Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nemoto, Takahiro; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Arakawa, Ryoki; Choyama, Yuya; Nagasumi, Satoru; Hasegawa, Toshinari; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Watanabe, Masashi; Onishi, Takashi; Kawamoto, Taiki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-003, 17 Pages, 2024/06
In order to investigate the cause of the increase in differential pressure in the primary helium circulator filter that occurred during the RS-14 cycle, a clogged filter was investigated. As a result of the investigation, deposits caused by silicone oil were confirmed on the surface of the filter element. These results revealed that the cause of filter clogging was silicone oil mixed into the primary system due to performance deterioration of the charcoal filter in the gas circulator of primary helium purification system. As a measure to prevent the recurrence of this event, in addition to the conventional management based on operating hours for replacing of charcoal filter in the gas circulator of primary helium purification system, we have established a new replacement plan for every three years.
Hasegawa, Toshinari; Nagasumi, Satoru; Nemoto, Takahiro; Nakajima, Kunihiro; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Arakawa, Ryoki; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Kawamoto, Taiki
Proceedings of 2024 International Congress on Advanced in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2024) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/06
The filter element of the primary gas circulators (PGC) in High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) and its deposits were investigated by Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) observation and Energy Dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) analysis to find the cause of the increase of the filter differential pressure during the operation in 2021. SEM observation showed that the clumpy deposits and fibrous deposits smaller than the filtration pore size and the rod-shaped deposits larger than the pore size were present on the filter element. EDX analysis showed that the clumpy deposits and fibrous deposits could include silicone oil in the primary helium purification system (PHPS) gas circulators and that the rod-shaped deposits were thermal insulators inside of the co-axial double pipes in the primary cooling system. It is considered that silicone oil leaked from the PHPS gas circulators due to deterioration in the absorption performance of the activated charcoal filter. Next, it could be vaporized and reach PGC's filter element after passing through the reactor core. Since those deposits including silicone oil were present over the entire surface of the filter element, the filter differential pressure could be increased due to a reduction in the pore size and a rise in its flow resistance. The thermal insulator was unrelated to filter clogging because it was present mainly in the lower part of the filter element. Therefore, silicone oil could increase the filter differential pressure, and the graphite powder, which is the cause of the previous issue was unrelated.
 Ge
Ge
Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Aratani, Hidekazu*; Kanai-Nakata, Yuina*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Hamamoto, Satoru*; Kiss, Takayuki*; Sekiyama, Akira*; Tanaka, Arata*; Ebihara, Takao*; et al.
New Physics; Sae Mulli, 73(12), p.1062 - 1066, 2023/12
 symmetry for anisotropic
symmetry for anisotropic 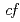 hybridization in the heavy-fermion superconductor CeNi
hybridization in the heavy-fermion superconductor CeNi Ge
Ge
Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Aratani, Hidekazu*; Kanai-Nakata, Yuina*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Hamamoto, Satoru*; Kiss, Takayuki*; Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Higashiya, Atsushi*; Imada, Shin*; et al.
Physical Review B, 108(16), p.165121_1 - 165121_10, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Furuike, Yoshihiko*; Ouyang, D.*; Tominaga, Taiki*; Matsuo, Tatsuhito*; Mukaiyama, Atsushi*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Fujiwara, Satoru*; Akiyama, Shuji*
Communications Physics (Internet), 5(1), p.75_1 - 75_12, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:59.84(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kusano, Kanya*; Ichimoto, Kiyoshi*; Ishii, Mamoru*; Miyoshi, Yoshizumi*; Yoden, Shigeo*; Akiyoshi, Hideharu*; Asai, Ayumi*; Ebihara, Yusuke*; Fujiwara, Hitoshi*; Goto, Tadanori*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 73(1), p.159_1 - 159_29, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:39.36(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The PSTEP is a nationwide research collaboration in Japan and was conducted from April 2015 to March 2020, supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. It has made a significant progress in space weather research and operational forecasts, publishing over 500 refereed journal papers and organizing four international symposiums, various workshops and seminars, and summer school for graduate students at Rikubetsu in 2017. This paper is a summary report of the PSTEP and describes the major research achievements it produced.
