Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Arai, Yoichi; Watanabe, So; Nakahara, Masaumi; Funakoshi, Tomomasa; Hoshino, Takanori; Takahatake, Yoko; Sakamoto, Atsushi; Aihara, Haruka; Hasegawa, Kenta; Yoshida, Toshiki; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.168 - 174, 2025/05
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting a project named "Systematic Treatment of RAdioactive liquid waste for Decommissioning (STRAD)" project since 2018 for fundamental and practical studies for treating radioactive liquid wastes with complicated compositions. Fundamental studies have been conducted using genuine liquid wastes accumulated in a hot laboratory of the JAEA called the Chemical Processing Facility (CPF), and treatment procedures for all liquid wastes in CPF were successfully designed on the results obtained. As the next phase of the project, new fundamental and practical studies on primarily organic liquid wastes accumulated in different facilities of JAEA are in progress. This paper reviews the representative achievements of the STRAD project and introduces an overview of ongoing studies.
Taguchi, Miki*; Miyata, Noboru*; Miyazaki, Tsukasa*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Ozawa, Satoru*; Hasegawa, Ryuichi*; Morimitsu, Yuma*; Kawaguchi, Daisuke*; Yamamoto, Satoru*; Tanaka, Keiji*
Polymer Journal, 7 Pages, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Polymer Science)Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shibata, Daisuke*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Hasegawa, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Fukaya, Akane*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2024-014, 54 Pages, 2025/02
XAFS measurements in the soft X-ray region are suitable for evaluating the chemical state of the surface layer of a measurement sample because the X-ray transmittance is low. In this study, the purpose of the study was to confirm the difference between the coagulated surface layer and the inside of the simulated waste glasses by measuring the K-edge of the glass constituent elements boron, oxygen, sodium, and silicon, and the L edge of the waste component cerium. As a result, the B K-edge XANES spectra showed that the proportion of B-O tetracoordinate sp
edge of the waste component cerium. As a result, the B K-edge XANES spectra showed that the proportion of B-O tetracoordinate sp structures (BO
structures (BO ) on the surface layer of the coagulated glass samples was higher than that on the cut surface inside the glass samples, which is expected to improve the water resistance of the coagulated surface. On the other hand, the O K-edge XANES spectra suggested that the O abundance in the coagulated surface layer was lower than that in the cut surface inside the glass samples, and that alkali metal elements may be concentrated in the coagulated surface layer. However, no difference was observed in the Na K-edge XANES spectra between the coagulated surface layer and the cut surface, and no difference was observed in the Si K-edge XANES spectra between the solidified surface and the inside of glass samples. In addition, the Ce L
) on the surface layer of the coagulated glass samples was higher than that on the cut surface inside the glass samples, which is expected to improve the water resistance of the coagulated surface. On the other hand, the O K-edge XANES spectra suggested that the O abundance in the coagulated surface layer was lower than that in the cut surface inside the glass samples, and that alkali metal elements may be concentrated in the coagulated surface layer. However, no difference was observed in the Na K-edge XANES spectra between the coagulated surface layer and the cut surface, and no difference was observed in the Si K-edge XANES spectra between the solidified surface and the inside of glass samples. In addition, the Ce L -edge XANES spectra confirmed that the Ce valence in the surface layer of coagulated glass samples were oxidized compared to the inside of glass samples.
-edge XANES spectra confirmed that the Ce valence in the surface layer of coagulated glass samples were oxidized compared to the inside of glass samples.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Onodera, Naoyuki
EPJ Web of Conferences, 302, p.03005_1 - 03005_9, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)We implemented the ensemble data assimilation (DA) method, the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LETKF), into the mesh-refined lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) for turbulent flows. Both the LETKF and the mesh-refined LBM were fully implemented on GPUs, so that they are efficiently computed on modern GPU-based supercomputers. We examined the DA accuracy against the flow around a cylinder. The result showed that our method enabled accurate DA with spatially- and temporarily-sparse observation data; the error of the assimilated velocity field with the observation interval of 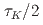 and the observation resolution
and the observation resolution 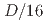 (1.56% of the total computational grids) was smaller than the amplitude of the observation noise, where
(1.56% of the total computational grids) was smaller than the amplitude of the observation noise, where 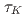 is the period of the K
is the period of the K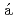 rm
rm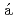 n vortex and
n vortex and  is diameter of the square cylinder.
is diameter of the square cylinder.
Aoki, Takeshi; Hasegawa, Takeshi; Kurahayashi, Kaoru; Nomoto, Yasunobu; Shimizu, Atsushi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Sakaba, Nariaki
Proceedings of 11th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2024), 6 Pages, 2024/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is planning to perform a test named HTTR heat application test coupling HTTR (High temperature engineering test reactor) and a hydrogen production plant. The present study reports results of the safety design and safety analysis for HTTR heat application test facility. As a safety design, safety classification of structures, systems, and components was defined in the test facility based on their safety functions. As a preliminary safety analysis, a thermal-hydraulic analysis was performed with RELAP5 code. The safety analysis revealed that newly identified events for HTTR heat application test facility except for the rupture of heat transfer tube of steam generator was enveloped by the licensing basis events in conventional HTTR. The preliminary analysis proved that the safety criteria is satisfied in the candidate of licensing basis event.
