Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ohashi, Tomonori*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Steinle-Neumann, G.*; Hattori, Takanori; Yuan, L.*; Suzuki, Akio*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (Internet), 120(1), p.240926a_1 - 240926a_13, 2025/06
We explore the structures of dry and hydrated (H O and D
O and D O) Na
O) Na Si
Si O
O melt at 0-6 GPa and 1000-1300 K and glasses recovered from high pressure and temperatures by in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The structures of the melts at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K are also investigated by ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation. In-situ neutron experiments revealed that the D-O distance increases with compression due to the formation of -O-D-O- bridging species, which is reproduced by the molecular dynamics simulations. The pressure-induced -O-D-O- formation reflects a more rigid incorporation of hydrogen, which acts as a mechanism for the experimentally observed higher solubility of water in silicate melts. Together with shrinking modifier domains, this process dominates the compression behavior of hydrous Na
melt at 0-6 GPa and 1000-1300 K and glasses recovered from high pressure and temperatures by in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The structures of the melts at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K are also investigated by ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation. In-situ neutron experiments revealed that the D-O distance increases with compression due to the formation of -O-D-O- bridging species, which is reproduced by the molecular dynamics simulations. The pressure-induced -O-D-O- formation reflects a more rigid incorporation of hydrogen, which acts as a mechanism for the experimentally observed higher solubility of water in silicate melts. Together with shrinking modifier domains, this process dominates the compression behavior of hydrous Na Si
Si O
O melt, whereas the compression of dry Na
melt, whereas the compression of dry Na Si
Si O
O at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K is governed largely by bending of the Si-O-Si angle. The molecular dynamics simulations on hydrous Na
at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K is governed largely by bending of the Si-O-Si angle. The molecular dynamics simulations on hydrous Na Si
Si O
O melts further suggest that the sodium ions are scavenged from its network-modifying role via 2(
melts further suggest that the sodium ions are scavenged from its network-modifying role via 2(![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-O
Si-O + Na
+ Na )
) 
![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-(O-
Si-(O-![$$^{[5]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZVLV4SI.gif) Si-O)
Si-O) + 2Na
+ 2Na and Si-O
and Si-O + Na
+ Na + Si-OH
+ Si-OH  Si-(O-H-O-Si)
Si-(O-H-O-Si) + Na
+ Na with increasing pressure.
with increasing pressure.
Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Machida, Shinichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*
Physical Review B, 111(22), p.224413_1 - 224413_6, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:1The crystal and magnetic structures of antiferromagnetic Mn deuterides formed by hydrogenating Mn metal at high temperature and high pressure, fcc  -MnDx and hcp
-MnDx and hcp  -MnDx, were investigated by in-situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms partially occupied the octahedral interstitial positions of the fcc and hcp metal lattices. The site occupancies increased rapidly with decreasing temperature from
-MnDx, were investigated by in-situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms partially occupied the octahedral interstitial positions of the fcc and hcp metal lattices. The site occupancies increased rapidly with decreasing temperature from  700 to
700 to  450 K and remained down to 300 K. N
450 K and remained down to 300 K. N el temperature of 543(10) K was determined for
el temperature of 543(10) K was determined for  -MnD
-MnD . For
. For  -MnD
-MnD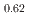 , saturation magnetic moment and N
, saturation magnetic moment and N el temperature were determined to be 0.82(1)
el temperature were determined to be 0.82(1) 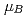 and 347(3) K, respectively. The N
and 347(3) K, respectively. The N el temperatures determined for
el temperatures determined for  -MnD
-MnD and
and  -MnD
-MnD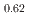 are consistent with those predicted by the respective Slater-Pauling curves proposed in previous studies. The updated N
are consistent with those predicted by the respective Slater-Pauling curves proposed in previous studies. The updated N el temperatures provide insights into the development of more accurate Slater-Pauling curves based on electronic band structure calculations.
el temperatures provide insights into the development of more accurate Slater-Pauling curves based on electronic band structure calculations.
Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Nakano, Satoshi*; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Abe, Jun*
Koatsuryoku No Kagaku To Gijutsu, 34(3), p.134 - 142, 2024/09
A diamond anvil cell (DAC) for high-pressure neutron diffraction experiments has been developed at the PLANET beamline, Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility, in J-PARC. The conically supported diamond anvils were used for high-pressure generation. We succeeded in obtaining the neutron data for D O ice up to 69.4 GPa. In addition, the gasket materials suitable for the neutron diffraction measurements were investigated. 11 kinds of alloys were tested and SUS304, Inconel718 and M2052 (73Mn-20Cu-5Ni-2Fe, at%) alloys showed excellent performance. Especially, M2052 null-matrix alloy has proven to be useful for neutron diffraction experiments where the beam inevitably hits the gasket. We then obtained refinable neutron diffraction profiles in Rietveld analysis from D
O ice up to 69.4 GPa. In addition, the gasket materials suitable for the neutron diffraction measurements were investigated. 11 kinds of alloys were tested and SUS304, Inconel718 and M2052 (73Mn-20Cu-5Ni-2Fe, at%) alloys showed excellent performance. Especially, M2052 null-matrix alloy has proven to be useful for neutron diffraction experiments where the beam inevitably hits the gasket. We then obtained refinable neutron diffraction profiles in Rietveld analysis from D O ice at least up to 43.3 GPa.
O ice at least up to 43.3 GPa.
Mori, Yuichiro*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Takano, Masahiro*; Kakizawa, Sho*; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 634, p.118673_1 - 118673_8, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:41.61(Geochemistry & Geophysics)To investigate silicon effects on the hydrogen-induced volume expansion of iron, neutron diffraction and X-ray diffraction experiments were conducted to examine hcp-Fe Si
Si under high pressures and high temperatures. Neutron diffraction experiments were performed on the deuterated hcp-Fe
under high pressures and high temperatures. Neutron diffraction experiments were performed on the deuterated hcp-Fe Si
Si at 13.5 GPa and 900 K, and at 12.1 GPa and 300 K. By combining the P-V-T equation of state of hcp-Fe
at 13.5 GPa and 900 K, and at 12.1 GPa and 300 K. By combining the P-V-T equation of state of hcp-Fe Si
Si , present results indicate that the hydrogen-induced volume expansion of hcp-Fe
, present results indicate that the hydrogen-induced volume expansion of hcp-Fe Si
Si is 10% greater than that of pure hcp iron. Using the obtained values, we estimated the hydrogen content that would reproduce the density deficit in the inner core, which was 50% less than that without the effect of silicon. Possible hydrogen content,
is 10% greater than that of pure hcp iron. Using the obtained values, we estimated the hydrogen content that would reproduce the density deficit in the inner core, which was 50% less than that without the effect of silicon. Possible hydrogen content,  , in the inner core and the outer core was calculated to be 0.07 and 0.12-0.15, respectively, when reproducing the density deficit of the inner core with hcp-Fe
, in the inner core and the outer core was calculated to be 0.07 and 0.12-0.15, respectively, when reproducing the density deficit of the inner core with hcp-Fe Si
Si Hx.
Hx.
Li, X.*; Zhu, R.*; Xin, J.*; Luo, M.*; Shang, S.-L.*; Liu, Z.-K.*; Yin, C.*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Dippenaar, R. J.*; Higo, Yuji*; et al.
CALPHAD; Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry, 84, p.102641_1 - 102641_6, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Thermodynamics)Kofu, Maiko; Kawamura, Seiko; Murai, Naoki; Ishii, Rieko*; Hirai, Daigoro*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013006_1 - 013006_9, 2024/01
Ohashi, Tomonori*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Hisano, Naoki*; Abe, Jun*; Suzuki, Akio*
American Mineralogist, 107(3), p.325 - 335, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.05(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The basaltic glass structure were investigated to 18 GPa using in situ X-ray and neutron diffraction. The O-O coordination number (CN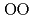 ) starts to rise with maintaining the mean O-O distance (r
) starts to rise with maintaining the mean O-O distance (r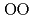 ) above 2-4 GPa, and then CN
) above 2-4 GPa, and then CN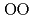 stops increasing and r
stops increasing and r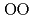 begins to shrink along with the increase in the Al-O coordination number (CN
begins to shrink along with the increase in the Al-O coordination number (CN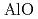 ) above 9 GPa. This is interpreted by the change in the contraction mechanism from tetrahedral network bending to oxygen packing ratio increase via the CN
) above 9 GPa. This is interpreted by the change in the contraction mechanism from tetrahedral network bending to oxygen packing ratio increase via the CN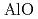 increase. The oxygen packing fraction exceeds the value for dense random packing, suggesting that the oxygen-packing hypothesis cannot account for the pressure-induced structural transformations of silica and silicate glasses. The CN
increase. The oxygen packing fraction exceeds the value for dense random packing, suggesting that the oxygen-packing hypothesis cannot account for the pressure-induced structural transformations of silica and silicate glasses. The CN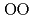 increase at 2-4 GPa reflects the elastic softening of silicate glass, which may causes anomalous elastic moduli of basaltic glass at
increase at 2-4 GPa reflects the elastic softening of silicate glass, which may causes anomalous elastic moduli of basaltic glass at  2 GPa.
