Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kusano, Kanya*; Ichimoto, Kiyoshi*; Ishii, Mamoru*; Miyoshi, Yoshizumi*; Yoden, Shigeo*; Akiyoshi, Hideharu*; Asai, Ayumi*; Ebihara, Yusuke*; Fujiwara, Hitoshi*; Goto, Tadanori*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 73(1), p.159_1 - 159_29, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:51.19(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The PSTEP is a nationwide research collaboration in Japan and was conducted from April 2015 to March 2020, supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. It has made a significant progress in space weather research and operational forecasts, publishing over 500 refereed journal papers and organizing four international symposiums, various workshops and seminars, and summer school for graduate students at Rikubetsu in 2017. This paper is a summary report of the PSTEP and describes the major research achievements it produced.
Takeda, Tetsuaki*; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Aihara, Jun; Aoki, Takeshi; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Ho, H. Q.; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Imai, Yoshiyuki; et al.
High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.5, 464 Pages, 2021/02
As a general overview of the research and development of a High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) in JAEA, this book describes the achievements by the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) on the designs, key component technologies such as fuel, reactor internals, high temperature components, etc., and operational experience such as rise-to-power tests, high temperature operation at 950 C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
 -synuclein studied by quasielastic neutron scattering
-synuclein studied by quasielastic neutron scatteringFujiwara, Satoru; Araki, Katsuya*; Matsuo, Tatsuhito; Yagi, Hisashi*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Shibata, Kaoru; Mochizuki, Hideki*
PLOS ONE (Internet), 11(4), p.e0151447_1 - e0151447_17, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:64.99(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Mikami, Satoshi; Maeyama, Takeshi*; Hoshide, Yoshifumi*; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Sato, Shoji*; Okuda, Naotoshi*; Demongeot, S.*; Gurriaran, R.*; Uwamino, Yoshitomo*; Kato, Hiroaki*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 139, p.320 - 343, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:90 Percentile:92.94(Environmental Sciences)Uesaka, Mitsuru*; Kobayashi, Hitoshi*; Kureta, Masatoshi; Nakatsuka, Shigehiro*; Nishimura, Kazuya*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Hori, Junichi*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Tagi, Kazuhiro*; Seki, Toshichika*; et al.
Reviews of Accelerator Science and Technology, 8, p.181 - 207, 2015/00
We choose nuclear data and nuclear material inspection for energy application and nondestructive testing of explosive and hidden nuclear materials for security application. 90 keV electrostatic accelerators of deuterium are commercially available for nondestructive testing. For nuclear data measurement, electrostatic ion accelerators and L-band and S-band electron linear accelerators (linac) are used for the neutron source. Compact or mobile X-band electron linac neutron sources are under development. Compact proton linac neutron source is used for nondestructive testing especially water in solids. Several efforts for more neutron intensity using proton and deuteron accelerators are also introduced.
Ohgama, Kazuya; Ando, Yoko; Yamaguchi, Mika; Ikuta, Yuko; Shinohara, Nobuo; Murakami, Hiroyuki; Yamashita, Kiyonobu; Uesaka, Mitsuru*; Demachi, Kazuyuki*; Komiyama, Ryoichi*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-004, 76 Pages, 2013/05
JAEA together with the Japan Nuclear Human Resource Development Network (JN-HRD Net), the University of Tokyo (UT) and the Japan Atomic Industrial Forum (JAIF) cohosted the IAEA-Nuclear Energy Management School in Tokai Village, aiming that Japan will be the center of nuclear HRD in the Asian region. In the school, not only lectures by IAEA experts, but also lectures by Japanese experts and technical visits were included for foreign participants. The school contributed to the internationalization of Japanese young professionals, development of nuclear human resource of other countries, and enhancement of cooperation between IAEA and Japan. Additionally, collaborative relationship within JN-HRD Net was strengthened by the school. In this report, findings obtained during the preparatory work and the school period are reported for future international nuclear HRD activities in Japan.
