Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

Liao, J.*; Huang, Z.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Zhang, B.*; Cheng, S.*; Xu, H.*; 梶本 亮一; 蒲沢 和也*; Bao, S.*; Wen, J.*
Physical Review B, 109(22), p.224411_1 - 224411_10, 2024/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Antiferromagnetic van der Waals family  P
P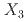 (
( = Fe, Mn, Co, and Ni;
= Fe, Mn, Co, and Ni; 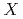 = S and Se) have attracted significant research attention due to the possibility of realizing long-range magnetic order down to the monolayer limit. Here, we perform inelastic neutron scattering measurements on single-crystal samples of MnPSe
= S and Se) have attracted significant research attention due to the possibility of realizing long-range magnetic order down to the monolayer limit. Here, we perform inelastic neutron scattering measurements on single-crystal samples of MnPSe , a member of the
, a member of the  P
P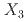 family, to study the spin dynamics and determine the effective spin model. The excited magnon bands are well characterized by a spin model, which includes a Heisenberg term with three intraplane exchange parameters (
family, to study the spin dynamics and determine the effective spin model. The excited magnon bands are well characterized by a spin model, which includes a Heisenberg term with three intraplane exchange parameters (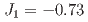 meV,
meV, 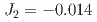 meV,
meV, 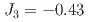 meV) and one interplane parameter (
meV) and one interplane parameter (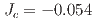 meV), and an easy-plane single-ion anisotropy term (
meV), and an easy-plane single-ion anisotropy term (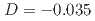 meV). Additionally, we observe the intersection of the magnon and phonon bands but no anomalous spectral features induced by the formation of magnon-phonon hybrid excitations at the intersecting region. We discuss possible reasons for the absence of such hybrid excitations in MnPSe
meV). Additionally, we observe the intersection of the magnon and phonon bands but no anomalous spectral features induced by the formation of magnon-phonon hybrid excitations at the intersecting region. We discuss possible reasons for the absence of such hybrid excitations in MnPSe .
.
Esser, S. P.*; Rahlff, J.*; Zhao, W.*; Predl, M.*; Plewka, J.*; Sures, K.*; Wimmer, F.*; Lee, J.*; Adam, P. S.*; McGonigle, J.*; et al.
Nature Microbiology (Internet), 8(9), p.1619 - 1633, 2023/09
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:74.53(Microbiology)CRISPR-Cas systems defend prokaryotic cells from viruses, plasmids, and other mobile genetic elements. Capitalizing on multi-omics approaches, we show here that the CRISPR-Cas systems of uncultivated archaea also play an integral role in mitigating potentially detrimental interactions with episymbionts. A comprehensive analysis of CRISPR-Cas-based infection histories revealed that uncultivated deep-subsurface archaeal primary-producers defend themselves from archaeal episymbionts of the DPANN superphylum of archaea, some of which are known to fuse their membranes with their host. We show that host cells counter these attacks by deploying one of two CRISPR-Cas systems (type I-B and type III-A) to target and disrupt essential genes in the episymbiont. However, genome-scale modeling of metabolic interactions between two deep subsurface host-symbiont systems revealed that host cells also benefit from the symbionts via metabolic complementation. We speculate that populations of these uncultivated archaeal episymbionts are currently transitioning from a parasitic lifestyle to one of mutualism, as must have occurred in countless mutualistic systems known today. By expanding our analysis to thousands of archaeal genomes, we conclude that CRISPR-Cas mediated resistance to archaeal episymbiosis evolved independently in various archaeal lineages and may be a wide-spread evolutionary phenomenon.
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Xi, N.*; Gao, Y.-P.*; Ma, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Qi, Z.*; Zhang, S.*; Huang, Z.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(12), p.1883 - 1889, 2023/09
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:93.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The magnetization of a quantum magnet can be pinned at a fraction of its saturated value by collective effects. One example of such a plateau phase is found in spin-1/2 triangular-lattice antiferromagnets. They feature strong geometrical frustration and the plateau phase therein is often interpreted as arising from an order-by-disorder mechanism driven by quantum fluctuations. Here we observe a one-third magnetization plateau under an applied magnetic field in the spin-1 antiferromagnet Na Ni
Ni BiO
BiO with a honeycomb lattice, which, with conventional magnetic interactions, would not be geometrically frustrated. Based on our elastic neutron scattering measurements, we propose the spin structure of the plateau phase to be an unusual partial spin-flop ferrimagnetic order. Our theoretical calculations indicate that bond-anisotropic Kitaev interactions are the source of frustration that produces the plateau. These results suggest that Kitaev interactions provide a different route to frustration and phases driven by quantum fluctuations in high-spin magnets.
