Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
小泉 光生; 伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Wei, T.*; 余語 覚文*; et al.
第45回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2024/11
Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is a non-destructive method applicable for measuring nuclear material using a time-of-flight (TOF) technique with a pulsed neutron source. To realize a high resolution compact NRTA system, use of a short-pulsed neutron source is essential. Laser-driven neutron sources (LDNSs) are well-suit for generating such neutron beams due to their short pulse width. The advances in laser technology will further reduce the system's size and improve practicality. In this study, we demonstrate the measurement of a neutron transmission TOF spectrum of a sample containing indium and silver using the LDNS of the Osaka University. The obtained spectrum was analyzed using the least-square nuclear-resonance fitting program, REFIT, showcasing for the first time the potential of an LDNS for nondestructive areal-density material characterization.
小泉 光生; 伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Lan, Z.*; Wei, T.*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.21916_1 - 21916_9, 2024/09
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:57.84(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Laser-driven neutron sources (LDNSs) can generate strong short-pulse neutron beams, which are valuable for scientific studies and engineering applications. Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is a nondestructive technique used for determining the areal density of each nuclide in a material sample using pulsed thermal and epithermal neutrons. Herein, we report the first successful NRTA performed using an LDNS driven by the Laser for Fast Ignition Experiment at the Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University. The key challenge was achieving a well-resolved resonance transmission spectrum for material analysis using an LDNS with a limited number of laser shots in the presence of strong background noise. We addressed this by employing a time-gated  Li-glass scintillation neutron detector to measure the transmission spectra, reducing the impact of electromagnetic noise and neutron and gamma-ray flashes. Output waveforms were recorded for each laser shot and analyzed offline using a counting method. This approach yielded a spectrum with distinct resonances, which were attributed to
Li-glass scintillation neutron detector to measure the transmission spectra, reducing the impact of electromagnetic noise and neutron and gamma-ray flashes. Output waveforms were recorded for each laser shot and analyzed offline using a counting method. This approach yielded a spectrum with distinct resonances, which were attributed to  In and
In and  Ag, as confirmed through neutron transmission simulation. The spectrum was analyzed using the least-square nuclear-resonance fitting program, REFIT, demonstrating the possibility of using an LDNS for nondestructive areal-density material characterization.
Ag, as confirmed through neutron transmission simulation. The spectrum was analyzed using the least-square nuclear-resonance fitting program, REFIT, demonstrating the possibility of using an LDNS for nondestructive areal-density material characterization.
Lan, Z.*; 有川 安信*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Morace, A.*; 早川 岳人*; 佐藤 博隆*; 加美山 隆*; Wei, T.*; 巽 湧太*; 小泉 光生; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.5365_1 - 5365_7, 2024/07
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:82.88(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The temperature measurement of material inside of an object is one of the key technologies for control of dynamical processes. For this purpose, various techniques such as laser-based thermography and phase-contrast imaging thermography have been studied. However, it is, in principle, impossible to measure the temperature of an element inside of an object using these techniques. One of the possible solutions is measurements of Doppler brooding effect in neutron resonance absorption (NRA). Here we present a method to measure the temperature of an element or an isotope inside of an object using NRA with a single neutron pulse of approximately 100 ns width provided from a high-power laser. We demonstrate temperature measurements of a tantalum (Ta) metallic foil heated from the room temperature up to 617 K. Although the neutron energy resolution is fluctuated from shot to shot, we obtain the temperature dependence of resonance Doppler broadening using a reference of a silver (Ag) foil kept to the room temperature. A free gas model well reproduces the results. This method enables element(isotope)-sensitive thermometry to detect the instantaneous temperature rise in dynamical processes.
余語 覚文*; Lan, Z.*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Wei, T.*; 森 隆人*; Golovin, D.*; 早川 岳人*; 岩田 夏弥*; et al.
