Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Joung, S.*; Ji, Y.-Y.*; Choi, Y.*; Lee, E.*; Ji, W.*; Sasaki, Miyuki; Ochi, Kotaro; Sanada, Yukihisa
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 20(4), p.P04027_1 - P04027_10, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0Baccou, J.*; Glantz, T.*; Ghione, A.*; Sargentini, L.*; Fillion, P.*; Damblin, G.*; Sueur, R.*; Iooss, B.*; Fang, J.*; Liu, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 421, p.113035_1 - 113035_16, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:97.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kitamura, Ryo; Bae, S.*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kim, B.*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Mibe, Tsutomu*; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 24(3), p.033403_1 - 033403_9, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.50(Physics, Nuclear)A negative muonium ion (Mu ) source using an aluminum foil target was developed as a low-energy muon source. An experiment to produce Mu
) source using an aluminum foil target was developed as a low-energy muon source. An experiment to produce Mu ions was conducted to evaluate the performance of the Mu
ions was conducted to evaluate the performance of the Mu ion source. The measured event rate of Mu
ion source. The measured event rate of Mu ions was
ions was 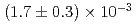 Mu
Mu /s when the event rate of the incident muon beam was
/s when the event rate of the incident muon beam was 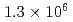 /s. The formation probability, defined as the ratio of the Mu
/s. The formation probability, defined as the ratio of the Mu ions to the incident muons on the Al target, was
ions to the incident muons on the Al target, was 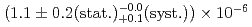 . This Mu
. This Mu ion source boosted the development of the muon accelerator, and the practicality of this low-energy muon source obtained using a relatively simple apparatus was demonstrated.
ion source boosted the development of the muon accelerator, and the practicality of this low-energy muon source obtained using a relatively simple apparatus was demonstrated.
Herranz, L. E.*; Jacquemain, D.*; Nitheanandan, T.*; Sandberg, N.*; Barr , F.*; Bechta, S.*; Choi, K.-Y.*; D'Auria, F.*; Lee, R.*; Nakamura, Hideo
, F.*; Bechta, S.*; Choi, K.-Y.*; D'Auria, F.*; Lee, R.*; Nakamura, Hideo
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 127, p.103432_1 - 103432_14, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:21.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Strasser, P.*; Abe, Mitsushi*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 198, p.00003_1 - 00003_8, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:98.57(Quantum Science & Technology)Kitamura, Ryo*; Otani, Masashi*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; et al.
Proceedings of 15th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.239 - 243, 2018/08
Muon acceleration is an important technique in exploring the new frontier of physics. A new measurement of the muon dipole moments is planned in J-PARC using the muon linear accelerator. The low-energy (LE) muon source using the thin metal foil target and beam diagnostic system were developed for the world's first muon acceleration. Negative muonium ions from the thin metal foil target as the LE muon source was successfully observed. Also the beam profile of the LE positive muon was measured by the LE-dedicated beam profile monitor. The muon acceleration test using a Radio-Frequency Quadrupole linac (RFQ) is being prepared as the first step of the muon accelerator development. In this paper, the latest status of the first muon acceleration test is described.
Kim, S. B.*; Zhang, Y.*; Won, S. M.*; Bandodkar, A. J.*; Sekine, Yurina; Xue, Y.*; Koo, J.*; Harshman, S. W.*; Martin, J. A.*; Park, J. M.*; et al.
Small, 14(12), p.1703334_1 - 1703334_11, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:128 Percentile:96.29(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Kitamura, Ryo*; Otani, Masashi*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Bae, S.*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; et al.
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.100 - 103, 2017/12
Muon acceleration is an important technique in exploring the new frontier of physics. A new measurement of the muon dipole moments is planned in J-PARC using the muon linear accelerator. The low-energy (LE) muon source using the thin metal foil target and beam diagnostic system were developed for the world's first muon acceleration. Negative muonium ions from the thin metal foil target as the LE muon source was successfully observed. Also the beam profile of the LE positive muon was measured by the LE-dedicated beam profile monitor. The muon acceleration test using a Radio-Frequency Quadrupole linac (RFQ) is being prepared as the first step of the muon accelerator development. In this paper, the latest status of the first muon acceleration test is described.
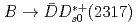 decay rates and a search for isospin partners of the
decay rates and a search for isospin partners of the 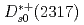
Choi, S.-K.*; Tanida, Kiyoshi; Belle Collaboration*; 174 of others*
Physical Review D, 91(9), p.092011_1 - 092011_12, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:53.49(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Kuno, Yusuke; Tazaki, Makiko; Akiba, Mitsunori*; Adachi, Takeo*; Takashima, Ryuta*; Omoto, Akira*; Oda, Takuji*; Choi, J.-S.*; Tanaka, Satoru*
Proceedings of INMM 53rd Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2012/07
This paper will present brief historical review of multilateral nuclear approach (MNA), and based on which, a basic concept of a reliable framework of nuclear fuel cycle, where the fuel-cycle services could be provided without discrimination and meet the international 3S requirements, is discussed.
