Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Otani, Masashi*; Cicek, E.*; Ego, Hiroyasu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; et al.
Proceedings of 31st International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2022) (Internet), p.636 - 641, 2022/09
The muon linac project for the precise measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic and electric dipole moments, which is currently one of the hottest issues of the elementary particle physics, is in progress at J-PARC. The muons from the J-PARC muon facility are once cooled to room temperature, then accelerated up to 212 MeV with a normalized emittance of 1.5  mm mrad and a momentum spread of 0.1%. Four types of accelerating structures are adopted to obtain the efficient acceleration with a wide beta range from 0.01 to 0.94. The project is moving into the construction phase. We already demonstrated the re-acceleration scheme of the decelerated muons using a 324-MHz RFQ in 2017. The high-power test of the 324-MHz Interdigital H-mode (IH) DTL using a prototype cavity was performed in 2021. The fabrication of the first module of 14 modules of the 1296-MHz Disk and Washer (DAW) CCL will be done to confirm the production process. Moreover, the final design of the travelling wave accelerating structure for the high beta region is also proceeding. In this paper, the recent progress toward the realization of the world first muon linac will be presented.
mm mrad and a momentum spread of 0.1%. Four types of accelerating structures are adopted to obtain the efficient acceleration with a wide beta range from 0.01 to 0.94. The project is moving into the construction phase. We already demonstrated the re-acceleration scheme of the decelerated muons using a 324-MHz RFQ in 2017. The high-power test of the 324-MHz Interdigital H-mode (IH) DTL using a prototype cavity was performed in 2021. The fabrication of the first module of 14 modules of the 1296-MHz Disk and Washer (DAW) CCL will be done to confirm the production process. Moreover, the final design of the travelling wave accelerating structure for the high beta region is also proceeding. In this paper, the recent progress toward the realization of the world first muon linac will be presented.
 Pu nuclear magnetic resonance in the candidate topological insulator PuB
Pu nuclear magnetic resonance in the candidate topological insulator PuB
Dioguardi, A. P.*; Yasuoka, Hiroshi*; Thomas, S. M.*; Sakai, Hironori; Cary, S. K.*; Kozimor, S. A.*; Albrecht-Schmitt, T. E.*; Choi, H. C.*; Zhu, J.-X.*; Thompson, J. D.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 99(3), p.035104_1 - 035104_6, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:42.34(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present a detailed nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) study of  Pu in bulk and powdered single-crystal plutonium tetraboride (PuB
Pu in bulk and powdered single-crystal plutonium tetraboride (PuB ), which has recently been investigated as a potential correlated topological insulator. The
), which has recently been investigated as a potential correlated topological insulator. The  Pu NMR spectra are consistent with axial symmetry of the shift tensor showing for the first time that
Pu NMR spectra are consistent with axial symmetry of the shift tensor showing for the first time that  Pu NMR can be observed in an anisotropic environment and up to room temperature. The temperature dependence of the
Pu NMR can be observed in an anisotropic environment and up to room temperature. The temperature dependence of the  Pu shift, combined with a relatively long spin-lattice relaxation time (
Pu shift, combined with a relatively long spin-lattice relaxation time ( ), indicate that PuB
), indicate that PuB adopts a nonmagnetic state with gaplike behavior consistent with our density functional theory calculations. The temperature dependencies of the NMR Knight shift and
adopts a nonmagnetic state with gaplike behavior consistent with our density functional theory calculations. The temperature dependencies of the NMR Knight shift and 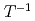 imply bulk gaplike behavior confirming that PuB
imply bulk gaplike behavior confirming that PuB is a good candidate topological insulator.
is a good candidate topological insulator.
