Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Ir
Ir Sn
Sn
Kaneko, Koji; Cheung, Y. W.*; Hu, Y.*; Imai, Masaki*; Tanioku, Yasuaki*; Kanagawa, Hibiki*; Murakawa, Joichi*; Moriyama, Kodai*; Zhang, W.*; Lai, K. T.*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 30, p.011032_1 - 011032_6, 2020/03
Ichikawa, Yasuaki*; Kimoto, Kazushi*; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2019-005, 32 Pages, 2019/10
It is important to evaluate the mechanical stability around the geological repository for high-level radioactive waste, during not only the design, construction and operation phases, but also the post-closure period over several millennia. The rock mass around the tunnels could be deformed in response to time dependent behaviors such as creep and stress relaxation. Therefore, this study has started as a joint research with Okayama University from 2016. This report summarize the results of the joint research performed in fiscal year 2017 and 2018. Based on the research results obtained in fiscal year 2016, automatic measurement system was developed, which can collect very large data on surface elastic wave propagation in a short time, also the applicability of various kinds of parameters derived from measured elastic wave data was examined.
Yano, Kimihiko; Kitagaki, Toru; Washiya, Tadahiro; Miyamoto, Yasuaki; Ogawa, Toru
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 5, p.225 - 228, 2018/11
According to the roadmap for decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi NPS, fuel debris retrieval will start from 2021, after a decade from fuel debris generation. Fuel debris will stay in the reactors until the end of defueling. In addition, it is not hard to anticipate that storage is necessary for fuel debris removed from reactors. In order to consider such a post-accident operation for fuel debris, it is indispensable to discuss the states and characteristics of fuel debris during several decades. Therefore, JAEA directed R&D strategy on mid- and long-term behavior of fuel debris tentatively and is making a start of fundamental studies on this issue in corporation with the domestic universities and other research institutes.
 Sr
Sr )
) Rh
Rh Sn
Sn from a lattice dynamics study
from a lattice dynamics studyCheung, Y. W.*; Hu, Y. J.*; Imai, Masaki*; Tanioku, Yasuaki*; Kanagawa, Hibiki*; Murakawa, Joichi*; Moriyama, Kodai*; Zhang, W.*; Lai, K. T.*; Yoshimura, Kazuyoshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(16), p.161103_1 - 161103_5, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:66.85(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kuwahara, Akira; Aiba, Yasuaki*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Nankawa, Takuya; Matsui, Makoto*
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 33(7), p.1150 - 1153, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:48.52(Chemistry, Analytical)Although high-temperature plasma sources have been used for direct isotope analysis of solid samples, the spectral resolution of diode laser absorption spectroscopy in high-temperature plasma is limited by the Doppler broadening of atomic absorption lines. Thus, a decrease in translational temperature is necessary to enhance the spectral resolution and distinguish isotope shifts due to mass number. In this study, a supersonic plasma wind tunnel, also called an arc-jet plasma wind tunnel, was used to enhance spectral resolution drastically, and a demonstration was carried out using natural stable xenon isotopes. As a result, the temperature was found to be about 180 K and the spectral resolution was about one order of magnitude higher than that of the conventional high-temperature source. Additionally, the method proposed herein was verified by using two xenon isotopes.
Kuwahara, Akira; Aiba, Yasuaki*; Nankawa, Takuya; Matsui, Makoto*
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 33(5), p.893 - 896, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.9(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Kimoto, Kazushi*; Ichikawa, Yasuaki*; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2017-009, 18 Pages, 2017/11
JAEA has started this study as joint research with Okayama University from 2016. In fiscal year 2016, several kinds of elastic wave velocity were measured using ultra sonic sensors and laser Doppler vibrometer to evaluate the anisotropy of different elastic wave in granite. The velocity measurements were carried out focused on transmitted wave and surface wave. The results showed that strong anisotropy was observed in transmitted P- wave velocity while weak anisotropy was observed in transmitted S-wave and group velocity estimated by surface velocity measurement. In addition, data obtained from surface velocity measurement was partitioned into transmitted and reflected waves and analyzed them in detail. It resulted that elastic wave due to mineral particles consist of granite was dispersed; however, significant dispersion was only observed at specific location.
