Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ichikawa, Tsubasa*; Hakoshima, Hideaki*; Inui, Koji*; Ito, Kosuke*; Matsuda, Ryo*; Mitarai, Kosuke*; Miyamoto, Koichi*; Mizukami, Wataru*; Mizuta, Kaoru*; Mori, Toshio*; et al.
Nature Reviews Physics (Internet), 6(6), p.345 - 347, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:99.15(Physics, Applied)Arai, Sora; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Kitamura, Ryo
JAEA-Technology 2023-009, 18 Pages, 2023/05
The linac located at the head of the J-PARC accelerators and required to provide the stable and high-quality beam. One of the accelerating cavities in the linac is the Separated-type Drift Tube Linac (SDTL). It is important to appropriately apply the RF power into the cavity for the stable operation. However, after the recovery from the Great East Japan Earthquake, the RF power could not be applied into the cavities for several SDTL cavities because the voltage standing wave ratio increased around the designed operating power. The investigation revealed that the inner surface of the cavity was exposed to high humidity and the backflow of oil from the rotary pump for a long period of time after the earthquake. It was suggested that the residue on the inner surface caused the multipactor resulted in the failure when the power was applied. The residue was wiped out with organic solvents and acids, resulted in solving the failure. This report describes the method and results of the cleaning for the cavity in 2021.
Kosaka, Satoshi*; Arai, Sora; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Kitamura, Ryo
JAEA-Technology 2023-003, 34 Pages, 2023/05
The negative hydrogen (H ) ion beam is accelerated with a peak current of 50 mA in the J-PARC linac. The linac consists of the H
) ion beam is accelerated with a peak current of 50 mA in the J-PARC linac. The linac consists of the H ion source and four kinds of accelerating cavities; a radio-frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ), a drift-tube linac (DTL), a separated-DTL (SDTL), and an annular-ring coupled structure linac (ACS). The accelerating electric field exists between the drift-tubes in the tank of the DTL. The quadrupole magnet for the beam focusing (DTQ) is installed in the drift-tube. The DTQ at J-PARC employs electromagnets to generate the magnetic field. It is important to set correctly the polarity of the magnetic field of the DTQ for tuning the beam. In this paper, we report the method of confirming the magnetic field polarity of DTQ, that is, the current wiring polarity by measuring DC current using a clamp meter on the power supply side and visually confirming the cable wiring connection on the electromagnet side.
ion source and four kinds of accelerating cavities; a radio-frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ), a drift-tube linac (DTL), a separated-DTL (SDTL), and an annular-ring coupled structure linac (ACS). The accelerating electric field exists between the drift-tubes in the tank of the DTL. The quadrupole magnet for the beam focusing (DTQ) is installed in the drift-tube. The DTQ at J-PARC employs electromagnets to generate the magnetic field. It is important to set correctly the polarity of the magnetic field of the DTQ for tuning the beam. In this paper, we report the method of confirming the magnetic field polarity of DTQ, that is, the current wiring polarity by measuring DC current using a clamp meter on the power supply side and visually confirming the cable wiring connection on the electromagnet side.
 Sr
Sr CoO
CoO at initial electrochemical process in an alkaline solution
at initial electrochemical process in an alkaline solutionMatsuzaki, Akira*; Hirayama, Masaaki*; Oguchi, Shoya*; Komo, Mamoru*; Ikezawa, Atsunori*; Suzuki, Kota*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Arai, Hajime*; Kanno, Ryoji*
Electrochemistry (Internet), 90(10), p.107001_1 - 107001_8, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Electrochemistry)Oxygen reduction and evolution reactions (ORR and OER) of perovskite-type La Sr
Sr CoO
CoO were characterized using two-dimensional model electrodes with different reaction planes. Synthesized by pulsed laser deposition, these thin and flat electrodes can reveal the reaction plane dependence of the ORR activity. From steady-state polarization measurements in KOH (aq.), the ORR activity was the highest on the (001) film during the first ORR/OER cycle, and it decreased significantly during the second cycle. In-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction clarified crystal structure changes in the bulk and surface regions of La
were characterized using two-dimensional model electrodes with different reaction planes. Synthesized by pulsed laser deposition, these thin and flat electrodes can reveal the reaction plane dependence of the ORR activity. From steady-state polarization measurements in KOH (aq.), the ORR activity was the highest on the (001) film during the first ORR/OER cycle, and it decreased significantly during the second cycle. In-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction clarified crystal structure changes in the bulk and surface regions of La Sr
Sr CoO
CoO , and these changes are associated with forming oxygen defects during the initial electrochemical process. Furthermore, the La
, and these changes are associated with forming oxygen defects during the initial electrochemical process. Furthermore, the La Sr
Sr CoO
CoO surface partially decomposed upon reacting. Therefore, the interfacial structures formed in the electrochemical reaction field is important for enhancing ORR and OER activities.
surface partially decomposed upon reacting. Therefore, the interfacial structures formed in the electrochemical reaction field is important for enhancing ORR and OER activities.
