Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsuoka, Hideki*; Barnes, S. E.*; Ieda, Junichi; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Bahramy, M. S.*; Saika, B. K.*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Wadachi, Hiroki*; Wang, Y.*; Yoshida, Satoshi*; et al.
Nano Letters, 21(4), p.1807 - 1814, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:75.94(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Ieda, Junichi; Barnes, S. E.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(5), p.053703_1 - 053703_4, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.71(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Barnes, S. E.*; Ieda, Junichi; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Scientific Reports (Internet), 4, p.4105_1 - 4105_5, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:173 Percentile:97.23(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The control of the magnetism of ultra-thin ferromagnetic layers using an electric field rather than a current, if large enough, would lead to many technologically important applications. To date, while it is usually assumed the changes in the magnetic anisotropy, leading to such a control, arises from surface charge doping of the magnetic layer, a number of key experiments cannot be understood within such a scenario. Much studied is the fact that, for non-magnetic metals or semi-conductors, a large surface electric field gives rise to a Rashba spin-orbit coupling which leads to a spin-splitting of the conduction electrons. For a magnet, this splitting is modified by the exchange field resulting in a large magnetic anisotropy energy via the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya mechanism. This different, yet traditional, path to an electrically induced anisotropy energy can explain the electric field, thickness, and material dependence reported in many experiments.
Tanabe, Kenji*; Chiba, Daichi*; Oe, Junichiro*; Kasai, Shinya*; Kono, Hideo*; Barnes, S. E.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Kobayashi, Kensuke*; Ono, Teruo*
Nature Communications (Internet), 3, p.845_1 - 845_5, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:82.44(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Yamane, Yuta; Sasage, Kohei*; An, Toshu*; Harii, Kazuya*; Oe, Junichiro*; Ieda, Junichi; Barnes, S. E.*; Saito, Eiji; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Physical Review Letters, 107(23), p.236602_1 - 236602_4, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:85.30(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Yamane, Yuta; Ieda, Junichi; Oe, Junichiro*; Barnes, S. E.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Applied Physics Express, 4(9), p.093003_1 - 093003_3, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:39.60(Physics, Applied) collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 84(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_18, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:75.18(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report on the event structure and double helicity asymmetry ( ) of jet production in longitudinally polarized
) of jet production in longitudinally polarized  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured
= 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured  = -0.0014
= -0.0014  0.0037 at the lowest
0.0037 at the lowest  bin and -0.0181
bin and -0.0181  0.0282 at the highest
0.0282 at the highest  bin. The measured
bin. The measured  is compared with the predictions that assume various
is compared with the predictions that assume various 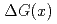 distributions.
distributions.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:193 Percentile:99.41(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
Yamane, Yuta; Ieda, Junichi; Oe, Junichiro*; Barnes, S. E.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Journal of Applied Physics, 109(7), p.07C735_1 - 07C735_3, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:62.69(Physics, Applied) and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.53(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
 +
+  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron production
= 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron productionAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 83(5), p.052004_1 - 052004_26, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:181 Percentile:98.32(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment at RHIC has measured the invariant differential cross section for production of 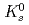 ,
,  ,
,  and
and  mesons in
mesons in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,
= 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,  and
and  , determining the high
, determining the high  and characterizing the low
and characterizing the low  regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
Barnes, S. E.*; Aprili, M.*; Petkovi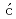 , I.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi
, I.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Superconductor Science and Technology, 24(2), p.024020_1 - 024020_6, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:45.23(Physics, Applied)Konishi, Satoshi; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Enoeda, Mikio; Hayashi, Takumi; Ohira, Shigeru; Yamada, Masayuki; Suzuki, Takumi; Okuno, Kenji; Sherman, R. H.*; Willms, R. S.*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 28, p.258 - 264, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:42.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Takumi; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Konishi, Satoshi; Inoue, Masahiko*; Hirata, Kazuhiro*; Okuno, Kenji; Naruse, Yuji; Anderson, J. L.*; Sherman, R. H.*; Willms, R. S.*; et al.
JAERI-M 93-083, 54 Pages, 1993/03
no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Takumi; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Konishi, Satoshi; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Inoue, Masahiko*; Hirata, Kazuhiro*; Okuno, Kenji; Naruse, Yuji; Anderson, J. L.*; Barnes, J. W.*; et al.
JAERI-M 93-081, 35 Pages, 1993/03
no abstracts in English
Ieda, Junichi; Barnes, S. E.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi
no journal, ,
Ieda, Junichi; Barnes, S. E.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi
no journal, ,
The control of the magnetic anisotropy (MA) of ultra-thin ferromagnetic layers using an electric field would lead to many technologically important applications. To date, while it is usually assumed the changes in the MA arises from surface charge doping of the magnetic layer, a number of key experiments cannot be understood within such a scenario. Much studied is the fact that, for non-magnetic conductors, a large surface electric field gives rise to a Rashba spin-orbit (RSO) coupling which leads to a spin-splitting of the conduction electrons. We develop a theory for the MA based on the RSO interaction and the Stoner model. The competition between the RSO fields and the exchange interaction leads to a large MA arising from the internal electric fields which exist at, e.g., ferromagnetic/metal and ferromagnetic/insulator interfaces. This different path to an electrically induced MA energy can explain the electric field, thickness, and material dependence reported in many experiments.
Ieda, Junichi; Barnes, S. E.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi
no journal, ,
Spin-orbit interaction leads to two competitive interactions, i.e., anisotropic exchange and anti-symmetric exchange interactions. Similarly, surface Rashba spin-orbit interaction gives rise to two effects in ferromagnets: one is prefer to the in-plane magnetic anisotropy while the other yields to the perpendicular magnetic anisotropy, and whether which is dominant depends on the electronic structure of ferromagnets. For the ultra-thin ferromagnetic layers, in particular, the surface Rashba spin-orbit interaction can be controlled by external electric fields and thus it is interesting to investigate electric field dependence of such a magnetic anisotropy. We present this new mechanism of perpendicular magnetic anisotropy.
Yamane, Yuta; Sasage, Kohei*; An, Toshu*; Harii, Kazuya*; Oe, Junichiro*; Ieda, Junichi; Barnes, S. E.*; Saito, Eiji; Maekawa, Sadamichi
no journal, ,
Yamane, Yuta; Sasage, Kohei*; An, Toshu*; Harii, Kazuya*; Oe, Junichiro*; Ieda, Junichi; Barnes, S. E.*; Saito, Eiji; Maekawa, Sadamichi
no journal, ,