 Sr
Sr )
) Rh
Rh Sn
Sn
Cheung, Y. W.*; Hu, Y. J.*; Goh, S. K.*; Kaneko, Koji; Tsutsui, Satoshi; Logg, P. W.*; Grosche, F. M.*; Kanagawa, Hibiki*; Tanioku, Yasuaki*; Imai, Masaki*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 807(3), p.032002_1 - 032002_4, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:83.41(Physics, Condensed Matter)Ichikawa, Yasuaki*; Kimoto, Kazushi*; Matsui, Hiroya; Kuwabara, Kazumichi; Ozaki, Yusuke
JAEA-Research 2016-018, 23 Pages, 2016/12
It is important to evaluate the stability of a repository for high-level radioactive waste not only during the design, construction and operation phases, but also during the post-closure period, for time frames likely exceeding several millennia or longer. The rock mass around the tunnels could be deformed through time in response to time dependent behavior. On the other hand, it was revealed that the chemical reaction of groundwater in a rock had an influence on the long-term behavior. An evaluation of the microcracks to have an influence on this mechanical and chemical coupled phenomena should be worked on chiefly. In fiscal year 2015, using a laser Doppler vibrometer that extends a frequency band up to 20 MHz, and measuring the surface wave transmitted through the granite specimens were estimated group velocity. As a result, group velocity until 100 kHz  500 kHz, revealed that tends to decrease while vibrating. The group speed estimate from a group delay was shown to be easier than the estimate by wave number - frequency spectrum. This is because in order to improve reliability, the estimated frequency band is by using a spatially averaged waveform. As a result obtained, in the case of the modeling by the viscoelastic theory of the granite and a microcrack nondestructiveness evaluation, it is thought that it is useful information in the future. In order to use the knowledge of this study, there is a need to clarify the correspondence between the microscopic properties of the medium such as a crack and crystal grain and the change of the group velocity.
500 kHz, revealed that tends to decrease while vibrating. The group speed estimate from a group delay was shown to be easier than the estimate by wave number - frequency spectrum. This is because in order to improve reliability, the estimated frequency band is by using a spatially averaged waveform. As a result obtained, in the case of the modeling by the viscoelastic theory of the granite and a microcrack nondestructiveness evaluation, it is thought that it is useful information in the future. In order to use the knowledge of this study, there is a need to clarify the correspondence between the microscopic properties of the medium such as a crack and crystal grain and the change of the group velocity.
Ichikawa, Yasuaki*; Kimoto, Kazushi*; Sato, Toshinori; Kuwabara, Kazumichi; Takayama, Yusuke
JAEA-Research 2015-025, 31 Pages, 2016/03
It is important to evaluate the stability of a repository for high-level radioactive waste not only during the design, construction and operation phases, but also during the post-closure period, for time frames likely exceeding several millennia or longer. The rock mass around the tunnels could be deformed through time in response to time dependent behavior. On the other hand, it was revealed that the chemical reaction of groundwater in a rock had an influence on the long-term behavior. An evaluation of the microcracks to have an influence on these mechanical and chemical coupled phenomena should be worked on chiefly. In fiscal year 2014, this study performed numerical analysis to examine the supersonic scattering attenuation decrement behavior in the crystalline rock and a measurement sequentially last year. The measurement of the head and surface waves were carried out. As a result, group speed was provided. On the other hand, the spread scattering analysis of the elastic wave by the FDTD (Finite Difference Time-Domain) method made a numerical analysis. However, a laboratory finding is different from expectation of the simulation, and crystal anisotropic influence of a microcrack and rock-forming minerals is thought about as a cause of this estrangement. Therefore it was revealed that it was necessary to examine these two points of influence more in future.
Sasaki, Akira; Kato, Susumu*; Takahashi, Eiichi*; Kishimoto, Yasuaki*; Fujii, Takashi*; Kanazawa, Seiji*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 55(2), p.026101_1 - 026101_10, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.59(Physics, Applied)A percolation model of discharge, which can reproduce stochastic behaviors of initial partial discharge to the growth of a stepped leader, is presented. The model uses macroscopic cells, from which a network of electric circuits is defined, and the spatial and temporal evolutions of the electric field and current in the discharge medium are calculated. For each cell, one of two states, either insulator or conductor, which corresponds to neutral gas or ionized plasmas, respectively, is decided. The decision is made on the basis of probability for each calculation cell at each time step, taking the effects of local electric field and current, which enhance ionization and sustain the discharge channel, respectively, into account. The stochastic behavior of discharge is discussed, in conjunction with the characteristic feature of ionization, that is, the ionization occurs not only ahead of the streamer tip where the electric field is enhanced but randomly in the discharge medium.
Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Fasoli, A.*; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Diamond, P. H.*; Medvedev, S.*; Wu, Y.*; Duan, X.*; Kishimoto, Yasuaki*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Pueschel, M. J.*; et al.