Han, B.*; Kim, J. K.*; Kim, Y.*; Choi, J. S.*; Lee, M. J.*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
Hoshasen To Sangyo, (130), p.20 - 23, 2011/06
no abstracts in English
Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ma, J.*; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
NIFS-PROC-85, p.30 - 33, 2011/02
The experiment of proton generation is performed for developing the laser-driven ion source. We observe proton signals in the laser-plasma interaction by using a thin-foil target. To get higher energy protons the size of the preformed plasma is reduced by changing the laser contrast level. In the high-contrast laser pulse case the maximum energy of the protons generated at rear side of the target increases.
Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ma, J.*; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 38(9), p.702 - 705, 2010/09
High-intensity laser and thin-foil interactions produce high-energy particles, hard X-ray, high-order harmonics, and terahertz (THz) radiation. A proton beam driven by a high-intensity laser has received attention as a compact ion source for medical applications. In this study we have tested simultaneous generation of protons and THz radiation from a thin-foil target. We use a Ti:sapphire laser system (J-KAREN) at JAEA. A laser beam is focused by an off-axis parabolic mirror at the thin-foil target. We observed the high-energy proton in the rear side of the target and THz radiation in the reflected direction. Next, high energy protons are observed by reducing the size of preformed plasma.
Choi, J.-S.*; Kuno, Yusuke
Genshiryoku eye, 55(5), p.59 - 63, 2009/05
The paper provides a historical account of some of the most relevant proposals, concepts, and studies of international control over technologies and materials in the proliferation sensitive parts of the nuclear fuel cycle. It also focuses on recent proposals which aim to reduce or eliminate the incentive of countries developing sensitive fuel cycle technologies, namely, enrichment and reprocessing. Many of these proposals include the reliable fuel supply and perhaps, spent fuel take-back. The objectives of the cooperative framework are to facilitate member parties to form partnerships for providing nuclear fuel-cycle service needs; to coordinate international safeguards and inspection of fuel-cycle facilities; to assure that member parties would receive the reliable and economically-competitive fuel-cycle services; and to enhance the profile of peaceful use of nuclear power in Asia Pacific.
Kuno, Yusuke; Choi, J.-S.*
Enerugi Rebyu, 29(4), p.14 - 15, 2009/04
The demand for peaceful use of nuclear power is remarkably increasing, in particular, in order to ensure global energy security, preventing global warming, whereas, the world concerns about the nuclear security is growing. Accordingly the education on as nuclear technology should involve the policy and technology study on nuclear non-proliferation. In the course of nuclear renaissance, the nuclear education should take into account the interdisciplinary study, not only carrying on the studies on nuclear engineering. The University of Tokyo (UT) brought a concept of nuclear socio engineering during realignment of nuclear-related courses. Education on nuclear non-proliferation has started as the key part of the nuclear socio engineering in cooperation with JAEA. This paper describes its content, function, management and perspectives.
Kuno, Yusuke; Choi, J.-S.*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 51(2), p.94 - 99, 2009/02
, 51(2), p.94 - 99, 2009/02
It is essential to review the concept of the safeguards and the nuclear proliferation resistance when next generation nuclear system incorporates those into its designing. This manuscript includes the basic idea, essence of nuclear proliferation resistance and how it effectively works, and finally what designer should consider.
Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Ma, J.*; Sagisaka, Akito; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 36(4), p.1872 - 1877, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:27.46(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A dependence of cut-off proton kinetic energy on laser prepulse duration has been observed. ASE pedestal duration is controlled by a fast electro-optic pulse slicer where the risetime is estimated to be 130 ps. We demonstrate a new correlated spectral technique for determining this risetime using a stretched, frequency chirped pulse.
 Zn
Zn
Haga, Yoshinori; Matsumoto, Yuji; Tateiwa, Naoyuki; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Choi, E. S.*; Bauer, E. D.*; Fisk, Z.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Ma, J.*; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sugiyama, Hironori*; et al.
no journal, ,
Kitamura, Ryo*; Otani, Masashi*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Bae, S.*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; et al.
no journal, ,
Muon acceleration is an important technique in exploring the new frontier of physics. A new measurement of the muon dipole moments is planned in J-PARC using the muon linear accelerator. The low-energy (LE) muons were generated using the thin metal foil target. The muon acceleration test using a Radio-Frequency Quadrupole linac (RFQ) is conducted as the first step of the muon accelerator development. In this paper, the result of the muon acceleration test is described.