Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Gd and
Gd and  Gd in the thermal energy region with the Li-glass detectors and NaI(Tl) spectrometer installed in J-PARC
Gd in the thermal energy region with the Li-glass detectors and NaI(Tl) spectrometer installed in J-PARC MLF
MLF ANNRI
ANNRIKimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Harada, Hideo; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Terada, Kazushi*; Hori, Junichi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.678 - 696, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:28.39(Nuclear Science & Technology)Saito, Kosuke; Nogami, Yoshitaka; Kodato, Kazuo; Matsuyama, Kazutomi; Endo, Hideo
JAEA-Research 2012-027, 118 Pages, 2012/09
This report is compilation of 4 years tests and experiments of simulated alpha-ray irradiation on diverse materials for glove box application at Plutonium Fuel Development Center, Tokai, JAEA. Specimens prepared from the materials are irradiated with  He
He ion beam whose kinetic energy was 5 MeV and sent to exterior observation, optical microscopy and tensile tests. Experiments revealed ion-irradiation generally makes tens of micrometers of deteriorated layer which is hardened and discolored on the surface of the specimens. According to dose, tensile properties such as tensile strength and elongation at break decrease generally. Tensile strength decrease is expected to ascribe to stress concentration on cracks of irradiation-damaged surface and rupture. Lead-contained glove, which is ordinarily used on highly
ion beam whose kinetic energy was 5 MeV and sent to exterior observation, optical microscopy and tensile tests. Experiments revealed ion-irradiation generally makes tens of micrometers of deteriorated layer which is hardened and discolored on the surface of the specimens. According to dose, tensile properties such as tensile strength and elongation at break decrease generally. Tensile strength decrease is expected to ascribe to stress concentration on cracks of irradiation-damaged surface and rupture. Lead-contained glove, which is ordinarily used on highly  -radiative environments, saturates the decrease of its tensile strength around fluence of 1.4e+14 cm
-radiative environments, saturates the decrease of its tensile strength around fluence of 1.4e+14 cm . In addition, deterioration was accelerated for tension-loaded material and the saturation is around 4.6e+13 cm
. In addition, deterioration was accelerated for tension-loaded material and the saturation is around 4.6e+13 cm for 100%-extended specimens. The candidates of alternative new materials are two kinds of developed chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) and conductive rubber, which were experimented and tested in like manner. From the results and inherent properties of these materials, one kind of CSM and conductive rubber are relatively promising. Gloves used at low-dose environments and vinyl chloride applied for glove ports were also experimented and tested, and quantitative data were which are useful for life-elongation measure obtained. The irradiation tests on this report are unprecedented ones with low-energy ion, and the obtained quantitative data of material properties and deterioration are scientifically rare and important.
for 100%-extended specimens. The candidates of alternative new materials are two kinds of developed chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) and conductive rubber, which were experimented and tested in like manner. From the results and inherent properties of these materials, one kind of CSM and conductive rubber are relatively promising. Gloves used at low-dose environments and vinyl chloride applied for glove ports were also experimented and tested, and quantitative data were which are useful for life-elongation measure obtained. The irradiation tests on this report are unprecedented ones with low-energy ion, and the obtained quantitative data of material properties and deterioration are scientifically rare and important.