Physical Review X, 13(1), p.011011_1 - 011011_12, 2023/01
被引用回数:34 パーセンタイル:96.82(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Neutrons are powerful tools for investigating the structure and properties of materials used in science and technology. Recently, laser-driven neutron sources (LDNS) have attracted the attention of different communities, from science to industry, in a variety of applications, including radiography, spectroscopy, security, and medicine. However, the laser-driven ion acceleration mechanism for neutron generation and for establishing the scaling law on the neutron yield is essential to improve the feasibility of LDNS. In this paper, we report the mechanism that accelerates ions with spectra suitable for neutron generation. We show that the neutron yield increases with the fourth power of the laser intensity, resulting in the neutron generation of 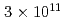 in
in 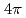 at a maximum, with
at a maximum, with 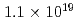 Wcm
Wcm , 900 J, 1.5 ps lasers. By installing a "hand-size" moderator, which is specially designed for the LDNS, it is demonstrated that the efficient generation of epithermal (0.1-100 eV) neutrons enables the single-shot analysis of composite materials by neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA). We achieve the energy resolution of 2.3% for 5.19-eV neutrons 1.8 m downstream of the LDNS. This leads to the analysis of elements and isotopes within sub-
, 900 J, 1.5 ps lasers. By installing a "hand-size" moderator, which is specially designed for the LDNS, it is demonstrated that the efficient generation of epithermal (0.1-100 eV) neutrons enables the single-shot analysis of composite materials by neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA). We achieve the energy resolution of 2.3% for 5.19-eV neutrons 1.8 m downstream of the LDNS. This leads to the analysis of elements and isotopes within sub- s times and allows for high-speed nondestructive inspection.
s times and allows for high-speed nondestructive inspection.
弘中 浩太; 伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 小泉 光生; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 余語 覚文*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*
第42回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2021/11
中性子共鳴透過分析(NRTA)はパルス中性子源を用いてTOF測定を行うことで核物質を非破壊測定する手法であるが、小型・高精度化には短パルスな小型中性子源が必要となる。近年発展著しいレーザー技術を用いたレーザー駆動中性子源(LDNS)は、そのような中性子源として将来を期待されている。我々はLDNSを用いたNRTAの実現可能性を調べるため、大阪大学LFEXレーザーを用いて中性子TOF測定実験を行った。
有川 安信*; 池田 裕二郎; 清水 裕彦*; 花山 良平*; 近藤 治靖*; 黒澤 俊介*
レーザー研究, 46(11), p.634 - 640, 2018/11
小型中性子源は、中性子回折, 中性子共鳴分析, 中性子ラジオグラフィなど様々な診断手法として使われてきた。中性子検出器の開発はこれらの全ての応用に不可欠であるが、その技術は中性子エネルギーと測定の目的に強く依存している。本論文では、小型中性子源の利用促進に関連する中性子測定技術について解説する。低速中性子用の従来型検出器による一般的な中性子検出技術と共に、レーザー駆動小型中性子源に適用できる高時間分解能かつ高感度な高エネルギー中性子用検出器について述べる。
Zhang, Z.*; 西村 博明*; 波元 拓哉*; 藤岡 慎介*; 有川 安信*; 錦野 将元; 河内 哲哉; 匂坂 明人; 細田 裕計*; 織茂 聡; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 83(5), p.053502_1 - 053502_5, 2012/05
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:60.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)ラウエ分光器を用いて17-77keVまでのレーザープラズマからの特性X線の定量計測を行った。ラウエ分光器では信号強度や露光時間によって検出器としてCSI蛍光体にCCDカメラかイメージングプレートのどちらかを選択して用いることができる。別の構成された計測器を用いたレーザープラズマX線及び、放射性同位体を用いてラウエ分光器の絶対感度較正を行った。実験におけるラウエ結晶からの積算反射率は、X線回折コードを用いた計算結果とよく一致していることがわかった。このラウエ分光器を用いた定量計測の結果から特性X線発生のための入射レーザーエネルギーから高速電子への変換効率について議論する。