with a honeycomb lattice, which, with conventional magnetic interactions, would not be geometrically frustrated. Based on our elastic neutron scattering measurements, we propose the spin structure of the plateau phase to be an unusual partial spin-flop ferrimagnetic order. Our theoretical calculations indicate that bond-anisotropic Kitaev interactions are the source of frustration that produces the plateau. These results suggest that Kitaev interactions provide a different route to frustration and phases driven by quantum fluctuations in high-spin magnets.
田上 浩孝; Cheng, S.*; 飛田 吉春; 守田 幸路*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 328, p.95 - 106, 2018/03
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:70.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)In analyzing the safety of core disruptive accidents in Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors (SFRs), it is important to evaluate whether the decay heat of debris bed can be removed. The decay heat removability changes depending on the shape of debris bed, which would be deformed by coolant vapor with time. In the present paper, a new model was developed to analyze debris bed behavior with SIMMER, which is a safety analysis code for SFRs. In the new model, the effects of inter-particle collisions and contacts are modeled as inter-particle interaction. Test simulation results show the roles of physical properties in the new model on the dense particle behavior. Assessment results of proposed model based on model experiments indicate that the new model is capable of describing the transient of the shape of the particle bed in the liquid driven by the gas phase. Considering the fact that the process of leveling behavior in model experiments is common for the debris bed in SFRs, the new model can be employed as an analysis tool for debris bed behavior.
Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Talou, P.*; Plompen, A. J.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 148, p.189 - 213, 2018/02
被引用回数:78 パーセンタイル:98.03(Physics, Nuclear)CIELO国際協力では、原子力施設の臨界性に大きな影響を与える重要核種( U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Fe,
Fe,  O,
O,  H)の中性子断面積データの精度を改善し、これまで矛盾していると考えられた点を解消することを目的として研究が行われた。多くの研究機関が参加したこのパイロットプロジェクトは、IAEAの支援も受けて、OECD/NEAの評価国際協力ワーキングパーティ(WPEC)のSubgroup 40として組織された。本CIELOプロジェクトは、新たな実験研究や理論研究を行う動機付けとなり、測定データを正確に反映し臨界性の積分テストに優れた新たな一連の評価済みライブラリとして結実した。本報告書は、これまでの研究成果と、本国際協力の次の段階の計画概要をまとめたものである。
H)の中性子断面積データの精度を改善し、これまで矛盾していると考えられた点を解消することを目的として研究が行われた。多くの研究機関が参加したこのパイロットプロジェクトは、IAEAの支援も受けて、OECD/NEAの評価国際協力ワーキングパーティ(WPEC)のSubgroup 40として組織された。本CIELOプロジェクトは、新たな実験研究や理論研究を行う動機付けとなり、測定データを正確に反映し臨界性の積分テストに優れた新たな一連の評価済みライブラリとして結実した。本報告書は、これまでの研究成果と、本国際協力の次の段階の計画概要をまとめたものである。
 by tuning nematicity and magnetism in FeSe
by tuning nematicity and magnetism in FeSe S
S superconductors
superconductors松浦 康平*; 水上 雄太*; 新井 佑基*; 杉村 優一*; 前島 尚行*; 町田 晃彦*; 綿貫 徹*; 福田 竜生; 矢島 健*; 廣井 善二*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 8, p.1143_1 - 1143_6, 2017/10
被引用回数:97 パーセンタイル:91.95(Multidisciplinary Sciences)A fundamental issue concerning iron-based superconductivity is the roles of electronic nematicity and magnetism in realising high transition temperature ( ). To address this issue, FeSe is a key material, as it exhibits a unique pressure phase diagram involving nonmagnetic nematic and pressure-induced antiferromagnetic ordered phases. However, as these two phases in FeSe have considerable overlap, how each order affects superconductivity remains perplexing. Here we construct the three-dimensional electronic phase diagram, temperature (
). To address this issue, FeSe is a key material, as it exhibits a unique pressure phase diagram involving nonmagnetic nematic and pressure-induced antiferromagnetic ordered phases. However, as these two phases in FeSe have considerable overlap, how each order affects superconductivity remains perplexing. Here we construct the three-dimensional electronic phase diagram, temperature ( ) against pressure (
) against pressure ( ) and iso-valent S-substitution (
) and iso-valent S-substitution ( ), for FeSe
), for FeSe S
S . By simultaneously tuning chemical and physical pressures, against which the chalcogen height shows a contrasting variation, we achieve a complete separation of nematic and antiferromagnetic phases. In between, an extended nonmagnetic tetragonal phase emerges, where
. By simultaneously tuning chemical and physical pressures, against which the chalcogen height shows a contrasting variation, we achieve a complete separation of nematic and antiferromagnetic phases. In between, an extended nonmagnetic tetragonal phase emerges, where  shows a striking enhancement. The completed phase diagram uncovers that high-
shows a striking enhancement. The completed phase diagram uncovers that high- superconductivity lies near both ends of the dome-shaped antiferromagnetic phase, whereas
superconductivity lies near both ends of the dome-shaped antiferromagnetic phase, whereas  remainslow near the nematic critical point.
