Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamaguchi, Taiki; Kawano, Yasunori; Fujieda, Hirobumi; Kurihara, Kenichi; Sugihara, Masayoshi*; Kusama, Yoshinori
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 50(4), p.045004_1 - 045004_15, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:36.93(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We have studied the viewing chord arrangement of the poloidal polarimeter in the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER). We have optimized the viewing chord arrangement based on the evaluation using a magnetohydrodynamic equilibrium reconstruction code. This reconstruction code has been developed in this study. We have successfully optimized viewing chord arrangements for three equilibria of the ITER operation scenario. The accuracy of the central safety factor within 3% has been achieved in each case. Furthermore, the viewing chord arrangement, which is optimized for the inductive operation scenario II at the start of the burn phase (S2-SOB), has been applied for other equilibria. As the result, the accuracy has not deteriorated drastically compared with the accuracy which is evaluated using the optimized arrangement for each equilibrium. The viewing chord arrangement for S2-SOB is proposed as the most promising candidate of the ITER poloidal polarimeter.
Yamaguchi, Taiki; Kawano, Yasunori; Fujieda, Hirobumi; Kurihara, Kenichi; Sugihara, Masayoshi*; Kusama, Yoshinori
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 50(4), p.045004_1 - 045004_15, 2008/04
The poloidal polarimeter will be installed in the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) to measure the safety factor profile. The number of viewing chords is restricted to about 15 channels. Therefore optimization of the viewing chord arrangement is necessary to diagnose the accurate safety factor profile. In this study, we studied the optimum viewing chord arrangement for the equilibria of ITER operation scenarios using the equilibrium reconstruction. For the burning phase of inductive scenario, the error of the safety factor on the magnetic axis was 35% if the viewing chords are not arranged in the peripheral region. It was improved to 3% by arranging the viewing chord of the upper port to peripheral region. This arrangement was used for the reconstruction of the burning phase in the noninductive scenario and of the phase of the plasma current 3.5 MA in the inductive operation scenario. As the result, the accuracy does not decrease drastically.
Fujieda, Hirobumi; Sugihara, Masayoshi*; Shimada, Michiya; Gribov, Y.*; Ioki, Kimihiro*; Kawano, Yasunori; Khayrutdinov, R.*; Lukash, V.*; Omori, Junji; Neyatani, Yuzuru
JAEA-Research 2007-052, 115 Pages, 2007/07
Impacts of plasma disruptions on ITER have been investigated to confirm the robustness of the design of the machine to the potential consequential loads. The loads include both electro-magnetic (EM) and heat on the in-vessel components and the vacuum vessel. Several representative disruption scenarios are specified. Disruption simulations with the DINA code and EM load analyses with a 3D finite element method code are performed for these scenarios. Some margins are confirmed in the EM load. Heat load on the first wall due to the vertical movement and the thermal quench (TQ) is calculated with a 2D heat conduction code. For vertical displacement event, beryllium (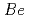 ) wall will not melt during the vertical movement, prior to the TQ. Significant melting is anticipated for the upper
) wall will not melt during the vertical movement, prior to the TQ. Significant melting is anticipated for the upper 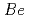 wall and tungsten baffle due to the TQ after the vertical movement. However, its impact could be mitigated by implementing a reliable detection system of the vertical movement and a mitigation system.
wall and tungsten baffle due to the TQ after the vertical movement. However, its impact could be mitigated by implementing a reliable detection system of the vertical movement and a mitigation system.
Shimada, Michiya; Sugihara, Masayoshi; Fujieda, Hirobumi*; Gribov, Y.*; Ioki, Kimihiro*; Kawano, Yasunori; Khayrutdinov, R.*; Lukash, V.*; Omori, Junji
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Several representative disruption scenarios are specified and disruption simulations are performed with the DINA code and EM load analyses with the 3D FEM code for these scenarios based on newly derived physics guidelines. Although some margin is confirmed in the EM loads due to induced eddy and halo currents on the in-vessel components for all of the representative scenarios, but the margin is not large. The heat load on various parts of the first wall due to vertical movements and thermal quenches is calculated. The beryllium wall will not melt during vertical movement. Melting is anticipated at the thermal quench during a VDE, though its impact could be reduced substantially by implementing a reliable detection and mitigation system, e.g., massive gas injection. With unmitigated disruptions, the loss of beryllium layer is expected to be within 30  m/event out of 10 mm thick beryllium first wall.
m/event out of 10 mm thick beryllium first wall.
