Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Masuda, Akihiko*; Nishiyama, Jun*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Satoh, Daiki; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Shima, Tatsushi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 153, p.08016_1 - 08016_3, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:60.69(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutron energy spectra behind concrete and iron shields were measured for quasi-monoenergetic neutrons above 200 MeV using a Bonner sphere spectrometer (BSS). Quasi-monoenergetic neutrons were produced by the  Li(p,xn) reaction with 246-MeV and 389-MeV protons. The response function of BSS was also measured at neutron energies from 100 MeV to 387 MeV. In data analysis, the measured response function was used and the multiple neutron scattering effect between the BSS and the shielding material was considered. The neutron energy spectra behind the concrete and iron shields were obtained by the unfolding method using the MAXED code. Ambient dose equivalents were obtained as a function of a shield thickness successfully. For the case of the 244 MeV neutron incidence, the multiple neutron scattering effect on the effective dose is large under 50 cm thickness of the concrete shield.
Li(p,xn) reaction with 246-MeV and 389-MeV protons. The response function of BSS was also measured at neutron energies from 100 MeV to 387 MeV. In data analysis, the measured response function was used and the multiple neutron scattering effect between the BSS and the shielding material was considered. The neutron energy spectra behind the concrete and iron shields were obtained by the unfolding method using the MAXED code. Ambient dose equivalents were obtained as a function of a shield thickness successfully. For the case of the 244 MeV neutron incidence, the multiple neutron scattering effect on the effective dose is large under 50 cm thickness of the concrete shield.
Theis, C.*; Carbonez, P.*; Feldbaumer, E.*; Forkel-Wirth, D.*; Jaegerhofer, L.*; Pangallo, M.*; Perrin, D.*; Urscheler, C.*; Roesler, S.*; Vincke, H.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 153, p.08018_1 - 08018_5, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)At CERN, gas-filled ionization chambers PTW-34031 (PMI) are commonly used in radiation fields including neutrons, protons and  -rays. A response function for each particle is calculated by the radiation transport code FLUKA. To validate a response function to high energy neutrons, benchmark experiments with quasi mono-energetic neutrons have been carried out at RCNP, Osaka University. For neutron irradiation with energies below 200 MeV, very good agreement was found comparing the FLUKA simulations and the measurements. In addition it was found that at proton energies of 250 and 392 MeV, results calculated with neutron sources underestimate the experimental data due to a non-negligible gamma component originating from the target
-rays. A response function for each particle is calculated by the radiation transport code FLUKA. To validate a response function to high energy neutrons, benchmark experiments with quasi mono-energetic neutrons have been carried out at RCNP, Osaka University. For neutron irradiation with energies below 200 MeV, very good agreement was found comparing the FLUKA simulations and the measurements. In addition it was found that at proton energies of 250 and 392 MeV, results calculated with neutron sources underestimate the experimental data due to a non-negligible gamma component originating from the target  Li(p,n)Be reaction.
Li(p,n)Be reaction.
Masuda, Akihiko*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Satoh, Daiki; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Nishiyama, Jun*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 849, p.94 - 101, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.50(Instruments & Instrumentation)Quasi-monoenergetic high-energy neutron fields induced by  Li(p,n) reactions are used for the response evaluation of neutron-sensitive devices. The quasi-monoenergetic high-energy field consists of high-energy monoenergetic peak neutrons and unwanted continuum neutrons down to the low-energy region. A two-angle differential method has been developed to compensate for the effect of the continuum neutrons in the response measurements. In this study, the two-angle differential method was demonstrated for Bonner sphere detectors, which are typical examples of moderator-based neutron-sensitive detectors, to investigate the method's applicability and its dependence on detector characteristics. Through this study, the adequacy of the two-angle differential method was experimentally verified, and practical suggestions were made pertaining to this method.
