Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Chudo, Hiroyuki; Yokoi, Naoto*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Harii, Kazuya*; Suzuki, Jun*; Imai, Masaki; Sato, Masahiro*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Saito, Eiji*
Physical Review Letters, 134(13), p.130603_1 - 130603_5, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Harii, Kazuya*; Umeda, Maki; Arisawa, Hiroki*; Hioki, Tomosato*; Sato, Nana; Okayasu, Satoru; Ieda, Junichi
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(7), p.073701_1 - 073701_4, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:22.15(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Fe
Fe O
O /Pt heterostructures
/Pt heterostructuresIeda, Junichi; Okayasu, Satoru; Harii, Kazuya*; Kobata, Masaaki; Yoshii, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Ishida, Masahiko*; Saito, Eiji
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 58(8), p.1301106_1 - 1301106_6, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.40(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The combination of spin-driven thermoelectric (STE) devices based on spin Seebeck effect (SSE), and radioactive isotopes as heat sources, has potential as a next-generation method of power generation in applications such as power supplies for space probes. However, there has been very limited knowledge available indicating the irradiation tolerance of spin thermoelectric devices. Through analysis using a heavy ion-beam accelerator and the hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HAXPES) measurements, we show that a prototypical STE device based on Y Fe
Fe O
O /Pt heterostructures has tolerance to irradiation of high-energy heavy-ion beams. We used 320 MeV gold ion beams modeling cumulative damages due to fission products emitted from the surface of spent nuclear fuels. By varying the dose level, we confirmed that the thermoelectric and magnetic properties of the SSE elements are not affected by the ion-irradiation dose up to
/Pt heterostructures has tolerance to irradiation of high-energy heavy-ion beams. We used 320 MeV gold ion beams modeling cumulative damages due to fission products emitted from the surface of spent nuclear fuels. By varying the dose level, we confirmed that the thermoelectric and magnetic properties of the SSE elements are not affected by the ion-irradiation dose up to 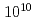 ions/cm
ions/cm fluence and that the SSE signal is extinguished around
fluence and that the SSE signal is extinguished around 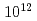 ions/cm
ions/cm , in which the ion tracks almost fully cover the sample surface. In addition, the HAXPES measurements were performed to understand the effects at the interface of Y
, in which the ion tracks almost fully cover the sample surface. In addition, the HAXPES measurements were performed to understand the effects at the interface of Y Fe
Fe O
O /Pt. The HAXPES measurements suggest that the chemical reaction that diminishes the SSE signals is enhanced with the increase of the irradiation dose. We share the current understandings of the damage analysis in Y
/Pt. The HAXPES measurements suggest that the chemical reaction that diminishes the SSE signals is enhanced with the increase of the irradiation dose. We share the current understandings of the damage analysis in Y Fe
Fe O
O /Pt for developing better STE devices applicable to harsh environmental usages.
/Pt for developing better STE devices applicable to harsh environmental usages.
Shamoto, Shinichi*; Akatsu, Mitsuhiro*; Matsuura, Masato*; Kawamura, Seiko; Harii, Kazuya*; Ono, Masao*; Chang, L.-J.*; Ito, Takashi; Nemoto, Yuichi*; Ieda, Junichi
Physical Review Research (Internet), 4(1), p.013245_1 - 013245_7, 2022/03
Ultrasound injection effect on a magnetic Bragg peak of yttrium iron garnet has been studied by quasielastic neutron scattering. The magnetic Bragg peak is vastly enhanced with decreasing temperature. The energy width increases proportionally to the square root of the sample temperature increase induced by the ultrasound injection. Because the magnetic Bragg peak is enhanced by the lattice vibration, the enhancement is expected to relate to the spin-lattice coupling closely. An observed sharp drop above 100 K in the longitudinal mode suggests the degradation of the spin-lattice coupling. It is consistent with the decline of spin Seebeck effect with increasing temperature above 100 K, proving the degradation mechanism by the spin-lattice coupling.
Chudo, Hiroyuki; Matsuo, Mamoru*; Harii, Kazuya*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Express, 13(10), p.109102_1 - 109102_2, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:57.14(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Okayasu, Satoru; Harii, Kazuya*; Kobata, Masaaki; Yoshii, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Ishida, Masahiko*; Ieda, Junichi; Saito, Eiji
Journal of Applied Physics, 128(8), p.083902_1 - 083902_7, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.27(Physics, Applied)Takahashi, Ryo*; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Matsuo, Mamoru; Harii, Kazuya*; Onuma, Yuichi*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.3009_1 - 3009_6, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:81.26(Multidisciplinary Sciences) Fe
Fe O
O
Kobata, Masaaki; Yoshii, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Kawasaki, Ikuto; Okane, Tetsuo; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Harii, Kazuya; Ieda, Junichi; Okayasu, Satoru; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 30, p.011192_1 - 011192_6, 2020/03
High energy X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HAXPES) measurements were carried out for the Spin Seebeck system Pt/Y Fe
Fe O
O (YIG). This system was found to show anomalous Hall effect, possible due to the formation of intermetallic compounds between Fe
(YIG). This system was found to show anomalous Hall effect, possible due to the formation of intermetallic compounds between Fe and Pt. To reveal this possibility, we have measured the Fe 1s photoelectron peaks by using HAXPES. It was found that the Fe ions consist of Fe
and Pt. To reveal this possibility, we have measured the Fe 1s photoelectron peaks by using HAXPES. It was found that the Fe ions consist of Fe in YIG and metallic Fe. The formation of the metallic state is consistent with the proposed origin of the anomalous Hall effect. Other spectra such as Pt 4f will be presented at the conference.
in YIG and metallic Fe. The formation of the metallic state is consistent with the proposed origin of the anomalous Hall effect. Other spectra such as Pt 4f will be presented at the conference.
