Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Maeda, Toshikatsu; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Bamba, Tsunetaka
International Journal of Corrosion, 2011(1), p.796457_1 - 796457_6, 2011/09
Static leach tests were conducted for simulated HLW glass in MgCl solution for up to 92 days to investigate the dissolution mechanism of HLW glass under coastal repository condition. Under the condition that magnesium ion exists in leachate, the dissolution rate of the glass did not decrease with time during leaching, while the rate decreased when the magnesium ion depleted in the leachate. In addition, precipitated layer consist of magnesium/silica was observed at the surface of the glass after the leach tests. The present results imply that dissolution of the glass is accompanied with formation of magnesium silicate consuming silica; a glass network former. As a consequence, the glass dissolved with an initial high dissolution rate.
solution for up to 92 days to investigate the dissolution mechanism of HLW glass under coastal repository condition. Under the condition that magnesium ion exists in leachate, the dissolution rate of the glass did not decrease with time during leaching, while the rate decreased when the magnesium ion depleted in the leachate. In addition, precipitated layer consist of magnesium/silica was observed at the surface of the glass after the leach tests. The present results imply that dissolution of the glass is accompanied with formation of magnesium silicate consuming silica; a glass network former. As a consequence, the glass dissolved with an initial high dissolution rate.
Maeda, Toshikatsu; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Bamba, Tsunetaka; Usui, Hideo
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 9(3), p.233 - 242, 2010/09
An experimental approach was proposed to understand the mechanism and model for slow dissolution of high-level radioactive waste glass under disposal conditions where silica is nearly saturated in contacting pore water. Based on an extended literature survey covering recent experimental results on glass dissolution, we have reached a hypothesis that the slow dissolution is limited by diffusion of oxonium ions in an altered layer formed on the glass surface. We suggested several experimental methods such as an elaborate and systematic diffusion experiment using thin glass membranes of tens-of-micrometer thickness to validate the hypothesis. Also pointed out was that dissolution model applicable to glass waste form performance evaluation takes into account the surface area evolution and stability of altered region of the waste form.
Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Makigaki, Hikaru*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Bamba, Tsunetaka; Noshita, Kenji*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1193, p.219 - 228, 2009/05
We developed a new flow-through test method using micro-reactor, and applied it to measurement of the dissolution/alteration kinetics for a simulated HLW glass (P0798). In this method, a glass coupon is placed just on a Teflon plate having a micro-channel, and a solution is injected into the inlet of micro-channel by micro-syringe pump at a constant flow rate. The injected solution flows through the micro-channel reacting with the glass to the outlet, and the outlet solution is retrieved at certain intervals to be analyzed for determination of the dissolution/alteration rate. This method has some major features, i.e., simple test apparatus with compact size, high S/V ratio, sensitive/precise measurement of the glass dissolution/alteration rate, adequate glass shape for analysis of reacted glass surface, and so on. By use of this method the dissolution/alteration rate for P0798 was measured as a function of pH, temperature, flow rate, and time, and some available results were obtained to evaluate the dissolution/alteration kinetics.
Makigaki, Hikaru*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Bamba, Tsunetaka; Noshita, Kenji*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1193, p.307 - 314, 2009/05
By using micro-reactor flow-through test method we measured the initial dissolution rate of P0798 glass at 25 C as a function of pH between 5.6 and 12. The results showed that the initial dissolution rate determined by dissolution rate of Si has "V-shaped" pH dependency similar to R7T7 glass reported by CEA, France. We also measured the initial dissolution rate at pH 5.6 as a function of temperature between 25 and 90
C as a function of pH between 5.6 and 12. The results showed that the initial dissolution rate determined by dissolution rate of Si has "V-shaped" pH dependency similar to R7T7 glass reported by CEA, France. We also measured the initial dissolution rate at pH 5.6 as a function of temperature between 25 and 90 C, and the activation energy was evaluated to be 51 kJ/mol, which value is slightly smaller than that of R7T7 glass at pH 9 reported by CEA. On the basis of these results and comparison, we discussed the dissolution kinetics of P0798 glass.
C, and the activation energy was evaluated to be 51 kJ/mol, which value is slightly smaller than that of R7T7 glass at pH 9 reported by CEA. On the basis of these results and comparison, we discussed the dissolution kinetics of P0798 glass.
Otsuka, Yoshiki*; Bamba, Tsunetaka
JAEA-Research 2007-059, 18 Pages, 2007/09
Alkaline degradation tests for 9 organic materials were conducted under the conditions of TRU waste disposal: anaerobic alkaline conditions. The tests were carried out at 90  C for 91 days. The sample materials for the tests were selected from the standpoint of constituent organic materials of TRU wastes. It has been found that cellulose and plastic solidified products are degraded relatively easily and that rubbers are difficult to degrade. It could be presumed that the alkaline degradation of organic materials occurs starting from the functional group in the material. Therefore, the degree of degradation difficulty is expected to be dependent on the kinds of functional group contained in the organic material.