Lee, J.; 伊藤 史哲*; 弘中 浩太; 小泉 光生; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 余語 覚文*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; 堀 順一*
no journal, ,
文部科学省補助金事業「核セキュリティ強化等推進事業費補助金」の下、核不拡散技術開発の一環として、レーザー駆動中性子源(LDNS)を用いた核共鳴透過分析(NRTA)技術開発を行っている。LDNSは発展段階にあるため、中性子共鳴透過分析(NRTA)に適用するにあたっては、いくつかの開発項目がある。本発表では、モデレータ,検出器・データ処理システムの開発について、その背景及び開発の進捗状況を報告する。
小泉 光生; 弘中 浩太; 伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 高橋 時音; 余語 覚文*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*
no journal, ,
レーザー駆動中性子源の中性子共鳴透過分析(NRTA)への適用可能性を実験的に実証することを目的とし、大阪大学レーザー科学研究所のLFEXレーザーを用いたパルス中性子源を利用して中性子透過実験を行い、中性子カウンティング法によるTOFスペクトルを取得した。その結果を報告する。
匂坂 明人; 小倉 浩一; 錦野 将元; Pirozhkov, A. S.; 河内 哲哉; 西内 満美子; 神門 正城; 近藤 公伯; 有川 安信*; 小島 完興*; et al.
no journal, ,
高強度レーザーと薄膜との相互作用により、高エネルギーの粒子,硬X線などが発生する。特にレーザー駆動陽子線については、医療やその他への応用が期待されている。今回、大阪大学設置のLFEXレーザーを用い、高エネルギーレーザーと薄膜ターゲットとの相互作用実験を行なった。レーザーは、3ビームをターゲットに照射した。3ビームの照射により、高エネルギー陽子を測定した。また、プラズマミラーの予備実験を開始した。
小泉 光生; 伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 弘中 浩太; 余語 覚文*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*
no journal, ,
文部科学省補助金事業「核セキュリティ強化等推進事業費補助金」の下、核不拡散技術開発の一環として、レーザー駆動中性子源(LDNS)を用いた核共鳴透過分析(NRTA)技術開発を行っている。核物質の分析にNRTAに適用するためには、LDNSで発生した高速中性子を、短いパルス幅を維持しつつ、中性子を100eV以下に減速する必要がある。そこで、シミュレーヨンを用い、中性子を減速するモデレーターの形状や素材の検討を進めた。
伊藤 史哲*; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; Lee, J.; 小泉 光生; 余語 覚文*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; 西村 博明*; 堀 順一*; et al.
no journal, ,
文部科学省補助金事業「核セキュリティ強化等推進事業費補助金」の下、核不拡散技術開発の一環として、レーザー駆動中性子源を用いた核共鳴透過分析(NRTA)技術開発を行っている。中性子飛行時間(TOF)測定に用いる中性子検出器及び解析手法の開発状況等について報告する。
高橋 時音; 小泉 光生; 伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 鈴木 敏*; 弘中 浩太; 余語 覚文*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; 西村 博明*; et al.
no journal, ,
The technique of NRTA is based on a neutron time-of-flight (TOF) method. Collimated pulsed neuron beams passing through a sample arrive a neutron detector placed at a distance from the neutron source. The neutron kinetic energy is deduced from the flight time between the neutron generator and the detector. Since the neutron reaction cross section of a nuclide has a characteristic resonance structure, neutrons having the resonance energy are strongly absorbed or scattered by the nuclide in a sample. Resonance dips appeared in the transmission spectrum are analyzed to deduce each nuclide areal density. The resolution of the observed dip strongly depends on the flight path length and the neutron pulse width. To realize a compact NRTA system by shortening the flight path length, a short-pulsed neutron generation is required. A laser-driven neutron source (LDNS), which can generate extremely short pulse neutron beams, is considered to potentially be such a short pulse neutron generator for a compact NRTA system. In addition, because laser light can be transported by mirrors, the laser system of the LDNS can be installed in separated place from an NRTA system which has to be in the nuclear controlled area. This enables maintenance of a laser system to be easy. Also, several analyzing system can be operated parallelly by switching laser path. In this presentation, we will overview a proposal of an application of the LDNS to an NRTA system for nuclear non-proliferation.