Okita, Hidefumi; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Miyakoshi, Ryosuke*; Nomura, Masahiro; Shimada, Taihei; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Seiya, Kiyomi*; Hara, Keigo*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.765 - 769, 2024/10
no abstracts in English
Nomura, Masahiro; Shimada, Taihei; Tamura, Fumihiko; Okita, Hidefumi; Miyakoshi, Ryosuke*; Seiya, Kiyomi*; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.85 - 88, 2024/10
no abstracts in English
Adachi, Kyosuke; Tamura, Fumihiko; Nomura, Masahiro; Shimada, Taihei; Miyakoshi, Ryosuke*; Okita, Hidefumi; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Seiya, Kiyomi*; Hara, Keigo*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.543 - 546, 2024/10
no abstracts in English
Tamura, Fumihiko; Sugiyama, Yasuyuki*; Okita, Hidefumi; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Seiya, Kiyomi*; Nomura, Masahiro; Shimada, Taihei; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.774 - 776, 2024/10
The 3GeV RCS of J-PARC accelerates proton beams with a maximum beam intensity of 8e13 ppp, utilizing the features of magnetic alloy (MA) cavities. The beam is extracted in a single turn by kicker magnets, and immediately after the beam is extracted, a short voltage jump occurs in the cavity. This is due to a delay in the voltage control feedback, which takes a certain amount of time to respond to the step-like decrease of beam current upon single-turn extraction. In a wideband (Q=2) MA cavity, this response delay is observed as a voltage jump. This voltage jump can cause damage to the cavity system if the voltage at the time of extraction is high. Therefore, we prepared a logic to suppress the output synchronously with the beam extraction as a function of the LLRF control system. The details of the function and test results are reported.
 C
C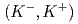 reaction at 1.8 GeV/
reaction at 1.8 GeV/ with the Superconducting Kaon spectrometer
with the Superconducting Kaon spectrometerIchikawa, Yudai; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Imai, Kenichi*; Nanamura, Takuya; Naruki, Megumi; Sato, Susumu; Sako, Hiroyuki; Tamura, Hirokazu; Tanida, Kiyoshi; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2024(9), p.091D01_1 - 091D01_13, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Tanaka, Satoshi*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Iwata, Ayako*; Aoki, Yuto; Aoki, Kazuhisa; Yanagisawa, Kenichi*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (70), p.3 - 22, 2024/09
Inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F), there are many locations with high radiation levels due to contamination by radioactive materials that leaked from the reactor. These pose a significant obstacle to the smooth progress of decommissioning work. To help solve this issue, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), under a subsidy from the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry's decommissioning and contaminated water management project, is conducting research and development on digital technologies to improve the radiation environment inside the decommissioning site. This project, titled "Development of Technology to Improve the Environment Inside Reactor Buildings (Enhancing Digital Technology for Environment and Source Distribution to Reduce Radiation Exposure)," began in April of FY 2023. In this project, the aim is to develop three interconnected systems: FrontEnd, Pro, and BackEnd. The FrontEnd system, based on the previously developed 3D-ADRES-Indoor (prototype) from FY 2021-2022, will be upgraded to a high-speed digital twin technology usable on-site. The Pro system will carry out detailed analysis in rooms such as the new office building at 1F, while the BackEnd system will serve as a database to centrally manage the collected and analyzed data. This report focuses on the FrontEnd system, which will be used on-site. After point cloud measurement, the system will quickly create a 3D mesh model, estimate the radiation source from dose rate measurements, and refine the position and intensity of the estimated source using recalculation techniques (re-observation instructions and re-estimation). The results of verification tests conducted on Unit 5 are also presented. Furthermore, the report briefly discusses the future research and development plans for this project.
Arai, Yoichi; Hasegawa, Kenta; Watanabe, So; Watanabe, Masayuki; Minowa, Kazuki*; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Hagura, Naoto*; Katsuki, Kenta*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Konishi, Yasuhiro*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 333(7), p.3585 - 3593, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.64(Chemistry, Analytical)Watanabe, Tsutomu*; Ishikawa, Shuhei*; Kawashima, Masayuki*; Shimoyama, Ko*; Onodera, Naoyuki; Hasegawa, Yuta; Inagaki, Atsushi*
Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 250, p.105783_1 - 105783_17, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:68.80(Engineering, Civil)This paper presents simulations of drifting snow using a Lagrangian particle dispersion model coupled with a large-eddy simulation code. The model accurately replicates observed features such as mass transport rate dependency on flow velocity and variations in particle size distribution. It also shows that the saltation layer height increases monotonically with flow velocity, contrary to conventional estimates. Additionally, the study confirms the transition from saltation to suspension near the estimated saltation layer height and finds that dense snow streamers are linked to small-scale low-speed streaks in near-surface flows.
