Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsushita, Taiki*; Ozawa, Akihiro*; Araki, Yasufumi; Fujimoto, Junji*; Sato, Masatoshi*
Physical Review B, 111(24), p.245131_1 - 245131_11, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0Nozaki, Yukio*; Sukegawa, Hiroaki*; Watanabe, Shinichi*; Yunoki, Seiji*; Horaguchi, Taisuke*; Nakayama, Hayato*; Yamanoi, Kazuto*; Wen, Z.*; He, C.*; Song, J.*; et al.
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 26(1), p.2428153_1 - 2428153_39, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yamanoi, Kazuto*; Sakakibara, Yuri*; Fujimoto, Junji*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Nozaki, Yukio*
Applied Physics Express, 16(6), p.063004_1 - 063004_6, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Fujimoto, Junji*; Funaki, Hiroshi*; Koshibae, Wataru*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Maekawa, Sadamichi*
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 58(8), p.1500407_1 - 1500407_7, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:27.91(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Komatsu, Yuya*; Shimizu, Ryota*; Sato, Ryuhei*; Wilde, M.*; Nishio, Kazunori*; Katase, Takayoshi*; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Miyauchi, Masahiro*; Adelman, J. R.*; et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 34(8), p.3616 - 3623, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:75.48(Chemistry, Physical)Fujimoto, Junji*; Koshibae, Wataru*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Physical Review B, 103(22), p.L220402_1 - L220402_5, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:46.19(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Al
Al Ga
Ga O
O scintillators by gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy
scintillators by gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopyFujimori, Kosuke*; Kitaura, Mamoru*; Taira, Yoshitaka*; Fujimoto, Masaki*; Zen, H.*; Watanabe, Shinta*; Kamada, Kei*; Okano, Yasuaki*; Kato, Masahiro*; Hosaka, Masahito*; et al.
Applied Physics Express, 13(8), p.085505_1 - 085505_4, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:29.86(Physics, Applied)To clarify the existence of cation vacancies in Ce-doped Gd Al
Al Ga
Ga O
O (Ce:GAGG) scintillators, we performed gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (GiPALS). GiPAL spectra of GAGG and Ce:GAGG comprised two exponential decay components, which were assigned to positron annihilation at bulk and defect states. By an analogy with Ce:Y
(Ce:GAGG) scintillators, we performed gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (GiPALS). GiPAL spectra of GAGG and Ce:GAGG comprised two exponential decay components, which were assigned to positron annihilation at bulk and defect states. By an analogy with Ce:Y Al
Al O
O , the defect-related component was attributed to Al/Ga-O divacancy complexes. This component was weaker for Ce, Mg:GAGG, which correlated with the suppression of shallow electron traps responsible for phosphorescence. Oxygen vacancies were charge compensators for Al/Ga vacancies. The lifetime of the defect-related component was significantly changed by Mg co-doping. This was understood by considering aggregates of Mg
, the defect-related component was attributed to Al/Ga-O divacancy complexes. This component was weaker for Ce, Mg:GAGG, which correlated with the suppression of shallow electron traps responsible for phosphorescence. Oxygen vacancies were charge compensators for Al/Ga vacancies. The lifetime of the defect-related component was significantly changed by Mg co-doping. This was understood by considering aggregates of Mg ions at Al/Ga sites with oxygen vacancies, which resulted in the formation of vacancy clusters.
ions at Al/Ga sites with oxygen vacancies, which resulted in the formation of vacancy clusters.
Fujimoto, Junji*; Matsuo, Mamoru
Physical Review B, 102(2), p.020406_1 - 020406_5, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:19.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Fujimoto, Junji*; Matsuo, Mamoru
Physical Review B, 100(22), p.220402_1 - 220402_5, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:3.89(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)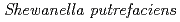
Fujimoto, Jun*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Watanabe, Naoko*; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Hydrometallurgy, 166, p.80 - 86, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:32.09(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)We examined recovery of REEs in Fe-Mn nodules by using 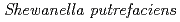 (Fe-reducing bacterium). In this method, Fe-Mn nodule decomposition and REE recovery were achieved simultaneously in a single solution system. Fe-Mn nodules were reductively decomposed in NaCl solution under anaerobic conditions with daily addition of sodium lactate as an electron donor. During the decomposition of Fe-Mn nodule, REEs released from the Fe-Mn nodule were adsorbed on bacterial cells. Of the conditions studied here, the best REE adsorption rates were obtained with 0.5M NaCl solution at pH7 with daily addition of 1 mmol sodium lactate.