Arai, Yosuke*; Kuroda, Kenta*; Nomoto, Takuya*; Tin, Z. H.*; Sakuragi, Shunsuke*; Bareille, C.*; Akebi, Shuntaro*; Kurokawa, Kifu*; Kinoshita, Yuto*; Zhang, W.-L.*; et al.
Nature Materials, 21(4), p.410 - 415, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:75.71(Chemistry, Physical) Sr
Sr CuO
CuO
Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Fujita, Masaki*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Arai, Masatoshi*
Physical Review B, 105(1), p.014508_1 - 014508_7, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.68(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Sr
Sr CuO
CuO (
( = 0.10 and 0.16)
= 0.10 and 0.16)Sato, Kentaro*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Arai, Masatoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(11), p.114703_1 - 114703_7, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:54.47(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kuroda, Kenta*; Arai, Yosuke*; Rezaei, N.*; Kunisada, So*; Sakuragi, Shunsuke*; Alaei, M.*; Kinoshita, Yuto*; Bareille, C.*; Noguchi, Ryo*; Nakayama, Mitsuhiro*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.2888_1 - 2888_9, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:80.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Otaka, Toshiki*; Sato, Tatsumi*; Ono, Shimpei; Nagoshi, Kohei; Abe, Ryoji*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Watanabe, So; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Nakatani, Kiyoharu*
Analytical Sciences, 35(10), p.1129 - 1133, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:33.49(Chemistry, Analytical) Se
Se studied by inelastic neutron scattering
studied by inelastic neutron scatteringIshikado, Motoyuki*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Ji, S.*; Arai, Masatoshi*; Shamoto, Shinichi
Condensed Matter (Internet), 4(3), p.69_1 - 69_10, 2019/09
The enhancement magnetic resonance mode of FeTe Se
Se is limited around Q = (
is limited around Q = ( , 0). Q dependence is found to be consistent with a theoretical simulation of the magnetic resonance mode with the sign-reversing order parameter of s
, 0). Q dependence is found to be consistent with a theoretical simulation of the magnetic resonance mode with the sign-reversing order parameter of s wave.
wave.
Abe, Ryoji*; Nagoshi, Kohei*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Watanabe, So; Sano, Yuichi; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Takagi, Hideaki*; Shimizu, Nobutaka*; Koka, Masashi*; Sato, Takahiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 404, p.173 - 178, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:51.69(Instruments & Instrumentation) surface under high voltage battery operation
surface under high voltage battery operationTaminato, So*; Hirayama, Masaaki*; Suzuki, Kota*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Minato, Taketoshi*; Arai, Hajime*; Uchimoto, Yoshiharu*; Ogumi, Zempachi*; Kanno, Ryoji*
Journal of Power Sources, 307, p.599 - 603, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:70.92(Chemistry, Physical)An epitaxial-film model electrode of LiCoO (104) was fabricated on SrRuO
(104) was fabricated on SrRuO (100)/Nb:SrTiO
(100)/Nb:SrTiO (100) using pulsed laser deposition. The 50 nm thick LiCoO
(100) using pulsed laser deposition. The 50 nm thick LiCoO (104) film exhibited lithium (de-)intercalation activity with a first discharge capacity of 119 mAh g
(104) film exhibited lithium (de-)intercalation activity with a first discharge capacity of 119 mAh g between 3.0 and 4.4 V, followed by a gradual capacity fading with subsequent charge-discharge cycles. In contrast, a 3.2 nm thick Li
between 3.0 and 4.4 V, followed by a gradual capacity fading with subsequent charge-discharge cycles. In contrast, a 3.2 nm thick Li PO
PO -coated film exhibited a higher intercalation capacity of 148 mAh g
-coated film exhibited a higher intercalation capacity of 148 mAh g with superior cycle retention than the uncoated film. In situ surface X-ray diffraction measurements revealed a small lattice change at the coated surface during the (de-)intercalation processes compared to the uncoated surface. The surface modification of LiCoO
with superior cycle retention than the uncoated film. In situ surface X-ray diffraction measurements revealed a small lattice change at the coated surface during the (de-)intercalation processes compared to the uncoated surface. The surface modification of LiCoO by the Li
by the Li PO
PO coating could lead to improvement of the structural stability at the surface region during lithium (de-)intercalation at high voltage.
coating could lead to improvement of the structural stability at the surface region during lithium (de-)intercalation at high voltage.