 Re]Organorhenium-labeled antibody fragments with renal enzyme-cleavable linkage for low renal radioactivity levels
Re]Organorhenium-labeled antibody fragments with renal enzyme-cleavable linkage for low renal radioactivity levelsUehara, Tomoya*; Koike, Miho*; Nakata, Hideo*; Hanaoka, Hirofumi*; Iida, Yasuhiko*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Akizawa, Hiromichi*; Endo, Keigo*; Arano, Yasushi*
Bioconjugate Chemistry, 18(1), p.190 - 198, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:57.65(Biochemical Research Methods)Renal localization of radiolabeled antibody fragments constitutes a problem in targeted imaging and radiotherapy. To estimate the applicability of the molecular design to metallic radionuclides, [ Re]tricarbonyl(cyclopentadienylcarbonate)rhenium ([
Re]tricarbonyl(cyclopentadienylcarbonate)rhenium ([ Re]CpTR-COOH) was conjugated with maleoyl-glycyl-lysine to prepare [
Re]CpTR-COOH) was conjugated with maleoyl-glycyl-lysine to prepare [ Re]CpTR-GK. The cleavage of the glycyl-lysine linkage of the compound generates a glycine conjugate of [
Re]CpTR-GK. The cleavage of the glycyl-lysine linkage of the compound generates a glycine conjugate of [ Re]CpTR-Gly. [
Re]CpTR-Gly. [ Re]CpTR-GK was conjugated to thiolated Fab fragments to prepare [
Re]CpTR-GK was conjugated to thiolated Fab fragments to prepare [ Re]CpTR-GK-Fab. The biodistribution of radioactivity after injection of [
Re]CpTR-GK-Fab. The biodistribution of radioactivity after injection of [ Re]CpTR-GK-Fab was compared with that of [
Re]CpTR-GK-Fab was compared with that of [ Re]CpTR-Fab. [
Re]CpTR-Fab. [ Re]CpTR-GK-Fab exhibited significantly lower renal radioactivity levels than did [
Re]CpTR-GK-Fab exhibited significantly lower renal radioactivity levels than did [ Re]CpTR-Fab. The analysis of urine samples collected for 6 h postinjection of [
Re]CpTR-Fab. The analysis of urine samples collected for 6 h postinjection of [ Re]CpTR-GK-Fab showed that [
Re]CpTR-GK-Fab showed that [ Re]CpTR-Gly was the major radiometabolite. In tumor-bearing mice, [
Re]CpTR-Gly was the major radiometabolite. In tumor-bearing mice, [ Re]CpTR-GK-Fab significantly reduced renal radioactivity levels without impairing the radioactivity levels in tumor. These findings indicate that the molecular design of radioparmaceuticals labeled with metallic radionuclides can be useful by using a radiometal chelate of high inertness and by designing a radiometabolite of high urinary excretion when released from antibody fragments following cleavage of a glycyl-lysine linkage. This study also indicates that a change in chemical structure of a radiolabel attached to a glycyl-lysine linkage significantly affected enzymes involved in the hydrolysis reaction.
Re]CpTR-GK-Fab significantly reduced renal radioactivity levels without impairing the radioactivity levels in tumor. These findings indicate that the molecular design of radioparmaceuticals labeled with metallic radionuclides can be useful by using a radiometal chelate of high inertness and by designing a radiometabolite of high urinary excretion when released from antibody fragments following cleavage of a glycyl-lysine linkage. This study also indicates that a change in chemical structure of a radiolabel attached to a glycyl-lysine linkage significantly affected enzymes involved in the hydrolysis reaction.
Oki, Koichi; Aoyama, Yoshio; Sukegawa, Yasuhiro*; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Sagawa, Hiroshi*; Hideo, Doi,*; Endo, Yasumi*
Waste Management 2005 Proceeding, CD-ROM, 8p., 8 Pages, 2005/03
We developed as a new technique to remove the influence of distance between radionuclides and detectors. We named the technique "the Facing Couple Method (FCM)". Partcality inspection which uses uranium source was parformed.Furthermore, the application possibility to a system was confirmed.
Oki, Koichi; Aoyama, Yoshio; Sukegawa, Yasuhiro*; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Sagawa, Hiroshi*; Hideo, Doi,*; Endo, Yasumi*
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (25), p.57 - 68, 2004/00
The system which measures and evaluates the quantity of uranium in the uranium contaminated waste in a large-sized container by NDA technology was manufactured.Practicality inspection which uses an uranium source was performed. Furthermore, the application possibility to a system was confirmed.
; Endo, Hideo; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Shinada, Masanori*;
JNC TN8440 2003-004, 24 Pages, 2003/05
The dissolution rate of high Pu content MOX fuel into the nitric acid was measured as a function of Pu content. MOX fuel sample which was pressed and sintered, were dissolved in boiling 7M nitric acid, and dissolution rate was measured by analysis of the Pu and U concentration in the solution. Dissolution rate of MOX fuel had the following tendencies : it decreased with increase of the Pu content and was reduced after 6 hours dissolution. These results agreed well to previous one, but dissolution rate was 3-6 times larger than that. It is estimated that the cause of this difference was due to the underestimate of surface area of MOX fuel powder and the difference of MOX O/M ratio.