(Fe-reducing bacterium). In this method, Fe-Mn nodule decomposition and REE recovery were achieved simultaneously in a single solution system. Fe-Mn nodules were reductively decomposed in NaCl solution under anaerobic conditions with daily addition of sodium lactate as an electron donor. During the decomposition of Fe-Mn nodule, REEs released from the Fe-Mn nodule were adsorbed on bacterial cells. Of the conditions studied here, the best REE adsorption rates were obtained with 0.5M NaCl solution at pH7 with daily addition of 1 mmol sodium lactate.
 and
and  cross sections of the
cross sections of the  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction at
O reaction at 
 1.2 MeV using pulsed
1.2 MeV using pulsed  beams
beamsMakii, Hiroyuki; Ueda, Hitoshi*; Temma, Yasuyuki*; Nagai, Yasuki*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Fujimoto, Shinya*; Segawa, Mariko; Mishima, Kenji*; Nishiyama, Jun*; Igashira, Masayuki*
AIP Conference Proceedings 1269, p.283 - 288, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction cross section plays an important role in stellar evolution at the stage of helium-burning. However, the cross section at low energy still has a large uncertainty mainly due to the poor determination of the ratio of
O reaction cross section plays an important role in stellar evolution at the stage of helium-burning. However, the cross section at low energy still has a large uncertainty mainly due to the poor determination of the ratio of 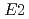 cross section to
cross section to  one. Hence, we have installed new system to make a precise measurement of the cross section. In this experiment, we used the high efficiency anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometers with a large S/N ratio, an intense pulsed
one. Hence, we have installed new system to make a precise measurement of the cross section. In this experiment, we used the high efficiency anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometers with a large S/N ratio, an intense pulsed  beams, and the monitoring system of target thickness. With use of the system we succeeded in removing a background due to neutron and could clearly detect the
beams, and the monitoring system of target thickness. With use of the system we succeeded in removing a background due to neutron and could clearly detect the  -ray from the
-ray from the  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction with high statistics. We determined the
O reaction with high statistics. We determined the  and
and 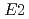 cross section down to
cross section down to 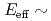 1.2 MeV, and thus obtained results are compared to recent theoretical calculations.
1.2 MeV, and thus obtained results are compared to recent theoretical calculations.
Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Kikuchi, Takayuki; Ishihara, Masahiro; Iyoku, Tatsuo; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Fujimoto, Nozomu
JAEA-Data/Code 2007-001, 57 Pages, 2007/02
Visual inspection by a TV camera and material properties measurement by surveillance test on core support graphite structures are planned for the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) to confirm their structural integrity and characteristics. The surveillance test is aimed to investigate the change of material and mechanical properties by aging effects such as fast neutron irradiation and oxidation. The obtained data will be used not only for evaluating the structural integrity of the core support graphite structure of the HTTR but also for design data to advanced Very High Temperature Reactor (VHTR) discussed at generation IV international forum. This report describes the material properties and installed position of surveillance specimens in the HTTR in order to carry out the surveillance test.
Tochio, Daisuke; Sumita, Junya; Takada, Eiji*; Fujimoto, Nozomu; Nakagawa, Shigeaki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 5(1), p.57 - 67, 2006/03
High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor(HTTR) of high temperature gas-cooled reactor at Japan Atomic Energy Agency(JAEA) achieved the reactor outlet coolant temperature of 950 C for the first time in the world at Apr. 19, 2004. To ensure the thermal integrity of fuel in high temperature test operation, it is necessary that fuel temperature is designed appropriately by fuel temperature designing method, and that estimated maximum fuel temperature is lower than the thermal limit temperature. In this report, by constructing newly a realistic core-shape representing model, the current fuel temperature estimation model is improved. Moreover fuel temperature in high-temperature test operation is estimated with the newly-constructed model, and it is confirmed that estimated maximum fuel temperature in high temperature test operation is lower than the thermal limit temperature.
C for the first time in the world at Apr. 19, 2004. To ensure the thermal integrity of fuel in high temperature test operation, it is necessary that fuel temperature is designed appropriately by fuel temperature designing method, and that estimated maximum fuel temperature is lower than the thermal limit temperature. In this report, by constructing newly a realistic core-shape representing model, the current fuel temperature estimation model is improved. Moreover fuel temperature in high-temperature test operation is estimated with the newly-constructed model, and it is confirmed that estimated maximum fuel temperature in high temperature test operation is lower than the thermal limit temperature.
Fujimoto, Tetsuro*; Sato, Kazujiro*; Takahashi, June*
PNC TN951 76-14, 59 Pages, 1976/09
The 4,800-hours flow test for MONJU dummy core fuel subassemblies was carried out at sodium flow rate of 19.5 - 20.2 kg/sec. subassembly, sodium temperature of 600 , oxygen impurities in sodium of 2 - 2.5ppm which are about the same condition as that for MONJU core fuel subassemblies. The result of this test showed that the pressure loss of dummy core fuel subassemblies increased up to 11% in 3,000 hours and became constant after that. The integrity of the dummy subassemblies is planned to be investigated by disassembling them and making a material examination. On the other hand,the pressure loss increase for these subassembkies was estimated at 5.4% in case of water flow test which was carried out before and after spdium test. The cause of this difference should be investigated hereafter.