Li(p,n) reactions are used for the response evaluation of neutron-sensitive devices. The quasi-monoenergetic high-energy field consists of high-energy monoenergetic peak neutrons and unwanted continuum neutrons down to the low-energy region. A two-angle differential method has been developed to compensate for the effect of the continuum neutrons in the response measurements. In this study, the two-angle differential method was demonstrated for Bonner sphere detectors, which are typical examples of moderator-based neutron-sensitive detectors, to investigate the method's applicability and its dependence on detector characteristics. Through this study, the adequacy of the two-angle differential method was experimentally verified, and practical suggestions were made pertaining to this method.
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Ito, Chikara; Harano, Hideki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(4), p.465 - 475, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)To prevent a fuel failure event from becoming a serious radiation accident, sodium-cooled fast reactors are equipped with a system for failed fuel detection and location (FFDL). The FFDL instrument employed in the prototype fast breeder reactor Monju is based on the gas tagging method, in which precise and accurate measurements of krypton and xenon isotope ratios (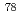 Kr/
Kr/ Kr,
Kr, 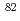 Kr/
Kr/ Kr and
Kr and  Xe/
Xe/ Xe) must be performed in a short time. Burnup measurements also contribute to accurate determination of
Xe) must be performed in a short time. Burnup measurements also contribute to accurate determination of 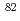 Kr/
Kr/ Kr. We have developed a highly sensitive resonance ionization mass spectrometer for the isotopic analyses, which uses resonance ionization of Kr and Xe atoms by a pulsed laser at wavelengths of 216.7 nm and 249.6 nm, respectively. In evaluating the performance of our spectrometer, we find that systematic errors caused by isotope shifts can be reduced to negligible levels, and that statistical errors of 3% at a nuclide concentration of 7 ppt can be achieved with a single measurement time of about 40 minutes for each Kr and Xe isotope ratio. This means that, within one hour, about 200 fuel assemblies can be individually identified with a probability of 99%, verifying the applicability of our spectrometer to the FFDL system of fast reactors.
Kr. We have developed a highly sensitive resonance ionization mass spectrometer for the isotopic analyses, which uses resonance ionization of Kr and Xe atoms by a pulsed laser at wavelengths of 216.7 nm and 249.6 nm, respectively. In evaluating the performance of our spectrometer, we find that systematic errors caused by isotope shifts can be reduced to negligible levels, and that statistical errors of 3% at a nuclide concentration of 7 ppt can be achieved with a single measurement time of about 40 minutes for each Kr and Xe isotope ratio. This means that, within one hour, about 200 fuel assemblies can be individually identified with a probability of 99%, verifying the applicability of our spectrometer to the FFDL system of fast reactors.
Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Masuda, Akihiko*; Nishiyama, Jun*; Harano, Hideki*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Satoh, Daiki; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nakane, Yoshihiro; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 4, p.332 - 336, 2014/04
Recently, many high-energy accelerators are used for various fields. Shielding data for high-energy neutrons are therefore very important from the point of view of radiation protection in high energy accelerator facilities. However, the shielding experimental data for high energy neutrons above 100 MeV are very poor both in quality and in quantity. In this study, neutron penetration spectral fluence and ambient dose through iron and concrete shields were measured with a Bonner sphere spectrometer (BSS). Quasi-monoenergetic neutrons were produced by the  Li(p,xn) reaction by bombarding a 1-cm thick Li target with 246-MeV and 389-MeV protons in the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) of the Osaka University. Shielding materials are iron blocks with a thickness from 10 cm to 100 cm and concrete blocks with a thickness from 25 cm to 300 cm.
Li(p,xn) reaction by bombarding a 1-cm thick Li target with 246-MeV and 389-MeV protons in the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) of the Osaka University. Shielding materials are iron blocks with a thickness from 10 cm to 100 cm and concrete blocks with a thickness from 25 cm to 300 cm.