Takeda, Tetsuaki*; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Aihara, Jun; Aoki, Takeshi; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Ho, H. Q.; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Imai, Yoshiyuki; et al.
High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.5, 464 Pages, 2021/02
As a general overview of the research and development of a High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) in JAEA, this book describes the achievements by the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) on the designs, key component technologies such as fuel, reactor internals, high temperature components, etc., and operational experience such as rise-to-power tests, high temperature operation at 950 C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
Fujiwara, Satoru*; Matsuo, Tatsuhito*; Sugimoto, Yasunobu*; Shibata, Kaoru
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 10(23), p.7505 - 7509, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:17.65(Chemistry, Physical)Characterization of the dynamics of disordered polypeptide chains is required to elucidate the behavior of intrinsically disordered proteins and proteins under non-native states related to the folding process. Here we develop a method using quasielastic neutron scattering, combined with small-angle X-ray scattering and dynamic light scattering, to evaluate segmental motions of proteins as well as diffusion of the entire molecules and local side-chain motions. We apply this method to RNase A under the unfolded and molten-globule (MG) states. The diffusion coefficients arising from the segmental motions are evaluated and found to be different between the unfolded and MG states. The values obtained here are consistent with those obtained using the fluorescence-based techniques. These results demonstrate not only feasibility of this method but also usefulness to characterize the behavior of proteins under various disordered states.
 -synuclein related to propensity to amyloid fibril formation
-synuclein related to propensity to amyloid fibril formationFujiwara, Satoru*; Kono, Fumiaki*; Matsuo, Tatsuhito*; Sugimoto, Yasunobu*; Matsumoto, Tomoharu*; Narita, Tetsuhiro*; Shibata, Kaoru
Journal of Molecular Biology, 431(17), p.3229 - 3245, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:49.83(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology) -synuclein (
-synuclein ( Syn) is an intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) with unknown function.
Syn) is an intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) with unknown function.  Syn is known to form amyloid fibrils, which are implicated with the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease and other synucleinopathies. Elucidating the mechanism of fibril formation of
Syn is known to form amyloid fibrils, which are implicated with the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease and other synucleinopathies. Elucidating the mechanism of fibril formation of  Syn is therefore important for understanding the mechanism of the pathogenesis of these diseases. Here, using the quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) techniques, we investigated the dynamic and structural properties of
Syn is therefore important for understanding the mechanism of the pathogenesis of these diseases. Here, using the quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) techniques, we investigated the dynamic and structural properties of  Syn. These results imply that fibril formation of
Syn. These results imply that fibril formation of  Syn requires not only the enhanced local motions but also the segmental motions such that the proper inter-molecular interactions are possible.
Syn requires not only the enhanced local motions but also the segmental motions such that the proper inter-molecular interactions are possible.
 symmetry in CeCu
symmetry in CeCu Ge
Ge ; Soft X-ray absorption and hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy
; Soft X-ray absorption and hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopyAratani, Hidekazu*; Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Kawada, Moeki*; Kanai-Nakata, Yuina*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Fujioka, Shuhei*; Hamamoto, Satoru*; Kuga, Kentaro*; Kiss, Takayuki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(12), p.121113_1 - 121113_6, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:22.43(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Matsuo, Tatsuhito; Arata, Toshiaki*; Oda, Toshiro*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Fujiwara, Satoru
Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports (Internet), 6, p.220 - 225, 2016/07
 -synuclein studied by quasielastic neutron scattering
-synuclein studied by quasielastic neutron scatteringFujiwara, Satoru; Araki, Katsuya*; Matsuo, Tatsuhito; Yagi, Hisashi*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Shibata, Kaoru; Mochizuki, Hideki*
PLOS ONE (Internet), 11(4), p.e0151447_1 - e0151447_17, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:63.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Fujiwara, Satoru
Acta Crystallographica Section D; Structural Biology (Internet), 72(1), p.71 - 82, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:35.61(Biochemical Research Methods)Matsuo, Tatsuhito; Takeda, Soichi*; Oda, Toshiro*; Fujiwara, Satoru
Biophysics and Physicobiology (Internet), 12, p.145 - 158, 2015/12
Matsuo, Tatsuhito; Arata, Toshiaki*; Oda, Toshiro*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Fujiwara, Satoru
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 459(3), p.493 - 497, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:15.16(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Tashiro, Koji*; Hanesaka, Makoto*; Yamamoto, Hiroko*; Wasanasuk, K.*; Jayaratri, P.*; Yoshizawa, Yoshinori*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; et al.