Sato, Masayasu; Sakurai, Shinji; Nishio, Satoshi; Tobita, Kenji; Inoue, Takashi; Nakamura, Yukiharu; Shinya, Kichiro*; Fujieda, Hirobumi*; DEMO Plant Design Team
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1277 - 1284, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:66.95(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Lukash, V.*; Sugihara, Masayoshi; Gribov, Y.*; Fujieda, Hirobumi*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 47(12), p.2077 - 2086, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:32.92(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Vertical directions of plasma movement after the thermal quench (TQ) of major disruptions in ITER are investigated using the predictive mode of the DINA code. Three dominant parameters in determining the direction of plasma movement are identified; (1) the rate of plasma current quench, (2) change of the internal plasma inductance li associated with the TQ and (3) the initial vertical position of plasma column before the TQ. It is shown that the reference ITER plasma moves upward after the TQ, if the current quench rate is higher than 200kA/ms and the drop of li does not exceed 0.2 for the present reference initial vertical position (55.5 cm above the center of machine).
Senda, Ikuo*; Fujieda, Hirobumi; Neyatani, Yuzuru; Tada, Eisuke; Shoji, Teruaki
JAERI-Data/Code 2003-012, 73 Pages, 2003/07
The tokamak transient simulation code, named SAFALY, was revised recently and the sensitivity analyses on the parameters in the code were carried out. This report is composed of two volumes. The formulation and the parameters in modeling the plasma and in-vessel components are described in the first volume. In this second volume, the results of the sensitivity studies are reported. The sensitivity studies were performed in two steps. In the first step, the responses of plasmas in the occurrence of plasma disturbances were analyzed for various initial conditions. For each disturbance, the initial condition of the plasma, which gave the largest increase of the fusion power, was identified. In the second step, by using initial conditions derived in the first step, the sensitivities of plasma reactions with respect to variation of the parameters in SAFALY code were analyzed. In the analyses, the increase of the fueling, the increase of the plasma confinement improvement factor and the increase of the auxiliary heating power were considered as plasma disturbances.
Senda, Ikuo*; Fujieda, Hirobumi; Neyatani, Yuzuru; Tada, Eisuke; Shoji, Teruaki
JAERI-Data/Code 2003-008, 37 Pages, 2003/06
Tokamak transient simulation code, named SAFALY, was revised. SAFALY code has been developed to simulate transient events in Tokamaks. Modeling of the plasma and algorithms of the simulation were revised. The code was also modified to deal with the variation of the plasma current. The code was improved to allow flexible modeling of in-vessel components. The data transfer between SAFALY and related codes was arranged to prepare data required in analyses with SAFALY, such as the distributions of heat/neutron loads and the radiation form factor between in-vessel components. The report is composed of two volumes. The formulation and the parameters in modeling plasma and in-vessel components are described in this first volume. Examples of simulation results, using the design of ITER-FDR in 2001, are presented and general properties of plasmas' responses with respect to perturbations are discussed. The results of the sensitivity studies with respect to simulation parameters and initial conditions will be reported in the second volume.
Senda, Ikuo*; Shoji, Teruaki; Tsunematsu, Toshihide; ; Fujieda, Hirobumi*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 42, p.395 - 399, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Senda, Ikuo*; Shoji, Teruaki; Tsunematsu, Toshihide; ; Fujieda, Hirobumi*
Nuclear Fusion, 37(8), p.1129 - 1145, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:33.08(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Tobita, Kenji; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Harano, Hideki*; Nishitani, Takeo; Kusama, Yoshinori; Kimura, Haruyuki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Fujieda, Hirobumi*; Shoji, Teruaki; Senda, Ikuo*; et al.