Kato, Masato; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Endo, Hideo
JNC TN8400 2003-013, 48 Pages, 2003/05
JNC have been manufacturing MOX fuels from Plutonium and Uranium mixed oxide powder (1:1 MOX) that were prepared by microwave direct denitration method. It is well known that MOX raw material oxidize in storage and manufacturing process due to heat generation by self-radiation. The oxidation process and rate of MOX powder were examined for three kinds of powders having different surface area. The examination of isothermal and non-isothermal oxidation was carried out by TG-DTA. The oxidized samples were analyzed by X-ray diffraction measurement. The oxidation of MOX powders proceeded in two steps and the oxidation process changed depending on the surface area of the powder as follows. Process 1 (Surface Area : 2.24m /g) First Step : MO
/g) First Step : MO
 MO
MO
 MO
MO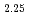 Second Step : MO
Second Step : MO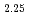
 MO
MO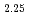 +M
+M O
O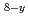 Process 2 (Surface Area : 5.59, 3.86m
Process 2 (Surface Area : 5.59, 3.86m /g) First Step : MO
/g) First Step : MO
 MO
MO +MO
+MO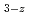
 MO
MO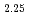 +MO
+MO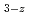 Second Step : MO
Second Step : MO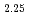 +MO
+MO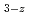
 MO
MO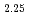 +M
+M O
O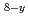 +MO
+MO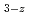 The kinetic analysis of the oxidation was evaluated by Avrami-Erofeev equation. The equation of O/M change on the MOX powder was obtained as function of temperature, keeping time and the surface area of the powder.
The kinetic analysis of the oxidation was evaluated by Avrami-Erofeev equation. The equation of O/M change on the MOX powder was obtained as function of temperature, keeping time and the surface area of the powder.
 I -Oxygen potential measurement of UO
I -Oxygen potential measurement of UO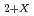 and (Pu
and (Pu U
U )O
)O
Kato, Masato; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Endo, Hideo
JNC TN8400 2002-020, 76 Pages, 2003/03
The ratio of oxygen to metal is one of important fuel specifications on UO and MOX fuels, because it effect on irradiation behavior. Oxygen potential of oxide fuels have been measured by various methods on the purpose of optimization of irradiation behavior and fabrication condition. In this repot the oxygen potential of UO
and MOX fuels, because it effect on irradiation behavior. Oxygen potential of oxide fuels have been measured by various methods on the purpose of optimization of irradiation behavior and fabrication condition. In this repot the oxygen potential of UO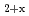 and (Pu
and (Pu U
U )O
)O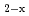 was measured by thermal gravimetry and differential thermal analysis (TG-DTA). Measurements of oxygen potential were carried out at 800
was measured by thermal gravimetry and differential thermal analysis (TG-DTA). Measurements of oxygen potential were carried out at 800 C, 1000
C, 1000 C and 1200
C and 1200 C in Ar/H
C in Ar/H /H
/H O mixture gas flow. Ratio of O/M was obtained from the weight change of the sample according to the partial oxygen pressure that was controlled by H
O mixture gas flow. Ratio of O/M was obtained from the weight change of the sample according to the partial oxygen pressure that was controlled by H /H
/H O ratio in atmosphere. The partial oxygen pressure in atmosphere was measured by stabilized zyrconia oxygen sensor. The experimental results agree approximately to the other works. Thermodynamic data,
O ratio in atmosphere. The partial oxygen pressure in atmosphere was measured by stabilized zyrconia oxygen sensor. The experimental results agree approximately to the other works. Thermodynamic data,  Go
Go ,
,  Ho
Ho ,
,  So
So , were evaluatedfrom the experimental data. The oxygen potential of UO
, were evaluatedfrom the experimental data. The oxygen potential of UO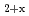 , (Pu,U)O
, (Pu,U)O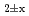 and PuO
and PuO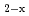 was modeled by lattice defect theory using the data of the literature and this work. The resulting equation well reproduce the large amount of oxygen potential-temperature-composition data for the Pu-U oxide system.
was modeled by lattice defect theory using the data of the literature and this work. The resulting equation well reproduce the large amount of oxygen potential-temperature-composition data for the Pu-U oxide system.
Kato, Masato; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Endo, Hideo
JNC TN8400 2002-019, 41 Pages, 2003/03
In Plutonium compounds the self-radiation induces expansion of lattice parameter and change in thermal conductivity. The expansion of the lattice parameter and thermal recovery of radiation damage in plutonium and uranium mixed dioxide (MOX) were studied in this paper. MOX powder had been kept in an ambient atmosphere for about two years. The lattice parameter of the powder was expanded up to about 0.23%. The change in lattice parameter was formulated as a function of amount of self-radiation. Three thermal recovery stage of radiation damage were observed in temperature ranges below 400 C, 400-800
C, 400-800 C and above 800
C and above 800 C. The recovery rate of three stages in total lattice expansion was about 25%, 55% and 20%, respectively, and activation energy in each recovery was estimated to be 0.14 eV 0.54 eV and 1.1 eV.