2 GPa.
Iizuka, Riko*; Goto, Hirotada*; Shito, Chikara*; Fukuyama, Ko*; Mori, Yuichiro*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.12632_1 - 12632_10, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.44(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The Earth's core consist of Fe-Ni alloy with some light elements (H, C, O, Si, S etc.). Hydrogen (H) is the most abundant element in the universe and one of the promising candidates. In this study, we have investigated the effects of sulfur(S) on hydrogenation of iron-hydrous silicate system containing saturated water in the ideal composition of the primitive Earth. We observed a series of phase transitions of Fe, dehydration of the hydrous mineral, and formation of olivine and enstatite with increasing temperature. The FeS formed as the coexisting phase of Fe under high-pressure and temperature condition, but its unit cell volume did not increase, suggesting that FeS is hardly hydrogenated. Recovered samples exhibited that H and S can be incorporated into solid Fe, which lowers the melting temperature as Fe(H )-FeS system. No detection of other light elements (C, O, Si) in solid Fe suggests that they dissolve into molten iron hydride and/or FeS in the later process of Earth's core-mantle differentiation.
)-FeS system. No detection of other light elements (C, O, Si) in solid Fe suggests that they dissolve into molten iron hydride and/or FeS in the later process of Earth's core-mantle differentiation.
Sano, Asami; Kakizawa, Sho*; Shito, Chikara*; Hattori, Takanori; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
High Pressure Research, 41(1), p.65 - 74, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:38.13(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We applied Kawai-type multi-anvil assemblies (MA6-8) for time-of-flight neutron-diffraction experiments to achieve high pressures and high temperatures simultaneously. To achieve sufficient signal intensities, the angular access to the sample was enlarged using slits and tapers on the first-stage anvils. Using SiC-binder sintered diamond for the second-stage anvils that transmits neutrons, sufficient signal intensities were achieved at a high-pressure of  23.1 GPa. A high-temperature experiment was also conducted at 16.2 GPa and 973 K, validating the use of tungsten carbide for the second-stage anvils. The present study reveals the capability of the MA6-8 cells in neutron-diffraction experiments to attain pressures and temperatures beyond the limits of the conventional MA6-6 cells used in the high-pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET at the MLF, J-PARC.
23.1 GPa. A high-temperature experiment was also conducted at 16.2 GPa and 973 K, validating the use of tungsten carbide for the second-stage anvils. The present study reveals the capability of the MA6-8 cells in neutron-diffraction experiments to attain pressures and temperatures beyond the limits of the conventional MA6-6 cells used in the high-pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET at the MLF, J-PARC.
 Si
Si at 14.7 GPa and 800 K
at 14.7 GPa and 800 KMori, Yuichiro*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Kakizawa, Sho*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Shito, Chikara*; Iizuka, Riko*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; et al.
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 116(6), p.309 - 313, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.53(Mineralogy)The Earth's core is believed to contain some light elements because it is 10% less dense than pure Fe under the corresponding pressure and temperature conditions. Hydrogen, a promising candidate among light elements, has phase relations and physical properties that have been investigated mainly for the Fe-H system. This study specifically examined an Fe-Si-H system using in-situ neutron diffraction experiments to investigate the site occupancy of deuterium of hcp-Fez Si
Si hydride at 14.7 GPa and 800 K. Results of Rietveld refinement indicate hcp-Fe
hydride at 14.7 GPa and 800 K. Results of Rietveld refinement indicate hcp-Fe Si
Si hydride as having deuterium (D) occupancy of 0.24(2) exclusively at the interstitial octahedral site in the hcp lattice. The effect on the site occupancy of D by addition of 2.6 wt% Si into Fe (Fe
hydride as having deuterium (D) occupancy of 0.24(2) exclusively at the interstitial octahedral site in the hcp lattice. The effect on the site occupancy of D by addition of 2.6 wt% Si into Fe (Fe Si
Si ) was negligible compared to results obtained from an earlier study of an Fe-D system (Machida et al., 2019).