Aoyama, Takafumi; Ishikawa, Takashi; Ito, Chikara; Iwata, Yoshihiro; Harano, Hideki*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 106(1), p.611 - 613, 2012/06
We studied the failed fuel detection and location (FFDL) system by means of laser resonance ionization mass spectrometry (RIMS). The applicability of the RIMS system for Monju and its installation were investigated in this study. It was found that the RIMS is able to identify the neighboring tag gas which is used for Monju with the 68% reliability. The newly designed RIMS system can be accommodated in the present facility and can be connected to primary cover gas lines without affects to the current FFDL function of the conventional system.
Masuda, Akihiko*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Harano, Hideki*; Nishiyama, Jun*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Satoh, Daiki; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nakamura, Takashi*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 59(1), p.161 - 166, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:66.29(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)In this study, responses of Bonner sphere spectrometer (BSS) for 245 and 388 MeV neutrons was measured at RCNP, Osaka University. The neutrons are generated in the  Li(p,n) reaction and its spectra consist of a high-energy peak and a continuum down to the low energy. Therefore, the observed counts of BSS caused by the continuum need to be subtracted. Adjusting a Li target angle and a collimator position, 0 deg and 30 deg component of generated neutron are available. While the 0 deg component contains both the peak and the continuum, the 30 deg component is considered to contain only the continuum. Therefore, the response of the peak is obtained. The spectra were measured using the time-of-flight (TOF) method with a NE213 scintillator.
Li(p,n) reaction and its spectra consist of a high-energy peak and a continuum down to the low energy. Therefore, the observed counts of BSS caused by the continuum need to be subtracted. Adjusting a Li target angle and a collimator position, 0 deg and 30 deg component of generated neutron are available. While the 0 deg component contains both the peak and the continuum, the 30 deg component is considered to contain only the continuum. Therefore, the response of the peak is obtained. The spectra were measured using the time-of-flight (TOF) method with a NE213 scintillator.
Shikaze, Yoshiaki; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Saegusa, Jun; Tsutsumi, Masahiro; Uchida, Yoshiaki*; Yoshizawa, Michio; Harano, Hideki*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Mizuhashi, Kiyoshi
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 158, 2011/01
no abstracts in English
 Se as a probe of neutron capture for the s-process branch-point nucleus
Se as a probe of neutron capture for the s-process branch-point nucleus 
Makinaga, Ayano*; Hohara, Shinya*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Goko, Shinji*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Goriely, S.*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Harano, Hideki*; et al.
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 28, p.239_1 - 239_4, 2010/12
no abstracts in English
Ito, Chikara; Iwata, Yoshihiro; Harano, Hideki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Aoyama, Takafumi
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 102(1), p.416 - 417, 2010/06
no abstracts in English
Aoyama, Takafumi; Ito, Chikara; Okazaki, Koki*; Harano, Hideki*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 75(751), p.468 - 470, 2009/03
no abstracts in English
 Se; Implications for the s-process branching at
Se; Implications for the s-process branching at  Se
SeMakinaga, Ayano*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Goriely, S.*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Goko, Shinji*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Harano, Hideki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 79(2), p.025801_1 - 025801_8, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:79.50(Physics, Nuclear)Photoneutron cross sections were measured for  Se immediately above the neutron separation energy with quasimonochromatic
Se immediately above the neutron separation energy with quasimonochromatic  -ray beams to experimentally constrain the E1
-ray beams to experimentally constrain the E1  strength function for
strength function for  Se. Two sets of the
Se. Two sets of the  strength function and the level density that equally meet the experimental constraint predict largely different neutron capture cross sections for
strength function and the level density that equally meet the experimental constraint predict largely different neutron capture cross sections for  Se. Based on the Maxwell-averaged cross sections of the latest compilation complemented with the predicted cross sections for
Se. Based on the Maxwell-averaged cross sections of the latest compilation complemented with the predicted cross sections for  Se, we calculated
Se, we calculated  N values of the main s-process component using a phenomenological model and deduced empirical abundances of the weak s-process component.
N values of the main s-process component using a phenomenological model and deduced empirical abundances of the weak s-process component.