C. The recovery rate of three stages in total lattice expansion was about 25%, 55% and 20%, respectively, and activation energy in each recovery was estimated to be 0.14 eV 0.54 eV and 1.1 eV.

Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Nishiyama, Motokuni; Endo, Hideo; Kono, Shusaku; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Sugata, Hiromasa*
JNC TN8400 2003-011, 32 Pages, 2003/01
MOX fuel containing Neptunium is being developed as candidate fuel for an advanced nuclear fuel recycle. In this report, influence of Np on the sintering behavior, phase separation behavior of MOX fuel pellets and the homogeneity of MOX fuel pellets were evaluated. It was observed that the high Np containing pellets had a low sintered density and the microstructure changes of the pellets during the sintering were slow compared with MOX without Np. The pellets were also analyzed via Ceramography, X-ray diffraction measurement and an electron probe microanalysis. The phase separation behavior of MOX with Np was similar to that of MOX. The homogeneity of the pellet produced with this experiment was acceptable to the fuel specification.
Hamada, Kazuya; Nakajima, Hideo; Okuno, Kiyoshi; Endo, Sakaru*; Kikuchi, Kenichi*; Kubo, Yoshio*; Aoki, Nobuo*; Yamada, Yuichi*; Osaki, Osamu*; Sasaki, Takashi*; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2002-027, 23 Pages, 2002/03
The Engineering Design Activities (EDA) for the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) was performed under the collaboration of Japan, EU, Russia and the US. The EDA was successfully completed in July 2001, in which the development of fabrication technology for advanced components, such as superconducting coils, was conducted. The ITER magnet system consists of Toroidal Field coils, a Central Solenoid (CS), Poloidal Field coils and Correction coils. The construction of these coils requires advanced technologies that fairly exceeded those available at the start of the EDA. Therefore, CS Model Coil and TF Model Coil projects were implemented. To fabricate the CS Model Coil, the fabrication technologies for high performance strand, large cable, winding, heat treatment, joint and insulation are indispensable. This report describes the above detailed fabrication technologies successfully developed in the CS Model Coil Project.
Nishimura, Kazuhisa; Shoji, Shuichi*; ; Sato, Seiichi*; ; Endo, Hideo
JNC TN8430 2001-005, 64 Pages, 2001/09
The external gelation process is one of the candidates of MOX particle fuel fabrication for advanced recycle system. It was necessary to perform preliminary fuel fabrication with uranium before starting MOX tests. As the result of the preliminary examination, Basics conditions of the fabrication were obtained: (1)Optimized uranyl nitrate solution and PVA solution, as raw materials were prepared. (2)The frequency of vibration and the amount of flow were obtained with optimized broth (mixture) in the vibration dropping process. (3)The influence of composition of broth and concentration of ammonia solution on gelation process was obtained. (4)Impurities after aging, washing and drying spHerical gel were surveyed, (5)The spherical gel were calcined to oxide particles and the particles were characterized by TG-DTA, therefore it is certain that outlook on the sintered particles as final products is very clear. On the top of that, there were no fatal technicalities of the external gelation process through material balance and a diameter dispersion of spherical gel and oxide particles. It is necessary to perform uranium examination to solve some new problems, for instant, surface crack of spherical gel. Although almost of all the preparations are completed and fabrication examination of MOX particles with vibration dropping equipment are ready for starting.
Endo, Hideo; Seki, Masayuki; ; ;
JNC TN8410 2001-004, 45 Pages, 2001/02
(1)Purpose. Mechanical strength in the position welded by resistance welding system was examined in 1999. The test specimens were destroyed in the welding position in a shorter time than expected in the creep tsst. Therefore, test specimens were prepared to evaluate the cause of destruction. (2)Procedure. Inner-pressure enclosed creep test specimens were prepared by resistance welding method. Cladding material with low deviation of thickness and high re-crystallization rate was used. Heat treatment after resistance welding was performed to remove the influence of residual stress and the precipitation of carbides. (3)Summary of result. (a)Before preparation of specimens, the welding condition was fixed. Three test specimens were prepared. Two specimens without heat treatment were transported to MMS in Oarai Engineering Center on Aug, 4, 2000. One specimen with heat treatment was transported to MMS after evaluating the residual stress to get optimum heat treatment condition. (b)Specimens were prepared with welding end plugs to both ends of ferritic ODS cladding. Enclosing sides were welded with highly strong Ferritic/Martensitic steel end plugs. The other sides were welded with ferritic ODS end plugs. (3)Some kinds of electrical wave data were obtained during performing welding. position was evaluated with supersonic detector after performing welding. (4)Mechanical strength of welding position in high temperature 800 C was confirmed to be equal to or larger than that of cladding material. (4)Conclusion. The highly qualified specimens in the present were successfully prepared.