) was negligible compared to results obtained from an earlier study of an Fe-D system (Machida et al., 2019).
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Kira, Hiroshi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
High Pressure Research, 40(3), p.325 - 338, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.81(Physics, Multidisciplinary)To understand the practical effects of pressure-transmitting media (PTM) on neutron diffraction using Paris-Edinburgh presses, diffraction patterns of MgO were collected to approximately 20 GPa using PTMs of Pb, AgCl, 4:1 methano-ethanol (ME) mixture with and without heating, N , and Ar. Hydrostaticity in the sample chamber estimated from the MgO 220 peak width improves in the order of Pb, AgCl, Ar, ME mixture, N
, and Ar. Hydrostaticity in the sample chamber estimated from the MgO 220 peak width improves in the order of Pb, AgCl, Ar, ME mixture, N , and the heated ME mixture. Unlike previous results using a diamond anvil cell, the unheated ME mixture is superior to Ar even after freezing, probably due to the cup on the anvil face. Considering these results and the sizable coherent scattering of Ne, which would show good hydrostaticity, we conclude that the ME mixture (preferably the heated one) is the best PTM in neutron experiments up to 20 GPa, while Ar can be substituted when a sample is reactive to alcohols.
, and the heated ME mixture. Unlike previous results using a diamond anvil cell, the unheated ME mixture is superior to Ar even after freezing, probably due to the cup on the anvil face. Considering these results and the sizable coherent scattering of Ne, which would show good hydrostaticity, we conclude that the ME mixture (preferably the heated one) is the best PTM in neutron experiments up to 20 GPa, while Ar can be substituted when a sample is reactive to alcohols.
Saito, Hiroyuki*; Machida, Akihiko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 587, p.412153_1 - 412153_6, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:24.90(Physics, Condensed Matter)The site occupancy of deuterium (D) atoms in face-centered-cubic nickel (fcc Ni) was measured along a cooling path from 1073 to 300 K at an initial pressure of 3.36 GPa via in situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms predominantly occupy the octahedral (O) sites and slightly occupy the tetrahedral (T) sites of the fcc metal lattice. The O-site occupancy increases from 0.4 to 0.85 as the temperature is lowered from 1073 to 300 K. Meanwhile, the T-site occupancy remains c.a. 0.02. The temperature-independent behavior of the T-site occupancy is unusual, and its process is not yet understood. From the linear relation between the expanded lattice volume and D content, a D-induced volume expansion of 2.09(13) 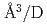 atom was obtained. This value is in agreement with the values of 2.14-2.2
atom was obtained. This value is in agreement with the values of 2.14-2.2 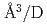 atom previously reported for Ni and Ni
atom previously reported for Ni and Ni Fe
Fe alloy.
alloy.
Saito, Hiroyuki*; Machida, Akihiko*; Iizuka, Riko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10, p.9934_1 - 9934_8, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:19.04(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Neutron powder diffraction profiles were collected for iron deuteride (FeDx) while the temperature decreased from 1023 to 300 K for a pressure range of 4-6 GPa. The  ' deuteride with a double hexagonal close-packed (dhcp) structure, which coexisted with other stable or metastable deutrides at each temperature and pressure condition, formed solid solutions with a composition of FeD
' deuteride with a double hexagonal close-packed (dhcp) structure, which coexisted with other stable or metastable deutrides at each temperature and pressure condition, formed solid solutions with a composition of FeD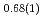 at 673 K and 6.1 GPa and FeD
at 673 K and 6.1 GPa and FeD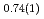 at 603 K and 4.8 GPa. Upon stepwise cooling to 300 K, the D-content x increased to a stoichiometric value of 1.0 to form monodeuteride FeD
at 603 K and 4.8 GPa. Upon stepwise cooling to 300 K, the D-content x increased to a stoichiometric value of 1.0 to form monodeuteride FeD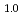 . In the dhcp FeD
. In the dhcp FeD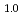 at 300 K and 4.2 GPa, dissolved D atoms fully occupied the octahedral interstitial sites, slightly displaced from the octahedral centers in the dhcp metal lattice, and the dhcp sequence of close-packed Fe planes contained hcp-stacking faults at 12%. Magnetic moments with 2.11
at 300 K and 4.2 GPa, dissolved D atoms fully occupied the octahedral interstitial sites, slightly displaced from the octahedral centers in the dhcp metal lattice, and the dhcp sequence of close-packed Fe planes contained hcp-stacking faults at 12%. Magnetic moments with 2.11  0.06 B/Fe-atom aligned ferromagnetically in parallel on the Fe planes.
