Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Niu, X.*; Elakneswaran, Y.*; Li, A.*; Seralathan, S.*; Kikuchi, Ryosuke*; Hiraki, Yoshihisa; Sato, Junya; Osugi, Takeshi; Walkley, B.*
Cement and Concrete Research, 190, p.107814_1 - 107814_17, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Construction & Building Technology)Tsuru, Tomohito; Han, S.*; Chen, Z.*; Lobzenko, I.; Inui, Haruyuki*
Materia, 63(10), p.695 - 702, 2024/10
VNbMoTaW, a typical high-entropy alloy with the BCC phase, is composed of metals with high melting points, and is called a reflectory high-entropy alloy. TiZrNbTaHf, which are also known as typical high-entropy alloys with the BCC phase, are also single phase and have a melting point 500  C lower than that of VNbMoTaW, but are known to exhibit excellent ductility at low temperatures below room temperature. Understanding what properties govern the mechanical properties is essential for designing alloys such as high-temperature resistant alloys with excellent high-temperature strength and low-temperature ductility. Given that both VNbMoTaW and TiZrNbTaHf are single-phase alloys, the key lies in the relationship between the constituent elements and the properties underlying the deformation, such as dislocations. This paper presents the results of the differences in mechanical properties of these two refractory high-entropy alloys, using experimental, theoretical, and computer simulations to investigate the key factors controlling ductility and strength.
C lower than that of VNbMoTaW, but are known to exhibit excellent ductility at low temperatures below room temperature. Understanding what properties govern the mechanical properties is essential for designing alloys such as high-temperature resistant alloys with excellent high-temperature strength and low-temperature ductility. Given that both VNbMoTaW and TiZrNbTaHf are single-phase alloys, the key lies in the relationship between the constituent elements and the properties underlying the deformation, such as dislocations. This paper presents the results of the differences in mechanical properties of these two refractory high-entropy alloys, using experimental, theoretical, and computer simulations to investigate the key factors controlling ductility and strength.
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Hibino, Kinya*; Kawata, Kazumasa*; Onishi, Munehiro*; Takita, Masato*; Munakata, Kazuoki*; Kato, Chihiro*; Shimoda, Susumu*; Shi, Q.*; Wang, S.*; et al.
Progress of Earth and Planetary Science (Internet), 11, p.26_1 - 26_14, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Liss, K.-D.*; Han, J.-K.*; Blankenburg, M.*; Lienert, U.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Xu, P. G.; Yukutake, Eitaro*; Kawasaki, M.*
Journal of Materials Science, 59(14), p.5831 - 5853, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:69.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Tsuru, Tomohito; Han, S.*; Matsuura, Shutaro*; Chen, Z.*; Kishida, Kyosuke*; Lobzenko, I.; Rao, S.*; Woodward, C.*; George, E.*; Inui, Haruyuki*
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.1706_1 - 1706_10, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:98.85(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Refractory high-entropy alloys (RHEAs) have attracted attention because of their potential for use in ultrahigh-temperature applications. Unfortunately, their body-centered-cubic (BCC) crystal structures make them more brittle than the ductile and fracture-resistant face-centered-cubic (FCC) HEAs. RHEAs also display significantly lower creep strengths than a leading Ni-base superalloy and its FCC matrix. To overcome these drawbacks and develop RHEAs into viable structural materials, improved fundamental understanding is needed of factors that control strength and ductility. Here we investigate two model RHEAs, TiZrHfNbTa and VNbMoTaW, and show that the former is plastically compressible down to 77 K, whereas the latter is not below 298 K. We find that hexagonal close-packed (HCP) elements in TiZrHfNbTa lower its dislocation core energy, increase its lattice distortion, and lower its shear modulus relative to VNbMoTaW whose elements are all BCC, leading to the formers higher ductility and modulus-normalized yield strength. Consistent with our yield strength models, primarily screw dislocations are present in TiZrHfNbTa after deformation, but equal numbers of edge and screw segments in VNbTaMoW. Dislocation cores are compact in VNbTaMoW and extended in TiZrHfNbTa, and different macroscopic slip planes are activated in the two RHEAs, which we attribute to the concentration of HCP elements. Our findings demonstrate how electronic structure changes related to the ratio of HCP to BCC elements can be used to control strength, ductility, and slip behavior to develop the next generation of high-temperature materials for more efficient power plants and transportation.
Huang, M.-Z.*; Mohan, J.*; Visuri, A.-M.*; Fabritius, P.*; Talebi, M.*; Wili, S.*; Uchino, Shun; Giamarchi, T.*; Esslinger, T.*
Physical Review Letters, 130(20), p.200404_1 - 200404_8, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:90.49(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We measure superfluid transport of strongly-interacting fermionic lithium atoms through a quantum point contact with local, spin-dependent particle loss. We observe that the characteristic non-Ohmic superfluid transport enabled by high-order multiple Andreev reflections transitions into an excess Ohmic current as the dissipation strength exceeds the superfluid gap. We develop a model with mean-field reservoirs connected via tunneling to a dissipative site. Our calculations in the Keldysh formalism reproduce the observed non-equilibrium particle current, yet do not fully explain the observed loss rate or spin current.