Bandodkar, A. J.*; Gutruf, P.*; Choi, J.*; Lee, K.-H.*; Sekine, Yurina; Reeder, J. T.*; Jeang, W. J.*; Aranyosi, A. J.*; Lee, S. P.*; Model, J. B.*; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 5(1), p.eaav3294_1 - eaav3294_15, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:566 Percentile:99.88(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Interest in advanced wearable technologies increasingly extends beyond systems for biophysical measurements to those that enable continuous, non-invasive monitoring of biochemical markers in biofluids. Here, we introduce battery-free, wireless microelectronic platforms that perform sensing via schemes inspired by the operation of biofuel cells. Combining these systems in a magnetically releasable manner with chrono-sampling microfluidic networks that incorporate assays based on colorimetric sensing yields thin, flexible, lightweight, skin-interfaced technologies with broad functionality in sweat analysis. A demonstration device allows simultaneous monitoring of sweat rate/loss, along with quantitative measurements of pH and of lactate, glucose and chloride concentrations using biofuel cell and colorimetric approaches.
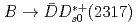 decay rates and a search for isospin partners of the
decay rates and a search for isospin partners of the 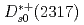
Choi, S.-K.*; Tanida, Kiyoshi; Belle Collaboration*; 174 of others*
Physical Review D, 91(9), p.092011_1 - 092011_12, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:53.35(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Choi, I. W.*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Tatsufumi*; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Yogo, Akifumi*; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; Daito, Izuru*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 57(2), p.025001_1 - 025001_9, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:12.55(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Projection images of a metal mesh produced by directional MeV electron beam together with directional proton beam, emitted simultaneously from a thin foil target irradiated by an ultrashort intense laser. The mesh patterns are projected to each detector by the electron beam and the proton beam originated from tiny virtual sources of  20 micron meter and
20 micron meter and  10 micron meter diameters, respectively. Based on the observed quality and magnification of the projection images, we estimate sizes and locations of the virtual sources for both beams and characterize their directionalities. To carry out physical interpretation of the directional electron beam qualitatively, we perform 2D particle-in-cell simulation which reproduces a directional escaping electron component, together with a non-directional dragged-back electron component, the latter mainly contributes to building a sheath electric field for proton acceleration.
10 micron meter diameters, respectively. Based on the observed quality and magnification of the projection images, we estimate sizes and locations of the virtual sources for both beams and characterize their directionalities. To carry out physical interpretation of the directional electron beam qualitatively, we perform 2D particle-in-cell simulation which reproduces a directional escaping electron component, together with a non-directional dragged-back electron component, the latter mainly contributes to building a sheath electric field for proton acceleration.
Choi, I. W.*; Kim, I. J.*; Pae, K. H.*; Nam, K. H.*; Lee, C.-L.*; Yun, H.*; Kim, H. T.*; Lee, S. K.*; Yu, T. J.*; Sung, J. H.*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 99(18), p.181501_1 - 181501_3, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:56.02(Physics, Applied)We report the manufacturing of a thin foil target made of conjugated polymer, and the simultaneous observation of laser accelerated ions and second harmonic radiation, when irradiated with ultrahigh-contrast laser pulse at a maximum intensity of 4 10
10 W/cm
W/cm . Maximum proton energy of 8 MeV is achieved along the target normal direction. Strong second harmonic with over 6% energy ratio compared to fundamental is emitted along the specular direction. Two-dimensional particle-in-cell simulations confirm the simultaneous generation of protons and high-order harmonics, which demonstrates the feasibility of applications requiring particle and radiation sources at once, effectively using the same laser and target.
. Maximum proton energy of 8 MeV is achieved along the target normal direction. Strong second harmonic with over 6% energy ratio compared to fundamental is emitted along the specular direction. Two-dimensional particle-in-cell simulations confirm the simultaneous generation of protons and high-order harmonics, which demonstrates the feasibility of applications requiring particle and radiation sources at once, effectively using the same laser and target.
Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ma, J.*; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
NIFS-PROC-85, p.30 - 33, 2011/02
The experiment of proton generation is performed for developing the laser-driven ion source. We observe proton signals in the laser-plasma interaction by using a thin-foil target. To get higher energy protons the size of the preformed plasma is reduced by changing the laser contrast level. In the high-contrast laser pulse case the maximum energy of the protons generated at rear side of the target increases.
Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ma, J.*; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 38(9), p.702 - 705, 2010/09
High-intensity laser and thin-foil interactions produce high-energy particles, hard X-ray, high-order harmonics, and terahertz (THz) radiation. A proton beam driven by a high-intensity laser has received attention as a compact ion source for medical applications. In this study we have tested simultaneous generation of protons and THz radiation from a thin-foil target. We use a Ti:sapphire laser system (J-KAREN) at JAEA. A laser beam is focused by an off-axis parabolic mirror at the thin-foil target. We observed the high-energy proton in the rear side of the target and THz radiation in the reflected direction. Next, high energy protons are observed by reducing the size of preformed plasma.
Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Ma, J.*; Sagisaka, Akito; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 36(4), p.1872 - 1877, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:27.38(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A dependence of cut-off proton kinetic energy on laser prepulse duration has been observed. ASE pedestal duration is controlled by a fast electro-optic pulse slicer where the risetime is estimated to be 130 ps. We demonstrate a new correlated spectral technique for determining this risetime using a stretched, frequency chirped pulse.
 m thick copper tape target irradiated by s-, circularly-, and p-polarized 55-fs laser pulses
m thick copper tape target irradiated by s-, circularly-, and p-polarized 55-fs laser pulsesLi, Z.*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Bulanov, S. V.; Sagisaka, Akito; Ogura, Koichi; Yogo, Akifumi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Orimo, Satoshi; Mori, Michiaki; et al.
Physics Letters A, 369(5-6), p.483 - 487, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:52.85(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The energy spectra of energetic protons emitted in the normal direction from a 5- m thick copper tape irradiated by p-, circularly-, and s-polarized 55-fs laser pulses with intensity of 8-9
m thick copper tape irradiated by p-, circularly-, and s-polarized 55-fs laser pulses with intensity of 8-9 10
10 W/cm
W/cm are measured together with the angular distribution and energy spectra of hot electrons by the target normal direction. The protons with energy up to 1.34 MeV in the rear target normal direction and hot electrons in the laser propagation direction are found. The characters of protons and electrons driven by the circularly-polarized irradiation are close to that driven by the p-polarized one, which is much different from the case at laser intensity of 2-3
are measured together with the angular distribution and energy spectra of hot electrons by the target normal direction. The protons with energy up to 1.34 MeV in the rear target normal direction and hot electrons in the laser propagation direction are found. The characters of protons and electrons driven by the circularly-polarized irradiation are close to that driven by the p-polarized one, which is much different from the case at laser intensity of 2-3 10
10 W/cm
W/cm .
.
Yogo, Akifumi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Li, Z.*; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Nakamura, Shu*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Shirai, Toshiyuki*; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 14(4), p.043104_1 - 043104_6, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:64 Percentile:87.63(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Fast protons are observed by a newly-developed  time-of-flight spectrometer, which provides
time-of-flight spectrometer, which provides 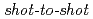 proton-energy distributions immediately after the irradiation of a laser pulse having an intensity of
proton-energy distributions immediately after the irradiation of a laser pulse having an intensity of 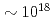 W/cm
W/cm onto a 5-
onto a 5- m-thick copper foil. The maximum proton energy is found to increase when the intensity of a fs-prepulse arriving 9 ns before the main pulse increases from 10
m-thick copper foil. The maximum proton energy is found to increase when the intensity of a fs-prepulse arriving 9 ns before the main pulse increases from 10 to 10
to 10 W/cm
W/cm . Interferometric measurement indicates that the preformed-plasma expansion at the front surface is smaller than 15
. Interferometric measurement indicates that the preformed-plasma expansion at the front surface is smaller than 15  m, which corresponds to the spatial resolution of the diagnostics. This sharp gradient of the plasma makes a beneficial effect on increasing the absorption efficiency of the main-pulse energy, resulting in the increase in the proton energy. This is supported by the result that the X-ray intensity from the laser plasma clearly increases with the prepulse intensity.
m, which corresponds to the spatial resolution of the diagnostics. This sharp gradient of the plasma makes a beneficial effect on increasing the absorption efficiency of the main-pulse energy, resulting in the increase in the proton energy. This is supported by the result that the X-ray intensity from the laser plasma clearly increases with the prepulse intensity.
Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Daido, Hiroyuki; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Li, Z.*; Ogura, Koichi; Yogo, Akifumi; Oishi, Yuji*; Nayuki, Takuya*; Fujii, Takashi*; et al.
Applied Physics B, 84(3), p.415 - 419, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:65.06(Optics)no abstracts in English
 A
A MnO
MnO (A=Ca,Sr)
(A=Ca,Sr)Kang, J.-S.*; Kim, J. H.*; Sekiyama, Akira*; Kasai, Shuichi*; Suga, Shigemasa*; Han, S. W.*; Kim, K. H.*; Choi, E. J.*; Kimura, Tsuyoshi*; Muro, Takayuki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 68(1), p.012410_1 - 012410_4, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:67.47(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Akino, Norio; Kubo, Shinji; Takase, Kazuyuki; Hino, Ryutaro; Choi, K.*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Ryutai Kogaku Bumon Koenkai 2000 Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
Ogura, Koichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Orimo, Satoshi; Sagisaka, Akito; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Sugiyama, Hironori*; et al.
no journal, ,
Ultrashort and high intensity laser can induce high energy protons. Proton beams have a wide range of applications such as in the production of radioisotopes and proton therapy. An energy of the proton beam has a wide distribution. The distribution of activity in depth is calculated while laser induced protons are injected into an iron plate.
Sagisaka, Akito; Yogo, Akifumi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Li, Z.*; Ogura, Koichi; Takai, Mamiko; Orimo, Satoshi; Hayashi, Yukio; Mori, Michiaki; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Orimo, Satoshi; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Mori, Michiaki; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kondo, Shuji; Yamamoto, Yoichi*; Shimomura, Takuya*; Tanoue, Manabu*; et al.
no journal, ,
We are investigating an intense fs-laser driven MeV proton source using a thin foil, and its applications. Simultaneous imaging of a sample with a proton and an X-ray beams has been demonstrated by a ultra-short pulse higt intensity Ti:Sapphire laser systems at JAEA and GIST. For generating a short-pulse proton beams and X-rays, an intense laser pulse irradiates a tape targets. The p-polarized laser pulse with 50 mm diameter is focused onto the cupper tape target at 45 degree incident angle with focal length of 238 mm (F/4.8), giving an intensity on target of 3-9 10
10 W/cm10
W/cm10 . The cupper and polyimide tape was 5, 7.5 micron in thickness and 20 mm in width. The target system supplies a fresh surface to the focus spot at every shot. We obtained simultaneously the projection image of a Ni mesh pattern having a periodically structured pattern by the proton detected CR39 and X-rays detected on imaging plate.
. The cupper and polyimide tape was 5, 7.5 micron in thickness and 20 mm in width. The target system supplies a fresh surface to the focus spot at every shot. We obtained simultaneously the projection image of a Ni mesh pattern having a periodically structured pattern by the proton detected CR39 and X-rays detected on imaging plate.
Ogura, Koichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Orimo, Satoshi; Sagisaka, Akito; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Sugiyama, Hironori*; et al.
no journal, ,
Protons with energies up to 3 MeV have been generated by the irradiation of a 7.5  m thickness target by a 1 Hz table top laser with intensity of 700mJ. These protons were used to induce the nuclear reaction 7Li(p,n)7Be. Simultaneously, energy of proton was detected by a time of flight method.
m thickness target by a 1 Hz table top laser with intensity of 700mJ. These protons were used to induce the nuclear reaction 7Li(p,n)7Be. Simultaneously, energy of proton was detected by a time of flight method.