remainslow near the nematic critical point.
Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Pigni, M.*; Dunn, M.*; Leal, L.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.02001_1 - 02001_9, 2017/09
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:96.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)CIELO共同研究では中性子断面積データの改善及びこれまでの評価で見られた断面積の不一致を解決することを目的として、原子力の臨界性に大きな影響を与える5核種( O,
O,  Fe,
Fe, 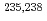 U,
U,  Pu)の中性子断面積を評価している。この国際パイロットプロジェクトでは、経済協力開発機構・原子力機関・核データ評価国際協力ワーキングパーティに設置されたサブグループ40の下でIAEAからのサポートを受けて、実験並びに理論的な研究を活発に実施している。これらの研究を通じて測定データを精度よく反映し、さらに臨界性に関する積分テストで良い結果を示す新しい評価済ライブラリを開発している。
Pu)の中性子断面積を評価している。この国際パイロットプロジェクトでは、経済協力開発機構・原子力機関・核データ評価国際協力ワーキングパーティに設置されたサブグループ40の下でIAEAからのサポートを受けて、実験並びに理論的な研究を活発に実施している。これらの研究を通じて測定データを精度よく反映し、さらに臨界性に関する積分テストで良い結果を示す新しい評価済ライブラリを開発している。
Cheng, S.; 松場 賢一; 磯崎 三喜男; 神山 健司; 鈴木 徹; 飛田 吉春
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 85, p.740 - 752, 2015/11
被引用回数:32 パーセンタイル:92.07(Nuclear Science & Technology)Studies on local fuel-coolant interactions (FCI) in a molten pool are crucial to the analyses of severe accidents that could occur for sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). To clarify the characteristics of this interaction, in recent years a series of simulated experiments, which covers a variety of conditions including much difference in water volume, melt temperature, water subcooling and water release site (pool surface or bottom), was conducted at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency by delivering a given quantity of water into a molten pool formed with a low-melting-point alloy. In this study, motivated by acquiring further evidence for understanding its mechanisms, interaction characteristics including the pressure-buildup as well as mechanical energy release and its conversion efficiency, are investigated using the SIMMER-III, an advanced fast reactor safety analysis code. It is confirmed that, similar to experiments, the water volume, melt temperature and water release site are observable to have remarkable impact on the interaction, while the role of water subcooling seems to be less prominent. The performed analyses also suggest that the most probable reason leading to the limited pressurization and resultant mechanical energy release for a given melt and water temperature within the non-film boiling range, even under a condition of much larger volume of water entrapped within the pool, should be primarily due to an isolation effect of vapor bubbles generated at the water-melt interface.
Cheng, S.; 松場 賢一; 磯崎 三喜男; 神山 健司; 鈴木 徹; 飛田 吉春
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2015/05
To clarify the mechanisms underlying local fuel-coolant interactions (FCI) in a molten pool, in this study, several latest calculations with reactor materials were performed using SIMMER-III, an advanced fast reactor safety analysis code. The performed SIMMER-III analyses suggest that despite of a comparatively larger temperature range of molten-fuel and sodium possibly varied during reactor accidents, the isolation effect of vapor bubbles generated at the melt-sodium interface seems to be the unique dominant mechanism that leads to the limited pressurization. Knowledge and fundamental data from this work might be utilized for future empirical-approach studies (e.g. those investigating the characteristics of critical coolant volume required for achieving the saturated pressurization at varied melt and coolant temperatures).