Harii, Kazuya; Seo, Y.-J.*; Tsutsumi, Yasumasa*; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Oyanagi, Koichi*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Shiomi, Yuki*; Ono, Takahito*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Nature Communications (Internet), 10, p.2616_1 - 2616_5, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:80.62(Multidisciplinary Sciences) Dy
Dy Fe
Fe O
O detected by the Barnett effect
detected by the Barnett effectImai, Masaki; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Ono, Masao; Harii, Kazuya; Matsuo, Mamoru; Onuma, Yuichi*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Letters, 114(16), p.162402_1 - 162402_4, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:70.48(Physics, Applied) Fe
Fe O
O micro bridge
micro bridgeArisawa, Hiroki*; Daimon, Shunsuke*; Oikawa, Yasuyuki*; Seo, Y.-J.*; Harii, Kazuya; Oyanagi, Koichi*; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Letters, 114(12), p.122402_1 - 122402_5, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:26.87(Physics, Applied)Imai, Masaki; Ogata, Yudai*; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Ono, Masao; Harii, Kazuya; Matsuo, Mamoru*; Onuma, Yuichi*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Letters, 113(5), p.052402_1 - 052402_3, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:66.33(Physics, Applied)Ogata, Yudai; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Gu, B.; Kobayashi, Nobukiyo*; Ono, Masao; Harii, Kazuya; Matsuo, Mamoru; Saito, Eiji; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 442, p.329 - 331, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:62.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Fe
Fe O
O cantilevers
cantileversSeo, Y.-J.*; Harii, Kazuya; Takahashi, Ryo*; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Oyanagi, Koichi*; Qiu, Z.*; Ono, Takahito*; Shiomi, Yuki*; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Letters, 110(13), p.132409_1 - 132409_4, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:53.63(Physics, Applied)We have fabricated ferrite cantilevers in which their vibrational properties can be controlled by external magnetic fields. Submicron-scale cantilever structures were made from Y Fe
Fe O
O films by physical etching combined with the use of a focused ion beam milling technique. We found that the cantilevers exhibit two resonance modes which correspond to horizontal and vertical vibrations. Under external magnetic fields, the resonance frequency of the horizontal mode increases, while that of the vertical mode decreases, quantitatively consistent with our numerical simulation for magnetic forces. The changes in resonance frequencies with magnetic fields reach a few percent, showing that an efficient magnetic control of resonance frequencies was achieved.
films by physical etching combined with the use of a focused ion beam milling technique. We found that the cantilevers exhibit two resonance modes which correspond to horizontal and vertical vibrations. Under external magnetic fields, the resonance frequency of the horizontal mode increases, while that of the vertical mode decreases, quantitatively consistent with our numerical simulation for magnetic forces. The changes in resonance frequencies with magnetic fields reach a few percent, showing that an efficient magnetic control of resonance frequencies was achieved.
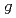 factor of rare earth metals
factor of rare earth metalsOgata, Yudai; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Ono, Masao; Harii, Kazuya; Matsuo, Mamoru; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Letters, 110(7), p.072409_1 - 072409_4, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:65.90(Physics, Applied)Takahashi, Ryo*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Ono, Masao; Harii, Kazuya; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Okayasu, Satoru; Ieda, Junichi; Takahashi, Saburo*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Nature Physics, 12, p.52 - 56, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:121 Percentile:96.21(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ono, Masao; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Harii, Kazuya; Okayasu, Satoru; Matsuo, Mamoru; Ieda, Junichi; Takahashi, Ryo*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Physical Review B, 92(17), p.174424_1 - 174424_4, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:76.79(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Harii, Kazuya; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Ono, Masao; Matsuo, Mamoru; Ieda, Junichi; Okayasu, Satoru; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 54(5), p.050302_1 - 050302_3, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:46.88(Physics, Applied)Chudo, Hiroyuki; Harii, Kazuya; Matsuo, Mamoru; Ieda, Junichi; Ono, Masao; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(4), p.043601_1 - 043601_4, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:73.32(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Chudo, Hiroyuki; Ono, Masao; Harii, Kazuya; Matsuo, Mamoru; Ieda, Junichi; Haruki, Rie*; Okayasu, Satoru; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Yasuoka, Hiroshi; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Express, 7(6), p.063004_1 - 063004_4, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:50 Percentile:85.14(Physics, Applied)A magnetic field is predicted to emerge on a particle in a rotating body even if the body is electrically neutral. This emergent field is called a Barnett field. We show that nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) enables direct measurement of the Barnett field in solids. We rotated both a sample and an NMR coil synchronously at high speed and found an NMR shift whose sing reflects that of the nuclear magnetic moments. This result provides direct evidence of the Barnett field. The use of NMR for Barnett field measurement enables the unknown signs of nuclear magnetic moments in solids to be determined.