Lan, Z.*; 余語 覚文*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 早川 岳人*; 小泉 光生; Wei, T.*; Shi, B.*; 石本 崇*; Golovin, D.*; 森 隆人*; et al.
no journal, ,
High penetration power of neutrons is potentially useful for realizing opaque object analysis in non-destructive way. Large-scale particle accelerators and nuclear reactors are mostly used for development of neutron analyzing method. A Laser-Driven Neutron Source (LDNS) has been proposed as a new approach of neutron generation for non-destructive analysis. Demonstration experiments on neutron resonance measurement ware performed at ILE, Osaka Univ., Japan. The Peta-watt laser LFEX was used to shoot a CD (deuterated plastic) foil target to produce accelerated charged deuterons. Neutrons are generated by nuclear reaction between a cylindrical beryllium and the accelerated deuteron, and then moderated by a high-density polyethylene (HDP). Neutrons of 1 20 eV were observed with a neutron detector at a 1.8 m using neutron resonance diagnosis technology. This report describes the results of the first experimental demonstration.
20 eV were observed with a neutron detector at a 1.8 m using neutron resonance diagnosis technology. This report describes the results of the first experimental demonstration.
余語 覚文*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; 岩本 晃史*; 早川 岳人*; 小泉 光生; Golovin, D.*; 森 隆人*; Lan, Z.*; et al.
no journal, ,
大阪大学のLFEXレーザー施設において、大強度レーザーを用いたパルス中性子源(LDNS)の開発およびそれを利用した応用研究を進めている。レーザーは、パルス巾が1.5psで、最大出力は、1kJ(1.5 10
10 Wcm
Wcm である。開発した中性子源は1cm程度の大きさで、数十マイクロメータに収束したレーザーをターゲットに照射し、それによって生成したMeVもの高速イオン(水素や重水素粒子)を直径5mmのベリリウムに当てて、核反応により中性子を生成するものである。中性子の生成量は、1ショットあたり10
である。開発した中性子源は1cm程度の大きさで、数十マイクロメータに収束したレーザーをターゲットに照射し、それによって生成したMeVもの高速イオン(水素や重水素粒子)を直径5mmのベリリウムに当てて、核反応により中性子を生成するものである。中性子の生成量は、1ショットあたり10 で、この生成量は、入射エネルギーの4乗で増加することが分かった。さらに、生成した中性子を数cmの大きさのモデレータで減速させ、離れた位置に設置した中性子検出器により、中性子発生から検出までの飛行時間を測定するTOF測定を行った。試料を透過させて中性子の減衰を調べる実験を行った結果、核反応の共鳴による減衰の観測に成功した。
で、この生成量は、入射エネルギーの4乗で増加することが分かった。さらに、生成した中性子を数cmの大きさのモデレータで減速させ、離れた位置に設置した中性子検出器により、中性子発生から検出までの飛行時間を測定するTOF測定を行った。試料を透過させて中性子の減衰を調べる実験を行った結果、核反応の共鳴による減衰の観測に成功した。
Lee, J.; 伊藤 史哲*; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 弘中 浩太; 余語 覚文*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*
no journal, ,
文部科学省補助金事業「核セキュリティ強化等推進事業費補助金」の下、核不拡散技術開発の一環として、レーザー駆動中性子源(LDNS)を用いた中性子共鳴透過分析(NRTA)の技術開発を行っている。LDNSから発生した高速中性子をNRTAに適当な熱外エネルギーまで減速するためには、モデレータが必要である。本発表では、シミュレーション計算から得られた結果を基にLDNSを用いたNRTAに適切なモデレータの構造や素材などについて報告する。
余語 覚文*; Lan, Z.*; 早川 岳人*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 小泉 光生; 森 隆人*; Wei, T.*; 藤岡 慎介*; et al.