Cheng, S.; 松場 賢一; 磯崎 三喜男; 神山 健司; 鈴木 徹; 飛田 吉春
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 75, p.20 - 25, 2015/01
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:67.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Studies on local fuel-coolant interactions (FCI) in a molten pool are important for severe accident analyses of sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). Motivated by providing some evidence for understanding this interaction, in this study several experimental tests, with comparatively larger difference in coolant volumes, were conducted by delivering a given quantity of water into a simulated molten fuel pool (formed with a low-melting-point alloy). Interaction characteristics including the pressure-buildup as well as mechanical energy release and its conversion efficiency are evaluated and compared. It is found that as water quantity increases, a limited pressure-buildup and the resultant mechanical energy release are observable. The performed analyses also suggest that only a part of water is probably vaporized during local FCIs and responsible for the pressurization and mechanical energy release, especially for those cases with much larger water volumes.
Cheng, S.; 松場 賢一; 磯崎 三喜男; 神山 健司; 鈴木 徹; 飛田 吉春
Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations, 2015, p.964327_1 - 964327_14, 2015/00
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:60.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)To clarify the mechanisms underlying local fuel-coolant interactions (FCI) in a molten pool, in recent years several experimental tests, with comparatively larger difference in coolant volumes, were conducted at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency by delivering a given quantity of water into a molten pool formed with a low-melting-point alloy. In this study, to further understand this interaction, interaction characteristics including the pressure-buildup as well as mechanical energy release and its conversion efficiency are investigated using the SIMMER-III, an advanced fast reactor safety analysis code. It is found that the SIMMER-III code not only reasonably simulates the transient pressure and temperature variations during local FCIs, but also supports the limited tendency of pressurization and resultant mechanical energy release as observed from experiments when the volume of water delivered into the pool increases. The performed analyses also suggest that the most probable reason leading to such limited tendency should be primarily due to an isolation effect of vapor bubbles generated at the water-melt interface.
Cheng, S.; 松場 賢一; 磯崎 三喜男; 神山 健司; 鈴木 徹; 飛田 吉春
Proceedings of 10th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-10) (USB Flash Drive), 12 Pages, 2014/12
In this study, motivated by acquiring further evidence for understanding the characteristics of pressure buildup from local fuel-coolant interactions in a simulated molten fuel pool, SIMMER-III, an advanced fast reactor safety analysis code, is utilized for analyses. It is found that, similar to previous reported experimental analyses, the water volume and melt temperature are observable to have remarkable impact on the interaction, while the role of water subcooling seems to be less prominent. In addition, from the numerical runs performed it is also recognized that the most probable reason leading to the limited pressurization for a given melt and water temperature within the non-film boiling range, even under a condition of comparatively larger volume of water delivered into the pool, should be due to an isolation effect of vapor bubbles generated at the water-melt interface. Knowledge and data gained from this study might be utilized for potential empirical-model development as well as future investigations using reactor materials.
Cheng, S.; 田上 浩孝; 山野 秀将; 鈴木 徹; 飛田 吉春; 竹田 祥平*; 西 津平*; 錦戸 達也*; Zhang, B.*; 松元 達也*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(9), p.1096 - 1106, 2014/09
被引用回数:27 パーセンタイル:87.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)Studies on debris bed self-leveling behavior with non-spherical particles are crucial in the assessment of actual leveling behavior that could occur in core disruptive accident of sodium-cooled fast reactors. Although in our previous publications, a simple empirical model (based model), with its wide applicability confirmed over various experimental conditions, has been successfully advanced to predict the transient leveling behavior, up until now this model is restricted to calculations of debris bed of spherical particles. Focusing on this aspect, in this study a series of experiments using non-spherical particles was performed within a recently-developed comparatively larger-scale experimental facility. Based on the knowledge and data obtained, an extension scheme is suggested with the intention to extend the base model to cover the particle-shape influence. Through detailed analyses, it is found that by coupling this scheme, good agreement between experimental and predicted results can be achieved for both spherical and non-spherical particles given current range of experimental conditions.
Cheng, S.; 田上 浩孝; 山野 秀将; 鈴木 徹; 飛田 吉春; 中村 裕也*; 竹田 祥平*; 西 津平*; Zhang, B.*; 松元 達也*; et al.