Kobunshi Rombunshu, 71(11), p.508 - 526, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:20.64(Polymer Science)The crystal structure analysis of various polymer substances has been reviewed on the basis of wide-angle high-energy X-ray and neutron diffraction data. The progress in structural analytical techniques of polymer crystals have been reviewed at first. The structural models proposed so far were reinvestigated and new models have been proposed for various kinds of polymer crystals including polyethylene, poly(vinyl alcohol), poly(lactic acid) and its stereocomplex etc. The hydrogen atomic positions were also clarified by the quantitative analysis of wide-angle neutron diffraction data, from which the physical properties of polymer crystals have been evaluated theoretically. The bonded electron density distribution has been estimated for a polydiacetylene single crystal on the basis of the so-called X-N method or by the combination of structural information derived from X-ray and neutron diffraction data analysis. Some comments have been added about future developments in the field of structure-property relationship determination.
Matsuo, Tatsuhito; Arata, Toshiaki*; Oda, Toshiro*; Fujiwara, Satoru
Biophysics, 9, p.99 - 106, 2013/07
Fujiwara, Satoru; Plazanet, M.*; Oda, Toshiro*
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 431(3), p.542 - 546, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:10.38(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Fujiwara, Satoru; Nakagawa, Hiroshi
Hamon, 23(1), p.72 - 80, 2013/02
no abstracts in English
Matsuo, Tatsuhito; Natali, F.*; Plazanet, M.*; Zaccai, G.*; Fujiwara, Satoru
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 82(Suppl.A), p.SA020_1 - SA020_5, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Troponin is a protein that regulates the muscle contraction depending on the intracellular Ca concentration. K247R mutation of TnT is known to cause the hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. In this work, neutron scattering was used to detect possible changes in dynamics of troponin caused by mutation. Elastic incoherent neutron scattering experiments were carried out on solution samples of the wild type, and K247R mutant at the IN13 spectrometer at the Institut Laue-Langevin, at temperatures between 280 K and 292 K with an interval of 3 K. From the measured scattering data, force constants (
concentration. K247R mutation of TnT is known to cause the hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. In this work, neutron scattering was used to detect possible changes in dynamics of troponin caused by mutation. Elastic incoherent neutron scattering experiments were carried out on solution samples of the wild type, and K247R mutant at the IN13 spectrometer at the Institut Laue-Langevin, at temperatures between 280 K and 292 K with an interval of 3 K. From the measured scattering data, force constants ( k
k ), which reflect the resilience of the protein, were calculated. The
), which reflect the resilience of the protein, were calculated. The  k
k values for the wild type and K247R mutant were 0.077 (0.035) N/m and 0.046 (0.026) N/m (mean(s.d.)), respectively. This suggests that the disease-causing mutant is more flexible than the wild type. The large flexibility might modulate Ca
values for the wild type and K247R mutant were 0.077 (0.035) N/m and 0.046 (0.026) N/m (mean(s.d.)), respectively. This suggests that the disease-causing mutant is more flexible than the wild type. The large flexibility might modulate Ca signal transmission mechanism, leading to the functional aberration.
signal transmission mechanism, leading to the functional aberration.