0.06 B/Fe-atom aligned ferromagnetically in parallel on the Fe planes.
 glass up to 10 GPa
glass up to 10 GPaUrakawa, Satoru*; Inoue, Toru*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Kohara, Shinji*; Wakabayashi, Daisuke*; Sato, Tomoko*; Funamori, Nobumasa*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
Minerals (Internet), 10(1), p.84_1 - 84_13, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:55.04(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The structure of hydrous amorphous SiO is fundamental to investigate the effects of water on the physicochemical properties of oxide glasses and magma. The hydrous SiO
is fundamental to investigate the effects of water on the physicochemical properties of oxide glasses and magma. The hydrous SiO glass with 13 wt.% D
glass with 13 wt.% D O was synthesized under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions and its structure was investigated by small angle X-ray scattering, X-ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction experiments at pressures of up to 10 GPa and room temperature. This hydrous glass is separated into a SiO
O was synthesized under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions and its structure was investigated by small angle X-ray scattering, X-ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction experiments at pressures of up to 10 GPa and room temperature. This hydrous glass is separated into a SiO rich major phase and a D
rich major phase and a D O rich minor phase. Medium-range order of the hydrous glass shrinks compared to the anhydrous SiO
O rich minor phase. Medium-range order of the hydrous glass shrinks compared to the anhydrous SiO glass due to disruption of SiO
glass due to disruption of SiO linkage by formation of Si-OD deuterioxyl, while the pressure response is similar. Most of D
linkage by formation of Si-OD deuterioxyl, while the pressure response is similar. Most of D O molecules are in the small domains and hardly penetrate into SiO
O molecules are in the small domains and hardly penetrate into SiO major phase.
major phase.
Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 9(1), p.12290_1 - 12290_9, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:83.03(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Hexagonal close-packed iron hydride, hcp FeHx, is absent from the conventional phase diagram of the Fe-H system, although hcp metallic Fe exists stably over extensive temperature ( ) and pressure (
) and pressure ( ) conditions, including those corresponding to the Earth's inner core.
) conditions, including those corresponding to the Earth's inner core. 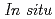 X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements at temperatures ranging from 298 to 1073 K and H pressures ranging from 4 to 7 GPa revealed that the hcp hydride was formed for FeH
X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements at temperatures ranging from 298 to 1073 K and H pressures ranging from 4 to 7 GPa revealed that the hcp hydride was formed for FeH compositions when
compositions when 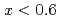 . Hydrogen atoms occupied the octahedral interstitial sites of the host metal lattice both partially and randomly. The hcp hydride exhibited a H-induced volume expansion of 2.48(5)
. Hydrogen atoms occupied the octahedral interstitial sites of the host metal lattice both partially and randomly. The hcp hydride exhibited a H-induced volume expansion of 2.48(5) 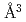 /H-atom, which was larger than that of the face-centered cubic (fcc) hydride. The hcp hydride showed an increase in
/H-atom, which was larger than that of the face-centered cubic (fcc) hydride. The hcp hydride showed an increase in  with
with  , whereas the fcc hydride showed a corresponding decrease. The present study provides guidance for further investigations of the Fe-H system over an extensive
, whereas the fcc hydride showed a corresponding decrease. The present study provides guidance for further investigations of the Fe-H system over an extensive  -
- -
- region.