C for 91 days. The sample materials for the tests were selected from the standpoint of constituent organic materials of TRU wastes. It has been found that cellulose and plastic solidified products are degraded relatively easily and that rubbers are difficult to degrade. It could be presumed that the alkaline degradation of organic materials occurs starting from the functional group in the material. Therefore, the degree of degradation difficulty is expected to be dependent on the kinds of functional group contained in the organic material.
Bamba, Tsunetaka
JAEA-Review 2007-003, 46 Pages, 2007/03
In the case of the direct disposal of spent nuclear fuel in a deep geological formation, the release of radionuclides from the spent fuel matrix will be controlled by the rate at which uranium is released into the environment. In this paper the mechanism and kinetics of nuclear fuel corrosion under waste disposal conditions are reviewed, and the many published observations on fuel corrosion are discussed. The influence of a wide range of parameters on fuel corrosion are discussed: These include the pre-oxidation of the fuel, pH, O concentration, carbonate concentration, temperature, groundwater species, the effect of water radiolysis, and the formation of corrosion product deposits. The relevance of the data recorded on unirradiated UO
concentration, carbonate concentration, temperature, groundwater species, the effect of water radiolysis, and the formation of corrosion product deposits. The relevance of the data recorded on unirradiated UO to the interpretation of spent fuel behavior is included.
to the interpretation of spent fuel behavior is included.
Tanaka, Tadao; Mukai, Masayuki; Bamba, Tsunetaka
Proceedings of International Symposium on Environmental Modeling and Radioecology, p.275 - 278, 2007/03
Migration behavior of Ce, one of redox-sensitive elements, was studied in natural aquifer loess zone in P.R.China. Migration parameters such as distribution coefficient were obtained by column migration and batch sorption tests. The batch sorption test indicates Ce is irreversibly incorporated near loess surface as Ce(IV). Cerium showed large retardation in migration in the aquifer loess zone. Predicted migratory mobility of Ce in the aquifer, which was calculated by using the distribution coefficient determined by the batch and column tests, could reproduce that in the field test conservatively.
Maeda, Toshikatsu; Bamba, Tsunetaka*; Mizuno, Tsuyoshi*; Terakado, Shogo; Kitagawa, Isamu; Numata, Masami
Haikibutsu Gakkai Rombunshi, 17(4), p.271 - 281, 2006/07
no abstracts in English
Ozawa, Tatsuya; Maeda, Toshikatsu; Mizuno, Tsuyoshi; Bamba, Tsunetaka; Nakayama, Shinichi; Hotta, Katsutoshi*
JAEA-Technology 2006-001, 11 Pages, 2006/02
Melting treatment is a candidate solidification technique for nonflammable low-level radioactive wastes including metals, incineration ashes, and glasses. Simulated incineration ashes of a wide range of chemical compositions were molten at 1,600 C to produce lab-scale slag form. No visible pores and separated phases were observed in the slag specimens. It was found by optical observation that some precipitates and small voids were uniformly distributed in many of the specimens. The precipitates were identified to be iron oxides by XRD analysis. The present tests indicate that melting treatment is technically capable to produce stable slag from incineration ashes, which is one of representative TRU-cotaminated radioactive wastes.
C to produce lab-scale slag form. No visible pores and separated phases were observed in the slag specimens. It was found by optical observation that some precipitates and small voids were uniformly distributed in many of the specimens. The precipitates were identified to be iron oxides by XRD analysis. The present tests indicate that melting treatment is technically capable to produce stable slag from incineration ashes, which is one of representative TRU-cotaminated radioactive wastes.
Maeda, Toshikatsu; Bamba, Tsunetaka*; Hotta, Katsutoshi*; Mizuno, Tsuyoshi*; Ozawa, Tatsuya
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 4(4), p.242 - 247, 2005/12
no abstracts in English
Mizuno, Tsuyoshi*; Maeda, Toshikatsu; Bamba, Tsunetaka*
JAERI-Conf 2005-007, p.225 - 229, 2005/08
no abstracts in English
Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Mitsui, Seiichiro*; Makino, Hitoshi*; Ishiguro, Katsuhiko*; Kamei, Gento*; Kawamura, Kazuhiro*; Maeda, Toshikatsu; Ueno, Kenichi*; Bamba, Tsunetaka*; Yui, Mikazu*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu, 10(1-2), p.69 - 84, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
Maeda, Toshikatsu; Bamba, Tsunetaka*; Mizuno, Tsuyoshi*
Haikibutsu Gakkai Rombunshi, 15(1), p.45 - 51, 2004/01
no abstracts in English
Maeda, Toshikatsu; Tanaka, Tadao; Mukai, Masayuki; Ogawa, Hiromichi; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Munakata, Masahiro; Matsumoto, Junko; Kozai, Naofumi; Bamba, Tsunetaka; Fan, Z.*; et al.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 2(3), p.336 - 341, 2003/09
no abstracts in English
Ogawa, Hiromichi; Tanaka, Tadao; Mukai, Masayuki; Maeda, Toshikatsu; Munakata, Masahiro; Matsumoto, Junko; Bamba, Tsunetaka; Li, S.*; Wang, Z.*; Li, Z.*; et al.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 2(3), p.332 - 335, 2003/09
The filed migration test using TRU nuclide was carried out as a cooperative research project between JAERI and CIRP (China Institute for Radiation Protection). This report introduced the outline of the filed migration test and described the outline of the special number of Field Test on Migration of TRU-nuclide and main results as a summary report.
