Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
成田 弘一*; Nicolson, R. M.*; 元川 竜平; 伊藤 文之*; 森作 員子*; 後藤 みどり*; 田中 幹也*; Heller, W. T.*; 塩飽 秀啓; 矢板 毅; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 58(13), p.8720 - 8734, 2019/07
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:75.87(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Current industrial practices to extract rhodium from virgin ores carry a heavy environmental burden. Improving the efficiency of the hydrometallurgical processes to separate and recover rhodium from other precious metals provides an opportunity to improve the materials and energy balances, but the presence of mixed chloride-rhodium species following leaching by acid chloride media complicates the recovery process. In this work we have applied a broad range of analytical techniques (FT-IR spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, EXAFS, water-transfer analysis, small-angle neutron scattering, NMR spectroscopy, and electrospray mass spectrometry), which together show that the amino-amide reagent preferentially transports chlorido-rhodium species as a 1:2 neutral assembly from aqueous 2.0 M HCl phase into an organic phase. The extractants then ligate in the outer coordination shell of the chloride-rhodium anion, making this an efficient separation process. In this study, we found that protonation to the extractants induced to form a proton chelate ring, which pre-organises the ligand to present an array of charge diffuse C-H bonds. This templated arrangement of positive dipoles favors complexation to the charge diffuse chloride-rhodium anion over the more charge-dense chloride anion.
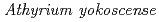 and tobacco plants
and tobacco plants吉原 利一*; 鈴井 伸郎; 石井 里美; 北崎 真由*; 山崎 治明*; 北崎 一義*; 河地 有木; 尹 永根; 七夕 小百合*; 橋田 慎之介*; et al.
Plant, Cell & Environment, 37(5), p.1086 - 1096, 2014/05
被引用回数:27 パーセンタイル:66.15(Plant Sciences)Cadmium (Cd) accumulations in a Cd hyper-accumulator fern, 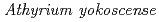 (
(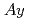 ), and tobacco,
), and tobacco, 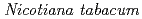 (
(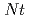 ), were kinetically analysed using the positron-emitting tracer imaging system under two medium conditions (basal and no-nutrient). In
), were kinetically analysed using the positron-emitting tracer imaging system under two medium conditions (basal and no-nutrient). In 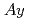 , maximumly 50% and 15% of the total Cd accumulated in the distal roots and the shoots under the basal condition, respectively. Interestingly, a portion of the Cd in the distal roots returned to the medium. In comparison with
, maximumly 50% and 15% of the total Cd accumulated in the distal roots and the shoots under the basal condition, respectively. Interestingly, a portion of the Cd in the distal roots returned to the medium. In comparison with 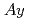 , a little fewer Cd accumulations in the distal roots and clearly higher Cd migration to the shoots were observed in
, a little fewer Cd accumulations in the distal roots and clearly higher Cd migration to the shoots were observed in 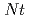 under the basal condition (maximumly 40% and 70% of the total Cd, respectively). The no-nutrient condition down-regulated the Cd migration in both species, although the regulation was highly stricter in
under the basal condition (maximumly 40% and 70% of the total Cd, respectively). The no-nutrient condition down-regulated the Cd migration in both species, although the regulation was highly stricter in 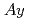 than in
than in 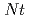 (almost no migration in
(almost no migration in 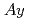 and around 20% migration in
and around 20% migration in 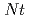 ). In addition, the present work enabled to estimate physical and physiological Cd accumulation capacities in the distal roots, and demonstrated condition-dependent changes especially in
). In addition, the present work enabled to estimate physical and physiological Cd accumulation capacities in the distal roots, and demonstrated condition-dependent changes especially in 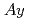 . These results clearly suggested occurrences of species-/condition-specific regulations in each observed parts. It is probable that integration of these properties govern the specific Cd tolerance/accumulation in
. These results clearly suggested occurrences of species-/condition-specific regulations in each observed parts. It is probable that integration of these properties govern the specific Cd tolerance/accumulation in 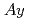 and
and 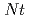 .
.