Proceedings of 8th IAEA Technical Meeting on Steady State Operation of Magnetic Fusion Devices (CD-ROM), 20 Pages, 2015/05
The standard D shaped H-mode operation showed excellent plasma confinement ut has important issues of transient and steady state heat flux. To solbe this issues, we proposed new scenario using plasma shaping as one of possible scenario of future tokamak reactor.
Ichikawa, Yasuaki*; Kimoto, Kazushi*; Sato, Toshinori; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Kuwabara, Kazumichi
JAEA-Research 2014-027, 25 Pages, 2015/02
The rock and the rock mass are known to show time-dependent behavior such as creep and the stress-relaxation. It is to evaluate long-term rock mechanics stability that the important theme understanding the property. From the research study until now, it is rock mechanics and chemical coupled phenomenon to have an influence on the long-term behavior. It is a theme to develop technique to model this coupled phenomenon, and to analyze. About an evaluation of the microcrack to have an influence on this coupled phenomenon, it is the theme that we should work on in a long-term rock mass behavior study chiefly. This study developed numerical analysis to check the ultrasonic scattering decrement behavior by the microcrack of the crystalline rock and the measurement technique. The FDTD method which modelled a crack was used for numerical analysis by split node. It depends on the simulation technique that it developed that useful knowledge was provided by elastic wave modeling. On the other hand, the ultrasonic measurement in a rock sample was measured by the water immersion method. As a result, we understood that we could acquire useful information to evaluate the scattering decrement of an elastic wave in a rock sample.
Takayama, Yusuke*; Ikuta, Yuki*; Iizuka, Atsushi*; Kawai, Katsuyuki*; Taki, Tomihiro; Sakao, Ryota; Ichikawa, Yasuaki*
Unsaturated Soils; Research & Applications, p.659 - 665, 2014/06
In this paper, a multiple unsaturated soil barrier consisting of gravel, sand and bentonite-mixed soil layers is considered as a hardly permeable covering to prevent rainwater from infiltrating into waste deposits. Not only the quite low permeability of bentonite-mixed soil layer but also a function of capillary barrier between granular layers having different water-retention capabilities is expected to prevent water infiltration. A series of numerical simulation is carried out to evaluate performance of the multiple soil barrier using saturated/unsaturated soil/water coupled FE computation technique. The multiple unsaturated soil barrier system considered here is 10m long and 1.5 m thick consisting of sandy soil surface, sand filter, gravel layer, sand filter and bentonite-mixed clayey layer. And the soil barrier system is assumed to be placed as a covering with a 5% inclination on the waste deposit. The performance of the multiple soil barrier system is shown as a management chart to maintain impermeable ability associated with possible rainfall intensity. Particularly, in this paper, actual rainfall record in Okayama area is employed to determine the rainfall intensity which is imposed as a boundary condition in the computation. According to the simulation results, it is found that the capillary barrier is a key issue in evaluating the long term performance of the barrier system. And, it is confirmed that the barrier system considered in this paper can work well against the maximum intensity of the rainfall in the past record.
Ichikawa, Yasuaki*; Kimoto, Kazushi*; Sato, Toshinori; Tanno, Takeo; Hikima, Ryoichi; Sanada, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Research 2013-045, 69 Pages, 2014/03
Rock mass is a complex material including several classes of discontinuities and inhomogeneous/anisotropic minerals. If observing rock samples, we know that crystalline rock is a complex of minerals, grain boundaries and microcracks. In this study, the series of experiments were managed by a flow-through type changing temperature, pH and applied stress. Attenuation of ultrasonic waves in rock is investigated experimentally using an intact but coarse-grained granite core sample. For ultrasonic measurements, piezoelectric transducers are used in a through-transmission mode. With the estimated response function, phase and amplitude spectra of the transmitted ultrasonic waves are investigated quantitatively to evaluate the attenuation and change in travel time.
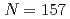 nucleus
nucleus  No
NoAsai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sakama, Minoru*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Ishii, Yasuo; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Ishii, Tetsuro; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
Physical Review C, 87(1), p.014332_1 - 014332_6, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:43.56(Physics, Nuclear)The spin-parity and neutron configuration of the ground state of  No have been identified through
No have been identified through  -decay spectroscopy. The
-decay spectroscopy. The  No is the nucleus with the largest neutron number whose spin-parities and single-particle configurations have ever been identified. The neutron 9/2
No is the nucleus with the largest neutron number whose spin-parities and single-particle configurations have ever been identified. The neutron 9/2 [615] configuration was assigned to the ground state of
[615] configuration was assigned to the ground state of  No as well as to the 231.4 keV level in
No as well as to the 231.4 keV level in  Fm. This allowed us to establish energy spacings and order of the neutron single-particle orbitals in such heaviest nuclear region. The appearance of the 9/2
Fm. This allowed us to establish energy spacings and order of the neutron single-particle orbitals in such heaviest nuclear region. The appearance of the 9/2 [615] ground state at
[615] ground state at  =157 implies that the order of the neutron orbitals between the
=157 implies that the order of the neutron orbitals between the  =152 and 162 deformed shell gaps should change considerably with increasing neutron number.