Nemoto, Takahiro; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Arakawa, Ryoki; Choyama, Yuya; Nagasumi, Satoru; Hasegawa, Toshinari; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Watanabe, Masashi; Onishi, Takashi; Kawamoto, Taiki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-003, 17 Pages, 2024/06
In order to investigate the cause of the increase in differential pressure in the primary helium circulator filter that occurred during the RS-14 cycle, a clogged filter was investigated. As a result of the investigation, deposits caused by silicone oil were confirmed on the surface of the filter element. These results revealed that the cause of filter clogging was silicone oil mixed into the primary system due to performance deterioration of the charcoal filter in the gas circulator of primary helium purification system. As a measure to prevent the recurrence of this event, in addition to the conventional management based on operating hours for replacing of charcoal filter in the gas circulator of primary helium purification system, we have established a new replacement plan for every three years.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Onodera, Naoyuki
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 29, 4 Pages, 2024/06
We implemented the ensemble data assimilation (DA) of turbulence by using the mesh-refined lattice Boltzmann method with the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LBM-LETKF). We examined the accuracy of the data assimilation against a turbulent flow around a three-dimensional square cylinder. The DA error was comparable or less than the observation noise when the observation interval was a half of the period of the K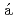 rm
rm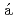 n vortex street and the number of observation points was 0.195% of computational grid points. The LBM-LETKF enables DA of turbulence with spatially- and temporally- sparse observations.
n vortex street and the number of observation points was 0.195% of computational grid points. The LBM-LETKF enables DA of turbulence with spatially- and temporally- sparse observations.
Hasegawa, Toshinari; Nagasumi, Satoru; Nemoto, Takahiro; Nakajima, Kunihiro; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Arakawa, Ryoki; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Kawamoto, Taiki
Proceedings of 2024 International Congress on Advanced in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2024) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/06
The filter element of the primary gas circulators (PGC) in High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) and its deposits were investigated by Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) observation and Energy Dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) analysis to find the cause of the increase of the filter differential pressure during the operation in 2021. SEM observation showed that the clumpy deposits and fibrous deposits smaller than the filtration pore size and the rod-shaped deposits larger than the pore size were present on the filter element. EDX analysis showed that the clumpy deposits and fibrous deposits could include silicone oil in the primary helium purification system (PHPS) gas circulators and that the rod-shaped deposits were thermal insulators inside of the co-axial double pipes in the primary cooling system. It is considered that silicone oil leaked from the PHPS gas circulators due to deterioration in the absorption performance of the activated charcoal filter. Next, it could be vaporized and reach PGC's filter element after passing through the reactor core. Since those deposits including silicone oil were present over the entire surface of the filter element, the filter differential pressure could be increased due to a reduction in the pore size and a rise in its flow resistance. The thermal insulator was unrelated to filter clogging because it was present mainly in the lower part of the filter element. Therefore, silicone oil could increase the filter differential pressure, and the graphite powder, which is the cause of the previous issue was unrelated.
Watanabe, So; Takahatake, Yoko; Hasegawa, Kenta; Goto, Ichiro*; Miyazaki, Yasunori; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 11(2), p.23-00461_1 - 23-00461_10, 2024/04
Hasegawa, Kenta; Goto, Ichiro*; Miyazaki, Yasunori; Ambai, Hiromu; Watanabe, So; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 11(2), p.23-00407_1 - 23-00407_8, 2024/04
Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Machida, Masahiko
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2024 (WM2024) (Internet), 15 Pages, 2024/03
In order to safely carry out the decommission of reactor buildings, it is extremely important to identify the radiation source distribution. It has been reported that when the structural model of the building is constructed by uniform cells, the source distribution can be estimated from the measured air dose rates by minimizing an evaluation function using the Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO). Moreover, if cells are non-uniform, we can estimate the distribution using the fused LASSO which minimizes the evaluation function that takes account of the connectivity between the adjacent cells. However, when a group of some cells is considered disconnected from the surrounding ones due to the precision of the measured structural data, the concentration of the group can be singularly high. Therefore, in order to avoid the problem, we propose a new evaluation function that can prevent the singularity. We estimated the distribution for the test model using the proposed evaluation function and confirmed the validity of the function. Moreover, we succeeded in estimating the source distribution in the pool canal circulation system room in JMTR in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency by the fused LASSO for the new function more accurately than previous analysis.
Okita, Hidefumi; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Nomura, Masahiro; Shimada, Taihei; Saha, P. K.; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Sugiyama, Yasuyuki*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2687(7), p.072005_1 - 072005_7, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Longitudinal phase space tomography is an effective measurement tool for acquiring the longitudinal phase space distribution. For the J-PARC synchrotrons, tomography, which can take into account the beam dynamics such as longitudinal space charge effect and nonlinearity, is desired, as the beam power increases. In this study, for the J-PARC synchrotron, the CERN's tomography, which employs the hybrid algorithm that can consider the beam dynamics for reconstruction, is introduced and benchmarked. The benchmark results show that the CERN's tomography has the ability to measure the longitudinal phase space distribution accurately, in the high-power beam operation at the J-PARC synchrotrons.