Fujiwara, Takeshi
JAEA-Testing 2012-004, 13 Pages, 2012/11
In the 4-Group partitioning process developed in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (presently: Japan Atomic Energy Agency), a heat-generating nuclide group including Sr and Cs is separated by inorganic ion exchangers. Hydrous titanic acid and zeolite are used as the inorganic ion exchangers. The mechanical durability of the particles of hydrous titanic acid used for Sr recovery is not enough in case of mixing with zeolite used for Cs recovery. The method of drying the hydrous titanic acid was improved to provide sufficient mechanical durability to the product of hydrous titanic acid in case of mixing with zeolite. A procedure of producing hydrous titanic acid from the raw material, titanyl sulfate, was established and documented with cares to be taken at each step.
 at the MLF, J-PARC
at the MLF, J-PARCTakahashi, Nobuaki; Shibata, Kaoru; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Nakajima, Kenji; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Nakatani, Takeshi; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Fujiwara, Satoru; Sato, Taku*; Tsukushi, Itaru*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(Suppl.B), p.SB007_1 - SB007_4, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:43.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Umeda, Koji; Oi, Takao; Osawa, Hideaki; Oyama, Takuya; Oda, Chie; Kamei, Gento; Kuji, Masayoshi*; Kurosawa, Hideki; Kobayashi, Yasushi; Sasaki, Yasuo; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-050, 82 Pages, 2007/12
This report shows the annual report which shows the summarized results and topic outline of each project on geological disposal technology in the fiscal year of 2006.
Fujiwara, Takeshi; Morita, Yasuji
JAEA-Research 2007-076, 29 Pages, 2007/11
In the 4-Group Partitioning Process developed in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (presently: Japan Atomic Energy Agency), we examined selective stripping method by DTPA for Am and Cm from the rare earth elements (REs) in DIDPA solvent. In the present study, the performance of the selective stripping and the optimization of the separation process was examined by a simulation program which uses the values of distribution ratios of Am and REs obtained by batch experiments. The validity of the simulation program was confirmed by comparing the results of the simulation with the results of continuous stripping tests of REs with DTPA solution from the DIDPA solvent using mini-mixer-settlers. The distributions of the REs in mini-mixer-settlers were adequately predictable in the condition with low concentration of the REs by the simulation program. It is effective to add the scrubbing steps by organic solvent in order to decrease the amount of REs that contaminate the Am and Cm product.
Fujiwara, Takeshi; Morita, Yasuji
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 6(3), p.358 - 364, 2007/09
Continuous stripping of rare earth elements (REs) with diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA) solution from the diisodecylphosphoric acid (DIDPA) solvent was examined with lab-scale mixer-settlers, to develop a process for the separation of trivalent actinides (An(III)) from the mixture of An(III) and REs. DIDPA is an extractant applied in the 4-Group Partitioning Process developed in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (presently: Japan Atomic Energy Agency) to separate transuranic elements from high-level liquid waste. The experiment on continuous stripping with the DTPA solution of a little higher pH than an appropriate pH for selective stripping of An(III) showed that Nd could be selectively stripped from the DIDPA solvent containing La and Nd. The yield was higher than 99.8%, and 97.6% of La was left in the solvent. The pH of the DTPA solution decreased in the stages near the solvent feed, which was explained by the extraction of ammonium ion. These findings make it possible to predict quantitatively the behavior of An(III) and REs in the various conditions of the DIDPA-DTPA continuous stripping system.
Otsuka, Satoshi; Ukai, Shigeharu; Sakasegawa, Hideo; Fujiwara, Masayuki; Kaito, Takeji; Narita, Takeshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 367-370(1), p.160 - 165, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:59 Percentile:95.87(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)This paper describes the effect on creep strength and microstructure of 9Cr-oxide dispersion strengthened martensitic steel (9Cr-ODS steel) brought by the differences in titanium concentration and consolidation temperature. The increase of titanium concentration to 0.30-0.35wt% was shown to provide remarkable improvement of creep strength accompanied by the increase of residual-alpha ferrite. The elevation of hot-extrusion temperature notably degraded the creep strength, however, appeared to increase the volume fraction of residual-alpha ferrite. Creep deformation process of 9Cr-ODS steel was discussed to explain these results based on microstructure observations.
Nakayama, Shinichi; Nagasaki, Shinya*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Oe, Toshiaki*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Sato, Seichi*; Sato, Tsutomu*; Tanaka, Satoru*; Tochiyama, Osamu*; Nagao, Seiya*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2007-003, 120 Pages, 2007/03
The 1st information exchange meeting on Radioactive Waste Disposal Research Network was held in Nuclear Science Research Institute of Japan Atomic Energy Agency on August 4, 2006. Radioactive Waste Disposal Research Network was established by under Interorganization Atomic Energy Research Program of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, and the objective is to bring both research infrastructures and human expertise in Japan to an adequate performance level, thereby contributing to the development of the fundamental research area in the field of radioactive waste disposal. This lecture material is a collection of research presentations and discussions during the information exchange meeting.