, oxygen impurities in sodium of 2 - 2.5ppm which are about the same condition as that for MONJU core fuel subassemblies. The result of this test showed that the pressure loss of dummy core fuel subassemblies increased up to 11% in 3,000 hours and became constant after that. The integrity of the dummy subassemblies is planned to be investigated by disassembling them and making a material examination. On the other hand,the pressure loss increase for these subassembkies was estimated at 5.4% in case of water flow test which was carried out before and after spdium test. The cause of this difference should be investigated hereafter.
Taira, Yoshitaka*; Fujimoto, Masaki*; Fujimori, Kosuke*; Kitaura, Mamoru*; Zen, H.*; Okano, Yasuaki*; Hosaka, Masahito*; Yamazaki, Junichiro*; Kato, Masahiro*; Hirade, Tetsuya; et al.
no journal, ,
For general positron sources, radioisotopes such as  Na are often used. However, there is a problem that positrons cannot probe the deep region of metal materials with a thickness of 1 mm or more. Gamma-ray induced positron annihilation lifetime measurement (GiPALS) is a method for generating positrons in bulk samples with a thickness of several centimeters and samples placed in vessels such as high temperature and/or pressure furnaces. The annihilation lifetime of positrons is about 200 ps for metal materials, so it is important to use gamma rays with a shorter pulse width for GiPALS in order to accurately measure the positron lifetime. We have succeeded in the proof-of-principle experiment for GiPALS of ultra-short pulse gamma rays with a pulse width of 2 ps, which was originally developed using 90
Na are often used. However, there is a problem that positrons cannot probe the deep region of metal materials with a thickness of 1 mm or more. Gamma-ray induced positron annihilation lifetime measurement (GiPALS) is a method for generating positrons in bulk samples with a thickness of several centimeters and samples placed in vessels such as high temperature and/or pressure furnaces. The annihilation lifetime of positrons is about 200 ps for metal materials, so it is important to use gamma rays with a shorter pulse width for GiPALS in order to accurately measure the positron lifetime. We have succeeded in the proof-of-principle experiment for GiPALS of ultra-short pulse gamma rays with a pulse width of 2 ps, which was originally developed using 90 collision laser Compton scattering at UVSOR.
collision laser Compton scattering at UVSOR.
Taira, Yoshitaka*; Fujimoto, Masaki*; Fujimori, Kosuke*; Kitaura, Mamoru*; Zen, H.*; Okano, Yasuaki*; Hosaka, Masahito*; Yamazaki, Junichiro*; Kato, Masahiro*; Hirade, Tetsuya; et al.
no journal, ,
For general positron sources, radioisotopes such as  Na are often used. However, there is a problem that positrons cannot probe the deep region of metal materials with a thickness of 1 mm or more. Gamma-ray induced positron annihilation lifetime measurement (GiPALS) is a method for generating positrons in bulk samples with a thickness of several centimeters and samples placed in vessels such as high temperature and/or pressure furnaces. The annihilation lifetime of positrons is about 200 ps for metal materials, so it is important to use gamma rays with a shorter pulse width for GiPALS in order to accurately measure the positron lifetime. We have succeeded in the proof-of-principle experiment for GiPALS of ultra-short pulse gamma rays with a pulse width of 2 ps, which was originally developed using 90
Na are often used. However, there is a problem that positrons cannot probe the deep region of metal materials with a thickness of 1 mm or more. Gamma-ray induced positron annihilation lifetime measurement (GiPALS) is a method for generating positrons in bulk samples with a thickness of several centimeters and samples placed in vessels such as high temperature and/or pressure furnaces. The annihilation lifetime of positrons is about 200 ps for metal materials, so it is important to use gamma rays with a shorter pulse width for GiPALS in order to accurately measure the positron lifetime. We have succeeded in the proof-of-principle experiment for GiPALS of ultra-short pulse gamma rays with a pulse width of 2 ps, which was originally developed using 90 collision laser Compton scattering at UVSOR.
collision laser Compton scattering at UVSOR.
 edges on the Heusler alloy Co
edges on the Heusler alloy Co MnSi
MnSiFujiwara, Hidenori*; Kogo, Junya*; Kasahara, Rika*; Nishioka, Takuma*; Fujimoto, Nao*; Nagai, Kodai*; Sekiyama, Akira*; Sumida, Kazuki; Takeda, Yukiharu; Saito, Yuji; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsushita, Taiki*; Ozawa, Akihiro*; Araki, Yasufumi; Fujimoto, Junji*; Sato, Masatoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English