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 1(4), p.TEP0022_1 - TEP0022_16, 2014/08
To clarify the mechanisms underlying the debris-bed self-leveling behavior, several series of experiments were elaborately designed and conducted within a variety of conditions in recent years, under the collaboration between Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and Kyushu University. The current contribution, including knowledge from both experimental analyses and empirical model development, is focused on a recently developed comparatively larger-scale experimental facility using gas-injection to simulate the coolant boiling. Based on the experimental observation and quantitative data obtained, influence of various experimental parameters, including gas flow rate ( 300 L/min), water depth (180 mm and 400 mm), bed volume (3
300 L/min), water depth (180 mm and 400 mm), bed volume (3  7 L), particle size (1
7 L), particle size (1  6 mm), particle density (beads of alumina, zirconia and stainless steel) along with particle shape (spherical and irregularly-shaped) on the leveling is checked and compared. As for the empirical model development, aside from a base model which is restricted to calculations of spherical particles, the status of potential considerations on how to cover more realistic conditions (esp. debris beds formed with non-spherical particles), is also presented and discussed.
6 mm), particle density (beads of alumina, zirconia and stainless steel) along with particle shape (spherical and irregularly-shaped) on the leveling is checked and compared. As for the empirical model development, aside from a base model which is restricted to calculations of spherical particles, the status of potential considerations on how to cover more realistic conditions (esp. debris beds formed with non-spherical particles), is also presented and discussed.
Cheng, S.; 松場 賢一; 磯崎 三喜男; 神山 健司; 鈴木 徹; 飛田 吉春
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 275, p.133 - 141, 2014/08
被引用回数:28 パーセンタイル:88.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)Analyses of severe accidents for SFRs have indicated that the accident might proceed into a transition phase where a large whole-core-scale pool containing sufficient fuel to exceed prompt criticality by fuel compaction might be formed. Local fuel-coolant interaction (FCI) in the pool is regarded as one of the probable initiators that could lead to such compactive fluid motions. To clarify the mechanisms underlying this interaction, in this study a series of experiments was conducted by delivering a given quantity of water into a simulated molten fuel pool. Based on the experimental data obtained from a variety of conditions, interaction characteristics including the pressure-buildup as well as resultant mechanical energy release and its conversion efficiency, is checked and compared. It is found that under our experimental conditions the water volume, melt temperature and water release position have remarkable impact on the interaction, while the role of water subcooling seems to be less prominent. The analyses also suggest that the pressurization and resultant mechanical energy release during local FCIs should be intrinsically limited, due to an observed suppressing role caused by the increasing of coolant volume entrapped within the pool as well as the transition of boiling mode. Evidence and data from this work will be utilized for verifications of advanced fast reactor safety analysis codes.
Cheng, S.; 松場 賢一; 磯崎 三喜男; 神山 健司; 鈴木 徹; 飛田 吉春
Proceedings of International Symposium on Future I&C for Nuclear Power Plants and International Symposium on Symbiotic Nuclear Power Systems (ISOFIC 2014/ISSNP 2014) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2014/08
Analyses of severe accidents for sodium-cooled fast reactors have shown that by assuming pessimistic conditions the accident might proceed into a transition phase where a whole-core-scale pool containing sufficient fuel to exceed prompt criticality by fuel compaction might be formed. Local fuel-coolant interaction in the pool is regarded as one of the probable initiators that could lead to such compactive fluid motions. From previous preliminary experimental analyses, it was recognized that for a given melt and water temperature within the non-film boiling range, with the increasing of water volume, a limited pressure buildup can be observed. In this study, to further understand this interaction, SIMMER-III, an advanced fast reactor safety analysis code, is utilized for analyses. It is found that the SIMMER-III code can reasonably simulate the transient pressure and temperature tendencies during local FCIs as understood from experiments. In addition, from the comparative analyses between different cases, the observed limited pressurization characteristics from experiments can be confirmed as well. To achieve a deeper and more systematic understanding on local FCIs, with the ongoing of experimental analyses, more numerical analyses over various situations, such as much difference in water subcooling, melt temperature as well as the water release site, have been also planned.