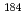 Re populated by the
Re populated by the 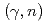 reaction from laser Compton scattering
reaction from laser Compton scattering  rays at the electron storage ring NewSUBARU
rays at the electron storage ring NewSUBARUHayakawa, Takehito; Miyamoto, Shuji*; Hayashi, Yukio; Kawase, Keigo*; Horikawa, Ken*; Chiba, Satoshi; Nakanishi, Kosuke*; Hashimoto, Hisanobu*; Ota, Takeshi*; Kando, Masaki; et al.
Physical Review C, 74(6), p.065802_1 - 065802_5, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:82.84(Physics, Nuclear)We report a half-life of the ground state of 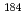 Re populated by the
Re populated by the  Re
Re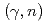
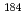 Re reaction with the laser Compton scattering
Re reaction with the laser Compton scattering  -rays generated through relativistic engineering. The
-rays generated through relativistic engineering. The  -rays are provided at the electron storage ring NewSUBARU. The previous experiment using deuteron-induced reactions has yielded a recommended half-life of the 3
-rays are provided at the electron storage ring NewSUBARU. The previous experiment using deuteron-induced reactions has yielded a recommended half-life of the 3 ground state of
ground state of 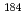 Re to be 38.0
Re to be 38.0  0.5 d, including a possible contribution from the 8
0.5 d, including a possible contribution from the 8 isomer (
isomer (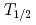 = 169
= 169  8 d) of
8 d) of 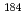 Re since the presence of the isomer was not known at that time. In contrast, the
Re since the presence of the isomer was not known at that time. In contrast, the 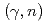 reaction has an advantage to selectively populate the ground state because this reaction does not bring large angular momentum. The measured half-life of 35.4
reaction has an advantage to selectively populate the ground state because this reaction does not bring large angular momentum. The measured half-life of 35.4  0.7 d is shorter than the previous half-life by about 7%. This difference is crucial for applications using the activation method.
0.7 d is shorter than the previous half-life by about 7%. This difference is crucial for applications using the activation method.
Narita, Takeshi*; Ukai, Shigeharu; Kaito, Takeji; Otsuka, Satoshi; Fujiwara, Masayuki
JAEA-Research 2006-050, 85 Pages, 2006/10
In 9Cr ODS martensitic steel, tungsten(W) is a solid solution strengthening element, whose addition increases high-temperature strength by the combined effect with oxide dispersion strengthening. However, its excessive addition results in the increase of ferrite phase causing precipitation of intermetallic compound (Laves phase) under high temperature irradiation condition and thus ductility degradation. The amount of W addition therefore should be as low as possible. In this report, the effects of W on microstructure and high temperature mechanical properties of 9Cr ODS martensitic steels were examined for obtaining insights into optimum W concentration in terms of high-temperature strength and ductility. The results obtained are as follows: (1)In the 9CrODS martensitic steel, addition of W exceeding 2mass% is shown to cause precipitation of Laves phase which degrades the ductility and fracture toughness. It can be said that the current specification of W concentration, i.e. 2mass%W, is appropriate. (2)Hardness and tensile strength is shown to increase with W concentration. This increase is caused by the increase of solid solution strengthening and residual-alpha ferrite. The retainment of residual-alpha ferrite is enhanced by the addition of W (ferrite former element). The improvement of tensile strength at 973K provided by the solid solution strengthening is shown to be equivalent to that provided by the retainment of residual-alpha ferrite. (3)It would be open task to explorer an improved alloy design concept, i.e. decrease of W as low as possible and increase of residual-alpha ferrite. The degradation of high-temperature strength by decreasing W addition can be made up by the increasing fraction of residual-alpha phase that is provided by reduction of austenite former elements and increasing addition of ferrite former elements.