region.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Okazaki, Nobuo*
High Pressure Research, 39(3), p.417 - 425, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:81.55(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have developed a technique for neutron diffraction experiments at pressures up to 40 GPa using a Paris-Edinburgh press at the PLANET beamline in J-PARC. To increase the maximum accessible pressure, the diameter of the dimple for sample chamber at the top of the sintered diamond anvils is sequentially reduced from 4.0 mm to 1.0 mm. As a result, the maximum pressure increased and finally reached 40 GPa. By combining this technique with the beam optics which defines the gauge volume, diffraction patterns sufficient for full-structure refinements are obtainable at such pressures.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Okazaki, Nobuo*
Nihon Kessho Gakkai-Shi, 59(6), p.301 - 308, 2017/12
PLANET is a neutron beamline dedicated to high-pressure experiments. Combining the intense neutron source of J-PARC and high-pressure devices designed for time-of-flight powder neutron diffraction enables precise structure analysis of crystal, liquid and amorphous solids over wide pressure and temperature region of 0-20 GPa and 77-2000K. This beamline is effective for various studies in geophysics, planetary science, physics and chemistry. This paper overviews the beamline and introduces recent results obtained at PLANET.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
 -phase in
-phase in  -based titanium aluminide intermetallics
-based titanium aluminide intermetallicsLiss, K.-D.*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Dippenaar, R. J.*; Higo, Yuji*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Reid, M.*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Shobu, Takahisa; Akita, Koichi
Metals, 6(7), p.165_1 - 165_22, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:63.36(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Titanium aluminides find application in modern light-weight, high-temperature turbines, such as aircraft engines, but suffer from poor plasticity during manufacturing and processing. Huge forging presses enable materials processing in the 10 GPa range and hence, it is necessary to investigate the phase-diagrams of candidate materials under these extreme conditions. Here we report on an in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction study in a large-volume-press of a modern (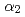 +
+  ) two-phase material, Ti-45Al-7.5Nb-0.25C, under pressures up to 9.6 GPa and temperatures up to 1686 K. At room temperature, the volume response to pressure is accommodated by the transformation
) two-phase material, Ti-45Al-7.5Nb-0.25C, under pressures up to 9.6 GPa and temperatures up to 1686 K. At room temperature, the volume response to pressure is accommodated by the transformation 

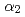 rather than volumetric strain, expressed by apparently high bulk moduli of both constituent phases. Crystallographic aspects, specifically lattice strain and atomic order are discussed in detail. It is interesting to note that this transformation takes place despite an increase in atomic volume, which is due to the high ordering energy of
rather than volumetric strain, expressed by apparently high bulk moduli of both constituent phases. Crystallographic aspects, specifically lattice strain and atomic order are discussed in detail. It is interesting to note that this transformation takes place despite an increase in atomic volume, which is due to the high ordering energy of  . Upon heating under high pressure, both the eutectoid and
. Upon heating under high pressure, both the eutectoid and  -solvus transition temperatures are elevated, and a third, cubic
-solvus transition temperatures are elevated, and a third, cubic  -phase is stabilized above 1350 K. Earlier research has shown that this
-phase is stabilized above 1350 K. Earlier research has shown that this  -phase is very ductile during plastic deformation, essential in near-conventional forging processes. Here, we were able to identify an ideal processing window for near-conventional forging, while the presence of the detrimental
-phase is very ductile during plastic deformation, essential in near-conventional forging processes. Here, we were able to identify an ideal processing window for near-conventional forging, while the presence of the detrimental  -phase is not present under operating conditions. Novel processing routes can be defined from these findings.
-phase is not present under operating conditions. Novel processing routes can be defined from these findings.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Arima, Hiroshi*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Abe, Jun*; Machida, Shinichi*; Okazaki, Nobuo*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Inamura, Yasuhiro
Koatsuryoku No Kagaku To Gijutsu, 26(2), p.89 - 98, 2016/06
PLANET is a high-pressure neutron beamline constructed at pulsed-neutron source in Materials and Life Science Facility (MLF) in J-PARC. The six-axis multi-anvil press designed for time of flight (TOF) neutron diffraction experiments enables routine data collection at high pressures and high temperatures up to 10 GPa and 2000 K, respectively. To obtain clean data, the beamline is equipped with the incident slits and receiving collimators that eliminate parasitic scattering from the high-pressure cell. The high performance of the diffractometer for the resolution (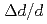
 0.6%) and the accessible d-spacing range (0.2 - 8.4
0.6%) and the accessible d-spacing range (0.2 - 8.4  ) together with low-parasitic scattering characteristics enables precise structure determination of crystals and liquids under high pressure and temperature conditions.
) together with low-parasitic scattering characteristics enables precise structure determination of crystals and liquids under high pressure and temperature conditions.