C was confirmed to be equal to or larger than that of cladding material. (4)Conclusion. The highly qualified specimens in the present were successfully prepared.
Shigetome, Yoshiaki; ; ; ; Endo, Hideo
JNC TN8400 2000-023, 84 Pages, 2000/07
This report presents the results of vibration packing experiments and computational simulations of particle compaction behavior. Both sphere and shard particles were evaluated in these works. Experiments with simulated fuel palticles were conducted to investigate the factors affecting packing behavior. The factors are classified into geometrical and dynamics factors. With regard to the geometrical factors for sphere packing, the experimental results prove that the achievablc packing fraction can be predicted by the equation derived by Ayer, which is relationship of inner diameter of cladding and diameters of particles. As for the dynamics factors, less vibration displacement is preferable, because it produccs faster packing with less segregation. Similar experiments were conducted for the shard particles. The results indicate the packing characteristics of the shard particles are different from the sphere particles. Optimum weight ratio between particle sizes is different from the ratio given by Ayer's equation. As for the dynamics factors, the sweeping frequencies while packing were sufficient to obtain high packing fraction. Computational simulations were performed to investigate the particle behavior while packing. The movement of infiltrating and bed particles while packing was well understood.
Endo, Hideo; Seki, Masayuki; ; ;
JNC TN8410 2000-007, 89 Pages, 2000/03
(1)Outline of examination. Various test specimens were made to evaluate and confirm the weld strength properties of the oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) cladding tube material (martensitic and ferritic steel), which had been manufactured in JFY 1997. The examination consisted of tensile tests (RT,650 C, 700
C, 700 C, 800
C, 800 C), internal pressure creep tests, internal pressure burst tests, and a rapid heating burst tests. (2)Examination results. The results of the tensile tests are as follows: (ferritic and martensitic) (a)All test specimens from RT to 700
C), internal pressure creep tests, internal pressure burst tests, and a rapid heating burst tests. (2)Examination results. The results of the tensile tests are as follows: (ferritic and martensitic) (a)All test specimens from RT to 700 C failed in the tube. The weld zones had not failed. (b)The test specimens at 800
C failed in the tube. The weld zones had not failed. (b)The test specimens at 800 C failed in the weld zones. There was little elongation. (ferritic) (a)The weld zone had fine grain structure and carbide precipitates. (martensitic) (a)Carbide had precipitated in the weld zone. From these results, the strength of weld zone decreased extremely at temperatures exceeding the endurance limit (700
C failed in the weld zones. There was little elongation. (ferritic) (a)The weld zone had fine grain structure and carbide precipitates. (martensitic) (a)Carbide had precipitated in the weld zone. From these results, the strength of weld zone decreased extremely at temperatures exceeding the endurance limit (700 C) All of the internal pressure burst test specimens and the rapid heating burst test specimens failed in the tube and not the weld zone. (3)The quality assurance method of the test specimens. The weld reliability of the test specimens were confirmed by the process control of the welding conditions, by using control test specimens, and ultrasonic testing. Confirmation of the process control of the welding conditions; current wave, the voltage waveform, the accelerogram, and the displacement ripple in the welding process was recorded to assure an abnormal value had not occurred. (Process control of welding condition) The results the current waveform, voltage waveform, accelerogram, and the displacement waveform were excellent. (test specimens) The weld joint was excellent based on metallography examination. (Ultrasonic testing) The length of the weld joint was measured and found to be adequate. The reliability the weld joint can be assured by using the above-mentioned method.
C) All of the internal pressure burst test specimens and the rapid heating burst test specimens failed in the tube and not the weld zone. (3)The quality assurance method of the test specimens. The weld reliability of the test specimens were confirmed by the process control of the welding conditions, by using control test specimens, and ultrasonic testing. Confirmation of the process control of the welding conditions; current wave, the voltage waveform, the accelerogram, and the displacement ripple in the welding process was recorded to assure an abnormal value had not occurred. (Process control of welding condition) The results the current waveform, voltage waveform, accelerogram, and the displacement waveform were excellent. (test specimens) The weld joint was excellent based on metallography examination. (Ultrasonic testing) The length of the weld joint was measured and found to be adequate. The reliability the weld joint can be assured by using the above-mentioned method.