 Al
AlOzawa, Akira*; Matsuta, Kensaku*; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Mihara, Mototsugu*; Yamada, Kazunari*; Yamaguchi, Takayuki*; Otsubo, Takashi*; Momota, Sadao*; Izumikawa, Takuji*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 74(2), p.021301_1 - 021301_4, 2006/08
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:89.22(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Fujiwara, Takeshi; Morita, Yasuji
JAEA-Research 2006-011, 24 Pages, 2006/03
In the 4-Group Partitioning Process developed in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (presently: Japan Atomic Energy Agency), the transuranic element and the rare earth elements are extracted from high-level liquid waste by diisodecylphosphoric acid (DIDPA). The concentration of the rare earth elements are about 50 times higher than that of Am and Cm in high-level liquid waste. It is, therefore, necessary to separate each other for the transmutation of Am and Cm, or volume reduction of the waste form of the long-lived nuclide. On the other hand, the Talspeak method is a separation method by the solvent extraction that gives selective stripping of Am and Cm from the solvent that contains the rare earth elements using di-2-ethylhexylphosphoric acid (DEHPA) as an extractant. In the present study, application of the DIDPA to the Talspeak method was examined for various conditions to separate Am from the rare earth elements by the batch examination.
Fujiwara, Takeshi; Morita, Yasuji
JAEA-Research 2006-003, 22 Pages, 2006/02
The precipitation method by denitration with formic acid is adopted in the 4-Group Partitioning Process for recovery of Tc and platinum group metals (PGM) from high-level liquid waste. A part of Sr and some other elements are precipitated with Tc and PGM at the precipitation step by denitration. As Sr is one of the target elements of the 4-Group Partitioning Process, it is necessary to recover the precipitated Sr from Tc and PGM fraction. The present study deals with the process for dissolving the precipitate of Tc and PGM at the precipitation step to recover the precipitated Sr from Tc and PGM fraction. It was possible to dissolve the precipitated Sr thoroughly by 0.010 mol/dm nitric acid without dissolving PGM precipitate. Ba and Ni were contained in dissolved Sr solution. Any Sr was not appeared in the dissolved solution of PGM precipitate which remained after the Sr dissolution by 0.010 mol/dm
nitric acid without dissolving PGM precipitate. Ba and Ni were contained in dissolved Sr solution. Any Sr was not appeared in the dissolved solution of PGM precipitate which remained after the Sr dissolution by 0.010 mol/dm nitric acid. The pH of the dissolved Sr solution was about 2. As the appropriate pH is 5 or higher to adsorb Sr on inorganic ion exchangers, it is demanded to adjust the pH of dissolved Sr solution for next treatment. Precipitation of Sr did not occur during adjusting the pH of dissolved Sr solution to neutral region with sodium hydroxide solution.
nitric acid. The pH of the dissolved Sr solution was about 2. As the appropriate pH is 5 or higher to adsorb Sr on inorganic ion exchangers, it is demanded to adjust the pH of dissolved Sr solution for next treatment. Precipitation of Sr did not occur during adjusting the pH of dissolved Sr solution to neutral region with sodium hydroxide solution.
Yamaguchi, Isoo*; Morita, Yasuji; Fujiwara, Takeshi; Yamagishi, Isao
JAERI-Tech 2005-054, 61 Pages, 2005/09
The HLW-79Y-4T type transportation cask for liquid radioactive fuel material (commonly called "Cendrillon") was imported from France and modified for Japanese regulation in order to obtain high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLW) for partitioning tests in JAERI by transportation from Tokai Establishment of Japan Nuclear Fuel Cycle Development Institute. The cask was used for the HLW transportation five times from 1982 to 1990. After that, it was kept and maintained for next transportation of HLW from facilities outside JAERI. Finally, we decided to decompose the cask because HLW can be obtained in JAERI Tokai. For the decomposition, radiation dose and contamination by radioactivity was first measured and then the methods to reduce those levels were determined. The cask was decomposed after the decontamination to separate the part that has high radiation level. The separated part was put in a vessel specially prepared. The present report describes those procedures for the decomposition of the transportation cask.
Otsuka, Satoshi; Ukai, Shigeharu; Fujiwara, Masayuki; Kaito, Takeji; Narita, Takeshi
JNC TN9400 2005-034, 197 Pages, 2005/08
Oxide dispersion strengthened(ODS) martensitic steel (9CrODS steel) has been identified as an attractive candidate for advanced fast reactor (FR) fuel cladding tube because of its superior high-temperature strength and radiation resistance. Our recent activities revealed that high-temperature strength of different lots of the cladding tubes is inconsistent each other, even though the same manufacturing process was applied to these tubes. This inconsistency means a critical problem that high-strength 9CrODS steel cladding tubes can not be manufactured reliably and consistently. In this report, a microstructure control technique for consistently and reliably manufacturing high-strength 9CrODS steel cladding tubes are examined based on a series of data concerning effect of excess oxygen concentration on high temperature strength and microstructure of 9CrODS steel.