Cheng, S.; 松場 賢一; 磯崎 三喜男; 神山 健司; 鈴木 徹; 飛田 吉春
Proceedings of 22nd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-22) (DVD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2014/07
Studies on local fuel-coolant interactions (FCI) in a molten pool are important for severe accident analyses of sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). To clarify the mechanisms underlying this interaction, in this study a series of experiments was conducted by delivering a given quantity of water into a simulated molten fuel pool (formed with a low-melting-point alloy). Based on the experimental data obtained from a variety of conditions, including difference in water volume, melt temperature and water subcooling, the characteristics of pressure-buildup during local FCIs was investigated. It is found that under our experimental conditions the water volume and melt temperature have remarkable impact on the interaction, while the role of water subcooling seems to be less prominent. The performed analyses also suggest that the pressurization from local FCIs should be intrinsically limited, due to a suppressing role caused by the increasing of coolant volume entrapped within the pool as well as the transition of boiling mode. Current work, which gives a palette of favorable data for a better understanding and an improved estimation of severe accidents in SFRs, is expected to benefit future analyses and verifications of computer models developed in advanced fast reactor safety analysis codes.
田上 浩孝; Cheng, S.; 飛田 吉春; Guo, L.*; Zhang, B.*; 守田 幸路*
Proceedings of 22nd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-22) (DVD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2014/07
SFRのシビアアクシデントにおいて、燃料デブリが冷却限界厚さを超えて堆積した場合、セルフ・レベリング挙動によってデブリベッド厚みが冷却限界を下回ることが期待される。ゆえに、SFRの安全解析においてセルフ・レベリング挙動を評価することは重要であるが、これを解析する手法は存在しない。そこで、本研究ではセルフ・レベリング挙動に固有の現象を解析するための新規手法を開発することを目的とする。デブリベッドのセルフ・レベリング挙動の特徴から、Bingham流体を仮定することで新規手法を開発した。新規手法は粒子間衝突を模擬した粒子間相互作用と粒子間接触の効果を模擬した2つのパートにより構成される。この新規手法に対して固気液三相流からなるセルフ・レベリング挙動模擬実験を用いて検証を行った。新規手法は、モデルパラメータに依存するものの模擬実験結果をよく再現する。このことから、本新規手法がSFR環境下におけるデブリベッドのセルフ・レベリング挙動に対する適用性を有することが示された。
Cheng, S.; 田上 浩孝; 山野 秀将; 鈴木 徹; 飛田 吉春; Zhang, B.*; 松元 達也*; 守田 幸路*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 63, p.188 - 198, 2014/01
被引用回数:33 パーセンタイル:91.09(Nuclear Science & Technology)To clarify the mechanisms underlying the debris bed self-leveling behavior, several series of experiments were elaborately designed and conducted in recent years under the constructive collaboration between Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and Kyushu University (Japan). Based on the experimental observations and quantitative data obtained from various conditions, a simple empirical approach to predict the self-leveling development depending on particle size, particle density and gas velocity was proposed. To confirm the rationality and wide applicability of this approach, over the past few years extensive efforts have been made by performing modeling investigations against a large number of experimental data covering various conditions (including difference in bubbling mode, bed geometry and range of experimental parameters). The present contribution synthesizes these efforts and gives detailed comparative analyses of the performed validations, thus, providing some insight for a better understanding of CDAs and improved verifications of computer models developed in advanced fast reactor safety analysis codes.
Cheng, S.; 松場 賢一; 磯崎 三喜男; 神山 健司; 鈴木 徹; 飛田 吉春
Proceedings of International Symposium on Symbiotic Nuclear Power Systems for 21st Century (ISSNP 2013) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2013/11
In the severe accident analyses for sodium-cooled fast reactors, there is the possibility that a whole-core-scale pool containing sufficient fuel to exceed prompt criticality by fuel compaction might be formed. Local fuel-coolant interaction in the pool is regarded as one of the probable initiators that could lead to such compactive fluid motions. To clarify the mechanisms underlying this interaction, an experimental system using simulant materials has been developed. The experiments were conducted by delivering a given quantity of water into a simulated molten fuel pool. Current paper presents the experimental design and knowledge from preliminary analyses of several typical runs (with water quantity varying from 5 cc to 40 cc). Interaction characteristics including the pressure-buildup as well as mechanical energy release and its conversion efficiency are evaluated and compared in detail. It is revealed that as water quantity increases, a limited pressurization and resultant mechanical energy release is observable.