 binding site of a
binding site of a  -lactamase from the halophile by anomalous X-ray diffraction
-lactamase from the halophile by anomalous X-ray diffractionArai, Shigeki; Shibazaki, Chie; Shimizu, Rumi; Adachi, Motoyasu; Tamada, Taro; Tokunaga, Hiroko*; Ishibashi, Matsujiro*; Tokunaga, Masao*; Kuroki, Ryota
Kyushu Shinkurotoronko Kenkyu Senta Nempo, 2014, p.17 - 19, 2016/03
no abstracts in English
Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Iida, Kazuki*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakatani, Takeshi; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2015-002, p.319 - 329, 2016/02
Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Kambara, Wataru; Krist, T.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Arai, Masatoshi; Iida, Kazuki*; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2015-002, p.339 - 348, 2016/02
We have developed a new Fermi chopper referred to as Magic chopper to realize the full optimization of the experimental condition for Multi-Ei method in a chopper spectrometer. In this study, the theoretical aspects of MAGIC chopper concept will be initially presented, and the performances of MAGIC chopper will be evaluated by both Monte Carlo simulation and neutron transmission experiment.
Ohara, Takashi; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Oikawa, Kenichi; Kaneko, Koji; Kawasaki, Takuro; Tamura, Itaru; Nakao, Akiko*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Munakata, Koji*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 49(1), p.120 - 127, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:59 Percentile:96.22(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Su, Y. H.; Oikawa, Kenichi; Kawasaki, Takuro; Kai, Tetsuya; Shiota, Yoshinori*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Shinohara, Takenao; Tomota, Yo*; Harada, Masahide; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.031015_1 - 031015_5, 2015/09
In this study, neutron imaging experiment was performed using NOBORU, BL10 of MLF at J-PARC. Four kinds of cast duplex stainless steel with ferrite and austenite microstructure were studied here, which were produced by different casting method at different temperature. Firstly, two-dimensional scintillation detector using wavelength-shifting fibers with pixel size of 0.52 mm  0.52 mm and illuminated area 55 mm
0.52 mm and illuminated area 55 mm  55 mm was used for data collection. Then, measurement by Micro Pixel Chamber based neutron imaging detector having higher spatial resolution about 0.2 mm was conducted. Data analysis code RITS (Rietveld Imaging of Transmission Spectra) will be used for microstructure including crystalline phase, lattice strain, crystallite size, texture evaluation.
55 mm was used for data collection. Then, measurement by Micro Pixel Chamber based neutron imaging detector having higher spatial resolution about 0.2 mm was conducted. Data analysis code RITS (Rietveld Imaging of Transmission Spectra) will be used for microstructure including crystalline phase, lattice strain, crystallite size, texture evaluation.
 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO by four-dimensional mapping of neutron cross-sections using the 4SEASONS chopper spectrometer
by four-dimensional mapping of neutron cross-sections using the 4SEASONS chopper spectrometerWakimoto, Shuichi; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Arai, Masatoshi; Fujita, Masaki*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Kawamura, Sho*; Matsuura, Masato*; Nakajima, Kenji; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.034013_1 - 034013_6, 2015/09
Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Iida, Kazuki*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Nakajima, Kenji; Harada, Masahide; Arai, Masatoshi
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.036001_1 - 036001_6, 2015/09
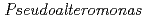 sp. AS-131 isolated from Antarctic Ocean
sp. AS-131 isolated from Antarctic OceanYonezawa, Yasushi*; Nagayama, Aiko*; Tokunaga, Hiroko*; Ishibashi, Matsujiro*; Arai, Shigeki; Kuroki, Ryota; Watanabe, Keiichi*; Arakawa, Tsutomu*; Tokunaga, Masao*
Protein Journal, 34(4), p.275 - 283, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:10.01(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Nucleoside diphosphate kinase isolated from psychrophilic 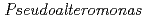 sp. AS-131 (ASNDK) was expressed in
sp. AS-131 (ASNDK) was expressed in  and purified to homogeneity. Comparing to mesophilic NDK isolated from
and purified to homogeneity. Comparing to mesophilic NDK isolated from 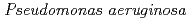 , ASNDK exhibited highly elevated thermolability: (1)
, ASNDK exhibited highly elevated thermolability: (1)  expression at 37
expression at 37 C as a denatured insoluble form, and (2) 30
C as a denatured insoluble form, and (2) 30 C lower optimum temperature of enzymatic activity. The subunit structure of ASNDK was suggested to be dimer, as in NDKs isolated from moderate halophiles.
C lower optimum temperature of enzymatic activity. The subunit structure of ASNDK was suggested to be dimer, as in NDKs isolated from moderate halophiles.