Aoyama, Takafumi; Ito, Chikara; Okazaki, Koki; Harano, Hideki; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(Suppl.6), p.43 - 50, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.93(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 Se; Implications for the s-process thermometer
Se; Implications for the s-process thermometerMakinaga, Ayano*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Goriely, S.*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Harano, Hideki*; Harada, Hideo; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 805(1-4), p.564 - 566, 2008/06
Photoneutron cross sections were measured for  Se near the neutron threshold energy with quasi-monochromatic
Se near the neutron threshold energy with quasi-monochromatic  rays. Using the
rays. Using the  Se(
Se( ,
, ) cross section as experimental constraints on the E1
) cross section as experimental constraints on the E1  strength function, we estimate the neutron capture rates for
strength function, we estimate the neutron capture rates for  Se. The solar abundance ratio of s-only nuclides
Se. The solar abundance ratio of s-only nuclides  Kr and
Kr and 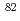 Kr are analyzed in terms of the s-process branching at
Kr are analyzed in terms of the s-process branching at  Se within the local approximation. The corresponding temperature and neutron density regimes are discussed in the light of the s-process scenario in massive stars.
Se within the local approximation. The corresponding temperature and neutron density regimes are discussed in the light of the s-process scenario in massive stars.
Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Kumada, Hiroaki; Terunuma, Toshiyuki*; Sakae, Takeji*; Harano, Hideki*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Suzuki, Toshikazu*; Matsufuji, Naruhiro*
Hoshasen, 34(2), p.135 - 139, 2008/04
Recently the traceability system (JCSS) of neutron standard based on the Japanese law "Measurement Act" has been instituted. In addition, importance of the neutron dose evaluation has been increasing in not only the neutron capture medical treatment but also the proton or heavy particle therapy. Against such a background, a symposium "Neutron dosimetry in neutron fields; From detection techniques to medical applications" was held on March 29, 2008 and recent topics on the measuring instruments and their calibration, the traceability system, the simulation technique and the medical applications were introduced. This article summarizes the key points in the discussion at the symposium.
 Zr using laser inverse Compton
Zr using laser inverse Compton  rays
raysHohara, Shinya*; Goko, Shinji*; Makinaga, Ayano*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Hara, Kaoru; Kitatani, Fumito; Harada, Hideo; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2006-009, p.66 - 69, 2006/11
no abstracts in English
Ito, Chikara; Nose, Shoichi; Harano, Hideki; Arima, Toshihiro*
JNC TN9400 2004-007, 44 Pages, 2004/01
In the experimental fast reactor JOYO, an on-line instrumented material irradiation rig developed to acquire various irradiation data. The Material Testing Rig Temperature Control (MARICO) is capable of collecting creep rupture strength data for fast reactor fuel cladding materials. The irradiation using MARICO rig began in 1994 with JOYO's 29th operational cycle and ended in 1998 with the 32nd cycle. A ruptured sample might not be able to be specified with a device of MARICO in the irradiation examination. To improve irradiation technology, the trace rare gas detection technique using laser resonance ionization mass spectrometry (RIMS) is applied to creep rupture experiment. The irradiation capsules are labeled with tagging gases. The identification uses isotope analysis of the tagging gas leaked out of the breached steel capsule, diffused in the argon cover gas. The RIMS device analyzed the isotopic composition of the cover gas of which it took a sample. As that result, the isotopic composition that it was measured with a RIMS device corresponded with the tag gas identified by the MARICO device.
Ito, Chikara; Harano, Hideki
Dai-16-Kai Shitsuryo Bunseki Ni Kansuru Kokusai Kaigi, 165 Pages, 2003/00
None
Harano, Hideki; Ito, Chikara
Nihon AEM Gakkai-Shi, 14(1-4), 307 Pages, 2003/00
None
Harano, Hideki; Ito, Chikara
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 492(1-2), p.317 - 323, 2002/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.31(Instruments & Instrumentation)None