mesh refinement (block-AMR) framework. The block-AMR method is essential for GPU computation and efficient description of the nuclear reactor. In this paper, we successfully implement a conjugate gradient method with a state-of-the-art multi-grid preconditioner (MG-CG) on the block-AMR framework. GPU kernel performance was measured on the GPU-based supercomputer TSUBAME3.0. The bandwidth of a vector-vector sum, a matrix-vector product, and a dot product in the CG kernel gave good performance at about 60% of the peak performance. In the MG kernel, the smoothers in a three-stage V-cycle MG method are implemented using a mixed precision RB-SOR method, which also gave good performance. For a large-scale Poisson problem with 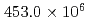 cells, the developed MG-CG method reduced the number of iterations to less than 30% and achieved
cells, the developed MG-CG method reduced the number of iterations to less than 30% and achieved  2.5 speedup compared with the original preconditioned CG method.
2.5 speedup compared with the original preconditioned CG method.