Ramadhan, R. S.*; Glaser, D.*; Soyama, Hitoshi*; Kockelmann, W.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Pirling, T.*; Fitzpatrick, M. E.*; Tremsin, A. S.*
Acta Materialia, 239, p.118259_1 - 118259_12, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.81(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Khalil, A. M. E.*; Han, L.*; Maamoun, I.; Tabish, T. A.*; Chen, Y.*; Eljamal, O.*; Zhang, S.*; Butler, D.*; Memon, F. A.*
Advanced Sustainable Systems (Internet), 6(8), p.2200016_1 - 2200016_16, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.06(Green & Sustainable Science & Technology)Dimitriou, P.*; Basunia, S*; Bernstein, L.*; Chen, J.*; Elekes, Z.*; Huang, X.*; Hurst, A.*; Iimura, Hideki; Jain, A. K.*; Kelley, J.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.15004_1 - 15004_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Evaluated Nuclear Structure Data File (ENSDF) includes the most extensive and comprehensive set of nuclear structure and decay data evaluations performed by the international network of Nuclear Structure and Decay Data evaluators (NSDD) under the auspices of the IAEA. In this report we describe some of the recent NSDD activities and provide future perspectives.
Singh, B.*; Basunia, M. S.*; Martin, M.*; McCutchan, E. A.*; Bara, I.*; Caballero-Folch, R.*; Canavan, R.*; Chakrabarti, R.*; Chekhovska, A.*; Grinder, M. M.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 160, p.405 - 471, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:75.77(Physics, Nuclear)Tang, C.*; Song, Q.*; Chang, C.-Z.*; Xu, Y.*; Onuma, Yuichi; Matsuo, Mamoru*; Liu, Y.*; Yuan, W.*; Yao, Y.*; Moodera, J. S.*; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 4(6), p.eaas8660_1 - eaas8660_6, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:83.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences) by tuning nematicity and magnetism in FeSe
by tuning nematicity and magnetism in FeSe S
S superconductors
superconductorsMatsuura, Kohei*; Mizukami, Yuta*; Arai, Yuki*; Sugimura, Yuichi*; Maejima, Naoyuki*; Machida, Akihiko*; Watanuki, Tetsu*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Yajima, Takeshi*; Hiroi, Zenji*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 8, p.1143_1 - 1143_6, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:96 Percentile:92.07(Multidisciplinary Sciences) No
NoLopez-Martens, A.*; Henning, G.*; Khoo, T. L.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Alcorta, M.*; Asai, Masato; Back, B. B.*; Bertone, P. F.*; Boilley, D.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 131, p.03001_1 - 03001_6, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:42.06(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Fission barrier height and its angular-momentum dependence have been measured for the first time in the nucleus with the atomic number greater than 100. The entry distribution method, which can determine the excitation energy at which fission starts to dominate the decay process, was applied to  No. The fission barrier of
No. The fission barrier of  No was found to be 6.6 MeV at zero spin, indicating that the
No was found to be 6.6 MeV at zero spin, indicating that the  No is strongly stabilized by the nuclear shell effects.
No is strongly stabilized by the nuclear shell effects.
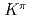 = 8
= 8 two-quasineutron isomer in
two-quasineutron isomer in  Pu
PuHota, S.*; Tandel, S.*; Chowdhury, P.*; Ahmad, I.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; Chiara, C. J.*; Greene, J. P.*; Hoffman, C. R.*; Jackson, E. G.*; Janssens, R. V. F.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 94(2), p.021303_1 - 021303_5, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:54.19(Physics, Nuclear)The decay of a 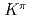 = 8
= 8 isomer in
isomer in  Pu and the collective band structure populating the isomer are studied using deep inelastic excitations with
Pu and the collective band structure populating the isomer are studied using deep inelastic excitations with 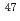 Ti and
Ti and  Pb beams, respectively. Precise measurements of
Pb beams, respectively. Precise measurements of 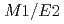 branching ratios in the band confirm a clean 9/2
branching ratios in the band confirm a clean 9/2 [734]
[734]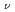
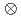 7/2
7/2 [624]
[624]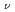 for the isomer, validating the systematics of K
for the isomer, validating the systematics of K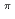 = 8
= 8 two-quasineutron isomers observed in even-
two-quasineutron isomers observed in even- ,
,  = 150 isotones. These isomers around the deformed shell gap at
= 150 isotones. These isomers around the deformed shell gap at  = 152 provide critical benchmarks for theoretical predictions of single-particle energies in this gateway region to superheavy nuclei.
= 152 provide critical benchmarks for theoretical predictions of single-particle energies in this gateway region to superheavy nuclei.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Kon, Akira; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Hayashi, Yukio; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Kanasaki, Masato*; et al.
IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 21(1), p.1601118_1 - 1601118_18, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:67 Percentile:95.26(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)This paper reviews the development of a high-contrast high-intensity petawatt-class Ti:sapphire chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) laser for research on high field science. We discuss in detail the design, performance and characterization of the laser. We also describe the on-going upgrade of the laser system and some applications for the laser in relativistic dominated laser-matter interactions.
 No and
No and 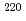 Th
ThHenning, G.*; Khoo, T. L.*; Lopez-Martens, A.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Alcorta, M.*; Asai, Masato; Back, B. B.*; Bertone, P. F.*; Boilley, D.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 113(26), p.262505_1 - 262505_6, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:81.81(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Fission barrier heights of a shell-stabilized superheavy nucleus  No have been determined as a function of spin up to 19
No have been determined as a function of spin up to 19 through the measured distribution of entry points of
through the measured distribution of entry points of  deexcitations in the excitation energy vs. spin plane. The fission barrier height of
deexcitations in the excitation energy vs. spin plane. The fission barrier height of  No was determined to be 6.0 MeV at spin 15
No was determined to be 6.0 MeV at spin 15 , and 6.6 MeV at spin 0
, and 6.6 MeV at spin 0 by extrapolation. This demonstrates that the shell effect actually enlarges the fission barrier in such heavy nuclei and keeps the barrier high even at high spin.
by extrapolation. This demonstrates that the shell effect actually enlarges the fission barrier in such heavy nuclei and keeps the barrier high even at high spin.
 Ni hole-states from (p,d) transfer reactions
Ni hole-states from (p,d) transfer reactionsSanetullaev, A.*; Tsang, M. B.*; Lynch, W. G.*; Lee, J.*; Bazin, D.*; Chan, K. P.*; Coupland, D.*; Hanzl, V.*; Hanzlova, D.*; Kilburn, M.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 736, p.137 - 141, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:69.34(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Cooper, W. A.*; Hirshman, S. P.*; Chapman, I. T.*; Brunetti, D.*; Faustin, J. M.*; Graves, J. P.*; Pfefferl , D.*; Raghunathan, M.*; Sauter, O.*; Tran, T. M.*; et al.
, D.*; Raghunathan, M.*; Sauter, O.*; Tran, T. M.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 56(9), p.094004_1 - 094004_8, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:19.11(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)An approximate model for a single fluid three-dimensional (3D) magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) equilibrium with pure isothermal toroidal flow with imposed nested magnetic flux surfaces is proposed. It recovers the rigorous toroidal rotation equilibrium description in the axisymmetric limit. The approximation is valid under conditions of nearly rigid or vanishing toroidal rotation in regions with significant 3D deformation of the equilibrium flux surfaces. Bifurcated helical core equilibrium simulations of long-lived modes in the MAST device demonstrate that the magnetic structure is only weakly affected by the flow but that the 3D pressure distortion is important. The pressure is displaced away from the major axis and therefore is not as noticeably helically deformed as the toroidal magnetic flux under the subsonic flow conditions measured in the experiment.
 No
NoHenning, G.*; Lopez-Martens, A.*; Khoo, T. L.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Alcorta, M.*; Asai, Masato; Back, B. B.*; Bertone, P. F.*; Boilley, D.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 66, p.02046_1 - 02046_8, 2014/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:68.16(Physics, Nuclear)Fission barrier heights of  No have been determined through the entry distribution method. The entry distribution is the initial distribution of excitation energy and spin from which the
No have been determined through the entry distribution method. The entry distribution is the initial distribution of excitation energy and spin from which the  deexcitation starts in the fusion-evaporation reaction. The initial distribution is extracted from measured
deexcitation starts in the fusion-evaporation reaction. The initial distribution is extracted from measured  -ray multiplicity and total
-ray multiplicity and total  -ray energy. This paper describes the details of the entry distribution method, and reports the first determination of the fission barrier heights of
-ray energy. This paper describes the details of the entry distribution method, and reports the first determination of the fission barrier heights of  No, which is the heaviest nucleus whose fission barrier has been measured.
No, which is the heaviest nucleus whose fission barrier has been measured.
 Ge
GeToh, Yosuke; Chiara, C. J.*; McCutchan, E. A.*; Walters, W. B.*; Janssens, R. V. F.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; Zhu, S.*; Broda, R.*; Fornal, B.*; Kay, B. P.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 87(4), p.041304_1 - 041304_5, 2013/04
Times Cited Count:92 Percentile:97.13(Physics, Nuclear)Excited states of  Ge have been investigated via the
Ge have been investigated via the  Ge +
Ge +  U reaction with
U reaction with 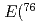 Ge
Ge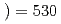 MeV by use of in-beam
MeV by use of in-beam  -ray spectroscopy using the
-ray spectroscopy using the  sphere array. The
sphere array. The  band was extended considerably and one new band was identified. Comparisons of the
band was extended considerably and one new band was identified. Comparisons of the  band with collective- and shell-model calculations suggest that
band with collective- and shell-model calculations suggest that  Ge may be a rare example of a nucleus exhibiting rigid triaxial deformation in the low-lying states.
Ge may be a rare example of a nucleus exhibiting rigid triaxial deformation in the low-lying states.