=152 and 162 deformed shell gaps should change considerably with increasing neutron number.
Zhang, Z.*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; Namimoto, Takura*; Fujioka, Shinsuke*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; Hosoda, Hirokazu*; Orimo, Satoshi; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 83(5), p.053502_1 - 053502_5, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:62.15(Instruments & Instrumentation)X-ray line spectra ranging from 17 to 77 keV were quantitatively measured with a Laue spectrometer, composed of a cylindrically curved crystal and a detector. Either a visible CCD detector coupled with a CsI phosphor screen or an imaging plate can be chosen, depending on the signal intensities and exposure times. The absolute sensitivity of the spectrometer system was calibrated using pre-characterized laser-produced X-ray sources and radioisotopes. The integrated reflectivity for the crystal is in good agreement with predictions by an open code for X-ray diffraction. The energy transfer efficiency from incident laser beams to hot electrons, as the energy transfer agency for specific X-ray line emissions, is derived as a consequence of this work.
Ichikawa, Yasuaki*; Tanno, Takeo; Hikima, Ryoichi; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Hiroya; Sato, Toshinori
JAEA-Research 2012-003, 34 Pages, 2012/04
A rock mass is a complex entity, including several classes of discontinuities and numerous heterogeneous and anisotropic minerals. From investigations of rock samples, we know that crystalline rock is a complex mix of minerals, grain boundaries and microcracks. Deformation and failure mechanisms may be more completely understood if we are able to correctly characterize the microscale composition and grain boundary properties. Amongst the rock-forming minerals, especially quartz and biotite in granite, numerous microcracks are developed. It is important to study coupled mechanical and chemical factors in crystalline rock for long-term behavior study. This report presents the results of the following FY2010 activities. (1) Explanation of nonlinear fracture mechanics, (2) Pressure dissolution experiments of using specimens of single quartz, (3) Theory study on the rate of quartz dissolution, (4) Homogenization theory for fractured rock
Ichikawa, Yasuaki*; Choi, J. H.*; Tanno, Takeo; Hirano, Toru*; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2011-007, 91 Pages, 2011/06
We first surveyed the classical theories of fracture mechanics, and discussed the subcritical crack growth (SCG), which is observed under less load than the fracture toughness Kc. This SCG is a result of coupled mechanical and chemical effect. The SCG for granite was treated on this basis. We performed pressure dissolution experiments using specimens of single crystal quartz, since the dissolution reaction is engaged with a deformation and failure process of polycrystalline rock. The series of experiments were managed by a flow-through type changing temperature, pH and applied stress. Si concentrations we here measured. We first surveyed the theories of pressure solution. Then we proposed a theory of saluting velocity of quart which accounts for the effects of temperature, chemical (pH), solid pressure and pore pressure.
Zhang, Z.*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; Ogura, Koichi; Yogo, Akifumi; Okano, Yasuaki*; et al.
Optics Express (Internet), 19(5), p.4560 - 4565, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:66.68(Optics)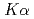 line emission from Mo and Ag plate were experimentally studied by using ultra-high intensity, clean femtosecond laser pulses. Absolutely yield of
line emission from Mo and Ag plate were experimentally studied by using ultra-high intensity, clean femtosecond laser pulses. Absolutely yield of 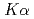 X-rays at 17 keV from Mo and 22 keV from Ag were measured as a function of the laser pulse contrast ratio and irradiation intensity. Significant enhancement of
X-rays at 17 keV from Mo and 22 keV from Ag were measured as a function of the laser pulse contrast ratio and irradiation intensity. Significant enhancement of 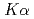 yields were obtained for both Mo and Ag with higher contrast ratios and high irradiance. The conversion efficiencies of 4.28
yields were obtained for both Mo and Ag with higher contrast ratios and high irradiance. The conversion efficiencies of 4.28  10
10 /sr for Mo and 4.84
/sr for Mo and 4.84  10
10 /sr for Ag, the highest values ever obtained, have been demonstarted with the contrast ratio of 10
/sr for Ag, the highest values ever obtained, have been demonstarted with the contrast ratio of 10 to 10
to 10 .
.