Tanaka, Tadao; Mukai, Masayuki; Maeda, Toshikatsu; Matsumoto, Junko; Ogawa, Hiromichi; Munakata, Masahiro; Kimura, Hideo; Bamba, Tsunetaka; Fujine, Sachio
Genshiryoku eye, 49(2), p.76 - 79, 2003/02
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Tadao; Mukai, Masayuki; Maeda, Toshikatsu; Munakata, Masahiro; Matsumoto, Junko; Ogawa, Hiromichi; Bamba, Tsunetaka*; Wang, Z.*; Yang, Y.*; Zhao, Y.*
Proceedings of International Symposium on Radioecology and Environmental Dosimetry, p.179 - 184, 2003/00
Migration behaviors of stable strontium element and radioactive nuclide strontium 90 in natural aquifer were studied by a field test, which was performed in the aquifer loess zone at 30 m under the ground surface of the field test site of China Institute for Radiation Protection. The migration behavior of stable strontium was a little different from that of  Sr. The difference was evaluated by applying the distribution coefficient considering Sr and coexistent ion concentrations. Migration behavior of radionuclide in natural environment has been generally demonstrated on field tests without radioactive tracers and/or large-scale column tests with radioactive tracers. Such tests seem to be valuable to improve reliability of the migratory evaluation.
Sr. The difference was evaluated by applying the distribution coefficient considering Sr and coexistent ion concentrations. Migration behavior of radionuclide in natural environment has been generally demonstrated on field tests without radioactive tracers and/or large-scale column tests with radioactive tracers. Such tests seem to be valuable to improve reliability of the migratory evaluation.
Bamba, Tsunetaka
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu, 8(2), p.205 - 206, 2002/03
no abstracts in English
 and Na
and Na O additives on properties synthetic rock of fly ash from municipal waste incinerator
O additives on properties synthetic rock of fly ash from municipal waste incineratorMitamura, Hisayoshi; Bamba, Tsunetaka; Maeda, Toshikatsu
Nihon Seramikkusu Kyokai Gakujutsu Rombunshi, 110(1277), p.55 - 59, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:19.02(Materials Science, Ceramics)Influence of additives and hot-pressing temperature on properties of the synthetic rock was investigated, which was developed for making harmless and stabilizing fly ash from municipal waste incinerator. Sintering test at 1200 C for 16 h revealed that addition of 20 and 1.5 wt% of TiO
C for 16 h revealed that addition of 20 and 1.5 wt% of TiO and Na
and Na O, respectively, is necessary for preparation of dense products. X-ray diffractometry showed that these additives promoted the formation of perovskite (CaTiO
O, respectively, is necessary for preparation of dense products. X-ray diffractometry showed that these additives promoted the formation of perovskite (CaTiO ) and gehlenite (Ca
) and gehlenite (Ca Al
Al SiO
SiO ) minerals. During hot pressing, bulk density of the synthetic rock increased steeply with temperature between 1000 and 1100
) minerals. During hot pressing, bulk density of the synthetic rock increased steeply with temperature between 1000 and 1100 C. On the other hand, its open porosity decreased rapidly with temperature between 1050 and 1150
C. On the other hand, its open porosity decreased rapidly with temperature between 1050 and 1150 C. These facts imply that the temperature of 1100
C. These facts imply that the temperature of 1100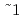 150
150 C is practical in hot pressing of fly ash.
C is practical in hot pressing of fly ash.
Kozai, Naofumi; Adachi, Yoshifusa*; Kawamura, Sachi*; Inada, Koichi*; Kozaki, Tamotsu*; Sato, Seichi*; Ohashi, Hiroshi*; Onuki, Toshihiko; Bamba, Tsunetaka
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 38(12), p.1141 - 1143, 2001/12
This study briefly reports characteristics of Fe-montmorillonite. Fe-montmorillonite was used as a simulant of buffer material in which corrosion products of carbon steel overpack, Fe , were diffused. We have found that this clay retains Se(VI) for which natural montmorillonite, such as Na+-type and Ca
, were diffused. We have found that this clay retains Se(VI) for which natural montmorillonite, such as Na+-type and Ca -type, has little retentivity.
-type, has little retentivity.