Proc. of 5th IAEA Technical Committee Meeting on Alpha Particles in Fusion Research, p.45 - 48, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Senda, Ikuo*; Shoji, Teruaki; ; Fujieda, Hirobumi*; Tsunematsu, Toshihide
JAERI-Tech 96-016, 23 Pages, 1996/03
no abstracts in English
Senda, Ikuo*; Shoji, Teruaki; Nishio, Satoshi; Tsunematsu, Toshihide; ; Fujieda, Hirobumi*
JAERI-Data/Code 95-010, 32 Pages, 1995/08
no abstracts in English
Senda, Ikuo*; Nishio, Satoshi; Tsunematsu, Toshihide; ; Fujieda, Hirobumi*
JAERI-Tech 94-018, 56 Pages, 1994/09
no abstracts in English
; Fujieda, Hirobumi*; Tsunematsu, Toshihide
JAERI-M 94-080, 151 Pages, 1994/06
no abstracts in English
Fujieda, Hirobumi*; ; Sugihara, Masayoshi
JAERI-M 92-178, 133 Pages, 1992/11
no abstracts in English
; Fujieda, Hirobumi*; Itami, Kiyoshi; Sugihara, Masayoshi
JAERI-M 92-145, 46 Pages, 1992/09
no abstracts in English
Takechi, Manabu; Fujieda, Hirobumi*; Sakurai, Shinji; Masaki, Kei; Shibama, Yusuke; Matsunaga, Go; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Sakasai, Akira
no journal, ,
We performed the evaluation of over current of poloidal coils and EM force of in-vessel coils with DINA code during disruption for design of in-vessel components of JT-60SA. We performed disruption simulation for the case of upward and downward VDE and major disruption of 5.5MA plasmas at end of burn. The maximum induced current of poloidal coils is about 1.7kA. It is found that amplitude of induced current does not depend on the direction of the plasma movement at disruption and current quench time. EM force of the fast position control coil with 24 turns is 1.2 times larger than that with 16 turns.
Takechi, Manabu; Matsunaga, Go; Kurita, Genichi; Sakurai, Shinji; Fujieda, Hirobumi*; Ide, Shunsuke; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Bolzonella, T.*; Ferro, A.*; Novello, L.*; et al.
no journal, ,
One of the important missions of JT-60SA is to demonstrate and develop steady-state high beta operation in order to supplement ITER toward DEMO. Specifications of plasma control system including the stabilizing plate, the RWM control coils, the error field correction coils and fast position control coils were determined based on simulations and expected plasma regime. Full non-inductive steady-state plasma with 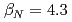 at
at 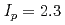 MA will be achieved with these control systems. Simulation of plasma disruption was also performed to evaluate design values of Electro Magnetic forces of components.
MA will be achieved with these control systems. Simulation of plasma disruption was also performed to evaluate design values of Electro Magnetic forces of components.
Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Miyamoto, Seiji; Fujieda, Hirobumi; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kusama, Yoshinori; Yoshino, Ryuji
no journal, ,
In tokamak fusion reactors with superconducting PF coil system, ramping-up of the plasma current for startup of discharges is essentially restrained at a rate much slower than the current tokamak with normal PF conductors. Therefore, the induced plasma current can penetrate deeply into the core region with higher electron temperature, i.e. low Ohmic resistivity, leading to a centrally peaked current profile. Consequently, such the high li, highly elongated configuration imperative to divertor formation has the dangerous property of causing vertical instability. Additional heating at early phase of the ramp-up has been addressed as one of startup procedures that retard the penetration of plasma current. A potential drawback, however, is the substantial increase of direct heat load to limiter. Hence, it follows that discharge optimization, e.g. timing of the heating, has been critical to plasma formation during the startup phase. The feasible ramp-up scenario to obtain a stable current profile while increasing bootstrap current fraction is discussed, as well as the interests: how quickly the plasma current needs to be ramped up and how slowly it can be.