no journal, ,
レーザー駆動中性子源は、高強度レーザーパルスを薄膜の1次ターゲットに集光して、プラズマの作る瞬間的な電場でMeVエネルギーイオン(陽子・重陽子)を発生し、それを2次ターゲット(ベリリウム等)に照射して、短パルスの高速中性子を発生する。2次ターゲットに小型の減速材を取り付けて、パルス熱外中性子を発生し、1.8mのビームラインで飛行時間法によるエネルギースペクトルを分析した。ビームラインに銀(Ag),タンタル(Ta),インジウム(In)の合板を設置したところ、3.81eV ( In), 4.28eV (
In), 4.28eV ( Ta), 5.19eV (
Ta), 5.19eV ( Ag)に共鳴吸収によるディップを計測した。これらの共鳴吸収スペクトルは、レーザー1パルスで発生する中性子で計測されたものである。講演では、実験結果の詳細と、将来的なシングルショット分析への応用可能性について議論する。
Ag)に共鳴吸収によるディップを計測した。これらの共鳴吸収スペクトルは、レーザー1パルスで発生する中性子で計測されたものである。講演では、実験結果の詳細と、将来的なシングルショット分析への応用可能性について議論する。
Lan, Z.*; 余語 覚文*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 小泉 光生; 早川 岳人*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Golovin, D.*; 森 隆人*; Wei, T.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Neutron resonance diagnosis technology has been developed on reactors and accelerators for over ten years. By employing neutron beams with high transmittance, it is possible to analyse elementary composition, internal temperature and shock waves of thick objects in a non-destructive way. We developed a new approach to generate short-pulse epithermal neutron beams using relativistic intensity laser for the neutron resonance spectral diagnosis, which is known as Laser-driven Epithermal Neutron Source (LDENS). The neutron resonance measuring experiment was implemented at ILE, Osaka Univ. with peta-watt laser LFEX. The experimental results in 2020 demonstrated that LDENS is applicable for neutron resonance measurement. In 2021 experiments, we developed the system to record neutron spectrum with higher quality. Multiple resonance peaks of various isotopes with different temperature were clearly measured. The presentation will introduce the experimental results and discussions including characteristic evaluation of LDENS and temperature dependency of neutron resonance peaks.
余語 覚文*; Lan, Z.*; 有川 安信*; 早川 岳人*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Wei, T.*; 巽 湧太*; 佐藤 博隆*; 加美山 隆*; 小泉 光生
no journal, ,
高強度レーザーで加速した陽子・重陽子をBe等のコンバータで中性子に変換するレーザー駆動中性子源を開発しており、これまでにレーザー1ショットで発生した単一パルスの中性子で、中性子共鳴スペクトルの計測に成功している。本発表では、サンプルを300-600Kの範囲で昇温し、共鳴吸収ピークのドップラー広がりが温度の平方根に依存する結果を得たので報告する。
伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 高橋 時音; 小泉 光生; 鈴木 敏*; 弘中 浩太; 余語 覚文*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*
no journal, ,
文部科学省補助金事業「核セキュリティ強化等推進事業費補助金」の下、核不拡散技術開発の一環として、レーザー駆動中性子源(LDNS)を用いた核共鳴透過分析(NRTA)技術開発を行っている。LDNSは、小さな領域から短いパルス幅の中性子を発生させることができ、NRTAにとって大きなメリットがあると考えられている。このLDNSを用いたNRTAの実証のために、大阪大学にあるLFEXレーザーを用いたTOF法による透過率測定を実施した。その結果について報告する。